Temple Architecture: Gujarat and Rajasthan | History Optional for UPSC (Notes) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Maru Gurjara Architecture |

|
| Evolution |

|
| Temples of Gujarat |

|
| Sun Temple at Modhera , Gujarat |

|
| Osian Temple , Jodhpur , Rajasthan |

|
| The Jain temple complex of Dilwara, Mount Abu |

|
Introduction
Gujarat Temples: Saurastra Style:
- Gujarat temples are designed in the Nagara style of architecture.
- After the Gupta period, the Maitrakas of Vallabhi introduced new structural elements, leading to the Saurastra style.
- This style features four types of superstructures:
- Kutina: Resembles the Dravida sikhara.
- Valabhi: Wagon-vault or salasikhara.
- Phamsana: Wedge-shaped, stepped pyramidal.
- Latina: Single sikhara with a curvilinear profile.
- The phamsana sikhara is topped with a Dravida type domical finial instead of traditional amalakas.
- Temples typically include a square garbha-grha(sanctum) and sometimes a mukha-mandapa(entrance porch).
- They can be sandhara(with a roofed ambulatory) or nirandhara(without an ambulatory).
- Wall decorations often feature ratha projections.
- Similar to Gupta traditions, these temples are built on a jagati(platform).
- Notable Maitraka temples from the 6th and 7th centuries include:
- Vishnu temple at Gop
- Bilvanatha temple at Bilesvara
- Surya temples at Pasnavada,Srinagar, and Jhamra
Maru Gurjara Architecture
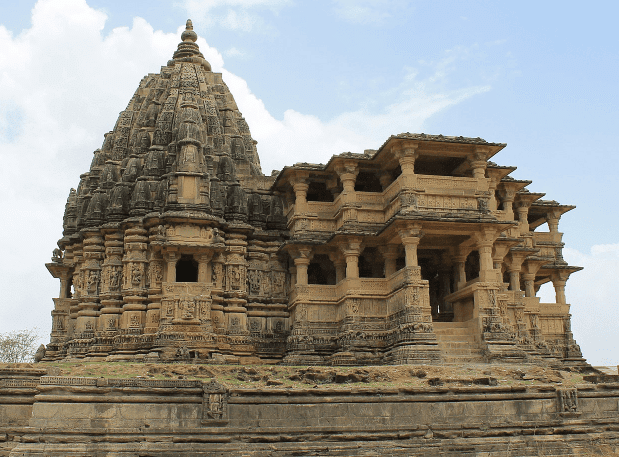
Māru-Gurjara Temple Architecture:
- Origin: Māru-Gurjara temple architecture emerged around the 6th century in the regions of Rajasthan and Gujarat.
- Craftsmanship: This architecture reflects the advanced understanding of structures and the refined skills of ancient Rajasthani craftsmen.
- Styles:There are two main styles within Māru-Gurjara architecture:
- Maha-Maru: Developed in regions like Marudesa, Sapadalaksa, Surasena, and parts of Uparamala.
- Maru-Gurjara: Originated in areas such as Medapata, Gurjaradesa-Arbuda, Gurjaradesa-Anarta, and parts of Gujarat.
- Cultural Significance: The term "Maru Gurjara" reflects the historical similarities in ethnicity, culture, and politics between ancient Rajasthan (Marudesh) and Gujarat (Gurjaratra).
- Meaning:"Maru Gurjara art" translates to "art of Rajasthan," highlighting the region's rich artistic heritage.
Evolution
- In the tenth century, the Solanki dynasty in Gujarat introduced several new features in architecture.
- The architectural style that developed during this period in regions like Anartta, Saurashtra, Kachha, and Lata is known as the "MARU-GURJARA" style.
- This style had its origins in the eighth century, combining two regional traditions called "Maha-Maru" and "Maha-Gurjara."
- Under the Solankis, the Maru-Gurjara style reached its peak of architectural perfection.
Maru Gurjara temples
Maru-Gurjara Style Temples are characterized by their unique architectural elements and divisions.
Key Components:
- Garbha-griha(inner sanctum),Gudha-mandapa(main hall), and a porch similar to the antrala of Nagara temples.
- Later examples feature a free-standing kirti-torana(decorative arch) and a temple tank.
Temple Elevation Divisions:
- Pitha(base),
- Mandovara(main hall),
- Shikhara(spire).
Mandovara Details:
- Comprises Vedhi-bandha(binding mouldings),Jangha(main wall section), and Varandika(cornice mouldings).
- Varandika topped with Khurachadya(ribbed tile sun-shade).
Shikhara Features:
- Base features Rathika(deity image).
- Curvilinear shape topped with Amalaka(disk),Candrika(capstone), and Kalasha(pot finial).
Gudha-mandapa Roof Styles:
- Phamsana(stepped-pyramidal) or Samvarana(bell roof).
Temples of Gujarat
Structural Temple Activities in Gujarat:
- Initiated by the Maitrakas of Valabhi during the post-Gupta period.
Known as the Saurashtra style, featuring four superstructures:
- Kutina
- Valabhi
- Phamsana
- Latina
Early Maitraka temples had a simple plan and elevation, with a square garbha-griha(sanctum) and sometimes a mukha-mandapa(entrance porch).
By the 8th century, there was a shift from the Saurashtra style to the Nagara style.
Examples include temples of Varaha at Kadvar and Surya near Somnath, featuring a rudimentary shikhara(spire) in triratha form, a garbha-griha with a pradakshina-patha(circumambulatory path), and a closed mandapa with a porch and sloping roof.
 |
Download the notes
Temple Architecture: Gujarat and Rajasthan
|
Download as PDF |
Sun Temple at Modhera , Gujarat

