UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 21 July 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/Polity
Govt cautions AIIMS, PGI on Science Congress body
Source: Indian Express

Why in news?
The Department of Science and Technology (DST) has advised top medical institutions, including all AIIMS, to refrain from involving representatives from the Indian Science Congress Association (ISCA) on their boards or committees at present.
- The DST has also recommended that the Health Ministry obtain a no-objection certificate before nominating any ISCA office-bearers to the governing bodies or committees of any autonomous organizations under its jurisdiction.
- Previously, ISCA members served as ex officio members of governing bodies in various institutions like AIIMS Delhi and AIIMS Patna.
- In a recent communication to the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, the DST mentioned that it does not acknowledge the current Executive Council of ISCA and has suspended all its office-bearers.
- Consequently, ISCA representatives should be excluded from the boards of medical institutions such as AIIMS and PGI Chandigarh.
Indian Science Congress (ISC)
About
- ISC is a unique event in the country that facilitates the interaction of scientific communities with students and the general public on scientific matters.
- The event is organized by the Indian Science Congress Association (ISCA).
- ISCA operates independently with the support of the Department of Science and Technology (DST) in the central government.
- Known as the largest gathering of scientists and students in the country, the Science Congress is an annual event spanning five days from January 3 to 7, a regular feature on the Prime Minister's calendar.
- The inaugural session of the Indian Science Congress took place in 1914 at the premises of the Asiatic Society, Calcutta.
Funding
- The DST covers the salaries of ISCA's permanent secretarial staff and provides an annual grant to support the organization of the Science Congress.
- In September 2023, DST halted its funding for the Science Congress due to financial irregularities and introduced stricter controls on the utilization of government funds through amended by-laws.
Declining glory of ISC
- In recent times, the Science Congress has garnered attention for negative reasons such as lack of substantial discussions, promotion of pseudoscience, extravagant claims by random speakers, and a dearth of meaningful outcomes.
- Consequently, several prominent scientists have proposed either discontinuing the event or withdrawing government support.
- The government provides an annual grant for organizing the Science Congress, with no further involvement in its execution.
