UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Class 6 to 12 NCERT Mindmaps for UPSC Preparation > Mind Map: Soils
Mind Map: Soils | Class 6 to 12 NCERT Mindmaps for UPSC Preparation PDF Download
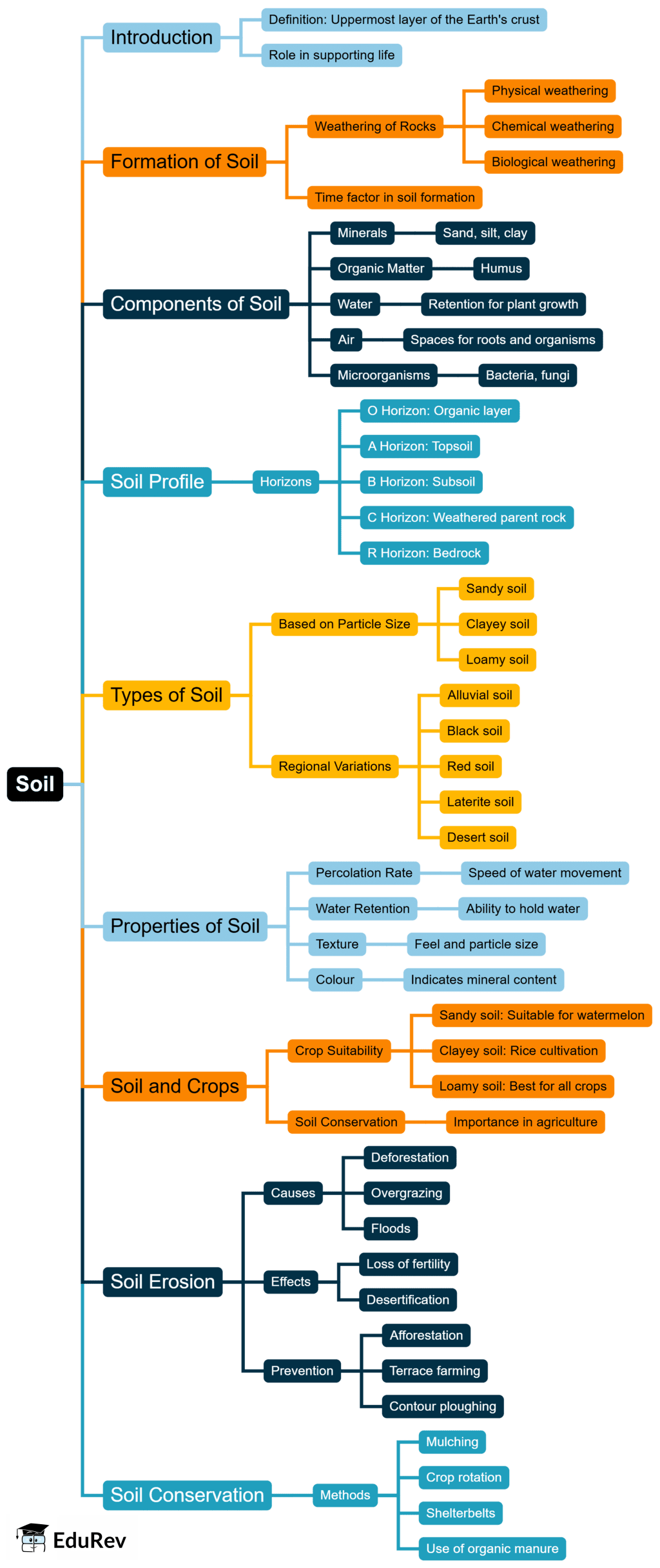
The document Mind Map: Soils | Class 6 to 12 NCERT Mindmaps for UPSC Preparation is a part of the UPSC Course Class 6 to 12 NCERT Mindmaps for UPSC Preparation.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
FAQs on Mind Map: Soils - Class 6 to 12 NCERT Mindmaps for UPSC Preparation
| 1. What are the different types of soils and their characteristics? |  |
Ans. The main types of soils include sandy, clayey, silty, loamy, and peaty soils. Sandy soils have larger particles and drain quickly, making them less fertile. Clayey soils have smaller particles, retain moisture, and are nutrient-rich but can be compacted. Silty soils are smooth and retain moisture well but can be prone to erosion. Loamy soils are a balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay, making them ideal for gardening. Peaty soils are rich in organic matter and moisture but can be acidic.
| 2. How do soil properties affect plant growth? |  |
Ans. Soil properties such as texture, structure, pH, and nutrient content significantly affect plant growth. Texture influences water retention and aeration; for instance, sandy soils drain quickly but may not hold nutrients well. Soil structure affects root penetration and water movement. pH levels can determine the availability of nutrients to plants, with most plants thriving in slightly acidic to neutral soils. Nutrient content is vital for plant health, as deficiencies can lead to poor growth.
| 3. What is soil erosion and how can it be prevented? |  |
Ans. Soil erosion is the removal of the top layer of soil due to factors like water, wind, and human activity. It can lead to loss of fertile land and degradation of ecosystems. Prevention methods include planting cover crops, maintaining vegetation cover, practicing no-till farming, implementing contour farming, and building terraces. These practices help to hold the soil in place and reduce the impact of erosive forces.
| 4. What role do microorganisms play in soil health? |  |
Ans. Microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and protozoa, play a crucial role in soil health by decomposing organic matter, recycling nutrients, and promoting soil structure. They help in breaking down complex organic materials into simpler compounds that plants can absorb. Some microorganisms form symbiotic relationships with plants, enhancing nutrient uptake. A healthy microbial community is essential for maintaining soil fertility and supporting plant growth.
| 5. How can soil quality be tested and improved? |  |
Ans. Soil quality can be tested through soil testing kits or professional laboratory analysis, which measure pH, nutrient levels, and organic matter content. To improve soil quality, one can add organic matter like compost, use cover crops to enhance nutrient content, practice crop rotation to maintain soil health, and apply appropriate fertilizers based on soil test results. Regular testing and amendments can lead to improved soil fertility and better crop yields.
Related Searches





















