UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 4th March 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Kaveri and Tungabhadra Rivers
Subject: Geography
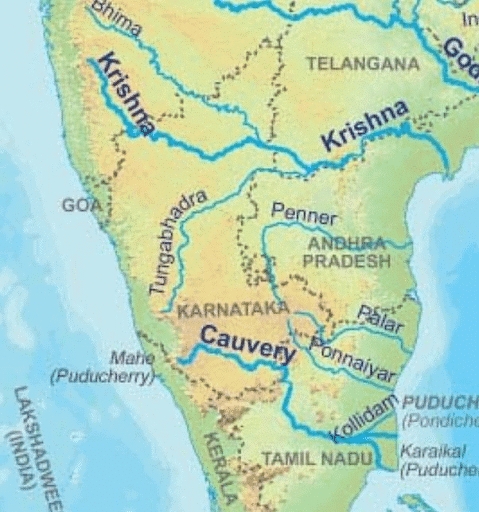
Why in News?
Acute scarcity of water has been reported in various parts of Karnataka as rivers carry less and less water
Background:
- Most of the areas in the arid Kalayana Karnataka region that are dependent on Krishna and Tungabhadra rivers are bracing for a crisis as south west monsoon failed.
About Kaveri River:
- Designation: The Cauvery River, also known as Kaveri, is revered as the 'Dakshin Bharat ki Ganga' or 'the Ganga of the South'.
- Origin: The river originates from Talakaveri on the Brahmagiri range near Cherangala village in Kodagu (Coorg), Karnataka.
- Course: It flows through Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, cascading down the Eastern Ghats in notable waterfalls.
- Delta Formation: Upon reaching the Bay of Bengal south of Cuddalore, Tamil Nadu, the river branches into numerous distributaries, forming a vast delta renowned as the "garden of southern India."
- Geographical Boundaries: Bounded by the Western Ghats to the west, the Eastern Ghats to the east and south, and ridges separating it from the Krishna basin and Pennar basin to the north.
About Tungabhadra River
- Geographical Route: The Tungabhadra River, primarily flowing through Karnataka, extends into Andhra Pradesh, where it merges with the Krishna River near Murvakonda.
- Name Origin: Named after its two tributaries, the Tunga and the Bhadra, originating from Gangamoola in Varaha Parvatha, Western Ghats.
- Course: After merging near Shimoga, it stretches for 531 km, with 382 km in Karnataka, forming the Karnataka-Andhra Pradesh boundary for 58 km, and running 91 km in Andhra Pradesh.
- Significance: The confluence of Tungabhadra and Krishna rivers is marked by the revered Sangameswaram Temple, a pilgrimage site. Hampi, a UNESCO-listed heritage site, lies along its banks.
- Climate Influence: Primarily influenced by the South-West monsoon, the river maintains perennial flow, although summer flows reduce significantly to as low as 2.83 to 1.42 cumec.
Source: The Hindu
Lahore Resolution
Subject: History

Why in News?
Pakistan has decided to hold its National Day celebrations in New Delhi again this year, which is observed on March 23, the day the Lahore Resolution was adopted in 1940 by the Muslim League.
About Lahore Resolution:
- Adoption: During the general session in Lahore from March 22 to March 24, 1940, the All-India Muslim League officially passed a resolution advocating for the creation of an independent state for India's Muslim population.
- Absence of "Pakistan": Notably, the resolution did not explicitly mention the term "Pakistan."
- Criticism: The Lahore Resolution faced opposition from several prominent Indian Muslims, including Abul Kalam Azad and the Deoband ulema led by Husain Ahmad Madani. These critics advocated for the idea of a united India.
What did the Resolution say?
- Geographically contiguous units are demarcated into regions which should be so constituted, with such territorial readjustments as may be necessary, that the areas in which the Muslims are numerically in a majority as in the North-Western and Eastern Zones of India, should be grouped to constitute “Independent States” in which the constituent units shall be autonomous and sovereign.”
- In other parts of India where the Mussalmans are in a minority, adequate, effective and mandatory safeguards shall be specially provided in the constitution for them and other minorities for the protection of their religious, cultural, economic, political, administrative and other rights and interests in consultation with them.”
What was the lead-up to the Lahore Resolution?
- Pre-1930s Muslim Agitation: Prior to the early 1930s, numerous Muslims in India had been advocating for improved representation and the protection of their rights within the Indian Union.
- Government of India Act, 1935: A significant development in this context was the provision of a separate electorate granted to Muslims under the Government of India Act, 1935. This was perceived as a step forward in addressing their concerns.
- Khaksar Tragedy: The Muslim League session occurred shortly after the Khaksar tragedy, which took place on March 19 in Lahore. Members of the Khaksar group, fighting for India's independence, were fired upon by British forces, resulting in numerous casualties.
Source: Indian Express
GS-II
India - Bhutan Relations
Subject: International Relations

