Cheat Sheet: Buddhism | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
Buddhism, originating in India over 2,600 years ago, has evolved into a major religion influencing cultures across South and South-East Asia. Founded by Siddhartha Gautama, the religion emphasizes the Middle Path and individual responsibility for happiness. This chronology document will explore key aspects of Buddhism, including its origin, tenets, major texts, councils, schools, and its role in shaping Indian culture and soft diplomacy.
Origin and Life of Siddhartha Gautama

Tenets of Buddhism
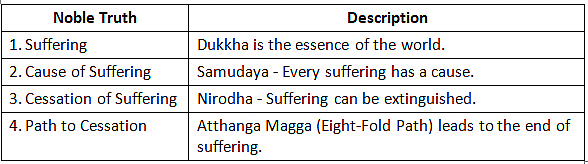
Four Noble Truths
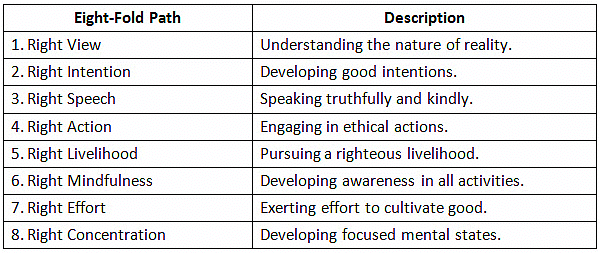
Eight-Fold Path
Major Buddhist Texts
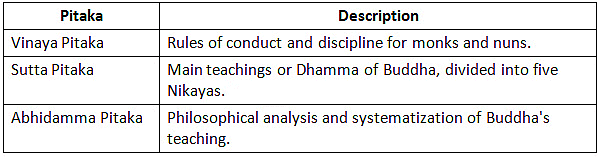
Three Pitakas
Other Important Texts

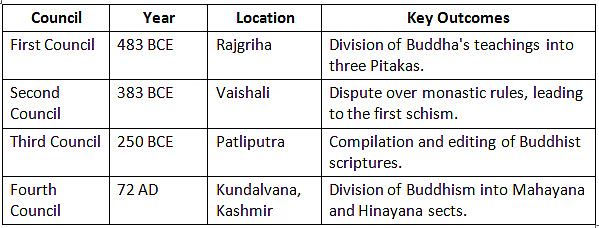
Buddhist Councils
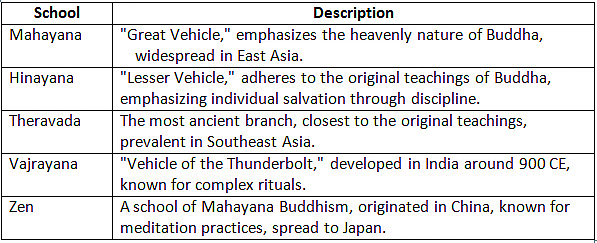
Schools of Buddhism
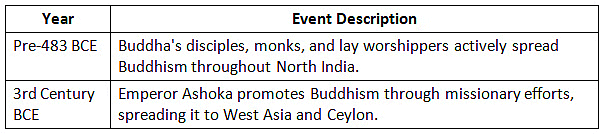
Spread of Buddhism in Ancient India
Contribution of Buddhism to Indian Culture

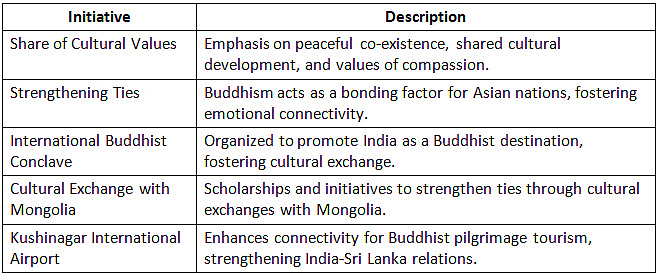
Buddhism as Soft Diplomacy
Conclusion
Buddhism, with its roots in ancient India, has not only shaped the spiritual landscape but also left an indelible mark on culture, diplomacy, and education. The religion's teachings, councils, diverse schools, and contribution to Indian culture showcase its profound impact. Through soft diplomacy, India continues to leverage its Buddhist heritage, promoting cultural exchanges and fostering ties with nations sharing this rich tradition.
|
216 videos|855 docs|219 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Buddhism - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the major tenets of Buddhism? |  |
| 2. What are some major Buddhist texts? |  |
| 3. How does Buddhism view suffering? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of impermanence in Buddhism? |  |
| 5. How does Buddhism emphasize mindfulness and meditation? |  |

















