International Relations: August 2024 UPSC Current Affairs | UPSC Mains: International Relations PDF Download
Bangladesh’s Political Upheaval and Its Impact on India
 A week after protests in Bangladesh led to the ousting of former Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina, who fled to India, her future remains uncertain. The Indian government, under Narendra Modi, has provided her with refuge while simultaneously beginning to engage with the new regime that replaced her Awami League government. India is also assessing the impact these political changes in Bangladesh will have on its bilateral relations.
A week after protests in Bangladesh led to the ousting of former Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina, who fled to India, her future remains uncertain. The Indian government, under Narendra Modi, has provided her with refuge while simultaneously beginning to engage with the new regime that replaced her Awami League government. India is also assessing the impact these political changes in Bangladesh will have on its bilateral relations.
- Sheikh Hasina's removal from power in Bangladesh marks a significant setback for India, given the strong bilateral ties forged over the past 15 years.
- Since her return to office in 2009, Ms. Hasina made her intentions clear to forge strong ties with Delhi.
- She initiated a nationwide crackdown on terror camps and launched a campaign against religious radicalization.
- Extradited over 20 most wanted individuals accused of terrorism and crime to India.
- Worked to reduce border tensions stemming from illegal immigration into India, notably addressing the 2001 BDR-BSF clashes that resulted in 15 deaths.
- Several agreements on border patrols and the historic 2015 land boundary agreement were signed.
- India reciprocated by supporting Bangladesh through trade concessions and Lines of Credit, aiding its economic transformation.
- Bangladesh progressed in human development indices, surpassing its neighbors, aided by support from the Manmohan Singh and Modi governments.
- Despite an increasingly authoritarian stance, Hasina maintained strong relations with India.
- She aligned with India on various issues, including boycotting SAARC over terrorism from Pakistan and supporting the Citizenship Amendment Act.
- Bangladesh's role became crucial in India's regional connectivity initiatives and energy exports.
- However, with her ouster, concerns arise regarding the future of many agreements and progress made, including recent power deals with the Adani group.
- India continues to engage with Bangladesh's interim government led by Muhammad Yunus.
Challenges complicating India's relationship with the new regime include:
- Sheikh Hasina's presence in India raises suspicion in Dhaka.
- India may prefer her to exit until tensions subside.
- If the new government demands her extradition, this could lead to further complications.
- Upcoming elections could result in the BNP coming to power, a party with which India had a challenging relationship from 2001-2006.
- PM Modi's appeal concerning the safety of Hindus and minorities in Bangladesh may be viewed as partisan in Dhaka.
- The recent changes in Dhaka are likely to impact Bangladesh's international relations, particularly with the U.S..
- The U.S. had introduced a special visa policy aimed at promoting democracy in Bangladesh.
- Relations with Pakistan, which were strained under Hasina, could also see improvement.
- Despite Hasina's close ties with China, including involvement in the Belt and Road Initiative, Beijing is expected to cultivate strong relations with the new government.
India-Vietnam Enhance Comprehensive Strategic Partnership

Why in News?
India and Vietnam have announced a new initiative designed to strengthen their bilateral 'comprehensive strategic partnership' over the next five years. This plan was discussed during a meeting between the Indian Prime Minister and Vietnamese Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh in New Delhi. The agreement marks a significant enhancement of relations between the two countries, concentrating on numerous sectors including trade, digital payments, and defense.
What are the Key Highlights of the Bilateral Meeting?
New Plan of Action:India and Vietnam established a new action plan for their partnership initiated in 2016, to be executed over the next five years (2024-2028). The goals include:
- Strengthening bilateral trade and economic ties.
- Enhancing collaboration in technology and development.
- Fostering partnerships in defense and security.
- Digital Payment Connectivity: The Indian PM announced an agreement between the central banks of both nations to implement digital payment connectivity. This will facilitate financial transactions, as Vietnam is also advancing in digital payments and aims to develop cross-border payment systems with other ASEAN countries.
- Credit Line Extension: India will provide a USD 300 million credit line to Vietnam to support military security and development projects. Notable initiatives include the inauguration of an Army Software Park in Nayachang, funded by India, and heightened cooperation on counter-terrorism and cybersecurity.
- MoUs Signed: Six Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs) were signed, covering diverse areas such as Agricultural Research, Customs capacity building, Law and Justice, Radio & Television, and Traditional Medicines.
- Trade and Economic Goals: Vietnam aims to elevate bilateral trade to USD 20 billion from the current USD 14.8 billion. Both nations agreed to expedite the review of the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement to enhance trade. Vietnam expressed interest in Indian investments across sectors such as IT, manufacturing, textiles, semiconductors, and renewable energy.
