International Relations: October 2024 UPSC Current Affairs | UPSC Mains: International Relations PDF Download
How a Direct Israel-Iran Conflict Affects India?

Why in News?
The conflict between Israel and Iran has entered a volatile phase, raising concerns across various sectors, particularly trade and economics. As tensions escalate, the implications for India, an emerging player in the global market are becoming increasingly significant.
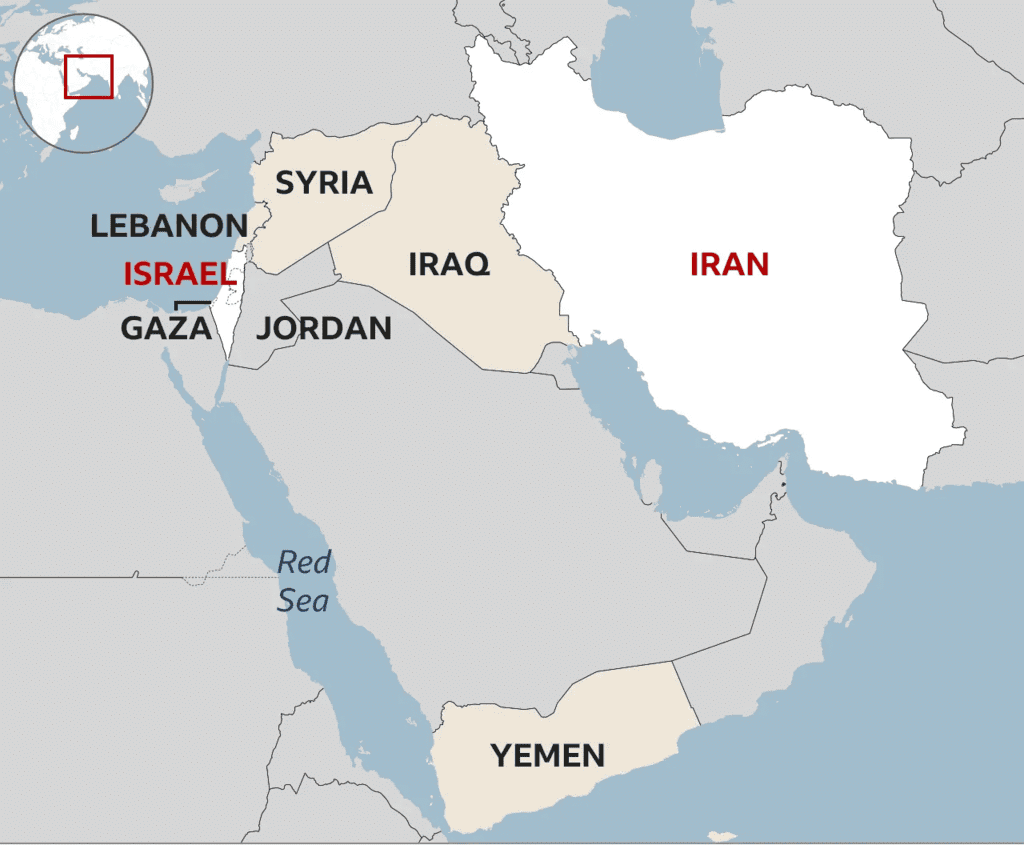
What are the Implications of the Israel-Iran Conflict on India?
- Disruption of Trade Routes: The ongoing conflict increases the risk of disruptions along crucial shipping routes for India's trade with Europe, the US, Africa, and West Asia. The Red Sea and Suez Canal are particularly vital, facilitating the movement of goods valued over USD 400 billion annually. This instability poses threats not only to shipping lanes but also to the overall security of maritime trade.
- Economic Impact on Exports: The conflict escalation has already impacted Indian exports negatively, with a recorded 9% drop in August 2024. A significant contributor was a 38% decrease in petroleum product exports due to the Red Sea crisis. The tea industry is also vulnerable, as Iran is a major importer of Indian tea, with exports reaching 4.91 million kg in early 2024.
