Economic Development: January 2023 UPSC Current Affairs | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
Startup India Innovation Week

Why in News?
- National Startup Awards 2022 given by Ministry of Commerce and Industry acknowledges startups and enablers who have been instrumental in revolutionizing the development story of India.
- Startup India organized industry-focused webinars on the topic "Championing the billion-dollar dream".
What is the Status of Startups in India?
- About:
- The Start-up ecosystem in India ranks third after that of the United States (US) and China.
- According to the India Venture Capital Report 2021 published by Bain and Company, the number of cumulative start-ups has grown at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 17% since 2012.
- Growth Drivers:
- Large Domestic Market: India has a large domestic market for technology-based products and services, providing a ready market for startups to sell their products and services.
- Government Support: The government of India has been actively promoting entrepreneurship through initiatives such as "Atma Nirbhar Bharat" and "Digital India," providing support to young companies.
- Access to Technology: Advancements in technology and internet penetration have enabled startups to scale up quickly, leading to the rise of several unicorns in the ecosystem.
- Rising Start-up Hubs: The major startup hubs in India are Bengaluru, Mumbai, and Delhi-NCR, providing a conducive environment for startups to grow and thrive.
- Bengaluru, in particular, has been dubbed the "Silicon Valley of India" due to the large number of technology companies based in the city.
- Problems Associated with Startup Ecosystem:
- Stringent Regulatory Environment: The market laws and regulations are not always tailored to the needs of startups, which can make it difficult for them to comply. This can be a significant burden for early-stage companies.
- Limited Infrastructure and Logistics: The lack of proper infrastructure and logistics can be a major challenge for startups, especially those operating in the e-commerce space.
- The inadequate transportation, warehousing and logistics infrastructure can make it difficult for startups to reach customers and deliver their products on time.
- Lack of Mentorship and Guidance: Startups often lack access to experienced mentors and guidance, which can make it difficult for them to navigate the business landscape and make informed decisions.
- Recent Government Initiatives to Support Startup Ecosystem:
- Start-up India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS): This scheme provides financial assistance to start-ups to help them prove their concept, develop prototypes, test products, and enter the market.
- National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing Innovations (NIDHI): It is an end-to-end plan for start-ups to double the number of incubators and start-ups in the duration of five years.
- Ranking of States on Support to Startup Ecosystems (RSSSE): The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry has been conducting the States’ Start-up Ranking Exercise since 2018.
Way Forward
- Encouraging Innovation: The government and private sector should encourage innovation by providing funding and support for research and development.
- This can include setting up R&D centres, providing tax incentives for companies that invest in R&D, and connecting startups with universities and research institutions.
- School-Entrepreneurship Corridor: The National Education Policy, 2020 promotes student entrepreneurs by providing vocational education in partnership with industry and thriving innovation at school level.
- This can have a favourable impact on the start-up ecosystem in India, if entrepreneurial skills are integrated with the education curriculum.
- Towards Social Acceptability of Start-ups: By collaborating with various unicorns of India, the government needs to work towards social acceptance of entrepreneurial careers and channelize the youth in the right direction to choose a career with ease.
- Vocal for Local, Local to Global: Indian start-ups have the potential to not only look at Indian traditional problems, but also offer customised solutions for markets abroad.
- Exclusive Startup Zones can be initiated at state levels linked with Atma Nirbhar Bharat Initiative making India an entrepreneurship and export hub.
Purchasing Managers Index
Why in News?
As per the S&P Global India Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI), the manufacturing sector in India had its most significant production growth in 13 months in December 2022.
- For the October to December quarter, the PMI averaged 56.3, the highest in a year. It indicates that the manufacturing sector is performing well and may be contributing to job creation.
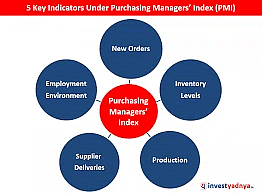
What is Purchasing Managers Index?
- It is a survey-based measure that asks the respondents about changes in their perception about key business variables as compared with the previous month.
