UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 17th August 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Sulina Channel
Subject: Geography

Why in News?
As Russia threatens ships in the Black Sea, a Romanian route ‘Sulina Channel’ provides a lifeline for Ukraine’s grain exports.
Sulina Channel
- The Sulina Channel is located in the southeastern part of Romania, specifically within the Danube Delta region.
- It connects the Danube River, one of Europe’s major rivers, with the Black Sea, providing a direct route for maritime transportation.
- The channel is approximately 64 km long, making it a significant watercourse for shipping and navigation.
- It is a vital trade route for cargo vessels, commercial ships, and other maritime traffic entering or leaving the Black Sea region.
- The construction of the Sulina Channel dates back to the 19th century when it was developed to improve the navigation of large ships and vessels in and out of the Danube Delta.
Significance for Ukraine
- The Sulina Channel, the only deep and wide channel among the Danube’s branches, serves as a crucial “riverine expressway” for transporting goods from inland Ukrainian ports to the Black Sea.
- Ukrainian grain ships sail from ports like Izmail and Reni on the Chilia Channel to Sulina, where the cargo is transferred to larger vessels.
- These vessels proceed to Constanta, Romania’s major seaport, for further transport into the Mediterranean.
- This route falls under NATO’s surveillance and protection, ensuring a degree of security against Russian aggression.
Source: The Hindu
Bindeshwar Pathak
Subject: Important Personalities

Why in News?
The founder of ‘Sulabh International’ Bindeshwar Pathak passed away. He was awarded the Padma Bhushan in 1991.
About Sulabh International:-
- Founded: 1970.
- Founded by: Dr Bindeshwar Pathak.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- Objectives: to achieve equitable sanitation and hygiene for all.
- It has been at the forefront of the Government of India’s flagship Swachh Bharat Abhiyan (Clean India Campaign) with a focus on ending open defecation.
- It stresses adopting a gender-inclusive approach in its intervention programmes.
- It has been awarded the Gandhi Peace Prize for 2016.
- ‘SULABH MUSEUM OF TOILETS’, was rated by Time magazine as One of the 10 unique museums in the world.
Areas of Functioning:-
- Equitable sanitation
- Rural sanitation
- Urban Sanitation
- Water for all
- Community toilets in slums
- Fecal sludge Management
- Awareness and advocacy
- Ensuring the Dignity of Manual Scavengers
Source: AIR
Rashtrapati Bhavan
Subject: Art and Culture

Why in News?
On the occasion of 77th Independence Day, President Droupadi Murmu on August 15 hosted ‘At Home’ reception at Rashtrapati Bhavan in Delhi.
About Rashtrapati Bhavan:-
- Location: on Rajpath, New Delhi, India.
- It is situated on Raisina Hill.
- Designed by: Sir Edwin Lutyens and Herbert Baker.
- Built in 1929.
- The Rashtrapati Bhavan (‘Presidential Palace’) is the official residence of the President of India.
- This presidential residence took seventeen years to build and was finished in 1929.
- The presidential office, guest rooms, and staff rooms are among the more than 300 rooms.
- It employs 750 people, including 245 working in the President’s Secretariat.
- The King George V’s silver chair, can be found at the Gift Museum of Rashtrapati Bhavan, where he sat at the Delhi Durbar in 1911.
- The Ashoka Hall of Rashtrapati Bhavan is used for ceremonial functions such as the swearing-in of Ministers.
- Rashtrapati Bhavan Museum
- It is a world-class museum inside the Bhavan with a high-tech story-telling format.
- It is a contextual narrative woven around original exhibits.
- Rashtrapati Bhavan Mughal Garden
- The designs for the Mughal Gardens were created by Sir Edwin Lutyens as early as 1917.
Source: AIR
GS-II
Empowering Artisans: PM Vishwakarma Scheme
Subject: Government Schemes