- Rising Shipping Costs: As shipping routes are altered due to conflict-related diversions, shipping costs have surged by 15-20%. This increase strains the profit margins of Indian exporters, particularly affecting low-end engineering products, textiles, and garments sensitive to freight costs.
- India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC): IMEC aims to create an efficient trade route linking India, the Gulf, and Europe to reduce dependency on the Suez Canal while countering China’s Belt and Road Initiative. However, the ongoing conflict threatens the corridor's progress and viability, impacting bilateral trade and regional economic dynamics.
- Impact on Crude Oil Prices: The conflict has led to a rise in global crude oil prices, with Brent crude nearing USD 75 a barrel. As Iran is a significant oil producer, any military escalation could disrupt oil supplies, further increasing prices. Higher oil costs may hinder central banks from reducing interest rates due to rising inflation complicating economic recovery.
- Effects on Indian Markets: India, relying heavily on oil imports (over 80% of its needs), is susceptible to price fluctuations. Sustained rises in oil prices may lead investors to shift from Indian equities to safer assets like bonds or gold, with major indices like the Sensex and Nifty already feeling the effects of the conflict.
- Gold as a Safe Haven: Gold prices have surged due to geopolitical tensions and changing investment strategies. In uncertain times, investors tend to flock to gold, driving its price even higher.
- Logistics Challenges: Indian exporters are currently in a "wait and watch" mode, with some urging the government to develop a reputable Indian shipping line to reduce reliance on foreign shipping companies that impose high transport charges.
What is the Status of India's Trade with Israel and Iran?
India-Israel Trade- Significant Growth: India-Israel trade has doubled over five years, increasing from around USD 5.56 billion in 2018-19 to USD 10.7 billion in 2022-23. In FY 2023-24, the bilateral trade reached USD 6.53 billion (excluding defense), facing a decline due to regional security issues and trade route disruptions.
- Key Exports: Major exports from India to Israel include diesel, diamonds, aviation turbine fuel, and Basmati rice, with diesel and diamonds accounting for 78% of total exports in 2022-23.
- Imports: India primarily imports space equipment, diamonds, potassium chloride, and mechanical appliances from Israel.
- India-Iran Trade:
- Declining Trade Volumes: In contrast to its robust trade with Israel, India’s trade with Iran has contracted over the past five years, totaling just USD 2.33 billion in 2022-23. For FY 2023-24, trade with Iran reached USD 1.52 billion during the first ten months (April-January).
- Trade Surplus: In 2022-23, India enjoyed a trade surplus of about USD 1 billion by exporting USD 1.66 billion worth of goods to Iran, mainly agricultural products, while importing USD 0.67 billion.
- Major Indian Exports to Iran: Include Basmati rice, tea, sugar, fresh fruits, pharmaceuticals, soft drinks, bovine meat, and pulses.
- Major Indian Imports from Iran: Include saturated methanol, petroleum bitumen, apples, liquefied propane, dry dates, and almonds.
What are the Global Implications of the Israel-Iran Conflict?
- Energy Supply and Pricing Dynamics: Iran, a member of OPEC, produces about 3.2 million barrels per day (bpd), which is roughly 3% of global output. Despite facing U.S. sanctions, Iranian oil exports have grown, primarily due to demand from China, highlighting Iran's strategic importance in the global oil market.
- OPEC's Spare Capacity: OPEC+ possesses considerable spare oil production capacity, with estimates suggesting that Saudi Arabia could increase output by up to 3 million bpd and the UAE by about 1.4 million. This buffer provides some protection against potential Iranian supply disruptions, although the situation remains fragile.
- Long-term Energy Security: The increasing diversity of global oil supply, particularly due to rising U.S. production, has offered a degree of insulation from price shocks linked to Middle Eastern conflicts. The U.S. produces about 13% of global crude oil and nearly 20% of total liquid production, helping stabilize the market amidst uncertainties.
- Potential for Escalation: While Israel has not yet attacked Iranian oil facilities, such strikes could provoke significant military responses from Iran. Historically, conflicts have escalated quickly in this region, often leading to unintended consequences for global supply chains.
