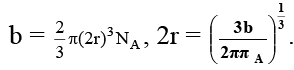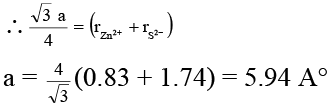JEE Advanced (Single Correct Type): States of Matter | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. At constant temperature the product of pressure and volume of a given amount of a gas is constant this is ______.
(a) Gay-Lussac law
(b) Charles’ law
(c) Boyle’s law
(d) None of these
Correct Answer is option (c)
According to Boyle’s law the product of volume and pressure of a given mass of gas is constant at constant temperature. PV= constant.
Q.2. Rate of diffusion of a gas is ________
(a) Directly proportional to its density
(b) Directly proportional to its molecular mass
(c) Directly proportional to the square of its molecular mass
(d) Inversely proportional to the square root of its molecular mass
Correct Answer is option (d)
Rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molecular mass.
Q.3. Non-ideal gases approach ideal behaviour under:
(a) High temperature and high pressure
(b) High temperature and low pressure
(c) Low temperature and high pressure
(d) Low temperature and low pressure
Correct Answer is option (b)
Non-ideal gases approach ideal behaviour under high temperature and low pressure
Q.4. At 25 degrees celsius and 730 mm pressure, 380 ml of dry oxygen was collected. If the temperature is constant, what volume will oxygen occupy at 760 mm pressure?
(a) 365 ml
(b) 449 ml
(c) 569 ml
(d) 621 ml
Correct Answer is option (a)
P1 = 730 mm V1 = 380 ml P2 =760 mm V2 = ?
At constant temperature, P1V1 = P2V2
V2 = P1V1/P2 = (760 x 380) / 760 = 365 mL
Q.5. The kinetic theory of gases predicts that total kinetic energy of gas depends on——–
(a) Pressure of the gas
(b) Temperature of the gas
(c) Volume of the gas
(d) Pressure, temperature and volume of the gas
Correct Answer is option (b)
The kinetic theory of gases predicts that total kinetic energy of gas depends on temperature of the gas.
Q.6. Gases deviate from ideal behaviour because molecules————-
(a) Are colourless
(b) Are spherical
(c) Attract each other
(d) Have high speeds
Correct Answer is option (c)
Gases deviate from ideal behaviour because molecules attract each other.
Q.7. Dominance of strong repulsive forces among the molecule of the gas:
(a) Depends on Z and indicates that Z = 1
(b) Depends on Z and indicates that Z > 1
(c) Depends on Z and indicates that Z<1
(d) Is independent of Z
Correct Answer is option (b)
Because of strong repulsive forces molecules of a gas cannot be compressed and Z > 1
Q.8. The term which accounts for intermolecular forces in a van der Waal equation is:
(a) (V – b)
(b) (RT)-1
(c) (P + a/V2)
(d) RT
Correct Answer is option (c)
(P + a/V2) represent the intermolecular forces in a van der Waal equation.
Q.9. The density of a gas A is twice that of gas B. Molecular mass of A is half of the molecular mass of B. The ratio of the partial pressure of A and B is __________.
(a) 1/4
(b) 1/2
(c) 4/1
(d) 2/1
Correct Answer is option (c)
PV =nRT ⇒ P = wRT/MV ⇒ P = dRT/M
PA / PB = (dA x MB) /(dB x MA) ⇒ 4/1
Q.10. A gas can be liquefied:
(a) Above its critical temperature
(b) At its critical temperature
(c) Below its critical temperature
(d) At any temperature
Correct Answer is option (c)
Gas can be liquefied below its critical temperature.
Q.11. 0.5 mole of each H2, SO2 and CH4 are kept in a container. A hole was made in the container. After 3 hours, decreasing order of partial pressures of gases in the container will be
(a) PSO2 > PCH4 > PH2
(b) PH2 > PSO2 > PCH4
(c) PCH4 > PSO2 > PH2
(d) PCH4 > PH2 > PSO2
Correct Answer is option (a)
Higher the molecular weight of a gas, lesser the rate of diffusion under similar condition so that number of moles of SO2 is least diffused, than CH4 and than H2.
Q.12. The density of nitrogen is maximum at
(a) STP
(b) 273 K and 2 atm
(c) 546 K and 1 atm
(d) 546 and 2 atm
Correct Answer is option (b)
d = PM/RT; so more is the value of P/T, more is the density.
Q.13. If 'b' is van der Waal constant of argon then the molecular diameter of argon molecule can be represented by the expression
(a) 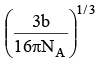
(b) 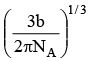
(c) 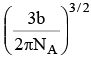
(d) 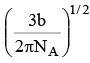
Correct Answer is option (b)
Q.14. In cubic ZnS lattice, if the radii of Zn2+ and S2– ions are 0.83 A° and 1.74 A°, the lattice parameter (edge length, a) of cubic ZnS is
(a) 11.87 A°
(b) 5.94 A°
(c) 5.14 A°
(d) 2.97 A°
Correct Answer is option (b)
In ZnS lattice, S2– ions are present as FCC with Zn2+ ions occupying alternate tetrahedral voids.
Q.15. NaCl is doped with 10–3 mol % FeCl3. The number of unoccupied of octahedral voids per mol of NaCl is
(a) 6.02 × 1018 mol–1
(b)12.04 × 1018 mol–1
(c) 3.01 × 1018 mol–1
(d)6.02 × 1013 mol–1
Correct Answer is option (b)
One Fe3+ ion replaces three Na+ ions.
As Na+ ions occupy all octahedral voids of NaCl crystal, due to replacement few octahedral voids fall vacant.
So, one Fe3+ ion creates two vacant octahedral voids.
10–3 mole FeCl3 creates unoccupied octahedral voids = 2 × 6.02 × 1023 × 10–3 = 12.04 × 1020
Hence, 100 mole of doped NaCl crystals create 12.04 × 1020 vacant octahedral voids.
Hence, 1 mole of doped NaCl crystals create 12.04 × 1018 vacant octahedral voids.
|
446 docs|930 tests
|