JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions (2018 - 2024): Motion | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
2024
Q1: A ball is thrown from the location (x₀, y₀) = (0,0) of a horizontal playground with an initial speed v₀ at an angle θ₀ from the +x-direction. The ball is to be hit by a stone, which is thrown at the same time from the location (x₁, y₁) = (L,0). The stone is thrown at an angle (180° - θ₁) from the +x-direction with a suitable initial speed. For a fixed v₀, when (θ₀, θ₁) = (45°, 45°), the stone hits the ball after time T₁, and when (θ₀, θ₁) = (60°, 30°), it hits the ball after time T₂. In such a case, (T₁/T₂)² is _____. [JEE Advanced 2024 Paper 2]
Ans: 2
For Case I :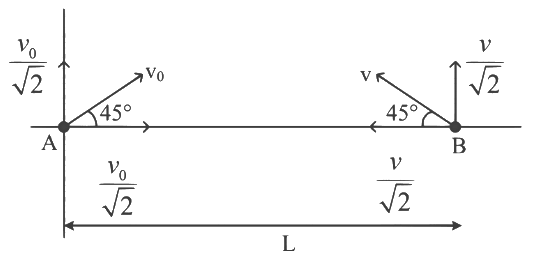

For Case II :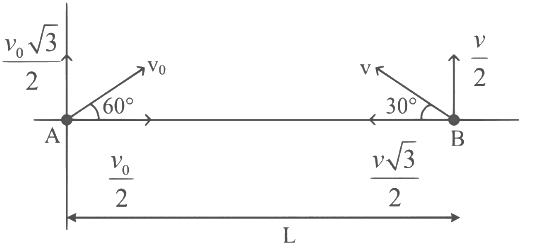
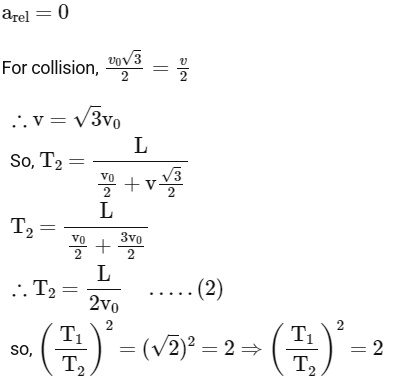
2023
Q1: A person of height 1.6 m is walking away from a lamp post of height 4 m along a straight path on the flat ground. The lamp post and the person are always perpendicular to the ground. If the speed of the person is 60 cm s−1, the speed of the tip of the person's shadow on the ground with respect to the person is ____________ cm s−1. [JEE Advanced 2023 Paper 1 ]
Ans: 40
Given that dx1 / dt= speed of person =60 cm/s
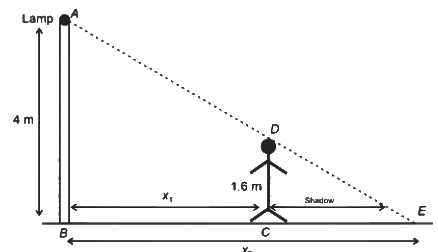
Also dx2/dt = speed of tip of person's shadow
Applying similar triangle rule in ΔABE and ΔDCE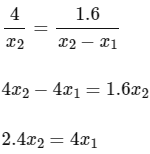
Differentiate both sides w.r.t.