Why in News?
The Union Cabinet has given its nod to the PM Vishwakarma Scheme, a groundbreaking initiative aimed at uplifting artisans and craftsmen in India.
What is PM Vishwakarma Scheme?
- Supporting Artisans: It will be a Central Sector Scheme with twofold objective: to nurture the Guru-Shishya Parampara:
- Age-old tradition of imparting skills within families, and
- To uplift artisans and craftsmen engaged in manual trades.
- Coverage: This comprehensive scheme encompasses 18 traditional trades in its initial phase, including blacksmiths, carpenters, potters, goldsmiths, tailors, and more, who form the bedrock of rural economies.
Key Highlights of Scheme
- Financial Provision: The scheme is fortified by a budgetary outlay of ₹13,000 crore, ensuring robust financial support to artisans and craftsmen.
- Recognition and ID: Artisans and craftspeople will receive recognition through the prestigious PM Vishwakarma certificate and an official ID card, validating their skills and contributions.
- Credit Support: The scheme provides access to credit support, offering up to ₹1 lakh in the first tranche and ₹2 lakh in the second tranche, with an advantageous interest rate of 5%.
- Skill Upgradation: To enhance expertise, the scheme includes skill upgradation programs encompassing both basic and advanced training. Participants will receive a stipend of ₹500 per day during training.
- Modern Tools and Incentives: Beneficiaries will be granted up to ₹15,000 to acquire modern tools, further improving the quality and efficiency of their work.
- Digital Transactions and Marketing: Embracing modern practices, the scheme encourages digital transactions and marketing support, linking artisans with broader markets.
Source: The Hindu
Key Cabinet decisions
Subject: Polity

Why in News?
The Union Cabinet has approved a slew of schemes ranging from the PMe-Bus Sewa to seven multi-tracking projects of the Indian Railways worth Rs 32,500 crore.
PMe-Bus Sewa
- Seeking to enhance green mobility, the Union Cabinet gave a nod to the PM e-Bus Sewa for augmenting city bus operations.
- An e-bus is any bus whose propulsion and accessory systems are powered exclusively by a zero-emissions electricity source.
- The scheme will be implemented in two segments:
- In 169 cities, 10,000 e-buses will be deployed using a public-private partnership (PPP) model;
- In this segment, depot infrastructure will also be developed or upgraded to support the new e-buses, including the creation of behind-the-meter power infrastructure like substations.
- In 181 other cities, infrastructure will be upgraded under the green urban mobility initiatives
- In this second segment, initiatives will focus on bus priority, infrastructure, multimodal interchange facilities, automated fare collection systems, and charging infrastructure.
- In 169 cities, 10,000 e-buses will be deployed using a public-private partnership (PPP) model;
- Cities with a population of three lakh and above will be covered under the scheme, including all the capital cities of Union Territories, and the northeastern and hill States.
- States or cities will be responsible for running the bus services and making payments to the bus operators.
- The Central government will support these bus operations by providing subsidies to the extent specified in the scheme.
PM Vishwakarma Scheme
- The Union Cabinet approved a ₹13,000 crore PM Vishwakarma scheme.
- It aims to provide subsidised loans to traditional artisans and craftsmen including weavers, goldsmiths, blacksmiths, laundry workers, and barbers.
- Key highlights:
- Artisans and craftspeople will be provided a recognition through PM Vishwakarma certificate and ID card.
- The craftsmen will be provided a subsidised loan of Rs 1 lakh in the first tranche, and another Rs 2 lakh in the second tranche, at a concessional interest rate of 5%.
- It also has a provision to provide skill upgradation, incentive for toolkit as well as digital transactions and marketing support.
- Skilling programme will take place at both basic and advanced types. Participants will get a stipend of ₹500 per day while undergoing training.
- Beneficiaries will also receive up to ₹15,000 to buy modern tools.
- The scheme also aims at improving the quality, as well as the reach of products and services of artisans and craftsmen and to ensure that Vishwakarmas are integrated with the domestic and global value chains.
Other decisions taken by Cabinet
- Extension of Digital India Programme
- The Union Cabinet approved a five-year extension and expansion of the Digital India programme, including an expansion of the Computer Emergency Response Team, India (CERT-in).
- The expansion of the programme, established in 2015, will have an outlay of ₹14,903 crore.
- The extended programme aims to re-skill and up-skill 6.25 lakh IT professionals and train another 2.65 lakh persons in information security.
- The Union Cabinet approved a five-year extension and expansion of the Digital India programme, including an expansion of the Computer Emergency Response Team, India (CERT-in).
- Bhashini
- The AI-enabled multi-language translation tool – Bhashini – will be rolled out in 22 Schedule Vlll languages.
- National Supercomputing Mission
- The National Supercomputing Mission, which has deployed 18 supercomputers, will add nine more such machines.
- These supercomputers will have so many applications in weather forecasting, geology, agriculture, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) modelling.
- Document verification for MSMEs
- DigiLocker, the online repository operated by the government for official documents, will be expanded to serve MSMEs.
- This will make it easier for them to get verified documents for business loans.
Source: Indian Express
GS-III
Mizoram of 1966: How Air Force’s ops quelled Operation Jericho
Subject: Defence and Security