- Strategic Alignment: Both countries reaffirmed their commitment to strengthening cooperation within the Indo-Pacific region, emphasizing the importance of maintaining freedom of navigation and overflight in the South China Sea. They highlighted the peaceful resolution of disputes in accordance with international law, particularly referencing the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) of 1982.
- Economic Diplomacy Dialogue: A new dialogue for economic diplomacy will be initiated at the deputy foreign minister level to tackle trade and investment challenges.
How has been the India-Vietnam Relations?
- Historical Ties and Diplomatic Relations: India and Vietnam have a robust Comprehensive Strategic Partnership.
- Historical connections were evident when Mahatma Gandhi and President Ho Chi Minh exchanged messages during their respective independence movements.
- Diplomatic relations were established in 1972, and in 2016, the partnership was elevated to a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership.
- Today, relations are guided by a "Joint Vision for Peace, Prosperity and People", adopted in 2020.
- Institutional Mechanisms: The 18th Joint Commission Meeting (JCM) on Economic, Trade, Scientific, and Technological Cooperation was held on 16th October 2023 in Hanoi.
- This meeting, along with previous JCM meetings, Foreign Office Consultations, and Strategic Dialogues at the Secretary level, reviews bilateral cooperation.
- Trade, Economic, and Development Cooperation:
- Trade Statistics: From April 2023 to March 2024, India-Vietnam trade reached USD 14.82 billion, with India's exports to Vietnam totaling USD 5.47 billion and imports at USD 9.35 billion.
- The ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement, concluded in 2009, facilitates preferential trade and is currently under review.
- Key Exports and Imports: India exports engineering goods, agricultural products, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, electronics, textiles, and plastics to Vietnam, while imports include computer and electronic goods, machinery, steel, chemicals, footwear, garments, and wooden products.
- Investments: Indian investments in Vietnam are estimated at around USD 2 billion, covering sectors like energy, mineral processing, agro-processing, IT, auto components, pharmaceuticals, hospitality, and infrastructure.
- Conversely, Vietnam's investments in India stand at approximately USD 28.55 million, mainly in consumer goods, electronics, construction, IT, and pharmaceuticals.
- Development Partnership: Under the Mekong-Ganga Cooperation framework, India has completed around 45 Quick Impact Projects across more than 35 Vietnamese provinces, with an additional 10 projects currently in implementation.
- The Mekong-Ganga Cooperation, established in 2000, includes six member countries: Cambodia, Lao PDR, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam, and India, focusing on sectors such as tourism, culture, education, IT, telecommunications, and transport.
- India has also supported the conservation and restoration of the UNESCO World Heritage site 'My Son' in Quang Nam Province, with the Archaeological Survey of India completing restoration of several temple groups in 2022.
- Defence Cooperation: India and Vietnam maintain a strong defense and security collaboration, guided by a 2009 MoU on Defense Cooperation and a 2015 Joint Vision on Defense Cooperation.
- In 2022, they signed a new "Joint Vision Statement on India-Vietnam Defence Partnership towards 2030" and a "Memorandum of Understanding on Mutual Logistics Support."
- In 2023, Vietnam received the indigenously built missile corvette INS Kirpan as a gift.
- Military-to-military cooperation includes staff talks, joint exercises, training, visits, and exchanges, including the VINBAX-2023 military exercise.
- A Vietnamese navy ship participated in the MILAN international maritime exercise in India in February 2024.
- Cultural Exchanges: Various MoUs between Indian and Vietnamese institutions encourage academic and cultural exchanges.
- Events like the Northeast India Festival in Ho Chi Minh City strengthen cultural ties.
- Additionally, Buddhist links highlight ancient civilizational connections, with Vietnamese Buddhist scholars and pilgrims frequently visiting India, including the Vietnamese Buddhist pagoda in Bodhgaya.
- The popularity of yoga in Vietnam is notable, with many yoga clubs and Indian instructors active in the country.
- The Swami Vivekananda Indian Cultural Centre in Hanoi fosters a deeper understanding of India and promotes closer ties through various cultural programs and activities.
Mains Question
Q: Discuss the significance of the Comprehensive Strategic Partnership established between India and Vietnam.
India’s Engagement at ASEAN Meet

Why in News?
Recently, India's External Affairs Minister (EAM) visited Vientiane, Laos, for the ASEAN meetings, which attracted considerable attention. This visit served as a vital platform for high-level dialogues with various global leaders, aimed at enhancing bilateral relations.
Key Highlights of the ASEAN Meet
- EAM underscored the significance of ASEAN as a foundational element of India's Act East Policy and Indo-Pacific vision.
