UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC > Woodward-Fieser Rules: Conjugated Dienes and Polyenes
Woodward-Fieser Rules: Conjugated Dienes and Polyenes | Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Woodward-Fieser Rules for Calculating the λmax of Conjugated Dienes and Polyenes |

|
| Core Chromophores With Base Values |

|
| Substituent Effects |

|
| Other Contributors |

|
Introduction
- As we have seen earlier in the chapter of Principle of UV-Vis Spectroscopy, absorption of a particular wavelength of light depends upon the π-electron system of the molecule. The more the conjugation of the π-electron system within the molecule, the higher the wavelength of light it can absorb. Robert Burns Woodward and Louis Fieser put down a set of rules which allows one to calculate the wavelength of maximum absorption (λmax) for a molecule empirically. These sets of rules to calculate the wavelength of maximum absorption or λmax of a compound in the ultraviolet-visible spectrum, based empirically have been called the Woodward-Fieser rules or Woodward’s-rules.
- These sets of article aims to guide the student on how to use these rules to calculate the wavelength of maximum absorption or λmax for different systems.
Woodward-Fieser Rules for Calculating the λmax of Conjugated Dienes and Polyenes
- Conjugated dienes and polyenes are found in most organic compounds. For example, even a benzene ring is a conjugated polyene. Therefore it is useful to know how to utilize the Woodward-Fieser rules to calculate the wavelength of maximum absorption of conjugated dienes and polyenes.
- According to Woodward’s rules the λmax of the molecule can be calculated using a formula:
λmax = Base value + Σ Substituent Contributions + Σ Other Contributions - Here the base value depends upon whether the diene is a linear or heteroannular or transoid diene, or whether it is a cyclic or homoannular diene (each of these will be explained in greater detail below). The sum of all substituent contributions are added to the base value to obtain the wavelength of maximum absorption of the molecule.
Table 1: Gives the values for the influence of different chromophores in conjugated diene systems as per Woodward-Fieser rules. The usage of these will become more evident in the examples which follow.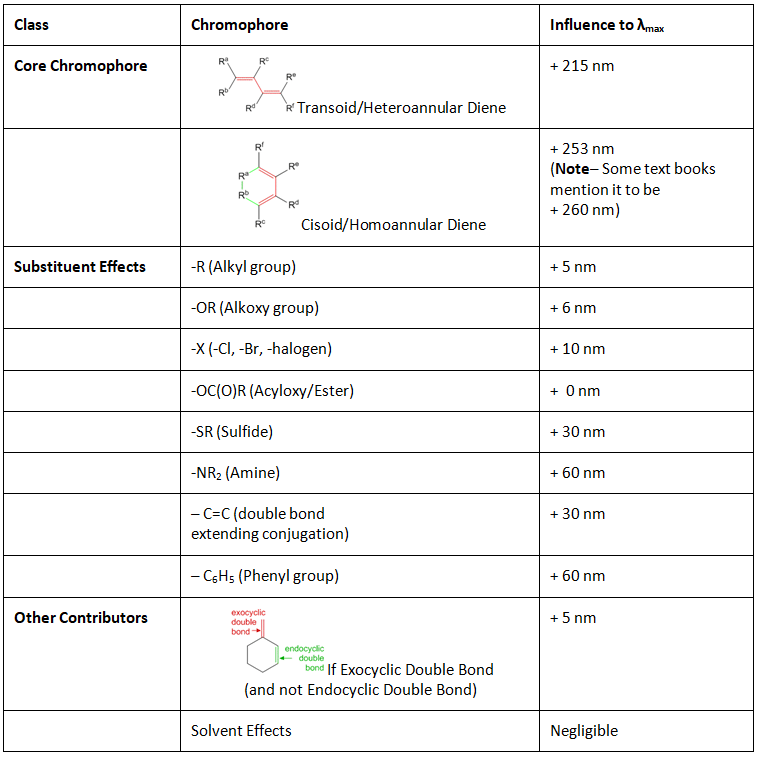
Let us discuss each of the above values and when to apply them in greater detail with examples:
Core Chromophores With Base Values
- Transoid Diene / Heteroannular diene / linear diene: This type of diene generally involves the attachement of two trans dienes together. Since the two double bonds attached are trans, it leads to a linear diene which is also called a heteroannular diene as the diene cannot be placed within one ring system as it would cause the ring to become very unstable (5 – 6 carbon rings are most stable with very few exceptions). The base value for a heteroannular diene system is 215 nm according to the Woodward-Fieser rules. Examples of heteroannular dienes are shown below.
 In the above example, it can be seen that one of the double bonds belongs to ring A while the other double bond belongs to ring B, hence making the double bond heteroannular. Since both double bonds are trans with respect to substituents making the diene a transoid diene. In general, heteroannular dienes are transoid. If the diene is not a part of a ring then it is just transoid.
In the above example, it can be seen that one of the double bonds belongs to ring A while the other double bond belongs to ring B, hence making the double bond heteroannular. Since both double bonds are trans with respect to substituents making the diene a transoid diene. In general, heteroannular dienes are transoid. If the diene is not a part of a ring then it is just transoid. - Cisoid diene / Homoannular diene / cyclic diene: This type of diene involves the conjugation of two cis dienes. Since the double bonds are cis to each other, the molecule often tends to form a closed ring system and therefore also called a cyclic or homoannular diene. The base value for homoannular diene system is 253 nm according to the Woodward-Fieser rules. Examples of homoannular dienes are shown below.
 In the above example, it can be seen that both the double bonds belong to ring B making this type of diene a homoannular diene. Since both double bonds are cis with respect to substituents making the diene a cisoid diene. In general, homoannular dienes are cisoid. If the diene is not a part of a ring (i.e. the green bonds do not exist) then it is just a cisoid diene.
In the above example, it can be seen that both the double bonds belong to ring B making this type of diene a homoannular diene. Since both double bonds are cis with respect to substituents making the diene a cisoid diene. In general, homoannular dienes are cisoid. If the diene is not a part of a ring (i.e. the green bonds do not exist) then it is just a cisoid diene.
Question for Woodward-Fieser Rules: Conjugated Dienes and Polyenes
Try yourself:
Which type of diene involves the attachement of two trans dienes together, resulting in a linear diene?View Solution
Substituent Effects
- Only the substituents attached directly to the double bond diene systems can influence the ultraviolet visible absorption of the molecules. If the substituents are not directly attached to the carbons of the diene system, it will not affect the UV-Visible absorption spectrum of the molecule (as shown below).