Why in News?
The use of air power in Mizoram in 1966 has become a hot topic of discussion after the PM of India mentioned it in the Lok Sabha while replying to the no confidence motion.
Mizoram of 1966:
- A period of protests and armed insurgency followed in the 1960s.
- A separatist movement (seeking independence from India) led by Mizo National Front (MNF) was gathering steam in the area now known as Mizoram, and then referred to as the Mizo Hills.
- The Centre had decided to station another Assam Rifles battalion in the Hills, in addition to the one Assam Rifles battalion and a few BSF companies already present.
- Outraged by this, the MNF leadership decided to launch ‘Operation Jericho’ to take control of Aizawl and overran Aizawl in a few days’ time (in late February).
- Operation Jericho had been described by a military writer as an expression of confidence and clinical planning not witnessed hitherto fore in the Indian subcontinent.
- A large number of volunteers who joined in the armed struggle were either ex-servicemen or personnel of the Assam Regiment battalions dismissed for lack of discipline.
- The Mizo rebels had besieged the HQs of 1 Assam Rifles and released all prisoners from the local jail.
- There was widespread looting of arms and cash from the government treasury.
- Proclamations of “independence” were made and a demand raised for the Assam Rifles to surrender.
What was the Government’s Response?
- The Army operations on the ground to clear rebel-held positions was led by Brig (later Maj Gen) Rustom Zal Kabraji, who was commanding the 61 Mountain Brigade, located at Agartala.
- Attempts were made to re-supply the Assam Rifles battalion with helicopters, but these were shot at by the Mizo rebels.
- The operations on the ground faced stiff resistance from the rebels, taking several days to reach Aizawl.
How was the IAF Involved?
- As the Army struggled to dislodge the rebels, the Indian Air Force (IAF) was called in.
- The IAF’s initial role was to re-supply the army installations, for which Dakotas and Caribou transport aircraft were pressed in from Guwahati and Jorhat.
- In one such mission, the Dakota received 21 bullet holes before it landed at Kumbhigram air base near Silchar.
- This was the event that necessitated the offensive air operations.
- The two IAF Squadrons, 29 Squadron and 14 Squadron, were primarily involved in the air ops.
- The 29 Squadron flew the Toofani (French origin Dassault Ouragan) based at Bagdogra, while the 14 Squadron flew Hunters out of Jorhat.
- The actual missions started on March 5. The air attack helped the Army regain control of vast areas that had been declared independent.
- By the end of the month, Brig Kabraji’s Brigade had regained control of Mizoram.
What Followed after the Quelling of Operation Jericho?
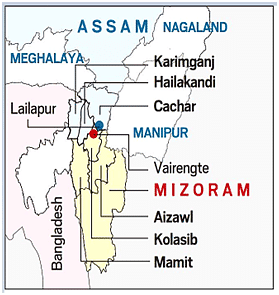
- Like several other northeastern states of India, Mizoram was previously part of Assam.
- In 1971, the government agreed to convert the Mizo Hills into a Union Territory (UT), which became UT of Mizoram in 1972.
- Following the Mizoram Peace Accord (1986) between the Government and the MNF, the Indian Parliament adopted the 53rd amendment of the Indian Constitution in 1986.
- This allowed for the creation of the State of Mizoram on 20 February 1987, as India's 23rd state.
Source: Indian Express
Deemed Forests
Subject: Environment and Ecology

Why in News?
The Odisha government has rescinded a contentious order that declared the discontinuation of the ‘deemed forests’ category under the amended Forest Act.
- This reversal comes after concerns were raised regarding the implications of the order on forest classification and protection.
Understanding ‘Deemed Forests’
- Definition: ‘Deemed forests’ refer to areas that are not formally classified as forests by central or state authorities in official records.
- Legal Ambiguity: The term ‘deemed forests’ lacks a clear legal definition, including under the Forest Conservation Act of 1980.
- Broad Interpretation: The Supreme Court’s T N Godavarman Thirumulpad Case (1996) embraced an expansive interpretation of forests. It encompassed statutorily recognized forests, irrespective of their reservation status, under the Forest Conservation Act.
- Inclusive Scope: ‘Forest land’ within Section 2 of the Act extends beyond the dictionary meaning to include areas recorded as forests in government records, regardless of ownership, according to the court.
Recent Relevance and Controversy
- News Spotlight: The issue of ‘deemed forests’ has gained attention, particularly in Odisha and Karnataka, where allegations of unscientific classification and impact on agriculture and mining persist.
- Calls for Reclassification: Advocates assert that ‘deemed forests’ should adhere to the dictionary meaning of forests, irrespective of ownership. Concerns have been raised about arbitrary classifications affecting farmers and mining activities.
- Classification Challenges: Critics argue that the existing subjective classification lacks a well-defined scientific criterion, leading to conflicts and hardships for communities.
Source: The Hindu
MoEF&CC’s U-turn to Merge Four Environmental Bodies
Subject: Environment and Ecology