- 2024 marks a decade since the announcement of India’s Act East Policy at the 9th East Asia Summit in 2014.
- The policy is designed to boost commerce, connectivity, and capacity building, fostering strategic and cultural relations with the Asia-Pacific region.
- India considers the ASEAN partnership essential for enhancing political, economic, and security cooperation.
- The meeting highlighted India’s commitment to a free, open, inclusive, and peaceful Indo-Pacific, grounded in a rules-based international order.
Focus Areas
- Discussions during the meeting revolved around increasing people-to-people connections and fostering bilateral cooperation.
- The visit aimed to strengthen partnerships and promote mutual interests within the region.
What is the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)?
- ASEAN is a regional intergovernmental organization established on August 8, 1967, in Bangkok, Thailand.
- The organization was created through the Declaration initially signed by Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand.
- ASEAN expanded to include Brunei Darussalam (1984), Vietnam (1995), Laos PDR and Myanmar (1997), and Cambodia (1999).
- It is projected that the region will become the fourth-largest economy in the world by 2050.
- ASEAN has successfully promoted economic integration among its members and facilitated the negotiation of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, which is the world's largest free trade agreement.
ASEAN Charter (2008)
- The ASEAN Charter granted the organization formal legal status and established an institutional framework.
- It codified norms, rules, and values, which enhanced accountability and compliance among member states.
ASEAN Summit
- The ASEAN Summit is the highest policy-making body, consisting of the Heads of State or Government of ASEAN member states, and convenes twice a year.
- The inaugural summit was held in Bali, Indonesia, in 1976.
India-ASEAN Relations
- India began formal engagement with ASEAN in 1992 as a "Sectoral Dialogue Partner," advancing to a "Dialogue Partner" in 1995.
- The partnership was elevated to a Strategic Partnership in 2012 and further to a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership in 2022.
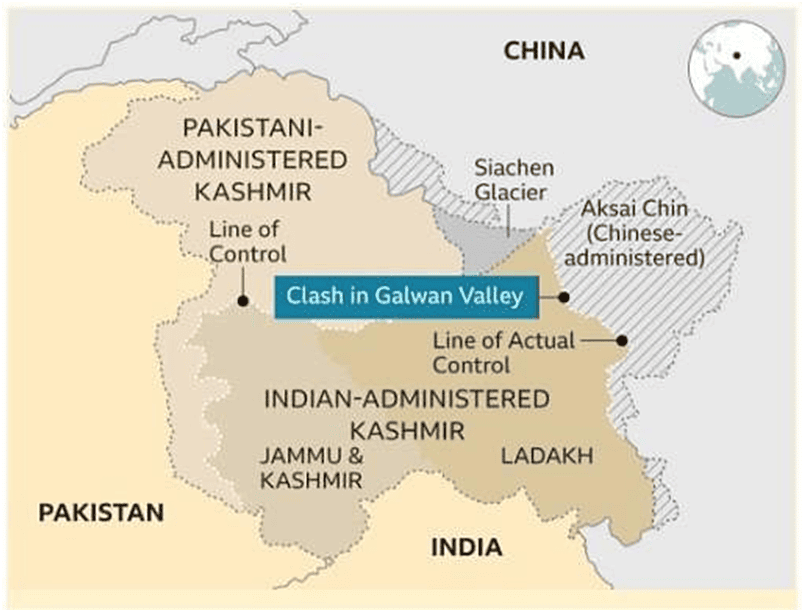
Chinese Bridge on Pangong Lake

Why in News?
China has finalized and started operations on a bridge that connects the north and south banks of Pangong Tso lake located in Eastern Ladakh. This infrastructure will enable the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) to significantly decrease the time required to mobilize troops and tanks.
What is the Pangong Lake Dispute?
About the Lake:
- Pangong Tso is a long, narrow, and deep endorheic lake situated at an altitude of over 14,000 feet in Ladakh, within the trans-Himalayas.
- The lake is divided between India and China, with India controlling about one-third and China two-thirds.
- The eastern end of the lake is located in Tibet.
- This tectonic lake was formed when the Indian plate emerged from Gondwanaland and collided with the Asian plate, leading to the creation of the Himalayan mountain range while occupying the space of the former Tethys Ocean.
Disputed “Fingers” Area:
- The northern bank of the lake features spurs known as "fingers."
- India asserts that the Line of Actual Control (LAC) runs through Finger 8, while controlling up to Finger 4, whereas China claims it is at Finger 2.
- Recent tensions have escalated, with Chinese forces obstructing Indian soldiers from advancing beyond Finger 2.