- Geopolitical Considerations: The U.S. is expected to pressure Israel to avoid major military escalations to maintain regional stability and prevent broader conflicts. Other global players, notably China, which has substantial energy ties with Iran, will be closely monitoring developments, as the conflict's outcome may reshape international energy strategies and alliances.
- Humanitarian Crises: A larger conflict could result in refugee flows, impacting Mediterranean countries like Italy and Greece, and straining international humanitarian resources.
What are the Possible Solutions to De-escalate the Iran-Israel Conflict?
- Immediate Ceasefire Agreement: Urging both Iran and Israel to agree to an immediate ceasefire can be a fundamental step towards reducing tensions and facilitating dialogue. Global powers, particularly the United States and China, should use their diplomatic influence to advocate for a ceasefire and promote negotiations.
- Regional Collaboration: Involving Gulf Arab states in discussions can provide a more comprehensive approach to de-escalation, addressing shared concerns regarding Iran's influence in the region.
- Humanitarian Aid and Support: Increasing humanitarian assistance to affected regions can alleviate suffering and foster goodwill, potentially easing hostilities.
- International Organisations: Engaging organizations like the United Nations to mediate discussions and facilitate conflict resolution efforts can provide neutral ground for negotiations.
- Long-term Peace Initiatives: Regional powers should work together to establish a comprehensive security framework that includes confidence-building measures, arms control agreements, and peaceful conflict resolution mechanisms. Addressing underlying issues such as historical grievances, territorial disputes, and religious extremism will create a conducive environment for lasting peace.
Mains Question
Q: Discuss the implications of the Israel-Iran conflict on India's trade and economic interests.
Jamaican Prime Minister’s Visit to India

Why in news?
Recently, the Prime Minister of Jamaica traveled to India with the aim of enhancing bilateral relations in several important areas, including trade and investment. This visit marks the first time a Jamaican Prime Minister has made a bilateral visit to India.
What are the Key Outcomes of the Visit?
Meeting the President of India:
- Both leaders recognized the necessity of further fortifying partnerships at multiple levels such as parliamentary, academic, and cultural exchanges.
- They also discussed collaboration in international forums.
- The President acknowledged Jamaica's participation in all three editions of the Voice of the Global South Summits and highlighted the shared commitment to reform multilateral institutions, particularly the UN Security Council, through groupings like L-69.
Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) Signings:
- The governments of India and Jamaica agreed to collaborate on various initiatives including:
- Sharing successful digital public infrastructure.
- Implementing a Cultural Exchange Programme.
- Cooperation in the field of sports.
- Specific MoUs were signed between NPCI International Payments Limited and Egov Jamaica Limited.
The Voice of the Global South Summit (VOGSS)
- The Voice of the Global South Summit is an innovative initiative led by India aimed at uniting countries from the Global South. This platform facilitates the sharing of perspectives and priorities on a wide range of issues.
- It reflects India’s philosophy of Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam, which translates to "One Earth, One Family, One Future," and aligns with the Prime Minister's vision of Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas, Sabka Vishwas, and Sabka Prayas.
How are the Relations between India and Jamaica?
- India was among the first countries to recognize Jamaica following its independence, establishing diplomatic relations in 1962.
- A resident mission was set up in Kingston in 1976 after a visit by Prime Minister Indira Gandhi.
- In 2020, Jamaica established its own Resident Mission in India.
- India and Jamaica have historically enjoyed cordial relations, which are rooted in shared history, democratic governance, Commonwealth membership, and mutual affection for cricket.
- Jamaica hosts a significant Indian diaspora of approximately 70,000 individuals, representing one of the girmitiya countries, which emphasizes the strong connection between the two nations. The year 2022 signifies 177 years of the Indian community's presence in Jamaica.
- Girmitiya countries are those where Indian indentured laborers settled, including Fiji, Guyana, Mauritius, South Africa, Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago, and Reunion Island.
- Both countries are members of international organizations such as the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) and G-77.
- As developing nations, India and Jamaica share common goals, including economic growth, equity, poverty eradication, and enhancing the quality of life for their citizens.
Maldives’ President State Visit to India

Why in news?
