UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 25th May 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I/Geography
TAIWAN
Source: Mint

Why in News?
China recently concluded war games around Taiwan, including simulated attacks and ship boarding practices.
Background:
- China initiated the "Joint Sword - 2024A" exercises shortly after Lai Ching-te assumed office as Taiwan's President, a move criticized by Beijing as separatist.
- Beijing considered the exercises as a response to Mr. Lai's inauguration speech, where he emphasized the autonomy of Taiwan from China.
About Taiwan:
- Taiwan, also known as the Republic of China (ROC), is situated in East Asia, bordered by the East and South China Seas.
- The main island of Taiwan covers 35,808 square kilometers and features mountainous terrain in the east and plains in the west.
- With Taipei as its capital, Taiwan is densely populated with approximately 23.9 million people.
- Taiwan boasts an export-oriented industrial economy focusing on manufacturing sectors like steel, machinery, electronics, and chemicals.
History:
- Taiwan was successively under Dutch rule, independent, then under Chinese and Japanese control before being returned to Nationalist Chinese rule in 1945.
- Following the Chinese Civil War in 1949, the Nationalist government relocated to Taiwan, leading to the island's separation from mainland China.
- While the ROC initially claimed authority over both the mainland and Taiwan, this assertion was relinquished in the 1990s.
- The PRC maintains a one-China policy, refusing diplomatic ties with nations recognizing the ROC.
GS-I/Geography
Cyclone Remal and its Landfall
Source: Mint

Why in News?
A cyclonic storm named "Remal" is predicted to intensify into a severe cyclonic storm by May 25, originating in the central Bay of Bengal. It is anticipated to make landfall between Sagar Island in West Bengal and Khepupara in Bangladesh around midnight on May 26.
Cyclone Overview
Definition of a Cyclone: A cyclone is a large-scale air system revolving around the center of a low-pressure region, typically leading to severe storms and adverse weather conditions.
Characteristics of Cyclones:
- Cyclones feature inward spiraling winds that rotate anti-clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
- The center of a cyclone is remarkably calm with low air pressure and average speeds reaching 120 kmph.
- Cyclones possess closed isobars, resulting in higher velocity, and they develop over oceans and seas exclusively, being seasonal phenomena.
Classification of Cyclones by Wind Speed
- Depression: Wind speeds range from 31 to 49 km/h.
- Deep Depression: Wind speeds range from 50 to 61 km/h.
- Cyclonic Storm: Wind speeds range from 62 to 88 km/h.
- Severe Cyclonic Storm: Wind speeds range from 89 to 117 km/h.
- Very Severe Cyclonic Storm: Wind speeds range from 118 to 166 km/h.
- Extremely Severe Cyclonic Storm: Wind speeds range from 167 to 221 km/h.
- Super Cyclonic Storm: Wind speeds exceed 222 km/h.
Landfall of a Cyclone
- Definition of Landfall: Landfall occurs when a tropical cyclone transitions from being over water to making contact with land. The eye of the storm, or its center, crosses over the coast during this event.
- Eye of a Cyclone: The "eye" of a cyclone is a region at its center with calm weather characterized by light winds, clear skies, and reduced precipitation.
Bay of Bengal: A Cyclone Hotspot
- Significance of the Bay of Bengal: Historical data emphasizes the Bay of Bengal's tendency to host cyclones, with a majority (58%) making landfall on India's eastern coast due to various geographical factors.
Cyclone Management in India
- National Cyclone Risk Mitigation Project (NCRMP): Launched by the Ministry of Home Affairs, this project aims to bolster coastal communities and infrastructure against cyclones and storm surges through various measures like capacity building and early warning systems.
- IMD's Color-Coding System: The Indian Meteorological Department uses colors - Green, Yellow, Orange, and Red - to indicate the severity of cyclones for public awareness.
- Coastal Zone Management Projects:
- Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM) Project.