Strategic Significance:
- Pangong Tso is strategically important as it lies along the Chushul approach path, which could serve as a route for potential Chinese offensives.
- During the 1962 war, China initiated its main offensive in this region, and Indian forces displayed remarkable bravery at Rezang La.
- China has constructed motorable roads along its banks and maintains a large-scale model of the area at its Huangyangtan base.

What are Indian Concerns Regarding the Bridge on Pangong Lake?
- The new bridge will facilitate quicker access for Chinese troops and tanks to the southern banks of the lake, including Rezang La, where Indian forces successfully outmaneuvered Chinese troops in 2020.
- In 2020, the Indian Army secured crucial heights on the southern bank of Pangong Tso, prompting the construction of this new Chinese bridge.
- This infrastructure is expected to bolster the capabilities of the PLA’s Moldo Garrison situated on the southern bank of the lake.
- The bridge will enable the rapid reinforcement of the Moldo Garrison by allowing the deployment of motorized brigades from the Rutog base.
How India Responded with Military Infrastructure Along LAC?
- Road Construction: Over the past five years, approximately 6,000 km of roads have been constructed in border areas, including 2,100 km along the northern borders, such as the Darbuk-Shyok-Daulat Beg Oldie (DSDBO) road.
- Tunnels: Projects aimed at ensuring all-weather connectivity are underway in Ladakh, such as the Zojila and Z-Morh tunnels, as well as in Arunachal Pradesh, including the Sela tunnel and Nechiphu bridge.
- Troop Habitat: In the last three years, Rs 1,300 crore has been allocated for infrastructure and habitat improvements in Ladakh, focusing on sustainable solutions like Sheela shelters and fuel cells.
- Air Power Infrastructure: Enhancements have been made to air power capabilities, including increased availability of heavy lift and logistics helicopters for resupplying materials, such as C17 Globemaster and C-130J Super Hercules deployments.
IPEF Elects India as Vice-Chair of Supply Chain Council

Why in News?
India has recently been elected as the Vice-Chair of the Supply Chain Council, which is one of the three key bodies formed under the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) involving 14 member countries.
What is the Supply Chain Council?
- The Supply Chain Council is one of the three entities established under the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF), focusing on enhancing supply chain resilience.
- This council consists of India and 13 other partner nations working together to improve the supply chains critical for national security, public health, and economic stability.
Objectives of the Supply Chain Council
- To conduct targeted, action-oriented initiatives aimed at fortifying supply chains for essential sectors.
- To facilitate cooperation among member countries to address vulnerabilities in supply chains.
Other Bodies Under IPEF
Crisis Response Network:
- This network serves as a platform for coordinated emergency responses to urgent disruptions in supply chains.
Labour Rights Advisory Board:
- This board promotes collaboration among workers, employers, and governments to enhance labor rights and workforce development across regional supply chains.
Recent Appointments:
- During the meetings of the supply chain bodies, leaders were elected to serve for two-year terms:
- USA: Chair, India: Vice Chair
- Crisis Response Network: Republic of Korea (Chair), Japan (Vice Chair)
- Labour Rights Advisory Board: USA (Chair), Fiji (Vice Chair)
Significance of the Meetings:
- The inaugural virtual meetings represent a significant advancement in collaboration among partner countries aimed at bolstering supply chain resilience in the region.
- The Supply Chain Council established its Terms of Reference and outlined initial priorities for its activities.
- These priorities will be further discussed during their first in-person meeting scheduled to take place in Washington in September 2024 as part of the Supply Chain Summit.
- The Crisis Response Network highlighted both immediate and long-term priorities, including planning for a tabletop exercise, with its first in-person meeting also aligned with the Supply Chain Summit.
- The Labour Rights Advisory Board focused on enhancing labor rights within IPEF supply chains and addressing labor provisions in the IPEF Clean Economy and Fair Economy Agreements.
Dual Use Defence Technology

Why in News?
Recently, officials from the United States have been engaging with Indian companies and exporters to discourage them from providing dual-use technology to Russia. Supplying items such as chemicals, aeronautic parts, and components for defense equipment can lead to sanctions from Western nations.
What are Dual Use Goods/Technologies?
About Dual Use Goods:
- Dual-use goods refer to items that can serve both civilian and military purposes.
- Examples include global positioning satellites, missiles, nuclear technology, chemical and biological tools, night vision technology, thermal imaging, and drones.
Examples of Dual-Use Technologies:
- Hypersonics: These systems travel at speeds exceeding five times the speed of sound and can be utilized for cost-effective satellite launches or as backups for satellite failures.