- The purpose of the PMI is to provide information about current and future business conditions to company decision makers, analysts, and investors.
- It is calculated separately for the manufacturing and services sectors and then a composite index is also constructed.
- The PMI is a number from 0 to 100.
- A print above 50 means expansion, while a score below that denotes contraction.
- A reading at 50 indicates no change.
- If PMI of the previous month is higher than the PMI of the current month, it represents that the economy is contracting.
- It is usually released at the start of every month. It is, therefore, considered a good leading indicator of economic activity.
- PMI is compiled by IHS Markit for more than 40 economies worldwide.
- IHS Markit is a global leader in information, analytics and solutions for the major industries and markets that drive economies worldwide.
- IHS Markit is part of S&P Global.
What is the Significance of PMI?
- The PMI is widely followed as an indicator of economic health because the manufacturing and services sector is a key driver of economic growth.
- In general, a high PMI reading is seen as a positive sign for the economy, as it indicates that the manufacturing and services sectors are performing well and contributing to economic growth.
- A low PMI reading is seen as a negative sign, as it indicates that the manufacturing and services sectors are struggling and may be dragging down overall economic performance.
Sugar Exports
 Why in News?
Why in News?
According to the Indian Sugar Mills Association (ISMA), sugar mills in India have entered into contracts to export 55 lakh tonnes of sweetener.
- The government has allowed sugar mills to export 60 lakh tonnes of sugar till May in the 2022-23 marketing year (October-September).
What is the Present Status of the Sugar Industry in India?
- About:
- Sugar industry is an important agro-based industry that impacts the rural livelihood of about 50 million sugarcane farmers and around 5 lakh workers directly employed in sugar mills.
- In (Oct-Sep) 2021-22 India emerges as the world’s largest producer and consumer of sugar and world’s 2nd largest exporter of sugar.
- Geographical Conditions for the Growth of Sugar:
- Temperature: Between 21-27°C with hot and humid climate.
- Rainfall: Around 75-100 cm.
- Soil Type: Deep rich loamy soil.
- Top Sugarcane Producing States: Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka.
- Growth Drivers for Sugar Industries:
- Impressive Sugar Season (Sep-Oct): All records of sugarcane production, sugar production, sugar exports, cane procured, cane dues paid and ethanol production was made during the season.
- High exports: The exports were the highest at about 109.8 LMT without any financial assistance and earned foreign currency of about Rs. 40,000 crores in the year 2021-22.
- Indian Government Policy Initiatives: Timely government initiatives in the last 5 years have taken them out of financial distress in 2018-19 to the stage of self-sufficiency in 2021-22.
- Encouraging Ethanol Production: The Government has encouraged sugar mills to divert sugar to ethanol and also export surplus sugar so that mills may have better financial conditions to continue their operations.
- Ethanol Blending with Petrol (EBP) Programme: The National Policy on Biofuels 2018, provides an indicative target of 20% ethanol blending under the Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme by 2025.
- Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP): The FRP is the minimum price that sugar mills have to pay to sugarcane farmers for procurement of sugarcane.
- It is determined on the basis of recommendations of the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) and after consultation with State Governments and other stakeholders.
- Problems Associated:
- Competition from Other Sweeteners: The Indian sugar industry is facing increasing competition from other sweeteners such as high fructose corn syrup, which is cheaper to produce and has a longer shelf life.
- Lack of Modern Technology: Many of the sugar mills in India are outdated and lack the modern technology needed to produce sugar efficiently. This makes it difficult for the industry to compete with other sugar-producing countries.
- Environmental Impact: Sugarcane cultivation requires large amounts of water and pesticides, which can have a negative impact on the environment.
- Additionally, sugar mills often release pollutants into the air and water, which can harm nearby communities.
- Political interference: Sugar industry in India is heavily influenced by politics, with the state and central government having a significant role in determining the prices, production, and distribution of sugar. This often leads to a lack of transparency and inefficiency.