- Coastal Regulation Zones (CRZ).
- Other Initiatives:
- National Disaster Response Force (NDRF).
- National Disaster Management Plan (NDMP).
- National Institute of Disaster Management (NIDM).
- State Disaster Management Authorities (SDMAs).
Coordination Efforts and Safety Measures
- Various measures have been implemented, such as broadcasting VHF alerts, positioning disaster relief teams, banning fishing activities, and leveraging early warning systems to ensure maritime safety and community preparedness.
GS-II/International Relations
G7
Source: New York Times

Why in News?
U.S. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen recently emphasized the need for market-driven countries to unite against China's state-driven industrial policies at a G7 finance meeting.
Background
- Concerns exist globally, beyond the G7, regarding China's heavy investments in strategic industries like electric vehicles, solar products, semiconductors, steel, etc.
- Without changes in China's approach, market-driven economies could face a flood of inexpensive Chinese exports, endangering their own manufacturers.
About G7
- G7 refers to the "Group of Seven" industrialized nations, consisting of the United States, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the European Union as a non-enumerated member.
Origin of G7
- In 1975, the current G7 members, excluding Canada, initiated the group during a global economic downturn caused by the OPEC oil embargo.
- Annual meetings were established to coordinate macroeconomic initiatives, with Canada officially joining the group a year later.
- Russia became part of the group in 1998 but was expelled in 2014 following its annexation of Crimea from Ukraine.
Key Details about G7
- The G7 convenes yearly to discuss global economic governance, international security, and energy policy, with decisions made during summits being non-binding.
- Leadership of the G7 rotates annually among member states, with the presiding country determining priorities and hosting the summit.
- G7 members share common values such as democracy, human rights, free markets, and adherence to international law.
- Collectively, G7 nations represent a significant portion of global GDP, population, and carbon emissions.
Concrete Achievements of G7
- Initiatives like Financial Action Task Force (FATF), European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD), Deauville Partnership, and Muskoka Initiative have been launched by the G7.
GS-II/Polity and Governance
Diplomatic Passport
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
Nearly a month after a Special Investigation Team (SIT) began probing allegations of sexual assault and abuse against Hassan MP Prajwal Revanna, sources in the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) have confirmed that the Karnataka government's request to revoke the diplomatic passport of the suspended Janata Dal (Secular) leader is "being processed."
Background:
- Members of Parliament, when using diplomatic passports, need to apply for prior political clearance directly to the MEA, even for private visits.
- Diplomatic passport holders do not require visa notes for travel to certain countries with which India has mutual visa waiver agreements.
- Germany, where Mr. Revanna allegedly fled to in April, allows diplomatic passport holders to stay for up to 90 days without a visa.
What is a diplomatic passport?
- Under the Passport Act of 1967, the Central government issues three classes of passports — ordinary, official, and diplomatic.
- Ordinary passports are for personal travel, official passports for designated officials working abroad, and diplomatic passports for representatives of the country with special privileges.
Are MPs entitled to diplomatic passports?
- Diplomatic passports are issued to individuals with diplomatic status, those on diplomatic assignments, and certain positions as determined by the Central Government.
- MPs and their spouses are entitled to diplomatic passports along with ordinary passports.
Conditions for revoking a diplomatic passport
- The passport authority can revoke a passport for providing wrong information, criminal convictions, pending criminal proceedings, or reasons of national interest.
- A passport can be impounded if the holder is convicted of an offence involving moral turpitude or if there are pending court proceedings against them.
GS-II/Polity and Governance
National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT)
Source: The Telegraph

Why in News?
Recently, the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) has sent notices to Think and Learn Pvt. Ltd. (TLPL), the parent company of Byju's, for alleged non-payment of dues to operational creditors.
About NCLT:
- The NCLT is a quasi-judicial body that was established under the Companies Act, 2013, and was set up on June 1, 2016, by the Government of India.
