Lanthanide Contraction | Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Shielding and its Effects on Atomic Radius |

|
| D Block Contraction (Scandide Contraction) |

|
| Effects on Ionization Energy and Properties |

|
| Solved Examples |

|
Introduction
- The Lanthanide Contraction applies to all 14 elements included in the Lanthanide series. This series includes Cerium(Ce), Praseodymium(Pr), Neodymium(Nd), Promethium(Pm), Samarium(Sm), Europium(Eu), Gadolinium(Gd), Terbium(Tb), Dysprosium(Dy), Holmium(Ho), Erbium(Er), Thulium(Tm), Ytterbium(Yb), and Lutetium(Lu).
- The atomic radius, as according to the Lanthanide Contraction, of these elements decreases as the atomic number increases. We can compare the elements Ce and Nd by looking at a periodic table. Ce has an atomic number of 58 and Nd has an atomic number of 60. Which one will have a smaller atomic radius? Nd will because of its larger atomic number.
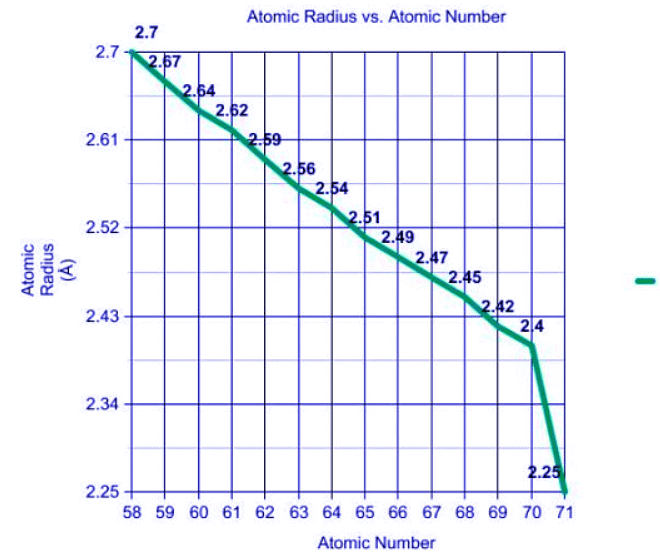
The graph shows the atomic radius decreasing as the atomic number is increasing, Lanthanide Contraction.
Shielding and its Effects on Atomic Radius
- The Lanthanide Contraction is the result of a poor shielding effect of the 4f electrons. The shielding effect is described as the phenomenon by which the inner-shell electrons shield the outer-shell electrons so they are not effected by nuclear charge.
- So when the shielding is not as good, this would mean that the positively charged nucleus has a greater attraction to the electrons, thus decreasing the atomic radius as the atomic number increases. The s orbital has the greatest shielding while f has the least and p and d in between the two with p being greater than d.
- The Lanthanide Contraction can be seen by comparing the elements with f electrons and those without f electrons in the d block orbital. Pd and Pt are such elements. Pd has 4d electrons while Pt has 5d and 4f electrons. These 2 elements have roughly the same atomic radius. This is due to Lanthanide Contraction and shielding.
- While we would expect Pt to have a significantly larger radius because more electrons and protons are added, it does not because the 4f electrons are poor at shielding. When the shielding is not good there will be a greater nuclear charge, thus pulling the electrons in closer, resulting in a smaller than expected radius.
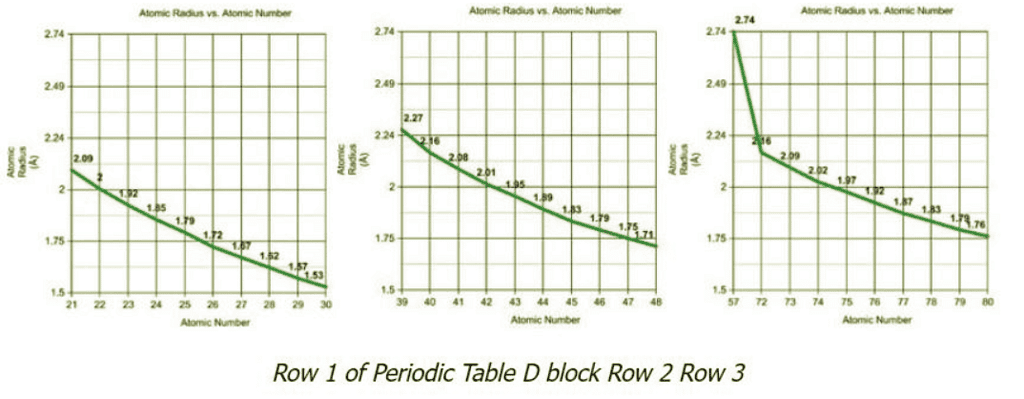
- The graphs depict the atomic radii of the first three rows of transition metals. We can apply the same principle as applied with the elements Pd and Pt to whole rows and columns. As we can see by comparing Row 1 with Row 2, the atomic radii differ greatly between the elements, but if we compare Row 2 with Row 3, the atomic radii do not have much difference.
- Elements with atomic number 23 and 41 lie in the same column of the periodic table and have a significantly large difference in atomic radii (atomic radii increases from Row 1 to Row 2), but elements 41 and 73, also in the same column, only differ slightly. This is the cause of introducing 4f electrons in Row 3.
- In Row 3, we would expect the elements to carry on the same trend as was witnessed between Rows 1 and 2 (large increase in atomic radii) but we do not. This is because the 4f orbitals are not doing a great job of shielding.
