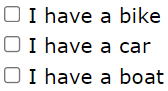HTML Input Types - Primary 3 PDF Download
This chapter describes the different types for the HTML <input> element.
HTML Input Types
Here are the different input types you can use in HTML:
- <input type="button">
- <input type="checkbox">
- <input type="color">
- <input type="date">
- <input type="datetime-local">
- <input type="email">
- <input type="file">
- <input type="hidden">
- <input type="image">
- <input type="month">
- <input type="number">
- <input type="password">
- <input type="radio">
- <input type="range">
- <input type="reset">
- <input type="search">
- <input type="submit">
- <input type="tel">
- <input type="text">
- <input type="time">
- <input type="url">
- <input type="week">
Note: The default value of the type attribute is "text".
Input Type Text
<input type="text"> defines a single-line text input field:
Example
<form>
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname">
</form>
This is how the HTML code above will be displayed in a browser:
First name:
Last name:
Input Type Password
<input type="password"> defines a password field:
Example
<form>
<label for="username">Username:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="username" name="username"><br>
<label for="pwd">Password:</label><br>
<input type="password" id="pwd" name="pwd">
</form>
This is how the HTML code above will be displayed in a browser:
Username:
Password:
The characters in a password field are masked (shown as asterisks or circles).
Input Type Submit
<input type="submit"> defines a button for submitting form data to a form-handler.
The form-handler is typically a server page with a script for processing input data.
The form-handler is specified in the form's action attribute:
Example
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname" value="John"><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname" value="Doe"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
This is how the HTML code above will be displayed in a browser:
First name:
| John |
Last name:
| Doe |

If you omit the submit button's value attribute, the button will get a default text:
Example
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname" value="John"><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname" value="Doe"><br><br>
<input type="submit">
</form>
Input Type Reset
<input type="reset"> defines a reset button that will reset all form values to their default values:
Example
<form action="/action_page.php">
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname" value="John"><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname" value="Doe"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
<input type="reset">
</form>
This is how the HTML code above will be displayed in a browser:
First name:
| John |
Last name:
| Doe |
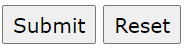
If you change the input values and then click the "Reset" button, the form-data will be reset to the default values.
Input Type Radio
<input type="radio"> defines a radio button.
Radio buttons let a user select ONLY ONE of a limited number of choices:
Example
<p>Choose your favorite Web language:</p>
<form>
<input type="radio" id="html" name="fav_language" value="HTML">
<label for="html">HTML</label><br>
<input type="radio" id="css" name="fav_language" value="CSS">
<label for="css">CSS</label><br>
<input type="radio" id="javascript" name="fav_language" value="JavaScript">
<label for="javascript">JavaScript</label>
</form>
This is how the HTML code above will be displayed in a browser:
о HTML
о CSS
о JavaScript
Input Type Checkbox
<input type="checkbox"> defines a checkbox.
Checkboxes let a user select ZERO or MORE options of a limited number of choices.
Example
<form>
<input type="checkbox" id="vehicle1" name="vehicle1" value="Bike">
<label for="vehicle1"> I have a bike</label><br>
<input type="checkbox" id="vehicle2" name="vehicle2" value="Car">
<label for="vehicle2"> I have a car</label><br>
<input type="checkbox" id="vehicle3" name="vehicle3" value="Boat">
<label for="vehicle3"> I have a boat</label>
</form>
This is how the HTML code above will be displayed in a browser:
Input Type Button
<input type="button"> defines a button:
Example
<input type="button" onclick="alert('Hello World!')" value="Click Me!">
This is how the HTML code above will be displayed in a browser:
Input Type Color
The <input type="color"> is used for input fields that should contain a color.
Depending on browser support, a color picker can show up in the input field.
Example
<form>
<label for="favcolor">Select your favorite color:</label>
<input type="color" id="favcolor" name="favcolor">
</form>
Input Type Date
The <input type="date"> is used for input fields that should contain a date.
Depending on browser support, a date picker can show up in the input field.
Example
<form>
<label for="birthday">Birthday:</label>
<input type="date" id="birthday" name="birthday">
</form>
You can also use the min and max attributes to add restrictions to dates:
Example
<form>
<label for="datemax">Enter a date before 1980-01-01:</label>
<input type="date" id="datemax" name="datemax" max="1979-12-31"><br><br>
<label for="datemin">Enter a date after 2000-01-01:</label>
<input type="date" id="datemin" name="datemin" min="2000-01-02">
</form>
Input Type Datetime-local
The <input type="datetime-local"> specifies a date and time input field, with no time zone.
Depending on browser support, a date picker can show up in the input field.
Example
<form>
<label for="birthdaytime">Birthday (date and time):</label>
<input type="datetime-local" id="birthdaytime" name="birthdaytime">
</form>
Input Type Email
The <input type="email"> is used for input fields that should contain an e-mail address.