Formation:
- The formation of the NCLT was based on the recommendations of the Balakrishna Eradi committee, which focused on laws concerning the insolvency and winding up of companies.
Functions:
- It was created to resolve civil corporate disputes that arise under the Companies Act, 2013.
- The NCLT has the authority to hear and make decisions on various cases such as mergers, acquisitions, oppression, mismanagement, winding up of companies, and other corporate law matters.
- It serves as an adjudicating authority for the Insolvency resolution process of companies and Limited Liability Partnerships under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016.
- The establishment of the NCLT integrates the corporate jurisdiction of several authorities including the Company Law Board (CLB), Board of Industrial and Financial Reconstruction (BIFR), and the Appellate Authority for Industrial and Financial Reconstruction.
- Additionally, it has powers related to the winding up of a company and other provisions originally vested in High Courts.
Composition:
- The NCLT is comprised of a President along with a necessary number of Judicial and Technical Members.
Principal Bench:
- The primary bench of the NCLT is located in New Delhi.
Powers:
- The NCLT is not restricted by the rules outlined in the Code of Civil Procedure and operates based on the principles of natural justice, while adhering to the provisions of the relevant Act and any regulations established by the Central Government.
- It can enforce its orders in a manner similar to a court.
- The NCLT has the authority to review its own orders, as well as to regulate its own procedures.
GS-II/International Relations
World Health Assembly
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
Recently, member states of the World Health Organization have agreed to share outcomes of the historic International Health Regulations (IHR) and pandemic agreement processes with the World Health Assembly.
About World Health Assembly:
- Decision-making body of the World Health Organization
- Attended by delegations from all WHO Member States
- Focuses on a specific health agenda prepared by the Executive Board
- Held annually in Geneva, Switzerland
Function:
- Determines the policies of the Organization
- Appoints the Director-General
- Supervises financial policies
- Reviews and approves the proposed program budget
Key facts about International Health Regulations (IHR):
- First adopted by the WHA in 1969 and last revised in 2005
- Conceived to maximize collective efforts to manage public health events while minimizing disruption to travel and trade
- 196 State Parties to the IHR, including all 194 WHO Member States, Liechtenstein, and the Holy See
- An instrument of international law legally binding on 196 countries
- Provides a legal framework defining countries' rights and obligations in handling public health events and emergencies crossing borders
- Introduces safeguards to protect rights of travelers regarding personal data, informed consent, and non-discrimination in health measures
GS-III/Defence and Security
INTEGRATED THEATER COMMANDS
Source: Indian Express

Why in News?
The Indian Armed Forces are currently finalizing plans for the establishment of integrated theatre commands.
Background
This significant defense reform aims to merge the three main defense services - the Indian Army, the Indian Navy, and the Indian Air Force (IAF) - to collaborate in specific adversary-based theaters with clearly defined military objectives in times of limited conflict or war.
Key Takeaways
- The three services presently function independently under their respective operational commands.
- Theaterization involves uniting personnel from all three services under a single theatre commander to operate collectively as a cohesive unit in conflicts, optimizing manpower and resources across services.
- Each service possesses its unique culture and principles. Through theatre commands, integration would combine personnel, assets, infrastructure, and logistics to function harmoniously to achieve military objectives within specified theaters.
- Efforts have been made to enhance integration among the services, including plans to designate Mumbai as the first tri-service common defense station, establish additional joint logistics nodes nationwide to enhance logistics integration, and streamline supply chains and inter-service officer postings.
- Presently, the Army and the IAF each have seven commands, while the Navy has three. There are also two tri-service commands - the Andaman and Nicobar Command, and the Strategic Forces Command (SFC), alongside the Headquarters Integrated Defence Staff (HQIDS).
- Following the establishment of theatre commands, three service command headquarters are likely to evolve into theatre command headquarters. The existing Andaman and Nicobar Command might be absorbed into one of the theatre commands, with HQIDS expected to function under the CDS.
