Notes: The Establishment of Company Power | Social Studies & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET PDF Download
India during the 18th century witnessed the decline of the Mughal Empire and the emergence of various crises. The death of Aurangzeb in 1707 marked the beginning of this period of instability, exacerbated by conflicts in the Deccan and invasions by Nadir Shah and Ahmed Shah Abdali. Successive Mughal emperors faced challenges, leading to the rise of regional powers.
India During the 18th Century
Three prominent Mughal provinces in the 18th century were Awadh, Bengal, and Hyderabad, each established by former Mughal nobility who had served as governors of large provinces. Hyderabad, under the rule of Nizam-ul-Mulk Asaf Jah, emerged as a significant power during this period.

Hyderabad
Nizam-ul-Mulk Asaf Jah, a prominent figure at the court of Mughal Emperor Farrukhsiyar, founded the Hyderabad state in 1724. Asaf Jah, known as the Nizam of Hyderabad, became one of the most powerful rulers in the region.
Throughout history, India's wealth and resources have attracted foreign invaders. The 15th century, marked by significant geographical discoveries, witnessed increased activities by European powers in India.
Portuguese
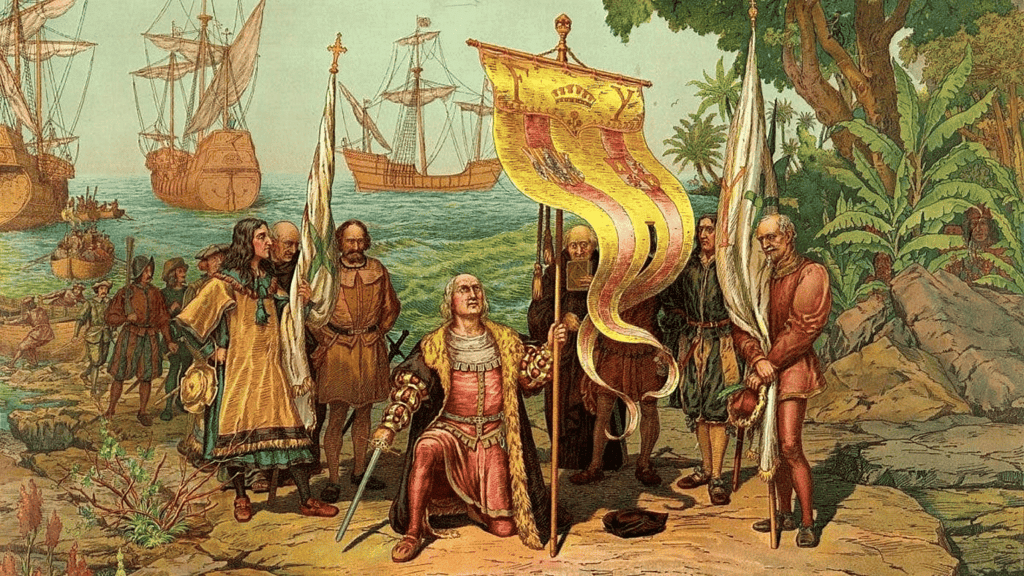 Portuguese Arrival
Portuguese Arrival
- The first European voyage to India was led by Vasco da Gama in 1498.
- The Portuguese Empire established the first European trading center at Kollam, Kerala in 1502, marking the beginning of the colonial era in India.
- In 1662, Portuguese princess Catherine was married to Charles II of England, and as part of her dowry, the Portuguese ceded the island of Bombay to the British.
Question for Notes: The Establishment of Company PowerTry yourself: Who established the Hyderabad state in 1724?
View Solution
Dutch
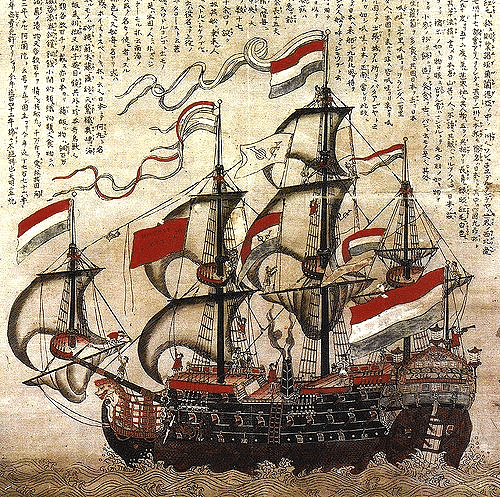 Dutch East India Company
Dutch East India Company
- The Dutch East India Company was established in 1602.
- They set up trading posts along various parts of the Indian coast and captured Ceylon from the Portuguese.
English
 English East India Company
English East India Company
- The English East India Company, initially known as the Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East Indies, was founded in 1600.
- In 1611, they established a factory in Masulipatnam and obtained permission from Mughal Emperor Jahangir to establish a factory in Surat in 1612.
- They established a second factory in Madras in 1640 after receiving permission from the Vijayanagar ruler.
- Victories in the Battle of Plassey (1757) and the Battle of Buxar (1764) consolidated the company's power, leading to its appointment as the revenue collector of Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa by Emperor Shah Alam II.
- The Anglo-Mysore wars (1766-99) and the Anglo-Maratha wars (1772-1818) further expanded British control over large areas of India.
French
- The French also established trading bases in India following the footsteps of the Portuguese, English, and Dutch.
The first French establishment in India was in Pondicherry on the Coromandel coast in 1674.