- The Sun Temple at Modhera, a prime example of the Solanki style Maru-Gurjara temples, is renowned for its distinctive features.
- Built on a terrace of solid brick faced with stone, the east-facing temple is constructed of golden-brown sandstone.
- Visitors enter through a decorated archway(kirti-torana) after ascending a broad flight of steps.
- Beyond the kirti-torana, the temple complex includes the sabha-mandapa,gudha-mandapa, and garbha-griha, all aligned on a single axis and featuring the basic components of pitha,mandovara, and shikhara.
- The temple complex is fronted by a temple tank(kunda or stepped well), which includes miniature shrines on its smaller steps.
Osian Temple , Jodhpur , Rajasthan
- Osian, anciently known as Ukesapura, was a significant religious city of the Gurjara–Pratiharas between the eighth and eleventh centuries.
- The temples in Osian were constructed on a broad pishtha, topped with an adhisthana featuring various mouldings like khura,kumbha,kalasha, and kapota.
- These mouldings were arranged to align with the ratha projections of the vimana.
- The kapota is typically carved with kudu arches.
- Above the pitha and adhisthana sits the mandovara.
- All the pagas of the mandovara in these panchratha temples feature devakoshthas, which are topped with miniature shikharas crowned by amalakas.
The Jain temple complex of Dilwara, Mount Abu
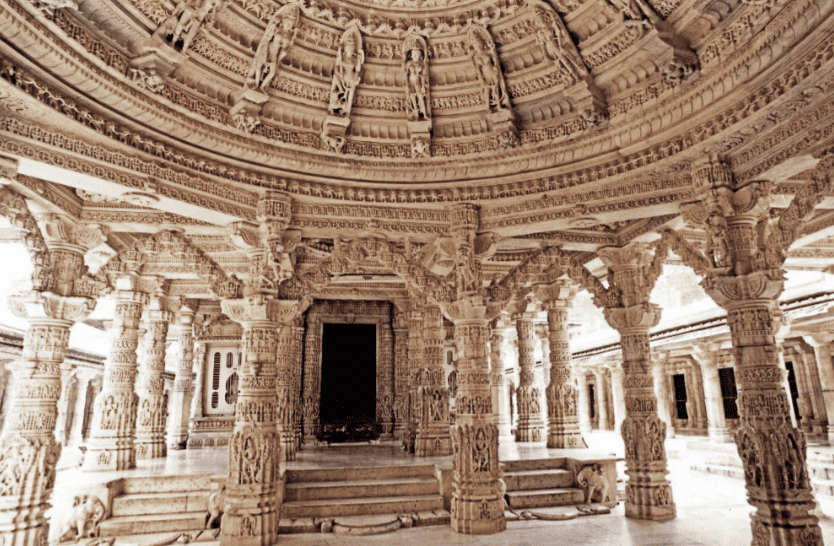
Vimala Vasahi and Luna Vasahi Temples:
- These temples show regional variations and intricate sculptural ornamentation, reflecting strong influences from the Maru-Gurjara and central Indian styles.
- Built mostly of white marble, they feature beautiful toranas (decorative arches), carved ceilings with lotus motifs, female bracket-figures, and open backyards with deva-kulikas (subsidiary shrines).
Vimala Vasahi Temple:
- The east-facing Vimala Vasahi, dedicated to Adinatha, consists of various parts including the mula-prasada(main shrine) made of black stone,gudha-mandapa(covered hall),sabha-mandapa(assembly hall), and deva-kulika.
- The entrance porch features a false dome leading to an octagonal mandapa (hall).
- Pillars in the mandapa support an impressive corbelled dome adorned with 16 celestial nymphs (apsaras).
- The dome's lintels are reinforced with a system of triangulated supports and intricately carved brackets.
|
71 videos|848 docs
|





