Way Forward
- Remote Sensing Technology: Despite the importance of sugarcane in the water, food and energy sectors in India, there are no reliable sugarcane maps for recent years and in time series.
- There is a need to deploy remote sensing technologies to map sugarcane areas.
- Diversification: The sugar industry in India should diversify its operations by exploring other products such as biofuels and organic sugar.
- This would help to reduce the risk associated with fluctuations in sugar prices.
- Encouraging Research and Development: The industry should invest in research and development to improve crop yields and reduce the environmental impact of sugar production.
- Encouraging Sustainable Practices: The industry should encourage sustainable practices, such as water conservation, integrated pest management, and reduced use of pesticides, in order to reduce the negative impact of sugar production on the environment.
Corporate Tax

Why In News?
Recently, corporate tax collections exceeded 3% of the GDP after a gap of two years in 2021-22.
- It is reflecting overall improvement in profitability of India Inc propelled by an increase in demand for goods and services.
- However, the corporate tax collection is yet to surpass its five-year high of 3.51% of GDP recorded in 2018-19.
What are the Key Highlights?
- In actual terms, the net corporate tax collection in 2021-22 stood at Rs 7.12 lakh crore.
- The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at the current market price was Rs 236.64 lakh crore.
- The percentage of net corporate tax to GDP worked out to be 3.01%.
- In 2019-20, government cut corporate tax rates for new manufacturing units by almost 10% points as it looked to pep up investments.
- The rate of Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT) too had been reduced to 15 % from 18.5 % in 2019.
- The Minimum Alternate Tax is a strategy designed to close the income tax loophole for all businesses. The MAT makes sure that no business, even one with strong financial standing and significant revenue, may escape paying income tax, even after claiming exemptions.
- The tax cut was reflected in the realization of corporate taxes in 2019-20, when collections fell to over Rs 5.56 lakh crore (2.77% of GDP).
Corporate Tax
- A corporate tax is a tax on a corporation’s profits. Taxes are paid on a company’s taxable income, which is revenue less general and administrative (G&A), selling and marketing, R&D, depreciation, and other operating expenditures.
- A corporate entity’s net income or profit from its operations, whether domestic or international, is subject to the direct tax which is the corporation tax or corporate tax.
- The Corporate Tax Rate is the amount of tax levied by the terms of the Income Tax Act of 1961.
- Depending on the kind of business entity and the various revenues generated by each corporate entity, the corporate tax rate is based on a slab rate structure.
- Corporate tax rates vary greatly amongst nations, with some having meager rates and being labeled as tax havens.
- The effective corporate tax rate, or the rate a corporation pays, is typically lower than the statutory rate, which is the declared amount before any deductions because corporate taxes can be reduced by a variety of deductions, government subsidies, and tax loopholes.
Corporate tax in India
As a source of revenue, the Indian government levies corporation taxes on businesses. The basis for calculating this tax is a company’s net income. These are the various sources of income a business receives.
- Profits earned by the business
- Income from renting a property
- Capital gains
- Income from other sources
Domestic companies
- Both public and private businesses that are registered under the Companies Act of 1956 must pay this tax.
- Currently, domestic businesses pay a 30% tax rate. Additionally, if net income is between Rs. 1 crore and Rs. 10 crores, the Income Tax Act imposes a 7% surcharge.
- A 12% surcharge is applied to a company’s net income exceeding Rs. 10 crores.
- 2019 saw the introduction of Section 115BAA by the Indian government through the Taxation (Amendment) Ordinance.
- This resulted in many changes to the Income Tax Act, including a reduction in the corporation tax rate for domestic businesses.
- Domestic firms now can pay tax at a rate of 25.168% thanks to Section 115BAA.
Foreign Companies
- On the money they earn within a certain period, foreign corporations are required to pay corporate income tax.
- Royalties and other fees are subject to a 50% corporation tax rate in India, while the remaining revenue is subject to a 40% tax rate.
- A 2% surcharge is applied to foreign companies with net incomes between Rs. 1 crore and Rs. 10 crore.
