Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Notes > Science Olympiad Class 7 > NCERT Summary: Acids, Base & Salts
Acids, Base & Salts Summary Class 7 NCERT Summary
Acids and Bases
Acids- Acids are sour in taste.
- Substances that are sour to taste are acidic in nature.
- Examples: Curd, lemon juice, orange juice, vinegar, etc.
Bases
- Bases are bitter to taste and soapy in touch.
- Those substances that are bitter to taste and soapy to touch are basic in nature.
- Examples: Baking soda, antacids, caustic lime, etc.
Indicators
- Chemicals that are used to check the acidic or basic nature of substances are called indicators.
- The indicators change their colour when added to a solution containing an acidic or a basic substance.
Natural Indicators
- Turmeric, litmus, china rose petals (Gudhal), etc., are some of the naturally occurring indicators.
- One of the most commonly used indicators is litmus solution (a natural indicator).
- Acids turn blue litmus paper to red, and bases turn red litmus paper to blue.
- Turmeric paste and China rose are also natural indicators.
- China rose indicator becomes dark pink when an acidic substance is added to it and turns to green when a basic substance is added to it.
- Turmeric paste remains yellow in acidic solutions but turns red in basic solutions.
Neutral Substances
- Substances that are neither acidic nor basic in nature are called neutral substances.
- Neutral substances do not affect the colour of indicators.
Neutralization
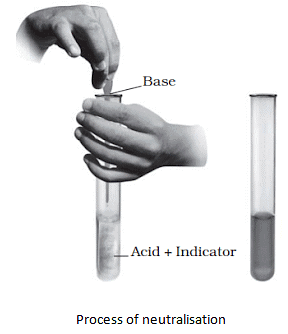
- When an acid is mixed with a base, it neutralizes the effect of each other. This reaction is known as the neutralization reaction.
- Water and salt are produced as products during the neutralization reaction.
- Heat is also produced during the neutralization reaction.
Acid + Base → Salt + Water + Heat - The salt produced during neutralization reactions can be acidic, basic, or neutral in nature.
Ant Sting
- Ant sting contains formic acid. The effect of this acid is neutralized by rubbing moist baking soda (sodium hydrogen carbonate) or calamine solution that contains zinc carbonate.
Indigestion
- Milk of Magnesia (magnesium hydroxide) is an antacid used to neutralize the effect of the acid produced in our stomach.
Soil treatment
- Excessive use of chemical fertilizers makes the soil acidic.
- Plants do not grow well on acidic or basic soil.
- When the soil is too acidic, it basic is treated with bases like quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide). If the soil is basic, organic matter is added to it.
Factory wastes
- The wastes of many factories contain acids which are neutralized by adding basic substances.
The document Acids, Base & Salts Summary Class 7 NCERT Summary is a part of the Class 7 Course Science Olympiad Class 7.
All you need of Class 7 at this link: Class 7
|
49 videos|125 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Acids, Base & Salts Summary Class 7 NCERT Summary
| 1. What is the difference between acids and bases? |  |
Ans. Acids and bases are two types of chemical substances with different properties. Acids are substances that release hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water, while bases are substances that release hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water. Acids have a sour taste, turn blue litmus paper red, and have a pH value less than 7. Bases have a bitter taste, turn red litmus paper blue, and have a pH value greater than 7.
| 2. How do acids and bases react with each other? |  |
Ans. Acids and bases can react with each other in a chemical reaction called neutralization. In this reaction, the hydrogen ions from the acid combine with the hydroxide ions from the base to form water. The remaining ions form a salt. For example, when hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), water (H2O) and sodium chloride (NaCl) are formed.
| 3. What are the uses of acids and bases? |  |
Ans. Acids and bases have various uses in everyday life. Some common uses of acids include:
- Vinegar, which contains acetic acid, is used for cooking and preserving food.
- Lemon juice, which contains citric acid, is used for flavoring food and beverages.
- Sulfuric acid is used in car batteries and as a laboratory reagent.
Some common uses of bases include:
- Sodium hydroxide is used in the production of soap and detergents.
- Calcium hydroxide is used in agriculture to neutralize acidic soils.
- Ammonia is used in household cleaning products.
| 4. How can the strength of acids and bases be determined? |  |
Ans. The strength of an acid or base can be determined by its pH value. pH is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Acids have a pH value less than 7, with lower values indicating stronger acids. Bases have a pH value greater than 7, with higher values indicating stronger bases.
| 5. Are there any natural sources of acids and bases? |  |
Ans. Yes, there are natural sources of acids and bases. Some examples include:
- Citrus fruits, such as lemons and oranges, contain citric acid.
- Milk contains lactic acid.
- Vinegar is produced by the fermentation of ethanol by acetic acid bacteria.
- Bases can be found in substances like baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) and limestone (calcium carbonate).
Related Searches
