- Integrated Network Systems-of-Systems: This technology enhances government capabilities by integrating diverse mission systems, enabling resilient and secure command, control, and communication.
- Microelectronics: Essential for both military and civilian systems, microelectronics are crucial for the production of personal computers, mobile phones, and defense equipment.
Export Controls Provisions Related to Dual Use Goods/Technologies:
- The trade and export of dual-use items are regulated by several multilateral export control regimes.
- Wassenaar Arrangement (WA): Initiated to enhance regional and international security through responsible transfers of conventional arms and dual-use technologies. India became a member in 2017.
- Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG): This group comprises nuclear fuel and technology supplier nations that aim to prevent the proliferation of nuclear weapons. India is not a member due to its non-signatory status to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty, but it practices voluntary non-proliferation.
- Australia Group: A forum that harmonizes export controls to prevent contributions to chemical and biological weapon developments. India joined in 2018.
- Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR): A partnership of 35 nations focused on preventing the spread of missile technology capable of carrying significant payloads over extensive distances. India joined in 2016.
- CWC and BWC: India is a signatory to international agreements aimed at disarmament and non-proliferation, including the Chemical Weapons Convention and the Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention.
- UN Security Council Resolution 1540: This resolution mandates member nations to regulate the export of potentially harmful goods to promote global peace.
What are Key Developments in Dual-Use Defence Technology in Relation to Russia?
- Fear of Sanctions: Indian companies risk facing sanctions under the Countering America's Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA) due to dealings with Russia.
- Limiting Financial Access: U.S. Treasury officials have cautioned Indian banks that engaging with Russia's military-industrial sector could jeopardize their access to the U.S. financial system.
India’s Position on Dual-Use Exports:
- The items flagged by the U.S. are not classified as Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies (SCOMET), which necessitate licensing for trade.
- Dual-use goods fall under the SCOMET list in India.
India’s Role and U.S. Concerns:
- The U.S. is concerned that certain SCOMET items are being integrated into Russia's defense manufacturing.
- India's exports to Russia surged by 40% in 2023, exceeding USD 4 billion, with engineering goods nearly doubling from USD 680 million in 2022 to USD 1.32 billion in 2023.
China’s Role and U.S. Concerns:
- The U.S. identifies China as the primary supplier of essential dual-use items, including machine tools and nitrocellulose for munitions and rocket propellants.
- Over 300 Chinese companies have been blacklisted for supplying critical dual-use items to Russia, while Iran has also supplied munitions and drones to Russia.
What is India’s Strategic Trade Control System?
About
- Strategic Trade Controls consist of laws and regulations aimed at managing the export of dual-use goods, services, and technologies across borders.
Important Legislations Include:
- Weapons of Mass Destruction and their Delivery Systems (Prohibition of Unlawful Activities) Act, 2005
- Arms Act, 1959
- Atomic Energy Act, 1962
- Chemical Weapons Convention Act, 2000
- Explosives Act, 1884
- These regulations are crucial for balancing commercial interests with national security considerations.
SCOMET List:
- India oversees the export of dual-use items, nuclear-related items, and military equipment through the SCOMET list, which serves as the National Export Control List.
Conclusion
- It is essential for India to balance the export of dual-use goods with national interests.
- Compliance with international regulations is crucial to avoid sanctions, especially in sensitive geopolitical situations involving Russia.
- India must safeguard its economic interests while maintaining strategic autonomy.
- Enhancing oversight and industry awareness is vital to ensure export policies are aligned with international standards, promoting both innovation and national security.
Mains Question
Q: What are dual-use goods and technologies? Discuss India’s national and international commitment in non-proliferation of dual-use goods and technologies.
Strengthening India-Japan Relations Amid Regional Tensions
Why in news?
India and Japan recently held their third 2+2 Foreign and Defence Ministerial Meeting in New Delhi. This meeting aimed at strengthening their strategic alliance in response to growing geopolitical challenges in the Indo-Pacific region. It emphasized the importance of their partnership in counterbalancing China's increasing assertiveness in the area.
Understanding 2+2 Meetings: A Diplomatic Framework
Participation Dynamics:
- Involves high-level representatives, specifically the Ministers responsible for Foreign Affairs and Defence from both countries.
- Aims to deepen the dialogue and enhance cooperation between the nations.
Enhanced Communication and Understanding:
- Establishes a framework for better understanding each other's strategic concerns and sensitivities.
- Takes into account the political contexts of both nations to strengthen their strategic relationship.
Adapting to Global Changes:
- Supports engagement amid a rapidly evolving global landscape.
- Provides a platform to address emerging geopolitical challenges and dynamics.
India's 2+2 Partners:
- United States: The oldest and most significant partner for India in 2+2 talks.