ISCA in conflict with the DST
- ISCA has been embroiled in ongoing disputes with the Department of Science and Technology (DST) in recent years due to allegations of financial irregularities and misappropriation of government funds.
- The association has taken legal action against the government, and the issue remains unresolved.
- For the first time in its history, the Science Congress, a significant event on the Prime Minister's annual schedule, could not be held this year.
- The Science Congress was canceled in 2021 and 2022 due to disruptions caused by the Covid pandemic.
GS 1/Social Issues
What is the Gender Gap in Education?
Source: The Hindu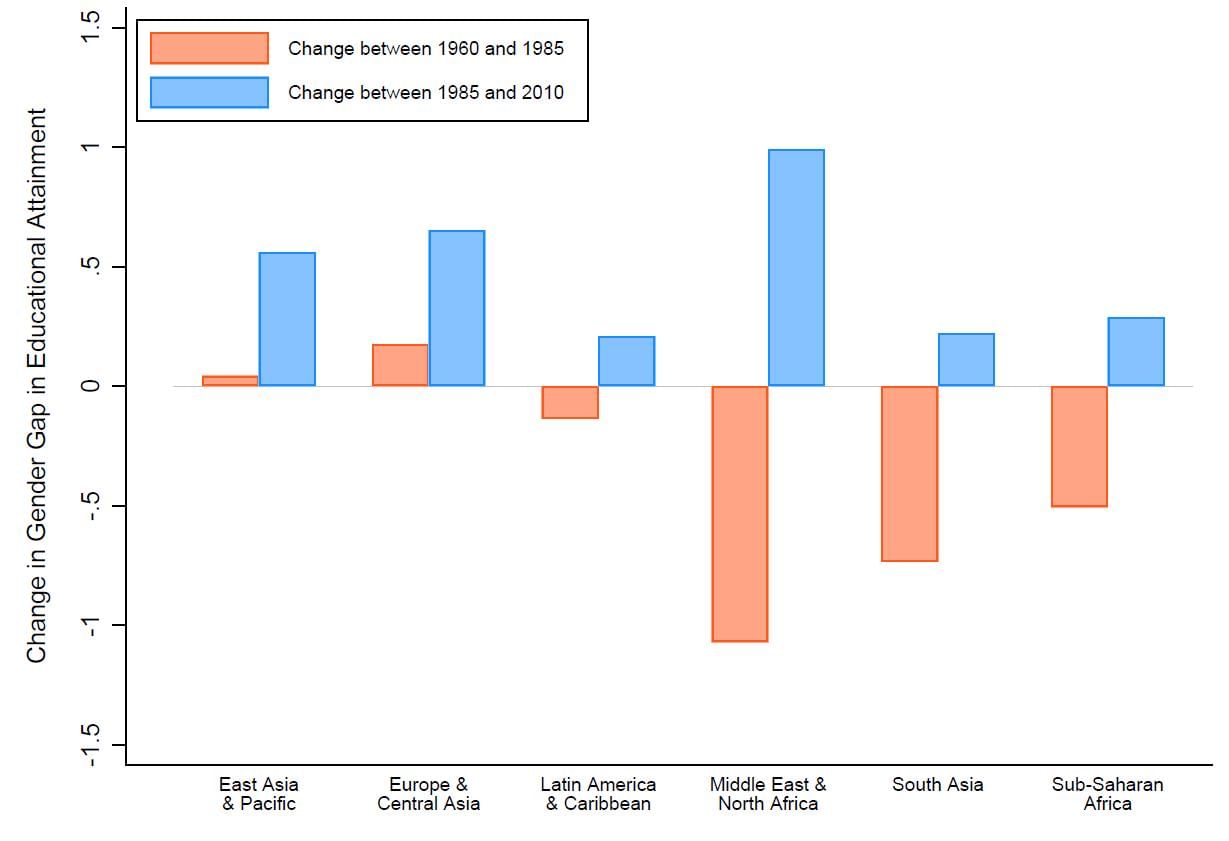
Why in News?
The World Economic Forum (WEF) report of 2024 on global gender gaps recently ranked India at 129 out of 146 economies, with a decline in the education sector being one of the reasons for India's rank slipping a couple of places this year.
Global Gender Gap Report 2024 (Ranking, India's Performance in Education Component)
The World Economic Forum's Global Gender Gap Report is an annual publication that evaluates the progress towards gender equality worldwide. Established in 2006, this report offers a comprehensive analysis of gender-based disparities across four key areas:
- Economic Participation and Opportunity
- Educational Attainment
- Health and Survival
- Political Empowerment
Key Components of the Report
- This dimension assesses gender disparities in the workplace, including labor force participation, wage equality for similar work, and the presence of women in high-ranking roles across industries.
- This category measures the gap between men and women in terms of access to education. It evaluates literacy rates and the enrollment levels in primary, secondary, and tertiary education.
- This area examines life expectancy and sex ratio at birth to understand the disparities in health outcomes between genders.
- This dimension looks at the representation of women in political decision-making positions, including the proportion of women in parliamentary seats and ministerial roles.
Methodology:
The report uses a scoring system ranging from 0 to 1, where 1 indicates full parity between men and women and 0 indicates absolute disparity. Countries are ranked based on their scores in each of the four categories, and an overall rank is assigned to each country.
Global Gender Gap 2024 Report
The World Economic Forum 2024 report on global gender gaps highlights significant disparities in education, ranking India 129th out of 146 countries, partly due to a decline in educational attainment indicators. This represents a drop from the previous year, where India had a perfect score in educational parity.