- The figure above highlights possible substituents in red given by the different -R groups. In the above examples 1 and 2, assignment of substituents must be given to all the atoms which are directly connected to the diene. Hence even though the structure has no substituents, the core carbon atoms have yet to be considered as alkyl-substituents. Hence in example 1, there are 3 alkyl substituents while in example 2, there are 4 alkyl substituents.
- If one sees down the list of substituents an interesting factor in affecting the absorbance is whether the substituent directly has a heteroatom (with lone pairs) linked to the conjugated diene system. Below is the list of possible substituent effects.

 |
Download the notes
Woodward-Fieser Rules: Conjugated Dienes and Polyenes
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
Other Contributors
- Exocylcic Double Bonds: Exocyclic doube bond by definition is a double bond where one of the participating carbon atoms is a part of a ring, while the other carbon atom is not part of the same ring. From the name we can understand that exo-cyclic would stand for a double bond outside the ring and endo-cyclic would stand for a double bond within the ring.
For each exocyclic double bond, we must add +5 nm to obtain the λmax. Below are a few examples as to what are exocyclic and what are endocyclic double bonds.
- The above figure differentiates between exocyclic (shown in red) and endocyclic (shown in green) double bonds.
- In example 1, the double bond present within ring A is exocyclic to ring B as it is attached to an atom which is shared between ring A and ring B, while the double bond present in ring B is not connected to any ring A atoms and is within just one ring, hence making it endocyclic.
- In example 2, both double bonds are present within ring B with connections to shared carbon atoms with ring A, making both the double bonds exocyclic.
- In example 3, there is a single double bond which is exocyclic at two points to two different rings. In such a case, the influence would be 2 times + 5 nm (i.e + 10 nm).
- Note: Double bonds which are common to two rings are endocyclic. Below we give an example of a double bond which although has carbon atoms shared between two rings (A and B), it is considered endocyclic as at any given time the double bond will only belong to one ring.