Recently, President Mohamed Muizzu of the Maldives completed a four-day state visit to India, during which he referred to New Delhi as a valued partner. This visit is notable given President Muizzu's previous focus on anti-India sentiments and derogatory comments made by his ministers about the Indian Prime Minister.
Key Outcomes of the Visit
- Strengthening Bilateral Ties: India reiterated its commitment to assisting the Maldives under its Neighbourhood First policy and the SAGAR vision (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
- Emergency Financial Assistance: India offered Treasury bills worth USD 100 million to help the Maldives with urgent financing needs. Additionally, a bilateral currency swap agreement of USD 400 million and Rs 30 billion was extended to further assist the Maldives in managing its financial challenges.
- Comprehensive Economic and Maritime Security Partnership: Both nations agreed to enhance their relationship into a Comprehensive Economic and Maritime Security Partnership that focuses on people-centric and future-oriented stability in the Indian Ocean Region.
- Development Cooperation: A priority will be given to the timely completion of the Greater Male Connectivity Project (GMCP) and a feasibility study for connecting Thilafushi and Giraavaru islands. Collaboration will also occur on developing a commercial port at Thilafushi and enhancing services at airports like Hanimaadhoo and Gan.
- Trade and Economic Cooperation: Discussions will start on a bilateral free trade agreement, local currency trade settlement, investment promotion, economic diversification, and boosting tourism.
- Digital and Financial Cooperation: Cooperation will be established in Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) through initiatives like India's Unified Payments Interface (UPI) and other digital services to improve e-governance. India has also introduced the RuPay card in the Maldives for easier payments by Indian tourists.
- Energy Cooperation: Renewable energy projects will be developed to help the Maldives achieve its climate objectives, including assisting in participation in the One Sun One World One Grid initiative.
- Health Cooperation: Jan Aushadhi Kendras will be established in the Maldives to provide affordable generic medicines from India. Joint efforts will also be made in mental health services and emergency medical evacuation capacity-building.
- Defence and Security Cooperation: Both countries acknowledged the importance of completing the Maldives National Defence Force (MNDF) 'Ekatha' harbour project at Uthuru Thila Falhu (UTF), which is funded by India and will enhance MNDF's operational capabilities.
- Food Security: Joint efforts will be made to establish an Agriculture Economic Zone and tourism investments, including a fish processing and canning facility in Haa Alifu atoll with Indian assistance.
- Capacity Building and Training: A Start-up Incubator-Accelerator will be set up in the Maldives to encourage youth innovation and entrepreneurship.
- People-to-People Linkages: The establishment of consulates in Bengaluru (India) and Addu City (Maldives) aims to enhance interactions between the citizens of both countries. Higher education institutions and skill centers will also be established, alongside an Indian Council for Cultural Relations Chair at the Maldives National University.
- Regional and Multilateral Cooperation: India and the Maldives reaffirmed their commitment to collaboration in regional and international forums, particularly in the Colombo Security Conclave (CSC).
- Political Exchanges: Both nations agreed to formalize cooperation between their respective parliaments, recognizing shared democratic values as a foundation for bilateral relations.
- Establishment of High-Level Core Group: A new group will be formed to ensure timely and effective implementation of the cooperation framework.
Why Maldivian President Softened His Anti-India Stance?
- Economic Crisis in the Maldives: The Maldives is currently grappling with a severe economic crisis, with foreign exchange reserves dropping to just USD 440 million, sufficient to cover only 1.5 months of imports. There is a looming threat of a debt default, as highlighted by Moody’s downgrade of the country's credit rating.
- Economic Dependence: The Maldives heavily relies on tourism, with Indian tourists being a major contributor. A decline in Indian visitors due to strained relations led to an estimated loss of USD 150 million for the Maldivian tourism economy. India remains the Maldives’ fifth-largest trading partner, supplying essential goods like food, medicine, and construction materials.
- Strategic Importance of India: India has historically played a crucial role in the Maldives' development and security. Alienating India could destabilize the region. The Maldivian President acknowledged India's role as the 'First Responder' in times of need, referencing India's support during the 2014 water crisis and the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Geopolitical Balancing with China: The softened stance reflects a pragmatic approach to balancing relations with both India and China, rather than shifting entirely towards China. This strategy allows the Maldives to benefit from India's partnerships while maintaining a diversified foreign policy.