Subsequent French settlements included Chandernagore in Bengal, Yanam in Andhra Pradesh, Mahe, and Karaikal.
Between 1744 and 1761, the British and French engaged in repeated attacks and conquests of each other's forts and towns in South Eastern India and Bengal.
Establishment of East India Company's Power
The East India Company solidified its power in India in various ways:
- After the death of Aurangzeb, the last powerful Mughal ruler, regional kingdoms emerged.
- In 1600, the East India Company acquired a charter from Queen Elizabeth I, granting it exclusive trading rights in the East.
East India Company's Trade in Bengal
The East India Company's trade in Bengal included:
- Establishment of the first English factory on the banks of the river Hugli in 1651.
- Obtaining a farman from Aurangzeb granting the company duty-free trade rights.
- Competition with Portuguese, Dutch, and French traders in the Indian Ocean.
- High demand for Indian goods like cotton, silk, pepper, cloves, cardamom, and cinnamon in Europe.
The Battle of Plassey
The Battle of Plassey unfolded as follows:
- Successive strong rulers like Murshid Quli Khan and Alivardi Khan governed Bengal.
- Concerned about Siraj-ud-daullah's power, the company orchestrated his defeat at Plassey in 1757, led by Robert Clive.
- The victory was largely due to the betrayal of Siraj-ud-daullah by Mir Jafar, one of his commanders.
- After Plassey, Mir Jafar became the Nawab but was later deposed and replaced by Mir Qasim.
- Following Mir Qasim's defeat at Buxar in 1764, Mir Jafar was reinstated.
- In 1765, the Mughal emperor appointed the company as the Diwan of Bengal, granting control over Bengal's revenue.
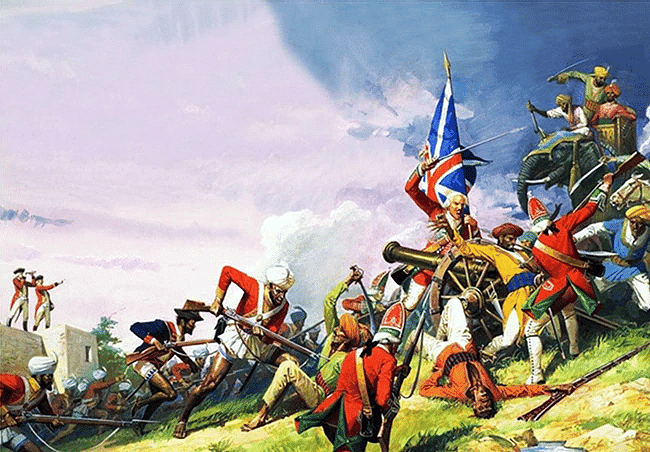 Battle of Plassey
Battle of Plassey
Conflict with the Marathas
The company also faced conflicts with the Marathas:
- From the late 18th century, the company aimed to suppress and eventually eliminate Maratha control.
The Marathas faced defeat, particularly in the Third Battle of Panipat in 1761, leading to a series of wars where the British gradually subdued them:
- The Treaty of Salbai in 1782 marked the inconclusive end of the first war.
- The Second Anglo-Maratha War (1803-05) saw British gains in Orissa and territories north of the Yamuna river, including Agra and Delhi.
- The Third Anglo-Maratha War (1817-19) conclusively crushed Maratha power, with the Peshwa being removed and territories south of the Vindhyas coming under complete British control.
Assertion of Paramountcy
Under Lord Hastings (Governor-General from 1813 to 1823), the British initiated a policy of 'paramountcy', claiming supreme authority over Indian states:
- Rani Channamma of Kittoor resisted British annexation, but was eventually arrested and died in prison in 1829.
- Rayanna continued the resistance, but was captured and executed by the British in 1830.
- Concerns about Russian expansion prompted British efforts to secure control over the North-West, including wars in Afghanistan and annexation of Sind and Punjab.
Doctrine of Lapse
Under Lord Dalhousie (Governor-General from 1848 to 1856), the Doctrine of Lapse was implemented to annex Indian kingdoms:
- The doctrine stated that if an Indian ruler died without a male heir, his kingdom would become part of British territory.
- Several kingdoms were annexed using this doctrine, including Satara (1848), Sambalpur (1850), Udaipur (1852), Nagpur (1853), Jhansi (1854), and Oudh (1856).
Introduction of New Administration
The Governor-General introduced various administrative reforms:
- Warren Hastings, during his tenure (1773 to 1785), expanded British power from Bengal to Bombay and Madras.
- The British territories were divided into administrative units called Presidencies, each governed by a Governor, with Warren Hastings serving as the Governor-General.
- A new system of justice was established, with each district having separate criminal and civil courts.
- Under the Regulating Act of 1773, a Supreme Court was established in Calcutta, along with a court of appeal known as the Sadar Nizamat Adalat.
|
75 videos|320 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: The Establishment of Company Power - Social Studies & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET
| 1. What was the significance of the Battle of Plassey in the establishment of East India Company's power in India? |  |
| 2. How did the Doctrine of Lapse play a role in the Company's expansion of power in India during the 18th century? |  |
| 3. What were some key factors that led to the conflict between the East India Company and the Marathas during the 18th century? |  |
| 4. How did the introduction of a new administration by the East India Company impact governance in India during the 18th century? |  |
| 5. What role did trade in Bengal play in the East India Company's rise to power in India during the 18th century? |  |
















