Notes: Administration and Architecture under the Delhi Sultanate. | Social Studies & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Art and Architecture of the Delhi Sultanate |

|
| Main Features of Sultanate Architecture |

|
| Administration Under Sultanate |

|
| Achievements & Legacy of the Sultanate |

|
Art and Architecture of the Delhi Sultanate
During the Delhi Sultanate period, art and architecture underwent a significant transformation, characterized by a fusion of Arabic and Indian styles, as described by Fergusson.

The palaces constructed by the Delhi Sultans showcased several distinct features not commonly found elsewhere. These included:
Main Features of Sultanate Architecture
- Arch and Dome Method: The use of arches and domes offered several advantages, such as providing a visually pleasing skyline and allowing for the construction of large halls with minimal pillars obstructing the view.
- Use of Superior Mortar: To ensure the stability of arches and domes, high-quality mortar was essential. The Sultans employed fine-quality mortar in their buildings to secure the stones in place.
- Slab and Beam Method: Unlike the traditional Indian method of stacking stones, the Sultanate architecture often employed the slab and beam method, wherein beams were placed over slabs of stones, allowing for more stable construction.
- Decoration: The Turks avoided depicting human and animal figures in their buildings and instead focused on geometric.

Administration Under Sultanate
Central Administration
The real administrator of the Delhi Sultanate was the king or Sultan himself. There was no hereditary principle of succession. The sultans of Delhi were considered to be the agents of God, responsible for enforcing the divine laws impressed by the Holy Quran. The Wazir was the most important minister in the Sultanate administration.
Judicial Administration
The Sultan was the highest judicial authority of the Delhi Sultanate, possessing wide powers as a perfect autocrat. The Department of Judiciary was known as Diwan-i-Qaza, headed by the Qazi.
Revenue Administration
The fiscal policy of the Sultanate was based on the taxation theory of the Hanafi school of thought, prescribing the levy of five kinds of taxes:
- Zakat: A religious tax paid by Muslims for the benefit and welfare of their religionists, charged at 2.5% of actual income or property.