D Block Contraction (Scandide Contraction)
- The d block contraction, also known as the Scandide Contraction, describes the atomic radius trend that the d block elements (Transition metals) experience. Normally the trend for atomic radius, moving across the periodic table is that the atomic radius decreases significantly. In the transition metals with D electrons as we move from left to right across the periodic table, the element’s atomic radius only decreases slightly.
- This is because they have the same amount of s electrons, but are only differing in d electrons. These d electrons are in an inner shell (penultimate shell) and electrons are getting added to this shell, another shell is not created. The d electrons are not good at shielding the nuclear charge, so the atomic radius does not change much as electrons are added. Almost like disregarding the D electrons being added.
 |
Download the notes
Lanthanide Contraction
|
Download as PDF |
Effects on Ionization Energy and Properties
- As the proton number increases and the atomic radius decreases, the ionization energy increases. This is due to a more positively charged nucleus and a greater pull on the electrons by the nucleus. A greater pull is the result of an increased effective nuclear charge. Effective nuclear charge is caused by the nucleus having a more positive charge than the negative charge on the electron (net positive charge).
- The density, melting point, and hardness increase from left to right throughout the Lanthanide Series. The Lanthanide Contraction makes chemical separation of the Lanthanides easier. The Lanthanide Contraction, while making the chemical separation of Lanthanides easier, it makes the separation of elements following the series a bit more difficult.
Solved Examples
Example 1: What is the cause of Lanthanide Contraction?
Ans: The Lanthanide Contraction is caused by a poor shielding effect of the 4f electrons.
Example 2: Which element has a greater atomic radius Gd or Tb and why?
Ans: Gd because as atomic number increases, the atomic radius decreases.
Example 3: Which element has a smaller atomic radius Dy or Yb and why?
Ans: Yb because it has a larger atomic number.
Example 4: Why do elements in Rows 2 and 3 that are in the same column have similar atomic radii?
Ans: Because the elements in Row 3 have 4f electrons. These electrons are do not shield good, causing a greater nuclear charge. This greater nuclear charge has a greater pull on the electrons.
Example 5: Place the following elements in order of increasing atomic radius: Eu, Ce, Pr, Ho.
Ans: Ho, Eu, Pr, Ce
Example 6: Which one of the following has the lowest density: Tb, Pm, Er, Tm, Ce
Ans: Ce
FAQs on Lanthanide Contraction - Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is shielding and how does it affect atomic radius? |  |
| 2. What is D-block contraction or Scandide contraction? |  |
| 3. How does the lanthanide contraction affect ionization energy? |  |
| 4. What are the effects of ionization energy on the properties of elements? |  |
| 5. Can you provide an example to illustrate the concept of lanthanide contraction? |  |





