- If its net income surpasses Rs. 10 crores, a 5% surcharge will be added.
Additional charges
- No matter the level of a company’s net income, a 4% Health and Education Cess is imposed on the total income tax and the surcharge.
- Additionally, under Section 115JB of the Act, businesses receiving advantages under Section 115BAA are excluded from paying Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT).
- MAT is applied to start with AY 2020–2021 at a rate of 15%.
The Taxation Laws (Amendment) Bill, 2019
- Currently, domestic companies with an annual turnover of up to Rs 400 crore pay income tax at the rate of 25%. For other domestic companies, the corporate tax rate is 30%. The Bill provides domestic companies with an option to pay tax at the rate of 22%, provided they do not claim certain deductions under the Income Tax Act.
- The Bill provides new domestic manufacturing companies with an option to pay income tax at the rate of 15%, provided they do not claim certain deductions. These new domestic manufacturing companies must be set up and registered after September 30, 2019, and start manufacturing before April 1, 2023.
- A company can choose to opt for the new tax rates in the financial year 2019-20 (i.e. assessment year 2020-21) or any other financial year in the future. Once a company exercises this option, the chosen provider will apply for all subsequent years.
- Provisions regarding payment of Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT) will not apply to companies opting for the new tax rates. MAT is the minimum amount of tax required to be paid by a company, in case its normal tax liability after claiming deductions falls below a certain limit. The Bill adds that the provisions regarding MAT credit will also not apply to companies opting for the new rates.
- The Ordinance reduces the MAT rate (applicable for companies not opting for the new tax rates) from 18.5% to 15% with effect from the financial year 2019-20. The Bill amends this provision by making it effective from the financial year 2020-21.
Conclusion
- The government has gradually cut the business tax rates to make India more competitive on a global scale.
- The reduced corporate tax rate of 25% was extended to all businesses with an annual turnover of up to Rs 400 crore by the Union Budget 2019–20. It was anticipated that this would apply to 99.3% of businesses.
- For newly created domestic manufacturing units, a favorable tax regime of 22% for existing businesses and 15% for corporations was also introduced, providing they do not take advantage of any specific deductions or incentives. The last day to use this is March 31, 2024.
- Also, India’s corporate tax collections exceeded 3% of the country’s gross domestic product (GDP) for the first time in two years.
Open Market Sale Scheme
 Why in News?
Why in News?
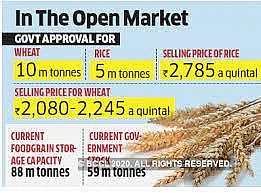
- The Food Corporation of India (FCI) will off load 30 LMT wheat from the Central pool stock to the market through various routes under the Open Market Sale Scheme (Domestic).
- Wheat will also be offered to State Governments/UTs for their schemes without e-auction.
What is an Open Market Sale Scheme (OMSS)?
- FCI sells surplus stocks of wheat and rice at predetermined prices through e-auction in the open market from time to time to enhance the supply of food grains.
- The purpose of OMSS is to dispose of surplus stocks of wheat and rice held by FCI, and to regulate the prices of wheat in the open market.
- FCI conducts weekly auctions for the OMSS for wheat on the platform of the National Commodity and Derivatives Exchange Limited (NCDEX).
- NCDEX is a commodity exchange platform in India that provides a platform for trading in various agricultural and other commodities.
What is the Food Corporation of India?
- The FCI is a government-owned corporation that manages the food security system in India.
- It was established in 1965 under the Food Corporation's Act 1964 with the objective of ensuring adequate availability of food grains throughout the country, and to maintain price stability in the market.
- The FCI also maintains buffer stocks of food grains to ensure food security during times of scarcity or crisis.
- The FCI is also responsible for distributing foodgrains throughout the country for public distribution system.
- FCI also conducts e-auction as one of the methods to dispose of its surplus food grains.
