UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC > Acute Osteomyelitis
Acute Osteomyelitis | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Acute Osteomyelitis - Etiology |

|
| Acute Osteomyelitis - Pathogenesis |

|
| Acute Osteomyelitis- Histopathology |

|
| Acute Osteomyelitis - Complications |

|
Acute Osteomyelitis - Etiology
- The primary causative agent in acute osteomyelitis is Staph aureus.
- Other responsible organisms include Streptococcus and pneumococcus, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, E. coli (in children), and anaerobes (in cases of trauma).
- Salmonella is associated with osteomyelitis in individuals with sickle cell anemia.
- The most common site affected is the lower femoral metaphysis.
Acute Osteomyelitis - Pathogenesis
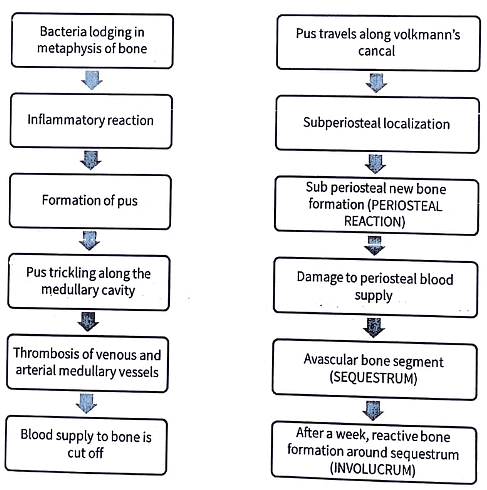
Question for Acute Osteomyelitis
Try yourself:
What is the primary causative agent in acute osteomyelitis?View Solution
Acute Osteomyelitis- Histopathology
- In acute osteomyelitis, there is evidence of bacteria, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and congested, thrombosed blood vessels.
- Chronic osteomyelitis is characterized by necrotic bone, the presence of granulation and fibrous tissues, minimal bacterial presence, and the absence of living osteocytes.
 |
Download the notes
Acute Osteomyelitis
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
Acute Osteomyelitis - Complications
Key complications include:
(i) Septicemia and pyemia
(ii) Septic arthritis
(iii) Chronic osteomyelitis (most prevalent complication)
(iv) Metastatic infection spreading to other bones, serous cavities, lungs, or the brain.
(v) Pathological fracture
(vi) Disrupted growth due to damage to the epiphyseal growth plate.
Complications specific to chronic osteomyelitis encompass sinus tract malignancy and soft tissue contractures.
Question for Acute Osteomyelitis
Try yourself:
Which of the following is a common complication of acute osteomyelitis?View Solution
Acute Osteomyelitis - Repeats
- Give the aetiopathogenesis and gross and microscopic features of acute osteomyelitis. (2012)
- Describe the pathological changes and complications of Acute Osteomyelitis. (2014)
The document Acute Osteomyelitis | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
7 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on Acute Osteomyelitis - Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the etiology of acute osteomyelitis? |  |
| 2. How does acute osteomyelitis develop? |  |
Ans. Acute osteomyelitis typically develops following an infection that spreads to the bone through the bloodstream or from nearby tissue. Infections can occur after trauma or surgery, or they can be hematogenous, meaning they spread from another site of infection in the body. The bacteria invade the bone tissue, leading to inflammation and the formation of pus.
| 3. What are the histopathological findings in acute osteomyelitis? |  |
Ans. Histopathological examination of bone tissue affected by acute osteomyelitis typically shows inflammation, including infiltration of neutrophils and other inflammatory cells. There may be necrosis of bone tissue, and abscess formation. The presence of bacterial colonies or organisms may also be observed.
| 4. What complications can occur with acute osteomyelitis? |  |
Ans. Acute osteomyelitis can lead to several complications if left untreated or if the infection spreads. These complications include the formation of bone abscesses, septic arthritis (infection of the adjacent joint), pathological fractures, and the spread of infection to surrounding tissues or organs. In severe cases, systemic complications such as sepsis can occur, which can be life-threatening.
| 5. How is acute osteomyelitis diagnosed? |  |
Ans. The diagnosis of acute osteomyelitis typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies (such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans), and laboratory tests. Blood tests may show an elevated white blood cell count and markers of inflammation. Imaging studies can help visualize the affected bone and any associated abscesses. In some cases, a bone biopsy may be performed to confirm the presence of bacteria and determine the appropriate antimicrobial treatment.
Related Searches





















