Practice Questions: Mixture and Alligation | Quantitative Techniques for CLAT PDF Download
Q1: In what ratio must tea worth Rs. 9 per kg be mixed with tea worth Rs. 14 per kg so that the resultant mixture costs Rs. 10 per kg?
(a) 1 : 4
(b) 4 : 1
(c) 3 : 2
(d) 2 : 5
Ans: (b)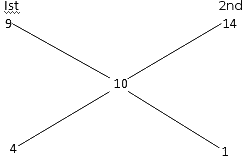
Required ratio = 4:1
Q2: In what ratio must water be mixed with milk worth Rs. 12 per litre so as to produce a mixture worth Rs. 10 per litre?
(a) 1 : 4
(b) 3 : 5
(c) 2 : 3
(d) 1 : 5
Ans: (d)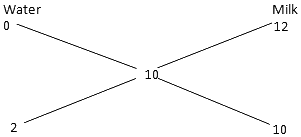
Ratio of water to milk = 1:5.
Q3: In an examination out of 1000 students 70% boys and 80% girls are passed. If total pass percentage was 76%, find the number of girls.
(a) 550
(b) 650
(c) 625
(d) 600
Ans: (d)
This question we will solve by Alligation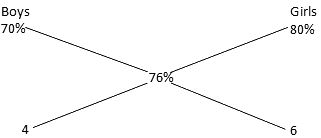
∴ Ratio of Boys to Girls = 2 : 3
∴ Girls = 3/5 x 1000 = 600.
Q4: If Rs. 85 is divided among 100 students such that each boy got a rupee and each girl got 50 P, find the number of girls.
(a) 50
(b) 60
(c) 30
(d) 70
Ans: (c)
Let all are boys then total sum = 100 x 100 = 10000 P.
Let all are girls then total sum = 100 x 50 = 5000 P.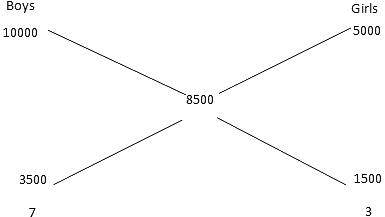
∴ Ratio of Boys to Girls = 7 : 3. Number of girls = 3/10 x 100 = 30.
Q5: A manufacturer mixes two kinds of tea costing Rs 35 and Rs 40 a Kg in the ratio of 8:7. What is his profit or loss percent if he sells the mixture @ Rs 37.50 a Kg?
(a) No profit or loss
(b) 455% profit
(c) 455% loss
(d) 25/56% loss
Ans: (b)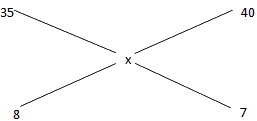
⇒ (40-x) / (x-35) = (8/7)
⇒ 280 – 7x = 8x – 280
⇒ 15x = 560
⇒ x = 37.33
∴ Profit % = 37.50 - 37.33 / 37.33 x 100 ≅ .455%
Q6: Find the ratio in which quantity of coffee of first kind of worth Rs 60.5 per kg mix to the second kind of coffee of worth Rs 35.5 per kg so that the resulting mixture is of worth Rs 40.5 per Kg
(a) 49:6
(b) 49:71
(c) 49:24
(d) 1 : 4
Ans: (d)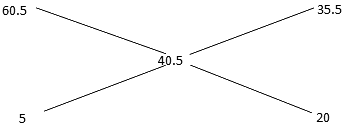
Ratio of the quantity of tea of the first kind to that of the second kind in the mixture should be 1 : 4.
Q7: A grocer wants to know the mixing ratio so that on mixing a sugar at Rs 32 a kg and Rs 48 a kg, he makes a mixture worth Rs 40 a kg.
(a) 1 : 1
(b) 4 : 3
(c) 2 : 3
(d) 3 : 2
Ans: (a)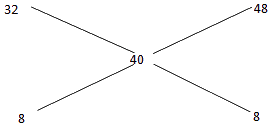
Ratio = 1 : 1.
Q8: In what ratio must milk be mixed with water worth Rs. 40 per gallon so as to produce a mixture worth Rs. 30 per gallon?
(a) 7 : 5
(b) 9 : 3
(c) 3 : 1
(d) 5 : 8
(e) None of these
Ans: (c)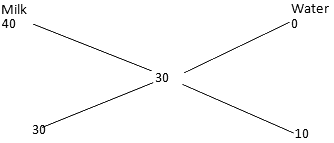
Ratio = 3:1
Q9: A shopkeeper mix mustard oil worth Rs. 90 per kg with mustard worth Rs. 60 per kg, so that the mixture costs him Rs. 75 a kg. Find the proportional ratio?
(a) 7: 5
(b) 1: 1
(c) 5: 7
(d) 5: 8
(e) None of these
Ans: (b)
Required ratio will be 75 - 60: 90 – 75 i.e. 15 : 15 ⇒ 1 : 1.
Q10: A wholesaler mixes two kinds of rice costing Rs 35 and Rs 55 a Kg . In what proportion must he mix the rice so that the mixture costs him Rs Rs 42 a Kg?
(a) 7: 5
(b) 9: 3
(c) 49:24
(d) 13 : 7
(e) 1 : 4
Ans: (d)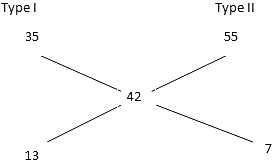
⇒ Ratio = 13:7.
|
57 videos|108 docs|73 tests
|
FAQs on Practice Questions: Mixture and Alligation - Quantitative Techniques for CLAT
| 1. What is mixture and alligation? |  |
| 2. How is mixture and alligation used in real-life scenarios? |  |
| 3. Can you explain the process of solving mixture and alligation problems? |  |
| 4. What are some common types of mixture and alligation problems? |  |
| 5. Are there any shortcuts or tricks to solve mixture and alligation problems quickly? |  |






