GS-III/Economy
 |
Download the notes
UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 25th May 2024
|
Download as PDF |
India's Opposition to China-led Investment Facilitation Proposal at WTO
Source: The Print
Why in News?
India is resisting pressure at the WTO to permit a 'plurilateral pact' on investment facilitation.
- An official has stated that India contests a proposal led by China on investment facilitation at the WTO, arguing that it is beyond the WTO's trade-related scope.
Understanding Plurilateral Agreements
- A plurilateral agreement involves multiple countries but does not necessarily involve all members of a larger organization like the WTO.
- These agreements are binding only on the signatories, not on the entire organization's membership under annexure-4 of the WTO.
- They enable deeper integration among interested parties without necessitating full consensus, which is challenging in larger multilateral frameworks.
China's Investment Facilitation for Development Agreement (IFD)
- The IFD Agreement, spearheaded by China with backing from other nations, aims to simplify and facilitate foreign investment.
- Main objectives include enhancing transparency of investment measures, expediting investment-related authorization processes, promoting international cooperation and information sharing, and encouraging sustainable investment practices.
- Proponents argue that the IFD would benefit all WTO members, particularly developing countries, by fostering a more predictable and transparent investment environment.
India's Firm Opposition at WTO MC13
- Investment as a Non-Trade Issue: India asserts that investment does not align with the WTO's traditional focus on trade matters and has historically been excluded from the WTO's purview.
- Sovereignty Concerns: India is apprehensive about potential encroachments on its policy autonomy. The IFD Agreement mandates government consultations with investors on policy issues, raising fears of compromising sovereign decision-making.
- Lack of Consensus: India and South Africa emphasize the absence of unanimous agreement among WTO members regarding the IFD's inclusion as a plurilateral agreement, suggesting that it should not be placed on the formal agenda without full consensus.
- Policy Autonomy: India fears that the IFD's requirements could limit its ability to regulate investments in line with national development priorities and strategies.
- Procedural Concerns: India argues that the IFD matter should have been discussed at the General Council rather than at MC13, considering the divisive nature of the proposal among WTO members.
Conclusion
- India's opposition to the IFD Agreement at the WTO stems from concerns related to safeguarding national sovereignty, upholding established WTO boundaries concerning trade and investment, and ensuring that any significant changes in the WTO framework garner broad-based consensus.
GS-III/Science and Technology
Ferroptosis Cases in Severe Covid Patients
Source: Science Daily
Why in News?
Columbia University study on COVID-19 fatalities identified ferroptosis as the primary cause of lung cell death, enhancing our understanding of lung disease progression.
What is Ferroptosis?
- Ferroptosis is a form of regulated cell death characterized by the iron-dependent buildup of lipid peroxides to lethal levels.
Other Forms of Cell Death:
- Apoptosis: A highly regulated process in multicellular organisms that eliminates unwanted or damaged cells without causing inflammation.
- Necrosis: Cell death involving rapid and uncontrolled cell lysis, often leading to inflammation and tissue damage.
- Autophagy: The degradation and recycling of cellular components through lysosomal machinery.
Mechanism of Ferroptosis:
- Iron Accumulation: Excess iron within cells, especially in labile pools, generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) through Fenton chemistry.
- Lipid Peroxidation: ROS from excess iron triggers lipid peroxidation, particularly of polyunsaturated fatty acids in cell membranes, causing membrane damage.
- Glutathione Depletion: Decrease in cellular GSH levels impairs the cell's ability to counteract oxidative stress.
- GPX4 Inhibition: Inhibition of GPX4 activity leads to the accumulation of lipid peroxides and cell death.
- Mitochondrial Dysfunction: Associated with alterations in mitochondrial functions and bioenergetics.
- Cellular Consequences: Accumulation of lipid peroxides and mitochondrial dysfunction result in cellular damage and death by ferroptosis.