- Political Realism: The tensions between the two countries, fueled by political rhetoric and social media disputes, were seen as harmful to their relationship. The visit aims to reinforce strong bilateral ties, given the economic and geopolitical significance of this partnership.
What is the Significance of Maldives for India?
- Strategic Location: The Maldives is located along crucial International Shipping Lanes (ISLs) in the Indian Ocean, which are essential for global trade and energy movement. Approximately 50% of India’s external trade and 80% of its energy imports transit through these routes.
- Countering Chinese Influence: India considers the Maldives a key player in counteracting China’s expanding influence in the region, ensuring its own security.
- Indian Ocean as India’s Backyard: A stable and positive maritime environment in the Indian Ocean is vital for India’s strategic priorities, making the Maldives an important partner.
- Climate Change Collaboration: Due to its vulnerability to climate change, the Maldives is a significant partner for India in developing strategies for climate adaptation and mitigation.
Mains Question
Q: With reference to the Maldives' economic crisis and India’s financial aid, discuss how economic factors influence diplomacy.
10 Point Plan for India-ASEAN Relations

Why in News?
Recently, India's Prime Minister presented a comprehensive 10-point plan during the 21st ASEAN-India Summit 2024 held in Vientiane, Laos. This event also coincided with the 44th ASEAN summit, themed "ASEAN: Enhancing Connectivity and Resilience." The year 2024 marks a decade since the introduction of India's Act East Policy in 2014, aimed at bolstering ties with ASEAN in the realms of trade, security, and connectivity within the Indo-Pacific region.
Key Facts About the 21st ASEAN-India Summit 2024
- ASEAN and India Overview: Together, ASEAN and India account for 7% of the global GDP and 26% of the world's population.
- Emerging Technologies:Collaborative efforts between India and ASEAN will focus on advanced technologies such as:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Blockchain
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Robotics
- Quantum Computing
- 6-G technology
- Digital Transformation:A joint statement was issued to promote digital transformation, which includes:
- Digital infrastructure
- Financial technology (fintech)
- Cybersecurity
- India plans to share its expertise in digital public infrastructure, such as Aadhaar and UPI, with ASEAN nations.
- ASEAN-India Trade Growth: Over the past decade, trade between India and ASEAN has doubled to more than USD 130 billion. However, the trade deficit has increased significantly, rising to USD 44 billion in FY23 from USD 8 billion in FY13.
- India's Role in ASEAN Trade: India is now ASEAN's sixth largest trading partner and the eighth largest source of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) among ASEAN Dialogue Partners.
- Trade in Local Currency: Some ASEAN countries, led by Malaysia, have begun conducting trade in local currencies, with expectations for others to follow suit.
- Investment Flows: The Global Value Chains (GVCs) between India and ASEAN have expanded, with total investments exceeding USD 125 billion from 2000 to 2023.
- Financial Integration: In June 2024, the Reserve Bank of India joined Project Nexus with ASEAN, allowing real-time cross-border transactions between India’s UPI and Singapore’s PayNow system.
- Regional Security: Both parties agreed to strengthen the ASEAN-India Comprehensive Strategic Partnership aimed at promoting regional peace, stability, and prosperity, aligning with the ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific (AOIP) and supported by India's Act East Policy (AEP).
- Code of Conduct for the South China Sea: Both India and ASEAN backed the full implementation of the Declaration on the Conduct of Parties (DOC) and advocated for an effective Code of Conduct (COC) consistent with the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) 1982.
- Defence and Security Cooperation: Collaboration will include enhancing maritime security and counter-terrorism efforts through joint military exercises and naval port calls, such as the ASEAN-India Maritime Exercise.
What is India's 10-Point Plan for ASEAN Cooperation?
- ASEAN-India Year of Tourism 2025: India will allocate USD 5 million for joint tourism initiatives.