Davos Summit 2023: WEF
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The World Economic Forum’s Annual Meeting 2023, held in the Swiss town of Davos, ended– a conference that started in a world possibly fundamentally altered, but whose processes and outcomes remained pretty much business as usual.
Details:
- The theme this year was ‘Cooperation in a Fragmented World’.
Key Takeaways
- On the economy:
- Most business leaders were upbeat about the economy, with the US and the European Union (EU) seemingly beyond the risk of a recession now.
- China ending its zero Covid curbs and opening shop again added to the positive outlook
- However, central banks of the major economies cautioned that concerns still remained, and said they would keep interest rates high to ensure inflation is under check.
- Many also pointed out that China opening up could mean a rise in its energy consumption, thereby driving up energy prices.
- On Ukraine:
- Ukraine kept up its demand for more military aid to fight its war against Russia, and more financial aid to rebuild after the war, saying the reconstruction fund commitments should start coming in now and not after the war ends.
- Climate:
- Everyone agreed upon the need for green energy and the need for more money to fight climate change.
- The World Economic Forum, supported by more than 45 partners launched the Giving to Amplify Earth Action (GAEA), a global initiative to fund and grow new and existing public, private and philanthropic partnerships (PPPPs) to help unlock the $3 trillion of financing needed each year to reach net zero, reverse nature loss and restore biodiversity by 2050.
- Projects launched:
- More than 50 “high-impact initiatives” was launched at the event.
- Maharashtra Institution for Transformation (MITRA) signed a partnership with the forum on urban transformation to give the state government “strategic and technical direction” while a thematic centre on healthcare and life sciences is to be set up in Telangana.
- The Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness and Innovations (CEPI) aims to develop new vaccines for future pandemics.
Who needs Davos?
- The jarring spectacle of the Davos event – where the uber-rich and powerful fly in on private jets to talk about poverty alleviation and climate action — came in for criticism yet again.
- However, others pointed out that despite its flaws, the conference is an opportunity for many decision-makers to meet and interact with each other
About WEF
- It was established in 1971 as a not-for-profit foundation and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
- The World Economic Forum is the International Organization for Public-Private Cooperation.
- The Forum engages the foremost political, business, cultural and other leaders of society to shape global, regional and industry agendas.
- The Forum strives in all its efforts to demonstrate entrepreneurship in the global public interest while upholding the highest standards of governance.
World Economic Situation and Prospects 2023

Why in News?
United Nations recently released its World Economic Situation and Prospects 2023 report.
Highlights of the Report
- Report is written by the UN’s Department of Economic and Social Affairs, the UN Conference on Trade and Development, and the regional economic commissions for Africa, Europe, Latin America and the Caribbean, Asia and the Pacific, and Western Asia.
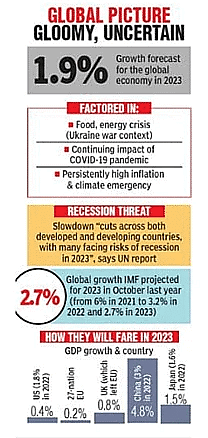
- Lowest Growth Rates: World output growth is projected to decelerate from an estimated 3.0 per cent in 2022 to 1.9 per cent in 2023, marking one of the lowest growth rates in recent decades.
- Reason: Series of severe and mutually reinforcing shocks — the COVID-19 pandemic, the war in Ukraine and resulting food and energy crises, surging inflation, debt tightening, as well as the climate emergency.
- Threat of Recession: Current downturn has slowed the pace of economic recovery from the COVID-19 crisis, threatening several countries with the prospects of recession in 2023.
- Employment Scenario: Most developing countries have seen a slower job recovery in 2022.
- Gender Inequality: Disproportionate losses in women’s employment during the initial phase of the pandemic have not been fully reversed.
- Forecast: Global growth is forecast to moderately pick up to 2.7 per cent in 2024.
- China is projected to grow at 4.8 per cent in the calendar year 2023 and 4.5 per cent in 2024.
- The US is estimated to register a 0.4 per cent economic growth this year and 1.7 per cent in 2024.