Why in News?
Some sources have disclosed the presence of a Chinese backed disinformation campaign circulating false narratives about India Bhutan relationship.
Background:
- The increasing presence of China in India’s neighbourhood is a matter of concern.
Significance of Bhutan for India:
- Geopolitical Significance: Bhutan, situated between India and China, serves as a crucial buffer state for India's security interests due to its strategic location.
- Assistance from India: India has provided Bhutan with support in defense, infrastructure, and communication sectors, aiding in maintaining Bhutan's sovereignty and territorial integrity.
- Border Infrastructure Development: India has assisted Bhutan in constructing and maintaining border infrastructure like roads and bridges, enhancing its defense capabilities and territorial integrity, exemplified during the Doklam standoff in 2017.
- Trade Relations: India stands as Bhutan's largest trading partner and serves as a primary export destination for Bhutanese goods.
- Hydropower Collaboration: Bhutan's hydropower potential contributes significantly to its revenue, with India playing a vital role in supporting Bhutan's hydropower project development.
- Cultural Bond: Both nations share strong cultural ties, being predominantly Buddhist. India has aided Bhutan in preserving its cultural heritage, and many Bhutanese students pursue higher education in India.
- Environmental Initiatives: Bhutan's commitment to carbon neutrality finds support from India, with assistance in renewable energy, forest conservation, and sustainable tourism initiatives, aligning with Bhutan's environmental goals.
Challenges in India-Bhutan Relations:
- China's Presence in Bhutan: China's increasing presence, especially along the disputed border with Bhutan, has raised concerns in India, Bhutan's closest ally, regarding Bhutan's sovereignty and security.
- Border Situation: India and Bhutan share a largely peaceful 699 km long border, but recent years have seen instances of border incursions by Chinese forces, notably the Doklam standoff in 2017, which strained relations between India, China, and Bhutan.
- Hydropower Development: Bhutan's hydropower sector, vital for its economy, has seen significant Indian involvement. However, concerns have arisen in Bhutan regarding the terms of some projects, seen as overly favorable to India, leading to public opposition.
- Trade Relations: India serves as Bhutan's largest trading partner, but concerns exist over the trade imbalance, with Bhutan importing more than it exports to India. Bhutan seeks greater access to the Indian market to address this deficit.
Source: The Hindu
Resolving Indigenous Issues: Tripartite Agreement in Tripura
Subject: Indian Polity

Why in News?
A Tripartite agreement was signed between the Government of India, the government of Tripura, and the Tipraha Indigenous Progressive Regional Alliance (TIPRA).
- This marks a significant step towards addressing the longstanding issues faced by the indigenous population of Tripura.
Ethno-Political Demands in Tripura: Historical Context
- Demographic Shifts: Tripura has experienced significant demographic changes, primarily due to the influx of refugees from East Pakistan, leading to the marginalization of indigenous tribes.
- Marginalization of Locals: The influx of refugees has resulted in the erosion of the socio-political influence and land rights of indigenous populations over time.
- Ethnic Tensions: The demographic shifts have heightened ethnic tensions and insurgency, exacerbating conflicts between indigenous tribes and non-tribal communities. This has led to demands for greater autonomy and recognition of tribal rights.
- Revival of Ethnic Nationalism: In recent years, there has been a resurgence of ethnic nationalism, particularly evident in the demand for Greater Tipraland. This movement seeks to unite indigenous tribes under a common identity and advocate for their collective interests, reflecting a push for greater autonomy and recognition.
Demand for Greater Tipraland
- Enhanced Autonomy: The core objective of Greater Tipraland is to secure greater autonomy for indigenous tribes within Tripura, allowing them to govern their affairs and preserve their cultural heritage.
- Recognition of Tribal Rights: TIPRA’s demands include linguistic recognition, economic empowerment, and political representation for indigenous communities, ensuring their rights are safeguarded and respected.
- Geographical Extent: The proposed Greater Tipraland encompasses not only the Tripura Tribal Areas Autonomous District Council (TTAADC) but also extends to tribal populations residing outside designated tribal areas, including those in neighboring states and Bangladesh.
Constitutional Framework for Such Demands
- Constitutional Provisions: Articles 2 and 3 of the Indian Constitution serve as the legal framework for creating new states and altering state boundaries. TIPRA aims to utilize these provisions to advocate for the establishment of Greater Tipraland.
- Regional Representation: Through political advocacy and grassroots mobilization efforts, TIPRA seeks to garner support for its demands within both the legislative and executive branches of government, at both the state and national levels.
- Challenges and Opportunities: While constitutional avenues exist for pursuing Greater Tipraland, navigating political complexities and addressing competing interests present significant challenges. Nevertheless, TIPRA perceives these challenges as opportunities to engage in constructive dialogue and build consensus around its agenda.
Socio-Political Dynamics
- Coalition Building: TIPRA’s emergence as a major political force has reshaped Tripura’s political landscape, with alliances and partnerships forming to advance shared objectives, including the pursuit of Greater Tipraland.
- Opposition Criticism: Opposition parties, such as the Communist Party of India (Marxist), have criticized TIPRA’s demands as politically motivated, highlighting broader ideological divisions and electoral dynamics.
- Public Support: TIPRA’s demands have garnered widespread public support, particularly among indigenous communities, who see Greater Tipraland as a pathway to empowerment and self-determination.
Conclusion
- The demand for Greater Tipraland encapsulates the aspirations of Tripura’s indigenous tribes for self-governance, cultural preservation, and socio-economic empowerment.
- While challenges remain, the pursuit reflects a broader movement towards inclusive governance and recognition of indigenous rights in India’s northeastern region.
Source: Times of India
GS-III
 |
Download the notes
UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 4th March 2024
|
Download as PDF |
Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE)
Subject: Indian Economy

