Best Study Material for Class 7 Exam
Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Notes > Science Class 7 > NCERT Summary: Nutrition in Animals
Nutrition in Animals Summary Class 7 NCERT Summary Chapter 2
Introduction
- Animals and humans have heterotrophic mode of nutrition because they obtain their food directly or indirectly from plants.
Nutrition
- Nutrition is the process of taking energy from food materials.
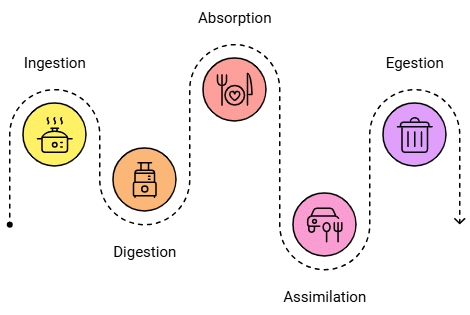
- It is a complex process and involves five important steps − ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion.

- Ingestion: It is the process of taking food. It takes place through mouth.
- Digestion: It is the process of breaking down of complex food components into simpler molecules.
- Absorption: It is the process in which all the digested food is absorbed by the walls of intestine.
- Assimilation is the process in which the absorbed food is delivered to each and every cell of the body where they are used to produce energy and complex substances such as proteins, etc.
- Egestion: It is the process in which the undigested, stored waste is excreted out from the body as faeces via anus.
Heterotrophic Nutrition
The heterotrophs that derive their energy directly from plants are called herbivores and those who derive their energy indirectly i.e. by eating herbivores are called carnivores.
- Omnivores: They feed on both plants and animals e.g. bear, rat, man etc.
- Decomposers: They obtain nutrients by breaking down remains of dead plants and animals, includes some bacteria and fungi.
Nutrition in Humans
The humans have complex mode of taking nutrition from food which is described below.
Mouth
- Mouth includes teeth, salivary glands, and tongue.
Teeth
- Teeth break down the food.
- They are of four types of teeth: molars, premolars (4), canines (2), and incisors (4) in each jaw.
- Molars are 6, Premolars are 4, Canines are 2 and Incisors are 4 in numbers and present in each jaw.
Functions of teeth
- Molars and premolars are for chewing and grinding food.
- Canines are for piercing and tearing food.
- Incisors are for cutting and biting food.
- In total life span of humans, two sets of teeth grow – milk teeth and permanent teeth.
Salivary glands
- Saliva is secreted by salivary glands located under the tongue.
- Salivary gland contains a digestive enzyme salivary amylase, which breaks down starch into sugar.
- Tongue helps in chewing and swallowing of food.
- The food from mouth passes down the oesophagus to the stomach, through the movement of walls of oesophagus (peristalsis)
- Stomach mixes the food received from oesophagus with digestive juices.
- Inner lining of stomach secretes hydrochloric acid and digestive juices.
 |
Important Questions Test: Nutrition in Animals
|
Start Test |
Start Test
Stomach
- Mucus: It protects the lining of stomach against the action of the acid.
- Hydrochloric acid: creates an acidic medium and helps in digestion of proteins.
- Digestive juices: break down protein into simple substance.
Pepsin breaks proteins into polypeptides
(i) Rennin changes soluble milk proteins into curd which is insoluble.
(ii) The food from stomach moves into the small intestine.
Digestion in small intestine
- It is the longest part (about 7.5 m long) of the alimentary canal.
- It is the site where complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats takes place.
- All the digested food is absorbed by the walls of intestine. This process is known as absorption.
- Villi:They are innner lining of small intestine which has tiny finger-like projections..
- Villi increase the surface area for more efficient food absorption.
- The absorbed food is delivered to each and every cell of the body where they are used to produce complex substances such as proteins, etc. This process is known as assimilation.
- It receives intestinal juice from two glands: liver and pancreas that help in further digestion of food.
Liver
- It is the largest gland of the body and secretes bile juice.
- Bile juice is stored in gall bladder and plays an important role in the digestion of fats.
Pancreas
- Pancreas contains enzymes that help in complete digestion of all food components.
- Amylase breaks starch into maltose
- Lipase breaks complex fats into simple fats.
Functions of enzymes secreted in small intestine:
- Maltase changes maltose to glucose
- Sucrase changes sucrose to glucose
- Lactase changes lactose to glucose
- Peptidase changes polypeptides to amino acids
 |
Download the notes
NCERT Summary: Nutrition in Animals
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
Digestion in large intestine
- The digested food from small intestine goes into blood stream and the undigested and unabsorbed material and water enters the large intestine.
- The function of large intestine is absorption of water and some salts from undigested food.
- From large intestine, the waste material is stored in rectum in the form of semi-solid faeces.
- The undigested, stored waste is excreted out from the body as faeces via anus. This process is known as egestion.
The document Nutrition in Animals Summary Class 7 NCERT Summary Chapter 2 is a part of the Class 7 Course Science Class 7.
All you need of Class 7 at this link: Class 7
|
112 videos|252 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Nutrition in Animals Summary Class 7 NCERT Summary Chapter 2
| 1. What are the main modes of nutrition in animals? |  |
| 2. How do herbivores digest plant material? |  |
Ans. Herbivores have specialized digestive systems that allow them to break down tough plant materials. They usually possess a larger and more complex stomach or multi-chambered stomachs, such as ruminants, which help in the fermentation of cellulose by bacteria. This process allows them to extract nutrients from the plant material efficiently.
| 3. What is the role of enzymes in animal nutrition? |  |
Ans. Enzymes play a crucial role in the digestion of food in animals. They act as biological catalysts that speed up the chemical reactions involved in breaking down complex food molecules into simpler substances. Different enzymes target specific types of nutrients, such as proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, making it possible for animals to absorb these nutrients into their bloodstream.
| 4. What is the significance of water in the nutrition of animals? |  |
Ans. Water is essential for all living organisms, including animals. It serves as a solvent for biochemical reactions, helps in the transportation of nutrients and waste products, regulates body temperature, and aids in digestion. Adequate water intake is crucial for maintaining overall health and proper functioning of the body.
| 5. How do carnivores differ from herbivores in their digestive systems? |  |
Ans. Carnivores typically have shorter digestive tracts compared to herbivores because meat is easier to digest than plant material. They possess sharper teeth for tearing flesh and a highly acidic stomach that helps in breaking down proteins. In contrast, herbivores have flat molars for grinding plant material and longer intestines to facilitate the breakdown of cellulose.
Related Searches