Key Findings and Statistics w.r.t Education Attainment
- Enrollment and Literacy Rates: Despite high enrollment rates for women in primary, secondary, and tertiary education, the literacy rate gap between men and women stands at 17.2 percentage points. The latest figures show that girls constitute 48% of the school population, with a slight decline in secondary education but a higher retention rate at the higher secondary level.
- Higher Education: The Gross Enrollment Ratio (GER) for women in higher education is 28.5%, slightly above the male GER of 28.3%. Female enrollment has increased by 32% since 2014-15.
- Infrastructure Development: Building more schools, especially since the mid-90s, has significantly boosted girls' enrollment. However, regional disparities persist, with some states lagging in secondary education infrastructure.
- Female Teachers: The presence of women teachers positively impacts girls' enrollment. Schools with only male teachers face lower enrollment of girls due to parental concerns.
- Transportation and Sanitation: Free transport and the provision of cycles have helped increase enrollment. However, inadequate sanitation facilities, particularly for menstruating girls, remain a major barrier.
Future Challenges:
- Higher Secondary and College Education: While some states report higher enrollment of girls in higher secondary education, concerns are rising about boys dropping out.
- STEM Education: Women make up only 42.5% of students in STEM fields, highlighting the need for targeted encouragement.
- Adult Literacy: The 2011 Census data reveals a significant gender gap in adult literacy, with only 64.63% of women being literate compared to 80.88% of men.
Recommendations:
- Improving School Infrastructure: Continued investment in building and maintaining school facilities, especially in rural areas.
- Increasing Female Teacher Presence: Recruiting and retaining more female teachers to create a comfortable learning environment for girls.
- Enhanced Sanitation Facilities: Ensuring proper maintenance of washrooms to prevent dropouts among older girls.
- Focus on Foundational Literacy: Strengthening foundational literacy programs and extending education to rural women to bridge the adult literacy gap.
By addressing these challenges, India can make significant strides toward closing the gender gap in education and achieving greater gender parity in the coming years.
GS3/Environment
Implementation of the Plastic Waste Trading Scheme
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) has initiated a nationwide audit of about 800 recyclers of plastic waste across the country. This was decided following the revelation that four firms in Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Karnataka had issued about 600,000 bogus certificates under the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) scheme.
An Overview Plastic Waste in India
Plastic, with its diverse applications, owes its commercial success to its physical and chemical properties. However, the uncontrolled disposal of plastic, especially plastic carry bags, has emerged as a significant environmental threat.
Plastic Waste Generation Statistics:
- In 2019-20, over 34 lakh tonnes of plastic waste were produced in India, marking a notable increase from the 30.59 lakh tonnes generated in 2018-19.
- This surge indicates a more than twofold rise in India's plastic waste output over the past five years, with an average annual growth rate of 21.8%.
Plastic Waste Management Rules:
- The government has introduced the Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016 (amended in 2018 and 2021) to tackle the escalating issue of plastic waste and promote its scientific management.
Efforts for the Scientific Management of Plastic Waste in India
The Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016
- These rules necessitate plastic waste generators to undertake measures to reduce plastic waste, ensure segregated storage at the source, and hand it over to local bodies or agencies.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
- Producers, importers, and brand owners are now accountable for collecting waste generated by their products under the EPR scheme.
- Producers must collaborate with local governments to develop a management plan for plastic waste within a specified timeframe.
The Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules 2018
- The amended rules now apply to Multilayered Plastic (MLP) and advocate the phasing out of non-recyclable or non-energy recoverable MLP.
The Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2021
- These rules aim to ban identified single-use plastic items with low utility and high littering potential by 2022.
- Notably, on August 12, 2021, the MOEFCC enforced a ban on specific single-use plastic items under these rules, effective from July 1, 2022.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) Certificates
- Under the EPR scheme, businesses utilizing plastic packaging material are obliged to recycle a certain percentage of the plastic used in the preceding two years.
- Companies failing to meet the recycling targets may face penalties.