- Khams: Refers to the state's share of the war booty, amounting to 1/5th of the total.
- Jaziya: A tax charged from Hindus in their capacity as Zimmis.
- Ushar: Land tax collected from Muslim peasants.
Generally, agricultural produce was taxed at one-third of its value, payable in cash or kind.
Achievements & Legacy of the Sultanate
The main achievement of the Delhi Sultanate was its successful defense of India from Mongol invasion, despite earlier suffering from the sacking of Delhi in 1398 by Timur.
The Sultanate ushered in a period of Indian cultural renaissance, resulting in an 'Indo-Muslim' fusion that left lasting monuments in architecture, music, literature, and religion.
- The Begumpuri Mosque, built in the reign of Muhammad-bin Tughlaq, served as the main mosque of Jahanpanah, his new capital in Delhi.
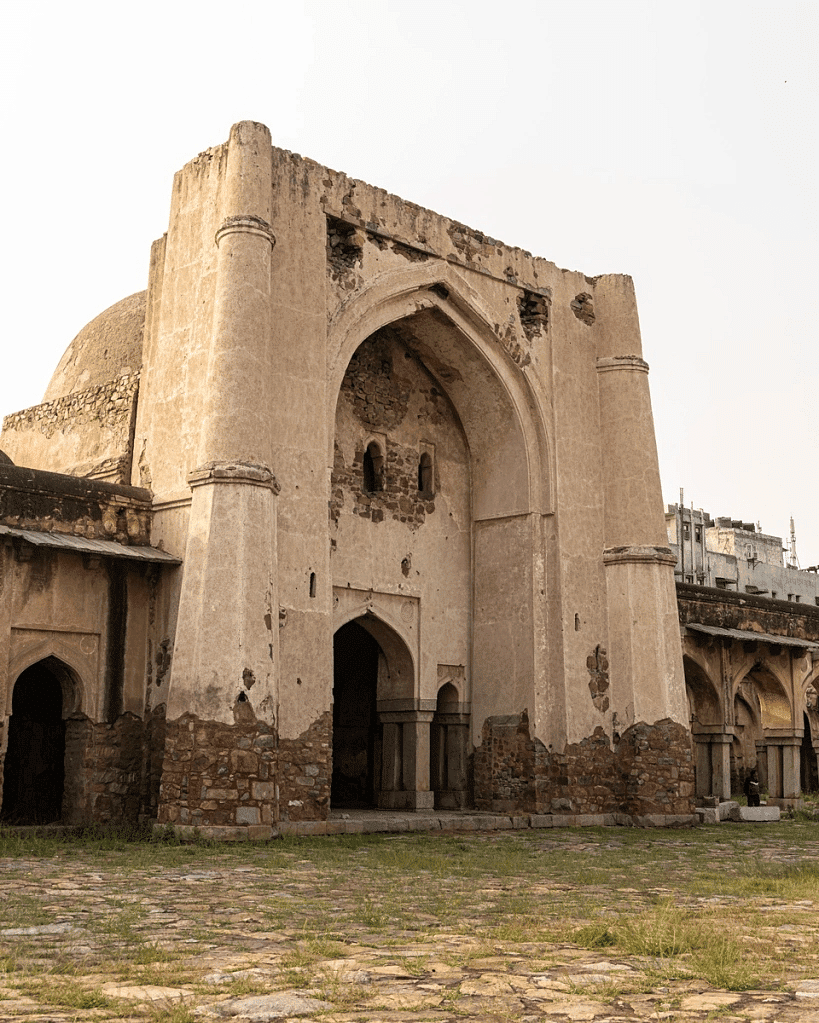 Begumpur Mosque
Begumpur Mosque
- The Moth Ki Masjid, constructed by Wazir Miya Bhoiya in 1505 during the reign of Sikandar Lodhi.
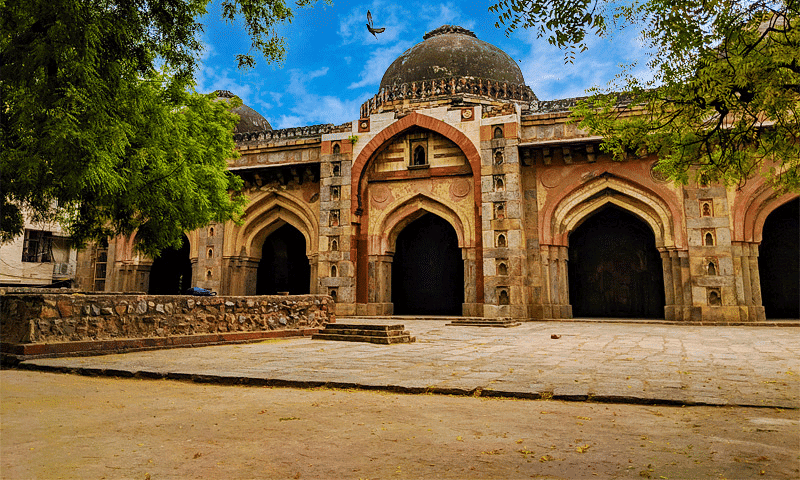 Moth ki Masjid
Moth ki Masjid
- The Khiljis conquered Gujarat and Malwa and conducted the first expeditions South of the Narmada river, reaching as far South as present-day Tamil Nadu.
- The Tughlaqs introduced a monetary economy in the provinces and districts, and encouraged agricultural development by digging village wells, providing seeds, and promoting cash crops like sugarcane.
- The Sultans based their laws on the Quran and the Sharia, allowing non-Muslims to practice their religion only if they paid Jizya or head tax.
- The Sultanate provided the foundation for the Mughal Empire, which expanded its territory further.
A Sanskrit Prashasti praising the Delhi Sultan Ghiyasuddin Balban explained that he ruled over a vast empire stretching from Bengal to Ghazni.
|
74 videos|121 docs|77 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Administration and Architecture under the Delhi Sultanate. - Social Studies & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET
| 1. What are the main features of Sultanate architecture? |  |
| 2. How was the administration structured under the Delhi Sultanate? |  |
| 3. What were some achievements and legacies of the Delhi Sultanate? |  |
| 4. How did art and architecture reflect the power and wealth of the Delhi Sultanate? |  |
| 5. What role did religion play in Sultanate architecture and administration? |  |
