Why in News?
In June, the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) issued a notification to reverse its decision of merging the following four bodies –
- National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA),
- Forest Survey of India (FSI),
- Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB), and
- Central Zoo Authority (CZA)
- National Tiger Conservation Authority is a statutory body, constituted under Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- It was established in 2005 following the recommendation of the Tiger Task Force.
- Objectives:
- To provide statutory authority to Project Tiger so that compliance of its directives become legal.
- To Foster accountability of Centre-State in management of Tiger Reserves.
- To address livelihood interests of local people in areas surrounding Tiger Reserves.
- Functions:
- To approve the tiger conservation plan prepared by the state government.
- To ensure that the tiger reserves and areas linking one protected area/tiger reserve with another are not diverted for ecologically unsustainable uses.
- To facilitate and support the tiger reserve management in the state for biodiversity conservation.
- NTCA conducts Tiger Census across India, every four years.
- Chairman: Union Minister of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
- Forest Survey of India was founded in 1981 based on the recommendation of the National Commission on Agriculture (NCA).
- FSI assesses forest cover of the country every 2 years by digital interpretation of remote sensing satellite data and publishes the results in a biennial report called 'State of Forest Report' (SFR).
- FSI provides training to the foresters cadres of various states of India.
- Headquarters: Dehradun, Uttarakhand
- Wildlife Crime Control Bureau is a statutory body established in 2007 under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Functions:
- To collect and collate intelligence related to organized wildlife crime activities and to disseminate the same to State and other enforcement agencies for immediate action so as to apprehend the criminals;
- To establish a centralized wildlife crime data bank;
- Co-ordinate actions by various agencies in connection with the enforcement of the provisions of the Act;
- Assist foreign authorities and international organization concerned to facilitate co-ordination and universal action for wildlife crime control;
- Capacity building of the wildlife crime enforcement agencies for scientific and professional investigation into wildlife crimes and
- Assist State Governments to ensure success in prosecutions related to wildlife crimes.
- It also assists and advises the Customs authorities in inspection of the consignments of flora & fauna as per the provisions of Wildlife Protection Act, CITES and EXIM Policy governing such an item.
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- Central Zoo Authority is a statutory body established in 1992 under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Objective:
- To complement and strengthen the national effort in conservation of the rich biodiversity of the country, particularly the fauna as per the National Zoo Policy, 1998.
- Every zoo in the country is required to obtain recognition from the Authority for its operation.
- The Authority’s role is more of a facilitator than a regulator. It, therefore, provides technical and financial assistance to such zoos which have the potential to attain the desired standard in animal management.
- It lays down guidelines and prescribes rules under which animals may be transferred among zoos nationally and internationally.
- It coordinates and implements programmes on capacity building of zoo personnel, planned breeding programmes and ex-situ research.
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- During the Covid-19 pandemic period, the Union government had proposed that the four bodies i.e., NTCA, CZA, WCCB and FSI be merged into a single organization.
- This proposal received severe criticism from activists saying that it would render key environmental organisations “toothless”.
- For example, in the existing structure, the NTCA can oppose a forest clearance for an infrastructure project for diverting Tiger Reserve areas.
- The proposed merger would have rendered this difficult as the NTCA would have come under the Deputy Director General of Forests, who is in charge of the Integrated Regional Office and reports to the MoEF&CC.
- The MoEF&CC argued that the proposal does not amount to a merger and that the intention was to get the various authorities to function at 19 regional offices, under one roof.
- However, recently in June 2023, the MoEF&CC dropped the merger plan, likely owing to technical and administrative difficulties in merging the institutions in question.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5275 docs|1115 tests
|
