Violations in Plastic Waste Recycling
The identified firms had issued an excessive number of EPR certificates compared to their actual recycling capabilities. They lacked evidence of selling the recycled plastic to the CPCB, indicating a breach of the EPR scheme regulations.
Reasons Behind Violations
- Recyclers' lack of understanding regarding the operational aspects of the EPR scheme is cited as a primary reason for the violations.
- This confusion parallels the early stages of implementing complex systems like GST or filing Income Tax returns online.
Conclusion
The saga of plastic waste mismanagement underscores the critical need for stringent enforcement, improved awareness, and enhanced regulatory mechanisms to combat the escalating environmental challenges posed by plastic pollution.
GS-III/Environment and Ecology
Zebra Mussel
Source: CBC
Why in News?
Zebra mussel, an invasive species capable of wiping out entire aquatic ecosystems, has been found for the first time in the Colorado River, the most important river in the American Southwest.
About Zebra Mussel:
- Zebra mussels are small invaders that look like fingernails.
- Scientific Name: Dreissena polymorpha
- Distribution:
- Originally from the Caspian and Black Seas, located south of Russia and Ukraine.
- Entered the Great Lakes in the late 1980s via ship ballast water.
- Spread to much of eastern Canada and the United States since then.
- Habitat: They live underwater, attaching themselves to various surfaces like rocks, wood, and pipes.
- Identification: Zebra mussels have a flat 'D' shaped shell with black stripes on a cream background. They are small in size and start as microscopic larvae called 'veligers'.
- Life Cycle: Short-lived creatures, they start reproducing at two years old.
- Impacts:
- They filter feed and reproduce rapidly.
- Disrupt food chains by consuming phytoplankton.
- Threaten native mussels by competing for food and suffocating them.
- Cluster on structures causing commercial damage.
GS-III/Science and Technology
Radome
Source: English Mathrubhumi

Why in News?
The Defence Metallurgical Research Laboratory (DMRL) has made a noteworthy achievement in creating homegrown fused silica radomes for missiles.
About Radome:
- A radome is a protective cover that shields a radar or antenna system from the weather.
- These covers can be rigid or flexible, made from different materials and shapes for various uses.
- The main purpose of a radome is to protect the antenna's signal quality from environmental factors.
- It also hides the antenna's electronics for security and prevents accidental collisions that could damage the antenna.
- Radomes are essential for maintaining the durability and performance of the antenna they enclose.
Fused silica radomes of DMRL:
- Fused silica is the best material for radomes because it has great electromagnetic and mechanical properties. It can handle sudden changes in temperature.
- The DMRL has become skilled at using cold isostatic pressing (CIP) technology. This allows them to make these important parts with high success rates and the properties they want.
- CIP is a method where you press powdered materials with high pressure from all directions. This helps to shape the material evenly and make it strong.
- This method improves the material's strength and properties by creating a dense, even structure.
- The DMRL uses CIP technology to press powdered fused silica into the shapes they need.
- After this, the material goes through a process called sintering to become a strong and compact structure.
Key Facts about Defence Metallurgical Research Laboratory (DMRL):
- It is a research laboratory of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- Location: Hyderabad.
- DMRL is responsible for developing advanced metallic and ceramic materials and related processing technologies for different important defence uses.
- Main expertises of the lab include:
- Product engineering, support in production, and analysis of metals, alloys, and composites
- Developing processes and engineering surfaces
- Creating and improving special alloys, inter-metallics, ceramics, and composites
- Metallurgy that extracts titanium and magnesium
- Deep knowledge in the relationships between processes, structures, properties, and performance of advanced materials.
GS-III/Science and Technology
 |
Download the notes
UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 21 July 2024
|
Download as PDF |
Rapid Apophis Mission for Space Safety (RAMSES)
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The European Space Agency recently declared that its new Ramses spacecraft might go with the asteroid Apophis before and after its safe, though quite near, encounter with Earth.
About Rapid Apophis Mission for Space Safety (RAMSES):
- It's a mission by the European Space Agency (ESA) to protect Earth from an asteroid named 99942 Apophis in 2029.