- Other Nations: Engaged in similar meetings with Australia, Japan, the UK, and Russia.
Diverse Dialogues:
- Covers various strategic topics, promoting a comprehensive understanding between the participating nations.
Indo-Pacific Cooperation:
- Both countries reaffirmed their commitment to maintaining a free and rule-based Indo-Pacific region, especially in light of China's military activities.
ASEAN Integration:
- Strong support was expressed for the unity and central role of ASEAN, particularly through the ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific, which advocates for peace and cooperation.
United Nations Principles:
- The discussions highlighted ASEAN's commitment to a regional order rooted in United Nations principles.
Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QUAD):
- Topics from the recent QUAD Foreign Ministers' Meeting were discussed, reinforcing the commitment to deeper collaboration.
Defense and Security Collaboration:
- Plans to extend security assistance to third countries to promote regional stability were emphasized, showcasing defense cooperation as a key component of their Strategic and Global Partnership.
Security Strategy and Exercises:
- Updates were provided on Japan's 2022 National Security Strategy and progress in multinational military exercises like Veer Guardian and Malabar.
Innovations in Defense Technology:
- Recent advancements in unmanned ground vehicles and robotics were acknowledged, including discussions on Japan's advanced radar system, UNICORN, aimed at minimizing radar detectability of warships.
Joint Security Declaration Update:
- Both nations agreed to modernize the 2008 Joint Declaration to address new security challenges and priorities in the changing global context.
Counterterrorism Efforts:
- There was a collective stance against terrorism and violent extremism, with a focus on eliminating terrorist safe havens and disrupting their financial and operational networks.
Role of Women in Peace Processes:
- Both countries supported the Women, Peace, and Security (WPS) agenda, promoting women's roles in peacekeeping and conflict resolution, based on the principles of UNSCR 1325.
Historical Beginnings:
- The relationship traces back to the 6th century with the introduction of Buddhism from India to Japan, significantly influencing Japanese culture and philosophy.
Post-World War II Initiatives:
- A symbolic act by Indian Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru in 1949, involving gifting an elephant to Ueno Zoo in Tokyo, marked the revival of post-WWII relations.
Diplomatic Milestones:
- The 1952 peace treaty established formal diplomatic ties as one of Japan's first post-war agreements.
Economic Support Post-WWII:
- India's iron ore significantly contributed to Japan's post-war economic recovery, with financial support through yen loans beginning in 1958.
Strategic Partnerships and Cooperation:
- Deepening Ties in the 2000s: The partnership evolved into a Global Partnership and later into a Special Strategic and Global Partnership by 2014, highlighting the increasing importance of bilateral relations.
- Vision for Future Cooperation: The "Japan and India Vision 2025," established in 2015, outlines collaborative goals for future cooperation.
- Security Collaborations: The 2008 Joint Declaration on Security Cooperation set the foundation for ongoing dialogues, including the "2+2" meetings and the signing of the Acquisition and Cross-Servicing Agreement (ACSA) in 2020.
- Economic Relations: As of 2021, Japan was India's 13th largest trading partner and fifth largest investor, showcasing strong economic ties.
Initiatives and Agreements:
- Industrial and Energy Partnerships: Initiatives like the "India-Japan Industrial Competitiveness Partnership" and "Clean Energy Partnership" focus on mutual investments and enhancing energy cooperation.
- Cultural and Social Exchanges: The sister-city agreement between Ahmedabad and Kobe in 2019 promotes cultural exchanges and enhances cooperation at the city level.
- Significant Investments: Japan has committed approximately 5 trillion yen for future projects, evidencing deep financial engagement.
- Official Development Assistance: India is the largest recipient of Japanese ODA, with key projects such as the Delhi Metro and High-Speed Railway initiative highlighting significant cooperation.
Cultural and Regional Engagements:
- Promoting Cultural Ties: The year 2017 was designated as the Year of Japan-India Friendly Exchanges, enhancing cultural relations between the two nations.
- Broadening Regional Cooperation: The Japan-Southwest Asia Exchange Year in 2022 signifies Japan's efforts to strengthen ties with India and other regions in Southwest Asia, promoting regional connectivity and cooperation.
Political Turbulence in Bangladesh Leads to Uncertainty in India- Bangladesh Relations

Why in news?
- India-Bangladesh relations have significantly evolved over the years, characterized by cooperation, mutual respect, and shared cultural and historical ties. However, this relationship is currently challenged by internal unrest and security issues. The recent political changes in Bangladesh, particularly the emergence of Muhammad Yunus as the leader of an interim government, present India with an opportunity to reset and strengthen its ties with Bangladesh, focusing on mutual cooperation and economic growth.
