UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC > Amphibia: Neoteny
Amphibia: Neoteny | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Neoteny in Amphibians: Retention and Precocious Development
1. Neoteny and Paedomorphosis Defined:
- Clarifying Terminology
- Two terms, paedogenesis and neoteny, are often used interchangeably but represent distinct evolutionary processes.
- Neoteny involves the retention of larval or embryonic traits in the adult body.
- Paedomorphosis (or paedogenesis) refers to the development of gonads and/or production of young by an otherwise immature, larval, or preadult animal.
- Amphibian Examples
- Some aquatic larval urodeles exhibit delayed or failed metamorphosis but become sexually mature, mate, and produce fertile eggs.
- The distinction between neoteny and paedogenesis becomes blurred in these cases, as they may be viewed as adults retaining larval traits (neoteny) or as larvae with precociously developed reproductive organs (paedomorphosis).
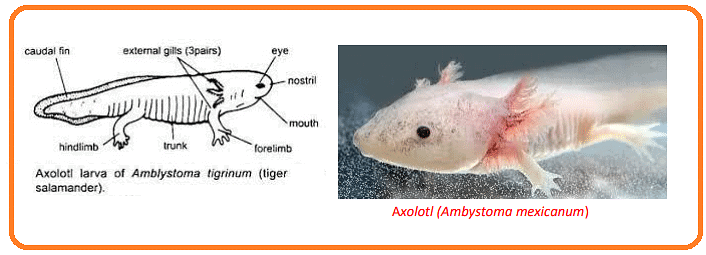
- Ambystoma mexicanum
- Axolotls from Lake Xochimilco (Mexico) and closely related species, like A. tigrinum, are classic examples.
- Under certain conditions, these larvae do not undergo metamorphosis, retaining gills and aquatic habitats while becoming sexually mature.
- The sexually mature but morphologically immature larval stage with external gills is termed an axolotl.
- Some axolotls brought to Paris in 1865 underwent metamorphosis, shedding gills and fins to become adult terrestrial salamanders.
- Factors Affecting Metamorphosis
- The causes and significance of neoteny are not fully understood.
- Environmental factors, such as abundance of food, cold temperature, or insufficient iodine (a thyroxin hormone component inducing amphibian metamorphosis), may affect metamorphosis.
- Axolotls respond to environmental changes; for instance, drying up of swamps, food scarcity, and rising temperatures induce metamorphosis.
- Temperature affects the response of larval tissues to thyroid hormones, with reduced responses at lower temperatures.
- Multifactorial Genetic Basis
- The genetic basis for metamorphosis appears multifactorial, variable, and subject to selective pressure.
- Genes for transformation are suppressed in neotenic populations but not entirely absent, as occasional metamorphosed individuals emerge.
- Causes and Implications
- The cause of neoteny in amphibians remains unclear, attributed to various extrinsic and intrinsic factors.
- Experiments, environmental changes, and genetic factors contribute to the intricate phenomenon of neoteny, providing a captivating area for further exploration.

Influencing Amphibian Development: Extrinsic and Intrinsic Factors
Extrinsic Factors
- Abundance of Food:
- Gadow (1903) suggests that ample food in aquatic life contributes to the retention of larval features.
- Deepwater and Coldness:
- Shufeldt proposes that deepwater and cold conditions inhibit thyroxin secretion, affecting metamorphosis.
- Saline Nature of Water:
- Weismann links neoteny to the saline nature of water, though the details of this connection are not specified.
- Low Temperature:
- Huxley (1929) suggests that low temperatures can halt metamorphosis.
Intrinsic Factors
- Insulin Hormone:
- Gressner (1928) suggests that insulin hormone inhibits metamorphosis.
- Threshold Levels of Thyroxin:
- Recent research, including insights from Etkin (1968), points to varying threshold levels of thyroxin and its analogues as primary influences on metamorphosis.
- Prolactin's Role:
- Etkin and colleagues establish the inhibitory role of prolactin in metamorphosis, proposing that the genetic regulation of thyroxin synthesis is influenced by prolactin levels.
- Genetic Mechanism of Thyroxin Level:
- Early premetamorphic stages maintain low thyroxin levels through genetic mechanisms (Etkin, 1968).
- Hormonal Control Mechanism:
- The hypothalamus responds to thyroid hormone levels in the blood by producing thyrotropin-releasing factor (TRF), initiating the production of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in the pituitary, influencing thyroid secretion, and ultimately triggering metamorphosis.
- Thyroxin and Tissue Responsiveness:
- Poor thyroid gland secretion and larval tissue unresponsiveness to hormones contribute to neoteny.
Deviation and Canalisation
- Canalisation of Development:
- Deviations from the normal developmental pathway, caused by intrinsic and extrinsic factors in axolotls, are considered "canalisation," buffering development against environmental changes.
- Adaptation and Advantage:
- Neoteny, viewed as a consequence of adaptations, may offer advantages in specific environments where the retention of larval traits is beneficial.
 |
Download the notes
Amphibia: Neoteny
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
Types and Significance of Neoteny
- Partial Neoteny:
- Tadpoles and larvae experiencing delayed metamorphosis during temporary ecological or physiological changes, such as winter, exhibit partial neoteny.
- Intermediate Neoteny:
- Axolotls reproduce sexually but undergo metamorphosis in suitable conditions, showcasing intermediate neoteny.
- Extreme or Total Neoteny:
- Seen in perennibranchiate salamanders like Necturus, Siren, and Proteus, these species remain larval throughout their lives, even resisting metamorphosis-inducing treatments like thyroxine.
- Significance:
- Initially considered a case of atavism by Weismann (1875), neoteny is now viewed as a secondary specialization and a physiological adaptation, supported by the diverse characteristics of neotenous perennibranchiate forms.
The document Amphibia: Neoteny | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
181 videos|346 docs
|
Related Searches