Why in News?
Recently, 22nd Foundation Day of the Bureau of Energy Efficiency was celebrated in New Delhi.
Background:-
- It was created in March 2002 under the provisions of the Energy Conservation Act 2001.
About Bureau of Energy Efficiency:-
- The The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) is a statutory body under the Ministry of Power, Government of India.
- The agency’s primary function is to encourage the efficient use of energy in India by developing programs and strategies that promote energy conservation.
- BEE focuses on self-regulation and market principles to enhance energy efficiency across various sectors.
Key Initiatives of BEE
- Standards & Labelling Scheme: BEE facilitates informed consumer choices through information on energy-efficient appliances.
- Energy Conservation Building Code: BEE promotes energy-efficient practices in building construction and design.
- Perform, Achieve, and Trade (PAT): BEE incentivizes energy-intensive industries to meet specific energy-saving targets.
- Energy Efficiency in Large Industry: BEE collaborates with large industries to enhance energy efficiency.
- Energy Efficiency in Small & Medium Industry: BEE assists small and medium-sized enterprises in improving energy efficiency.
- Energy Efficiency in States: BEE supports state-level initiatives, as evidenced by the State Energy Efficiency Index 2023.
- Demand Side Management (DSM): BEE employs strategies to manage energy demand effectively.
- National Energy Conservation Awards: Recognizing outstanding contributions to energy conservation.
- Awareness Campaigns: BEE conducts campaigns to raise awareness about energy efficiency, such as the #RaiseItBy1Degree campaign.
Source: PIB
Hangul
Subject: Environment and Ecology

Why in News?
Mating calls of endangered hangul indicate record uptick in population
Background:
- Kashmir’s highly shy and sensitive animal, hangul, has reported one of the healthiest rutting or mating season in the previous autumn. It is the state animal of Jammu & Kashmir.
About Hangul:
- State Animal: The Kashmir stag, also known as hangul, holds the prestigious status of being the state animal of Jammu & Kashmir.
- Endemic Species: The hangul is a subspecies of Central Asian red deer native to Kashmir and its surrounding areas.
- Habitat Challenges: Once widespread across Kashmir and parts of Himachal Pradesh, the hangul now faces survival challenges, with its population concentrated within 141 sq km of the Dachigam National Park.
- Migratory Patterns: A 2019 survey revealed that the hangul has started using an old migratory route stretching from Sind Valley to Tulail in Gurez Valley, previously active in the early 1900s.
- Population Distribution: As of 2023, there are 289 hanguls, with 275 in Dachigam National Park and 14 in Tral Wildlife Sanctuary, serving as their secondary habitat.
- Conservation Status: Classified as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List, highlighting the urgent need for conservation efforts to safeguard the species from extinction.
Source: The Hindu
Global Resource Outlook
Subject: Environment and Ecology