A New Regime in Bangladesh
- Muhammad Yunus’s Leadership: Known for his contributions in microfinance, Yunus promotes a political approach that emphasizes openness, inclusivity, and economic development.
- India’s Strategic Interests: India must carefully navigate the potential shifts in Bangladesh’s political landscape, particularly regarding security and economic partnerships.
- Strengthening Ties: This political transition provides India a chance to enhance value chain linkages and establish stronger cooperative relations with Bangladesh.
India-Bangladesh Relation Reboot
- As Bangladesh experiences political changes, India has the opportunity to forge a more robust partnership. The focus should be on mutual benefits, especially in economic collaboration and regional stability. Yunus's vision for social and economic progress could initiate a new era in India-Bangladesh relations, moving past historical grievances towards shared prosperity.
Historical Context of India-Bangladesh Relations
- The roots of India-Bangladesh relations date back to 1971 when India played a pivotal role in Bangladesh's liberation from Pakistan. This historical event laid the groundwork for a strong bilateral relationship, which has been reinforced through various agreements and collaborations since then.
Main Issues between India and Bangladesh
- Border Management: The India-Bangladesh border spans approximately 4,096 kilometers, making it one of the longest international borders in the world, presenting significant management challenges due to illegal migration, smuggling, and trafficking.
- Water Sharing Disputes: The allocation of river waters, especially concerning the Teesta River, remains a contentious issue, with both nations striving for a mutually beneficial resolution.
- Security Concerns: Political unrest in Bangladesh can impact India's internal security, particularly due to communal tensions and attacks on religious minorities in Bangladesh.
Current Issues and Challenges
- The recent political and social unrest in Bangladesh poses considerable challenges, affecting border management and India's internal security. For UPSC aspirants, comprehending these dynamic relations is crucial for both Prelims and Mains examinations.
Impact of Sheikh Hasina’s Resignation on India-Bangladesh Relations
- Sheikh Hasina's potential resignation could lead to political instability in Bangladesh. This scenario might empower radical factions, increasing security risks along the extensive India-Bangladesh border and potentially disrupting economic ties and trade policies.
Key Points
- Political Instability: The unrest may create a power vacuum, leading to conflicts among political groups and increased radical influence.
- Economic Impact: Changes in trade policies and delays in negotiations, such as those concerning the Teesta River, could disrupt economic cooperation.
- Regional Dynamics: A shift in Bangladesh’s foreign policy could alter regional alliances, necessitating proactive engagement from India.
- Security and Border Management: Effective management of the extensive border is essential for maintaining security and fostering positive relations.
Recent Developments
- Trade and Connectivity: Efforts are ongoing to enhance trade and connectivity through infrastructure projects including rail and road links.
- Cultural Exchange: Initiatives are being taken to promote cultural ties through events, educational exchanges, and tourism.
Implications of Upheaval in Bangladesh on its Trade Relations: Relations with India

Why in News?
The resignation of Sheikh Hasina as Prime Minister of Bangladesh signifies a crucial shift in South Asian geopolitics. Hasina fled the country amidst widespread protests and sought refuge in India, raising concerns about the stability of Bangladesh and its relations with India. This political upheaval could have extensive implications for the region and for India's national security.
What is the Current Situation in Bangladesh?
- Protests and Unrest: Bangladesh is currently facing significant protests regarding job quota issues, driven by authoritarian policies and the suppression of opposition. This has led to unrest on a scale not seen since Sheikh Hasina took office in 2008.
- Economic Challenges: The departure of Sheikh Hasina poses concerns about Bangladesh's economic recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic, which is already complicated by rising inflation and currency depreciation.
- Political Landscape: The Bangladesh Army is expected to establish an interim government, indicating the current situation's volatility. The potential resurgence of radical Islamist forces poses a threat to Bangladesh's secular governance.
- Disruption in Export Flow: Bangladesh's textile industry, a backbone of its export revenue, is experiencing significant disruptions due to the unrest. The ongoing protests have led to supply chain breakdowns, affecting production schedules and the movement of consignments. Bangladesh is responsible for 7.9% of global clothing trade, with its USD 45 billion garment sector employing over four million workers and constituting more than 85% of its merchandise exports. The country has a notable market presence in the EU, UK, and US, holding a 10% share of the US market. Due to the uncertainty, international buyers are reconsidering their supply sources, which may lead to a shift in orders to alternative markets, including India. If India captures a portion of the displaced orders, it could see an increase of USD 300-400 million in monthly business by redirecting 10-11% of Bangladesh’s textile exports to Indian hubs like Tiruppur.