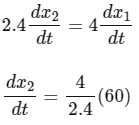
= 100 cm/s
This is the speed of the tip of the person's shadow with respect to the lamp post. But, we need to find the speed of the shadow's tip with respect to the person, which is the relative speed :

= 40 cms-1
2022
Q1: A projectile is fired from horizontal ground with speed v and projection angle θ. When the acceleration due to gravity is g, the range of the projectile is d. If at the highest point in its trajectory, the projectile enters a different region where the effective acceleration due to gravity is g′ = g / 0.81, then the new range is d' = nd . The value of n is ___________ . [JEE Advanced 2022 Paper 1]
Ans: 0.93 to 0.97
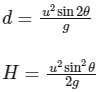
So, after entering in the new region, time taken by projectile to reach ground
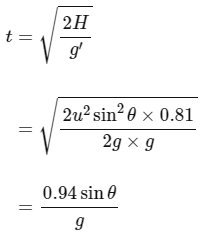
So, horizontal displacement done by the projectile in new region is
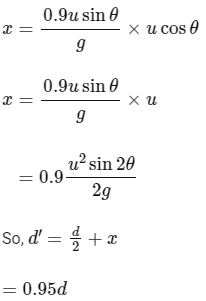
So, n = 0.95d
2020
Q1: Starting at time t = 0 from the origin with speed 1 ms-1, a particle follows a two-dimensional trajectory in the x-y plane so that its coordinates are related by the equation y = x2 / 2. The x and y components of its acceleration are denoted by ax and ay, respectively. Then [JEE Advanced 2020 Paper 2]
(a) ax = 1 ms-2 implies that when the particle is at the origin, ay = 1 ms-2
(b) ax = 0 implies ay = 1 ms-2 at all times
(c) at t = 0, the particle's velocity points in the x-direction
(d) ax = 0 implies that at t = 1s, the angle between the particle's velocity and the x axis is 45o
Ans: (b), (c) & (d)
Given, equation
y = x2 / 2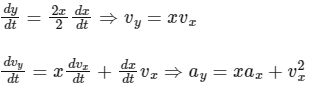
For option A :
when particle is at origin then x = 0.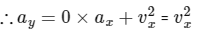
Given that at origin, vx = 1 m/s
So, ay= (1)2 = 1 ms-2
At origin, 0 × ax = 0 means ay does not depend on the value of ax.
For option B :
When ax = 0 ⇒ vx = constant
So vx will stay 1 ms-1.
when ax = 0,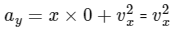
= 1 ms-2
For option C :
Velocity is always tangential to the path of motion of the particle. So at origin path is along x axis as tangent at origin along x axis.
For option D :
When ax = 0 ⇒ vx = constant
So vx will stay 1 ms-1.
At t = 1, x = 1 m
∴vy = xvx = 1 × 1 = 1
Now, slope of velocity at t = 1 is,
tanθ = vy / vx = 11 = 1
⇒ θ = 45o
2019
Q1: A ball is thrown from ground at an angle θ with horizontal and with an initial speed u0. For the resulting projectile motion, the magnitude of average velocity of the ball up to the point when it hits the ground for the first time is V1. After hitting the ground, the ball rebounds at the same angle θ but with a reduced speed of u0 / α. Its motion continues for a long time as shown in figure. If the magnitude of average velocity of the ball for entire duration of motion is 0.8 V1, the value of α is .................. [JEE Advanced 2019 Paper 2]
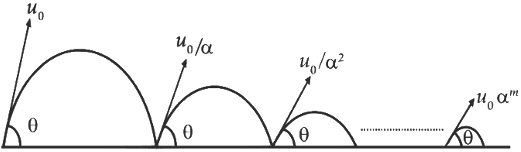
Ans: 4.0
For first projectile,
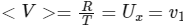
For journey,
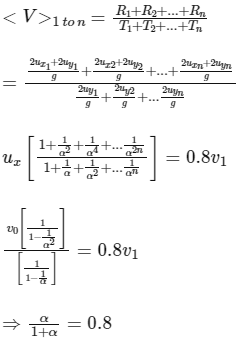
⇒ α = 4
2018
Q1: A ball is projected from the ground at an angle of 45o with the horizontal surface. It reaches a maximum height of 120 m and returns to the ground. Upon hitting the ground for the first time, it loses half of its kinetic energy. Immediately after the bounce, the velocity of the ball makes an angle of 30o with the horizontal surface. The maximium height it reaches after the bounce, in metres, is ______________. [JEE Advanced 2018 Paper 2]
Ans: 30
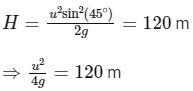
If speed is v after the first collision, then speed should remain 1/√2 times, because kinetic energy has reduced to half.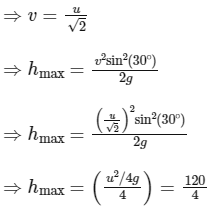
⇒ hmax = 30 m
|
268 videos|740 docs|171 tests
|
FAQs on JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions (2018 - 2024): Motion - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What topics are commonly covered in the Motion section of JEE Advanced? |  |
| 2. How can I effectively prepare for the Motion questions in JEE Advanced? |  |
| 3. Are there any specific strategies to solve complex Motion problems in JEE Advanced? |  |
| 4. What are some common mistakes students make in Motion questions during JEE Advanced? |  |
| 5. How important is understanding Motion for the overall JEE Advanced exam? |  |





