Depending on browser support, the e-mail address can be automatically validated when submitted.
Some smartphones recognize the email type, and add ".com" to the keyboard to match email input.
Example
<form>
<label for="email">Enter your email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email">
</form>
Input Type File
The <input type="file"> defines a file-select field and a "Browse" button for file uploads.
Example
<form>
<label for="myfile">Select a file:</label>
<input type="file" id="myfile" name="myfile">
</form>
Input Type Hidden
The <input type="hidden"> defines a hidden input field (not visible to a user).
A hidden field lets web developers include data that cannot be seen or modified by users when a form is submitted.
A hidden field often stores what database record that needs to be updated when the form is submitted.
Note: While the value is not displayed to the user in the page's content, it is visible (and can be edited) using any browser's developer tools or "View Source" functionality. Do not use hidden inputs as a form of security!
Example
<form>
<label for="fname">First name:</label>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br><br>
<input type="hidden" id="custId" name="custId" value="3487">
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
Input Type Month
The <input type="month"> allows the user to select a month and year.
Depending on browser support, a date picker can show up in the input field.
Example
<form>
<label for="bdaymonth">Birthday (month and year):</label>
<input type="month" id="bdaymonth" name="bdaymonth">
</form>
Input Type Number
The <input type="number"> defines a numeric input field.
You can also set restrictions on what numbers are accepted.
The following example displays a numeric input field, where you can enter a value from 1 to 5:
Example
<form>
<label for="quantity">Quantity (between 1 and 5):</label>
<input type="number" id="quantity" name="quantity" min="1" max="5">
</form>
Input Restrictions
Here is a list of some common input restrictions: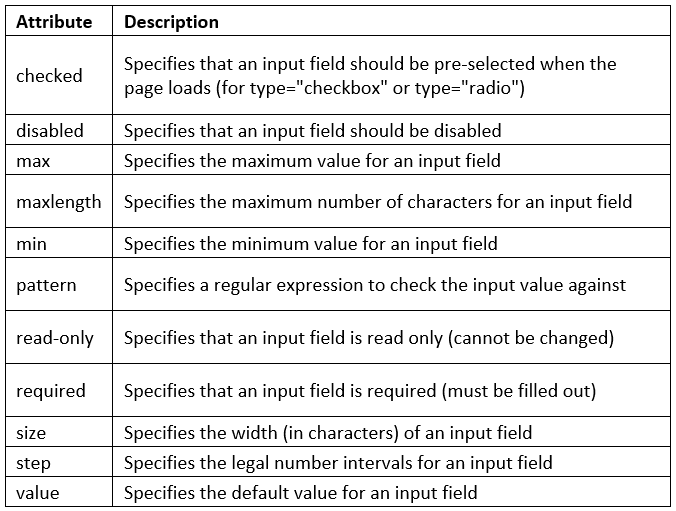
The following example displays a numeric input field, where you can enter a value from 0 to 100, in steps of 10. The default value is 30:
Example
<form>
<label for="quantity">Quantity:</label>
<input type="number" id="quantity" name="quantity" min="0" max="100" step="10" value="30">
</form>
Input Type Range
The <input type="range"> defines a control for entering a number whose exact value is not important (like a slider control). Default range is 0 to 100. However, you can set restrictions on what numbers are accepted with the min, max, and step attributes:
Example
<form>
<label for="vol">Volume (between 0 and 50):</label>
<input type="range" id="vol" name="vol" min="0" max="50">
</form>
Input Type Search
The <input type="search"> is used for search fields (a search field behaves like a regular text field).
Example
<form>
<label for="gsearch">Search Google:</label>
<input type="search" id="gsearch" name="gsearch">
</form>
Input Type Tel
The <input type="tel"> is used for input fields that should contain a telephone number.
Example
<form>
<label for="phone">Enter your phone number:</label>
<input type="tel" id="phone" name="phone" pattern="[0-9]{3}-[0-9]{2}-[0-9]{3}">
</form>
Input Type Time
The <input type="time"> allows the user to select a time (no time zone).
Depending on browser support, a time picker can show up in the input field.
Example
<form>
<label for="appt">Select a time:</label>
<input type="time" id="appt" name="appt">
</form>
Input Type Url
The <input type="url"> is used for input fields that should contain a URL address.
Depending on browser support, the url field can be automatically validated when submitted.
Some smartphones recognize the url type, and adds ".com" to the keyboard to match url input.
Example
<form>
<label for="homepage">Add your homepage:</label>
<input type="url" id="homepage" name="homepage">
</form>
Input Type Week
The <input type="week"> allows the user to select a week and year.
Depending on browser support, a date picker can show up in the input field.
Example
<form>
<label for="week">Select a week:</label>
<input type="week" id="week" name="week">
</form>