Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Science Class 8 > NCERT Summary: Combustion & Flame
Combustion & Flame Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary
Introduction
- Fuels are used to get energy in the form of heat. Cow dung, wood, coal, charcoal, petrol, diesel, compressed natural gas (CNG), etc. are the examples of fuels.
- Candle burns with a flame whereas coal does not.
Combustion
- It is a chemical process in which a substance reacts with oxygen to give off heat and light.
- Oxygen (in air) is essential for combustion.
- Substances that burn in air are called combustible substances (also called fuels) and those that do not burn in air are non-combustible substances.
Ignition temperature
It is the lowest temperature at which a substance catches fire.
Substances like kerosene oil and petrol have low ignition temperatures and are called inflammable substances.
Supporter of combustion
- The gaseous environment that supports combustion of a combustible substance is called supporter of combustion.
- Smaller the size of combustible particles, faster is the rate of combustion.
- Nature of combustible substances: Inflammable substances burn faster as compared to substances such as wood.
Control of fire
- Water is commonly used to extinguish fire. It is not suitable for fires involving oil, petrol, and electrical equipments.
- For fires involving oil, petrol, and electrical equipments, carbon dioxide is the best extinguisher.
Types of combustion
(i) Rapid combustion
The combustion in which substances burn rapidly to produce heat and light. In rapid combustion, external heat must be supplied (e.g., gas stove).
(ii) Spontaneous combustion
The combustion in which substances suddenly burst into flames, without the application of any apparent cause (e.g., phosphorus, coal dust).
(iii) Explosion
The combustion in which sudden reactions take place on ignition of some substances to produce heat, light, and sound (e.g., fireworks).
Zones of candle flame
- Dark zone (middle zone), luminous zone (innermost zone), and non-luminous zone (outer zone).
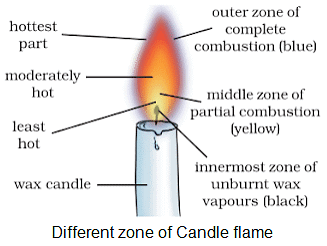
- A good fuel is one which is cheap is readily available burns easily in air at a moderate rate produces large amount of heat does not leave behind any undesirable substances.

Fuel efficiency
- It is expressed in terms of calorific value. The unit is kilo joule per kg.
Calorific value
- It is the amount of heat energy produced by complete combustion of 1 kg of a fuel.
- It is expressed in Kilo joule per kg (kJ/kg).
The document Combustion & Flame Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary is a part of the Class 8 Course Science Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
92 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Combustion & Flame Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary
| 1. What is combustion and what are its main types? |  |
Ans.Combustion is a chemical process in which a substance reacts rapidly with oxygen, producing heat and light. The main types of combustion are complete combustion, where a fuel burns in sufficient oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water, and incomplete combustion, where there is a limited supply of oxygen, leading to the formation of carbon monoxide or soot.
| 2. What is the role of the ignition temperature in combustion? |  |
Ans.Ignition temperature is the minimum temperature required to initiate combustion of a substance. If a substance reaches its ignition temperature, it will start burning. Different materials have different ignition temperatures, which play a crucial role in determining how easily they can catch fire.
| 3. How do fuels differ from one another? |  |
Ans.Fuels can differ in terms of their physical state (solid, liquid, or gas), composition, calorific value (the amount of energy released during combustion), and their environmental impact. For example, fossil fuels like coal and petroleum are solid and liquid fuels, respectively, whereas natural gas is a gaseous fuel.
| 4. What are the environmental impacts of combustion? |  |
Ans.Combustion can lead to several environmental impacts, including air pollution from the release of harmful gases like carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides. These emissions contribute to global warming and respiratory problems in humans. Additionally, incomplete combustion can produce particulate matter, which is detrimental to health.
| 5. What are the different ways to control combustion? |  |
Ans.Combustion can be controlled through various methods, such as ensuring an adequate supply of oxygen for complete combustion, using catalysts to lower the ignition temperature, and employing technology like scrubbers and filters to reduce emissions. Proper fuel management and combustion techniques can also help minimize environmental impact.
Related Searches

