- Positive Impact on Russia: Russian exports increased in 2022 as trade with China, India and Turkey surged.
- South Asia: Economic outlook has deteriorated due to high food and energy prices, monetary tightening and fiscal vulnerabilities.
- Average GDP growth is projected to moderate from 5.6 per cent in 2022 to 4.8 per cent in 2023.
- Challenging prospects for economies like Bangladesh, Pakistan and Sri Lanka, who have sought financial assistance from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) in 2022.
India-Specific Points
- Lower GDP Forecast: UN has cut its GDP growth forecast for India for the calendar year 2023 to 5.8 per cent from 6.4%.
- Reasons: Tighter monetary policy and weak global demand.
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has hiked the policy repo rate by 225 basis points in 2022 to 6.25 per cent.
- Annual inflation is estimated at 7.1 per cent in 2022, exceeding the 2 to 6 per cent medium-term inflation target band set by the Central Bank.
- Uneven Progress in the labour market: Unemployment rate in 2022 declined to pre-pandemic levels through stepped-up urban and rural employment, indicating strong domestic demand.
- However, youth employment remained below pre-pandemic levels, particularly among young women.
- Silver-Lining: India is a “bright spot” in the world economy presently and is on a “strong footing”.
- India will grow at 6.7 per cent in 2024, the fastest-growing major economy in the world.
- India’s inflation is expected to decelerate to 5.5 per cent in 2023 as global commodity prices moderate and slower currency depreciation eases imported inflation.
- SDG: India could reduce poverty globally by sustaining this growth rate in the coming future.
Report Recommendations
- Stronger international cooperation to address the global challenges created by the pandemic, the food and energy crisis, the climate crisis and the looming debt crisis
- Avoid fiscal austerity: It would stifle growth and disproportionately affect the most vulnerable groups, affect progress in gender equality and stymie development prospects across generations.
- Reallocation and Reprioritization of public expenditures through direct policy interventions that will create jobs and rejuvenate growth.
- SDG financing: Stronger international commitment is urgently needed to expand access to emergency financial assistance and scale up SDG financing for:
- Strengthening of social protection systems, ensuring continued support through targeted and temporary subsidies, cash transfers, and discounts on utility bills, which can be complemented with reductions in consumption taxes or custom duties.
- Strategic public investments in education, health, digital infrastructure, new technologies and climate change mitigation and adaptation can offer large social returns, accelerate productivity growth, and strengthen resilience to economic, social and environmental shocks.
The Recent Wave of Tech Layoffs

Why in the news?
- Recently, International Business Machines Corp (IBM), based in New York, was the latest to join the list of tech companies that have made large-scale layoffs since late 2022. The company announced that it would lay off approximately 3,900 employees.
- This comes after Big Tech's "midlife crisis," technology behemoths Alphabet, Amazon, Meta, and Microsoft have announced the layoff of thousands in the last few months.
- The United States Federal Reserve's rapid interest rate hikes to control high inflation and slowing consumer demand amid a global economic downturn are also in the background.
What is meant by Layoff?
- A layoff is when an employer terminates an employee's employment for reasons unrelated to the employee's performance.
- Employees may be laid off as a cost-cutting measure, as a result of a decline in demand for their products or services, as a result of a seasonal closure, or during an economic downturn.
- Employees who are laid off lose all wages and benefits but are eligible for unemployment insurance or compensation (typically in USA).
Who and how many people have been laid off?
- In 2022, the tech sector alone will have shed over 150,000 employees, with over 40,000 more job cuts announced since the start of the new year.
- Google's parent company Alphabet, Amazon, Microsoft, and Facebook-owner Meta accounted for 51,000 of the total tech layoffs announced in the last few months.
- According to the consulting firm Challenger, Gray & Christmas Inc., layoffs in the technology sector in 2022 will be 649% higher than the previous year.