Why in News?
Global Resource Outlook 2024 was launched on the final day of the Sixth United Nations Environmental Assembly (UNEA-6) at the UNEP headquarters in Nairobi, Kenya.
About Global Resource Outlook:
- Flagship Report: This report is the flagship publication of the International Resource Panel, a body of the United Nations Environment Programme.
- Focus: The report for this year emphasizes the crucial role of resources in achieving the goals outlined in Agenda 2030 and various multilateral environmental agreements, especially in addressing the triple planetary crisis.
- Scope: It encompasses comprehensive data, modeling, and assessments sourced from 180 countries, spanning seven global regions and four income groups. This extensive analysis aims to understand trends, impacts, and distributional effects associated with resource utilization.
Highlights of the report
- Global Inequality: Low-income countries consume significantly fewer materials compared to wealthy nations, despite generating fewer climate impacts.
- Growth of Resource Consumption: Over the past 50 years, global production and consumption of material resources have surged, growing more than threefold at an average annual rate of over 2.3%. This growth has been a primary driver of the triple planetary crisis.
- Driving Factors: Demand from upper-income countries largely propels the consumption and use of resources.
- Environmental Impacts: Extraction and processing of material resources, including fossil fuels, minerals, non-metallic minerals, and biomass, contribute over 55% of greenhouse gas emissions and 40% of particulate matter pollution.
- Impact on Biodiversity and Water: Agriculture and forestry-related resource extraction contribute to 90% of land-related biodiversity loss and water stress, as well as one-third of greenhouse gas emissions.
- Emissions from Extraction and Processing: Fossil fuels, metals, and non-metallic minerals extraction and processing, including sand, gravel, and clay, contribute to 35% of global emissions.
- Future Projections: Despite current challenges, resource exploitation is expected to rise by almost 60% from 2020 levels by 2060, reaching 160 billion tonnes.
Source: DTE
Plans for Non-Lapsable Defence Modernization Fund put on hold
Subject: Defence and Security

Why in News?
The Ministry of Defence (MoD) had informed Parliament recently a separate mechanism by the Ministry of Finance in consultation with the MoD to explore a special dispensation to operationalize a “Non-lapsable Defence Modernisation Fund” because the non-lapsable pool has drawbacks as it affects parliamentary scrutiny and accountability.
About Non-Lapsable Defence Modernisation Fund (DMF):
- DMF Establishment: The Defence Modernisation Fund (DMF) is established with the aim of creating a dedicated pool of funds that carry over from year to year. This ensures that any unutilized funds remain available for future defence modernization initiatives.
- Current Funding Structure: Presently, defence funding in India operates on a yearly basis, with any unspent funds being returned at the conclusion of each fiscal year.
- Purpose of DMF: The DMF is designed to complement regular budgetary allocations and offer certainty in funding for diverse defence capability development and infrastructure projects.
Recommendation by XV Finance Commission
- The 15th Finance Commission proposed a dedicated Modernisation Fund for Defence and Internal Security.
- It said the Union may constitute in the Public Account of India, a dedicated non-lapsable fund, Modernisation Fund for Defence and Internal Security (MFDIS).
Need for Non-Lapsable Funds:
- Addressing Budgetary Limitations: Yearly budget allocations lead to the surrender of unutilized funds, hindering defense modernization efforts.
- Creating Certainty: Non-lapsable funds offer certainty in funding availability, promoting stability and continuity in modernization initiatives.
- Enhancing Flexibility: These funds provide flexibility for addressing unforeseen contingencies and promoting long-term planning.
Significance of Non-Lapsable Funds:
- Certainty and Continuity: Non-lapsable funds guarantee funding for defence modernisation, eliminating the necessity for frequent requests for additional funds. This assurance ensures continuity in project execution.
- Flexibility: These funds offer flexibility in utilization, enabling the allocation of resources to unforeseen requirements or contingencies that may arise during the year.
- Long-term Planning: By allowing funds to carry over across fiscal years, non-lapsable funds facilitate long-term planning for defence modernization projects. This promotes systematic and strategic development in the realm of defence capabilities.
Challenges and Considerations
- Parliamentary Scrutiny: The establishment of a non-lapsable fund may raise concerns regarding reduced parliamentary scrutiny and accountability over defense spending. This could potentially lead to debates about the appropriate balance between flexibility and oversight in allocating defense resources.
- Operational Modalities: Determining the sources of funding and operational modalities for the Defence Modernisation Fund (DMF) requires careful consideration to ensure effectiveness and transparency. This includes defining the criteria for allocating funds, mechanisms for monitoring expenditure, and mechanisms for reporting to Parliament.
- Interagency Coordination: Coordination between the Ministry of Defence and the Ministry of Finance is essential for the successful implementation of the fund. This involves aligning budgetary processes, ensuring compliance with financial regulations, and facilitating communication between relevant government agencies to streamline decision-making and resource allocation.
Conclusion
- The proposal for a Non-Lapsable Defence Modernisation Fund represents a proactive approach to addressing the challenges associated with defence funding in India.
- While the concept offers several potential benefits, its implementation requires careful deliberation and collaboration between key stakeholders to ensure accountability, transparency, and optimal utilization of resources in support of national security objectives.
Source: The Hindu
|
39 videos|4544 docs|971 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 4th March 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the major rivers discussed in the article? |  |
| 2. What is the Lahore Resolution mentioned in the article? |  |
| 3. What is the Tripartite Agreement in Tripura mentioned in the article about? |  |
| 4. What is the role of the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) mentioned in the article? |  |
| 5. Why were the plans for the Non-Lapsable Defence Modernization Fund put on hold, as mentioned in the article? |  |




