Significance of the Study
- Targeting and preventing ferroptosis could provide new treatment avenues for COVID-19 lung disease and potential mutations.
- Inhibiting this type of cell death may enhance treatment outcomes for severe COVID-19 cases.
GS-III/Environment and Ecology
Shallow Aquifer Management
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation (GHMC) has recently initiated the Shallow Aquifer Management (SAM) model on a trial basis within the city.
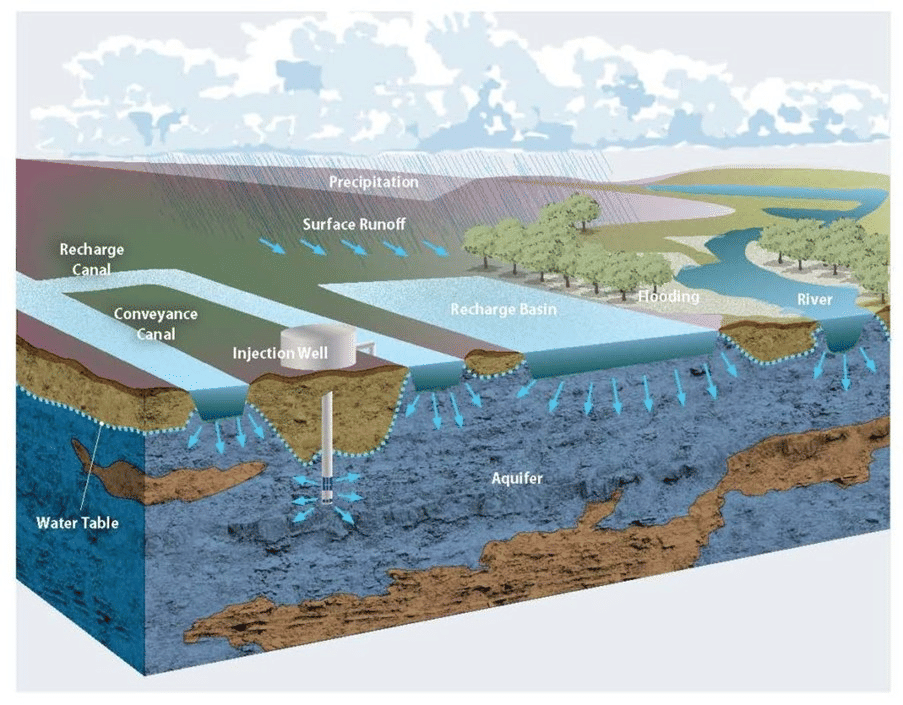
About Shallow Aquifer Management:
- It is a method of sustainable urban water management that tackles issues like groundwater depletion, borewell drying, and urban street flooding.
How is it Implemented?
- The project involves drilling shallow water injection borewells to depths of 100-120 feet and extracting water from shallow aquifers.
- By collecting water from the surrounding watershed and directing it through recharge pits, the underground layers are recharged whenever it rains, leading to a rise in the water table.
SAM Pilot Model in India
- This initiative is a part of the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) under the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- The National Institute of Urban Affairs is the nodal implementing agency for this project.
- In 2022, the AMRUT launched a SAM pilot program in 10 cities across nine states, including Bengaluru, Chennai, Dhanbad, Gwalior, Hyderabad, Jaipur, Kolkata, Pune, Thane, and Rajkot.
Understanding Aquifers
- An aquifer is a permeable rock or sediment layer saturated with groundwater, which gets replenished as precipitation seeps through the soil.
- Groundwater can move within the aquifer and resurface through springs and wells.
|
39 videos|4566 docs|979 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 25th May 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of Cyclone Remal and its landfall in Taiwan? |  |
| 2. What is the role of the G7 in addressing global issues? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of a diplomatic passport? |  |
| 4. How does the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) function in India? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of India's opposition to the China-led Investment Facilitation Proposal at WTO? |  |






