 Companies with Mass Layoffs
Companies with Mass Layoffs
- Meta Platforms Inc., which owns Facebook, announced in November last year that it had cut over 11,000 jobs, or 13% of its workforce. The mass layoffs were the first in Meta's 18-year history.
- Microsoft, the Bill Gates-founded technology corporation headquartered in Washington, announced plans to cut 10,000 jobs, or less than 5% of its workforce, by March 2023, incurring a $1.2 billion charge to earnings.
- Amazon: In early January, Amazon, the world's largest e-commerce, cloud computing, and streaming company and America's second-largest private employer after Walmart, announced that it would lay off 18,000 employees, or 6% of its workforce.
- Google: Alphabet, Google's parent company, announced on January 20 that it would be cutting 12,000 jobs, or 6% of its workforce, in a staff memo signed by CEO Sundar Pichai.
- Spotify is a music-streaming service. Spotify CEO Daniel Ek announced in an all-staff memo that the company would lay off 600 people, accounting for 6% of its global workforce.
- Salesforce: The San Francisco-based tech company Salesforce announced on January 4 that it was cutting 10% of its workforce and closing some offices.
- Twitter: Following Tesla CEO Elon Musk's $44 billion takeover, social media company Twitter Inc. made aggressive job cuts, laying off half of its workforce, or approximately 3,700 employees, in various departments such as communications, content curation, product, and engineering.
- Others: Cisco announced in November that it would lay off 5% of its workforce as part of a restructuring. HP also announced 6,000 job cuts by the end of fiscal year 2025.
Impact on Indian Professionals
- According to industry insiders, between 30% and 40% of those laid off are Indian IT professionals, with a significant number of them on H-1B and L1 visas.
- The H-1B visa is a non-immigrant visa that allows US companies to hire foreign workers in special occupations that require theoretical or technical expertise.
- Every year, technology companies rely on it to hire tens of thousands of employees from countries such as India and China.
- Many of them are now looking for ways to stay in the United States and find new jobs within the few months allowed under these foreign work visas.
Do the layoffs portend trouble for the tech industry?
- According to the CEOs, growth has slowed from pandemic levels. Analysts also predict that the five major technology companies, including Apple, will report dismal profits for the October to December (2022) period.
- Amazon is expected to report that earnings fell 38% and revenue grew at the slowest rate in more than 22 years.
- Meanwhile, Meta's profits could drop by 42%. These large tech companies, on the other hand, continue to be massive and profitable.
- Microsoft still reported a profit of more than $16 billion in the quarter ending December 2022, compared to a profit of about $11.6 billion in the same period in 2019.
- Meta earned $4.4 billion in profit in the quarter ending September 2022, despite a 52% drop from the previous year.
What do the layoffs say about the broader job market in the US?
- While the tech sector is experiencing job losses, data from the Labor Department show that the overall U.S. job market remains strong, with the number of Americans filing new claims for unemployment benefits declining.
- According to analysts, technology companies account for about 2% of total employment in the country, compared to larger industries that are still hiring.
- Despite the Fed's aggressive measures to reduce inflation, the labor market has remained resilient.
- Significance
- Furthermore, the tech companies have recently made significant investments, particularly in Artificial Intelligence-driven technology.
- While cloud revenues have declined, Microsoft is considering extending its $1 billion stake in OpenAI, the startup behind the viral new chatbot ChatGPT. It is also looking to acquire video game company Activision Blizzard, which would bring with it a workforce of 10,000 people.
- Smaller startups, meanwhile, which benefited from the pandemic digital boom, are attempting to cut costs while also facing reluctance from venture capitalists to invest in their projects.
|
38 videos|5264 docs|1112 tests
|
FAQs on Economic Development: January 2023 UPSC Current Affairs - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the objective of Startup India Innovation Week? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of Purchasing Managers Index (PMI)? |  |
| 3. How does Sugar Exports impact the economy? |  |
| 4. What are the benefits of Corporate Tax? |  |
| 5. What is the Open Market Sale Scheme and its impact on the economy? |  |

