- Celebrating a Decade of the Act East Policy: Events to commemorate this milestone will include a Youth Summit, Start-up Festival, Hackathon, Music Festival, and Think Tank initiatives.
- Women Scientists Conclave: A conclave focused on fostering ASEAN-India science collaboration specifically for women scientists.
- Educational Scholarships: Plans to double scholarships at Nalanda University and offer new scholarships for ASEAN students in Indian agricultural universities.
- Trade Agreement Review: The ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement is set for a review by 2025.
- Disaster Resilience: India will contribute USD 5 million to bolster ASEAN's disaster resilience.
- Health Ministers’ Track: There will be regular discussions between ASEAN and Indian health ministers to enhance health resilience.
- Cyber Policy Dialogue: Establishment of an ASEAN-India dialogue aimed at enhancing digital and cyber resilience.
- Green Hydrogen Workshop: India will support ASEAN's energy transition through a workshop focused on green hydrogen.
- Climate Resilience Initiative: ASEAN leaders have been invited to participate in India's "Plant a Tree for Mother" campaign.
India-Canada Diplomatic Row

Why in News?
India-Canada relations have recently encountered significant challenges following allegations of Indian involvement in the assassination of a Khalistani leader in Canada.
What are the Recent Developments in India-Canada Relations?
- Assassination of Nijjar: The killing of Hardeep Singh Nijjar, a Khalistani leader, in British Columbia has prompted accusations from the Canadian Prime Minister regarding Indian officials' involvement, which India has firmly dismissed as "absurd."
- Diplomatic Fallout: Diplomatic ties have sharply declined, with both nations expelling each other's diplomats and halting consular services.
- Support from Five Eyes Alliance: Canada has sought assistance from the Five Eyes intelligence alliance to bolster international support amidst escalating diplomatic tensions with India.
What are the Significant Areas of India-Canada Relationship?
- Political Relations: Diplomatic relations between India and Canada were established in 1947. Both countries value democratic principles, human rights, the rule of law, and pluralism, providing a robust foundation for their interactions. They collaborate within international forums such as the Commonwealth, G20, and United Nations to tackle global challenges like climate change, security, and sustainable development.
- Economic Cooperation: The total bilateral trade in goods between India and Canada reached USD 9.36 billion in 2023. Canada ranks as the 18th largest foreign investor in India, contributing approximately USD 3.3 billion from April 2000 to March 2023. Ongoing discussions for a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) aim to enhance trade relations across goods, services, investment, and trade facilitation.
- Diaspora Connections: Over 1.8 million individuals of Indian descent reside in Canada, including around 1 million Non-Resident Indians (NRIs), making it one of the largest Indian diasporas globally. This diaspora plays a crucial role in cultural exchange, economic activities, and fostering strong social connections between the two nations.
- Education and Space Innovation: Collaborative research initiatives in sectors such as healthcare, agricultural biotechnology, and waste management are being promoted through programs like IC-IMPACTS. Space cooperation includes agreements between ISRO and the Canadian Space Agency, leading to successful launches of Canadian satellites by ISRO. Additionally, Indian students represent about 40% of Canada’s international student population, contributing to cultural diversity.
- Nuclear Cooperation Agreement: Signed in 2010 and effective since 2013, this agreement facilitates uranium supply and establishes a Joint Committee for oversight.
- Strategic Importance: India is pivotal to Canada’s Indo-Pacific strategy, helping diversify the Canadian economy and enhance regional security dynamics. Cooperation focuses on maritime security, counter-terrorism, and maintaining stability in the Indo-Pacific region.
What are the Major Challenges in India-Canada Relations?
- Diplomatic Immunity Issue: Canada has cited the Vienna Conventions, stressing the need to safeguard its diplomatic personnel and citizens in India amid escalating tensions. India's response to these concerns will significantly influence the future of their bilateral relations.
- Khalistan Issue: India views Canada’s tolerance towards Khalistani separatist groups as a direct threat to its territorial integrity. The investigation by Canada into alleged Indian involvement in Nijjar's assassination has further strained diplomatic and political trust between the two countries.