- Apophis, about 375 meters wide, will come within 32,000 km of Earth on April 13, 2029, the closest pass by an asteroid of this size ever predicted.
- During this event, Apophis will be visible to the naked eye for a brief period across Europe, Africa, and parts of Asia.
- Fortunately, Apophis won't hit Earth, with astronomers ensuring no collision for the next century.
- The 2029 flyby is a rare opportunity for researchers to learn about the asteroid's properties affected by Earth's gravity, aiding in future defense planning.
- The mission named RAMSES will collaborate with NASA's OSIRIS-APEX mission, arriving shortly after Apophis' closest approach for comparative analysis.
GS-II/Polity and Governance
Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP) Scheme
Source: Business Standard

Why in News?
The tea industry has sought higher rates under the RoDTEP scheme to make exports more competitive in overseas markets.
About RoDTEP Scheme:
- RoDTEP Scheme Overview:
The RoDTEP scheme is a significant initiative by the Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry. It is designed to comply with WTO regulations and aims to reimburse exporters for various duties and taxes previously not refunded.
- Purpose of RoDTEP:
Introduced in September 2019 to replace the MEIS scheme, RoDTEP focuses on enhancing domestic exports. This shift was prompted by a WTO ruling against MEIS for providing subsidies on a wide range of goods.
- Extension and Implementation:
The RoDTEP benefits were extended to all goods starting January 1, 2021, as per the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) notification. The scheme aims to boost export sectors, promote competitiveness, generate employment, and support economic growth.
- Key Features:
- The scheme is inclusive, catering to both manufacturers and merchant exporters without turnover restrictions.
- Eligible goods must be directly exported.
- Rewards cover physical exports and outbound service shipments from India, with service providers also eligible for refunds on applicable levies.
- Refunds are calculated based on a percentage of the Freight On Board export value.
- Customs will oversee implementation through a streamlined IT system.
- Refunds will be in the form of transferable duty credits/electronic scrips, managed by CBIC.
- No rebates for exempted, credited, or remitted duties and taxes.
- Value caps apply to certain export products for rebate eligibility.
- Exclusions encompass goods subject to export restrictions, minimum pricing, deemed exports, and products from SEZ units.
What is Freight on Board (FOB)?
- It is also known as Free on Board (FOB), a term that shows who is responsible for damaged or lost goods while being shipped.
- FOB origin means the buyer is responsible and gains ownership once the seller ships the item.
- FOB destination means the seller keeps the risk of loss until the goods reach the buyer.
GS-II/Polity and Governance
National District Mineral Foundation Portal
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, the union Minister of Coal and Mines launched Mineral Exploration Hackathon and the National District Mineral Foundation (DMF) Portal.
About National District Mineral Foundation Portal:
- Objective: This platform serves as a central hub for gathering information about District Mineral Foundations nationwide.
- Aim: The goal of launching this website is to make accessing DMF data easier and monitoring the progress and utilization of resources.
- Features: The portal offers insights into 645 DMFs across the country, promoting transparency. It allows for a centralized view of activities, project supervision, dynamic analytics, and a collection of best practices for efficient implementation.
Key facts about the District Mineral Foundation
- It is a trust set up as a non-profit body under the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) (MMDR) Amendment Act 2015.
- Purpose: To work in the interest and benefits of persons and areas affected by mining-related operations in a manner as may be prescribed by the respective State Government.
- Funding: It is funded through the contributions from the holders of major or minor mineral concessions in the district, as may be prescribed by the Central or State Government.
- Jurisdiction:
- The operation of DMFs falls under the jurisdiction of the relevant State Government.
- The composition and functionsof the District Mineral Foundation shall be such as may be prescribed by the State Government.
- The fund for DMF is collected at the district level.
|
39 videos|4566 docs|979 tests
|