- Solvent effects: Since the conjugated diene base is relatively non-polar, contribution due to different solvents is very minor and can be ignored in most cases.
Question for Woodward-Fieser Rules: Conjugated Dienes and Polyenes
Try yourself:
Which set of rules is used to determine the ?max for molecules with more than 4 double bonds in a conjugated system?View Solution
Fieser-Kuhn Rules
Woodward-Fieser rules for dienes work well for conjugated systems with less than 4 double bonds in . For molecules having more than 4-double bonds, one must use the Fieser-Kuhn rules to determine the λmax.
The document Woodward-Fieser Rules: Conjugated Dienes and Polyenes | Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
FAQs on Woodward-Fieser Rules: Conjugated Dienes and Polyenes - Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are the Woodward-Fieser rules? |  |
| 2. How do the Woodward-Fieser rules calculate the λmax? |  |
Ans. The Woodward-Fieser rules calculate the λmax by adding the base value for the core chromophore to the contributions from substituents. The base values are assigned to different types of chromophores based on their structure and properties. The contributions from substituents are determined by specific rules that take into account the position and nature of the substituents.
| 3. What are core chromophores with base values? |  |
Ans. Core chromophores are the basic structural units that contribute to the absorption of light in conjugated dienes and polyenes. They have specific base values assigned to them, which represent the approximate contribution of the chromophore to the λmax. These base values are determined experimentally and are used as a starting point for calculating the overall λmax of a molecule.
| 4. How do substituents affect the λmax of conjugated dienes and polyenes? |  |
Ans. Substituents can have both electronic and steric effects on the λmax of conjugated dienes and polyenes. Electron-withdrawing substituents tend to shift the absorption to shorter wavelengths (higher energy), while electron-donating substituents shift it to longer wavelengths (lower energy). The position and nature of the substituents also play a role in determining the overall effect on the λmax.
| 5. Are there any other contributors to the Woodward-Fieser rules? |  |
Ans. Yes, apart from the core chromophores and substituents, there are other contributors to the Woodward-Fieser rules. These include the effects of ring size, conjugation length, and solvent polarity. Ring size and conjugation length can affect the energy levels of the molecular orbitals, leading to changes in the absorption properties. Solvent polarity can also influence the λmax by altering the electronic distribution within the molecule.
Related Searches

 In the above example, it can be seen that one of the double bonds belongs to ring A while the other double bond belongs to ring B, hence making the double bond heteroannular. Since both double bonds are trans with respect to substituents making the diene a transoid diene. In general, heteroannular dienes are transoid. If the diene is not a part of a ring then it is just transoid.
In the above example, it can be seen that one of the double bonds belongs to ring A while the other double bond belongs to ring B, hence making the double bond heteroannular. Since both double bonds are trans with respect to substituents making the diene a transoid diene. In general, heteroannular dienes are transoid. If the diene is not a part of a ring then it is just transoid. In the above example, it can be seen that both the double bonds belong to ring B making this type of diene a homoannular diene. Since both double bonds are cis with respect to substituents making the diene a cisoid diene. In general, homoannular dienes are cisoid. If the diene is not a part of a ring (i.e. the green bonds do not exist) then it is just a cisoid diene.
In the above example, it can be seen that both the double bonds belong to ring B making this type of diene a homoannular diene. Since both double bonds are cis with respect to substituents making the diene a cisoid diene. In general, homoannular dienes are cisoid. If the diene is not a part of a ring (i.e. the green bonds do not exist) then it is just a cisoid diene.























