Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 8 > NCERT Summary: Judiciary
Judiciary Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 5
What is the Role of the Judiciary?
Judiciary work is divided into the following types:
- Dispute Resolution: The judicial system resolves disputes between citizens, between citizens and the government, between two state governments and between the centre and state governments.
- Judicial Review: The judiciary is the final interpreter of the Constitution therefore, it has the power to strike down particular laws passed by the Parliament if it believes that these are a violation of the basic structure of the Constitution. This is called judicial review.
- Upholding the Law and Enforcing Fundamental Rights: Every citizen in India can approach the Supreme Court or High Court if they think their Fundamental Rights have been violated. The independence of the judiciary enables the courts to ensure there is no abuse of power by the legislature and the executive.
What is an Independent Judiciary?
- The other branches of the State, such as the legislature and the executive, cannot interfere with the judiciary's work.
- The courts operate independently and do not represent the government.
- Judges in the High Court and the Supreme Court are appointed with minimal interference from other government branches.
- Once a judge is appointed, it is quite challenging to remove them.
- The independence of the judiciary allows the courts to ensure that the legislature and the executive do not misuse their power. It also plays a vital role in safeguarding the Fundamental Rights of citizens, as anyone can approach the courts if they feel their rights have been breached.
What is the Structure of Courts in India?
There are three different levels of courts in our country:
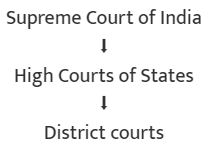
- Supreme Court of India: Based in New Delhi and led by the Chief Justice of India. Its rulings are mandatory for all other courts in the country.
- High Courts of States: Each state has a High Court, which is its highest court. There are currently 25 High Courts, with some states sharing them; for instance, Punjab and Haryana share a High Court in Chandigarh.
- Subordinate or District Courts: These are located at the district or Tehsil level, overseen by a District Judge. States are divided into districts, each managed by a District Judge. Some High Courts have benches in different areas for better access.
- A person can appeal to a higher court if they think a lower court's decision is unfair, through the appellate system.
High Courts were first set up in the three Presidency cities of Calcutta, Bombay, and Madras in 1862.
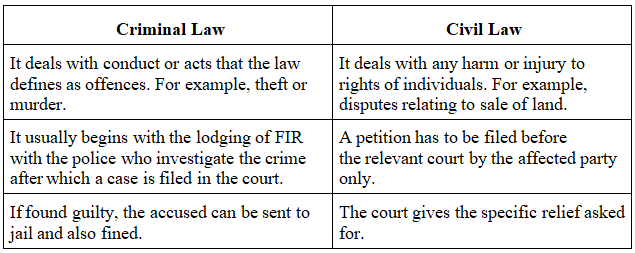
What are the Different Branches of the Legal System?
- The Indian legal system deals with civil and criminal cases:
Does Everyone Have Access to the Courts?
- Theoretically, all citizens of India can access the courts in this country.
- In reality access to courts has always been difficult for a vast majority of the poor in India.
- Legal procedures involve a lot of money and paperwork as well as take up a lot of time.
- For a poor person who cannot read and whose family depends on a daily wage, the idea of going to court to get justice often so remote.
PIL
- Public Interest Litigation (PIL) is introduced by Supreme Court in the early 1980s.
- It allowed any individual or organisation to file a PIL in the High Court or the Supreme Court on behalf of those whose rights were being violated.
- A letter or telegram addressed to the Supreme Court or the High Court could be treated as a PIL.
Importance of Judiciary
- The judiciary plays a vital role in democratic India.
- It monitors the powers of the executive and the legislature.
- Moreover, it protects the Fundamental Rights of citizens and ensures that power is not misused by the legislature and the executive.
The document Judiciary Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 5 is a part of the Class 8 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
69 videos|431 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Judiciary Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 5
| 1. What is the role of the judiciary in India? |  |
Ans. The judiciary in India is responsible for interpreting the law, ensuring justice, and protecting the rights of citizens. It acts as a guardian of the Constitution and has the power to review laws and executive actions to ensure they comply with constitutional provisions.
| 2. How is the Indian judiciary structured? |  |
Ans. The Indian judiciary is structured in a hierarchical manner, consisting of the Supreme Court at the top, followed by High Courts in each state, and then subordinate courts at the district level. This structure ensures that justice is accessible at different levels.
| 3. What are the key functions of the Supreme Court of India? |  |
Ans. The key functions of the Supreme Court of India include the interpretation of the Constitution, hearing appeals from lower courts, protecting fundamental rights, and resolving disputes between states or between the central government and states.
| 4. How does the judiciary ensure the protection of fundamental rights? |  |
Ans. The judiciary ensures the protection of fundamental rights by reviewing laws and actions that may violate these rights. Citizens can approach the courts for enforcement of their rights, and the judiciary has the authority to strike down laws that are unconstitutional.
| 5. What is the process of appointing judges in the Indian judiciary? |  |
Ans. Judges in the Indian judiciary are appointed through a process involving the President of India, who appoints the Chief Justice and other judges based on recommendations made by the Chief Justice and a collegium of senior judges. This process aims to maintain the independence of the judiciary.
Related Searches
