How does the Political Instability in Bangladesh Affect India?
- Loss of a Trusted Ally: India loses a vital partner in Sheikh Hasina, who played a key role in countering terrorism and enhancing bilateral relations. Hasina's regime allowed India to collaborate closely with Bangladesh on security matters, a relationship now at risk due to changing political dynamics.
- Economic Impact: India-Bangladesh bilateral trade reached USD 13 billion in FY 2023-24, with Bangladesh being India’s largest trade partner in the region. Hasina’s administration had provided duty-free access on most tariff lines under the South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA) agreement. However, Hasina's declining popularity and controversial governance could jeopardize India's regional standing.
- Western Scrutiny and Potential Backlash: India's support for Hasina has led to tension with Western allies, particularly the US, which has criticized her undemocratic practices. As Hasina's unpopularity rises, India may encounter backlash from Bangladeshi citizens who view India as an ally of the former leader, potentially straining India-Bangladesh relations.
What Challenges Lie Ahead for India in Engaging with a New Regime?
- Uncertain Political Environment: The nature of any new government, be it led by opposition parties or the military, will critically affect India’s strategic interests. A less India-friendly administration could re-energize anti-India militant groups, exacerbating security tensions along the borders. The Hindu minority could also face heightened risks if Islamist extremism grows. India must carefully navigate citizenship promises for Hindu refugees to avoid regional tensions.
- Regional Geopolitics: The political instability in Bangladesh may allow China to expand its influence in the region. India must be cautious as Beijing might offer attractive deals to the new regime, similar to past interventions in Sri Lanka and the Maldives. Engaging in strategic partnerships will be essential to prevent extremist elements from gaining ground and to support Bangladesh's economic stability.
- Impact on Indian Investments: Indian businesses and investments in Bangladesh may face uncertainties due to the political turmoil. Trade disruptions and payment delays could threaten the profitability and stability of these investments. The unrest could also affect Indian-owned textile manufacturing units in Bangladesh, with around 25% of them being Indian-operated. There is a possibility that these units might relocate back to India amid the instability.
- Infrastructure and Connectivity Concerns: Strong infrastructure and connectivity have been crucial for Indo-Bangladesh relations. India has extended USD 8 billion in credit since 2016 for various projects, including the Akhaura-Agartala rail link and the Khulna-Mongla Port rail line. However, current unrest poses risks to these essential connections, threatening trade and access to India’s Northeast region and potentially jeopardizing prior agreements.
- Balancing Act: India faces the challenge of balancing support for democratic movements while managing relationships with regional powers. It must avoid involvement in internal disputes while maintaining a strong diplomatic presence in Bangladesh.
How Should India Approach Its Foreign Policy Moving Forward?
- Building New Alliances: India is taking a cautious approach, closely monitoring the developments in Bangladesh while adopting a "wait-and-watch" strategy. This involves assessing events and their potential effects on regional stability. Additionally, India should engage with various political factions in Bangladesh to cultivate a more inclusive relationship, moving beyond the narrative of the 1971 liberation.
- Enhancing Security Measures: India should strengthen its security measures along the borders and in areas with significant Bangladeshi expatriate populations to mitigate potential spillover effects and maintain stability.
- Digital Connectivity Corridor: Developing a digital connectivity corridor can facilitate trade, technological exchange, and e-commerce. Evaluating the feasibility of a free trade agreement (FTA) with Bangladesh in light of the new political climate will also be vital.
- Geopolitical Manoeuvring: India must anticipate that Pakistan and China will seek to exploit the situation in Bangladesh for their advantage. Collaborating with international partners, including the US, UK, and European nations, will be crucial to mitigate these risks. Engaging with Gulf partners such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia to support Bangladesh's economic stabilization and counter extremist influences will be essential for maintaining regional stability and preventing Bangladesh from drifting away from its traditional allies.
Mains Question
Q: What are the repercussions of frequent political instability in India’s neighbouring countries? Evaluate the challenges in light of the recent political instability in Bangladesh.
|
88 videos|123 docs
|
FAQs on International Relations: August 2024 UPSC Current Affairs - UPSC Mains: International Relations
| 1. What are the main political challenges currently facing Bangladesh and how do they affect its relations with India? |  |
| 2. How is India strengthening its strategic partnership with Vietnam amidst regional tensions? |  |
| 3. What role does India play in the ASEAN meet, and what are the implications for its regional influence? |  |
| 4. What are the implications of the IPEF electing India as Vice-Chair of the Supply Chain Council? |  |
| 5. How does the political situation in Bangladesh impact its trade relations with India? |  |
