- Economic and Trade Barriers: Growing political discord has stalled efforts to finalize the CEPA. Bilateral trade has diminished, and Canadian investments in India are facing uncertainty due to the ongoing diplomatic crisis.
- Visa and Immigration Issues: Reduced Canadian diplomatic staff in India has resulted in significant delays for Indians applying for visas, particularly affecting students looking to enroll in Canadian institutions.
- Geopolitical Implications: The India-Canada diplomatic standoff may negatively impact India's G20 standing if allegations are proven, affecting relations with countries linked to both nations. Canada's focus on engaging India through its Indo-Pacific strategy is hampered by these political tensions, restricting cooperation on security and economic matters.
Way Forward
- Address Khalistan Issue: Open dialogue between the two governments is essential to resolve concerns about the Indian diaspora and Khalistani separatism. Mutual respect for sovereignty and legal frameworks is crucial for navigating these sensitive issues.
- Strengthen Economic Ties: Revitalizing the CEPA, focusing on technology, renewable energy, and infrastructure, is necessary to enhance trade and investment frameworks for mutual benefit.
- Balance Geopolitical Interests: Both nations must carefully manage their relationships with major powers like the United States, China, and Russia, adopting a cautious approach to enhance strategic partnerships without conflicts.
- Leverage Multilateral Forums: Utilizing platforms such as G7 and Five Eyes to address global challenges and promote shared values can contribute to strengthening bilateral ties.
Mains Question
Q: Discuss the factors contributing to the decline in India-Canada relations, particularly in the context of the Sikh diaspora and Khalistani separatism. How can both nations work towards improving their bilateral ties?
19th East Asia Summit (EAS)

Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister of India attended the 19th East Asia Summit held in Vientiane, Lao PDR.
Key Highlights of the Visit
- The Prime Minister advocated for a development-focused Indo-Pacific strategy as opposed to one based on expansionism.
- He reiterated India's support for Nalanda University and extended an invitation to EAS members for the Heads of Higher Education Conclave.
- During the summit, he addressed global issues such as terrorism, cyber threats, and maritime security, emphasizing the importance of resolving conflicts through dialogue.
- The Prime Minister congratulated Malaysia on taking on the role of the new Chair of ASEAN and expressed India's full support for their chairmanship.
- Currently, Lao PDR is serving as the chair of ASEAN.
What is the East Asia Summit (EAS)?
Establishment
- The East Asia Summit was established in 2005 as an initiative led by the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN).
- It is the only leader-led forum in the region that brings together key partners to discuss significant political, security, and economic issues.
- The concept of an East Asia Grouping was first proposed by Malaysian Prime Minister Mahathir Mohamad in 1991, with the inaugural summit taking place in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia on December 14, 2005.
Objectives
- The EAS operates on principles of openness, inclusiveness, respect for international law, and the central role of ASEAN.
Members
- The East Asia Summit serves as a crucial platform for strategic dialogue in the Indo-Pacific, comprising 18 member countries, including all ASEAN members.
- The EAS includes 10 ASEAN members: Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- It also has eight dialogue partners: Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Russia, and the United States.
Importance
- In 2023, EAS member countries accounted for approximately 53% of the global population and contributed around 60% of the world's GDP.
- India ranks as ASEAN's seventh-largest trading partner, while ASEAN is India's fourth-largest trading partner.
- Over the last decade, trade between India and ASEAN has doubled, exceeding USD 130 billion.
Strategically
- Connectivity initiatives in Southeast Asia, both in terms of infrastructure and digital networks, are essential to India's Act East Policy.
- Major projects like the India-Myanmar-Thailand Highway and the Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport are enhancing regional connectivity with East Asian nations.
- India also participates in capacity-building programs through the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) scheme with Southeast Asian countries such as Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam.
Culturally
- Buddhism, which originated in India, serves as a significant cultural and religious link among many Southeast Asian and East Asian nations.
- India's efforts to restore and support the International Buddhist Confederation aim to strengthen its spiritual and cultural relationships with Myanmar, Thailand, and Cambodia, reflecting its dedication to promoting Buddhist traditions.
Strengthening India-Pakistan Relations and SCO
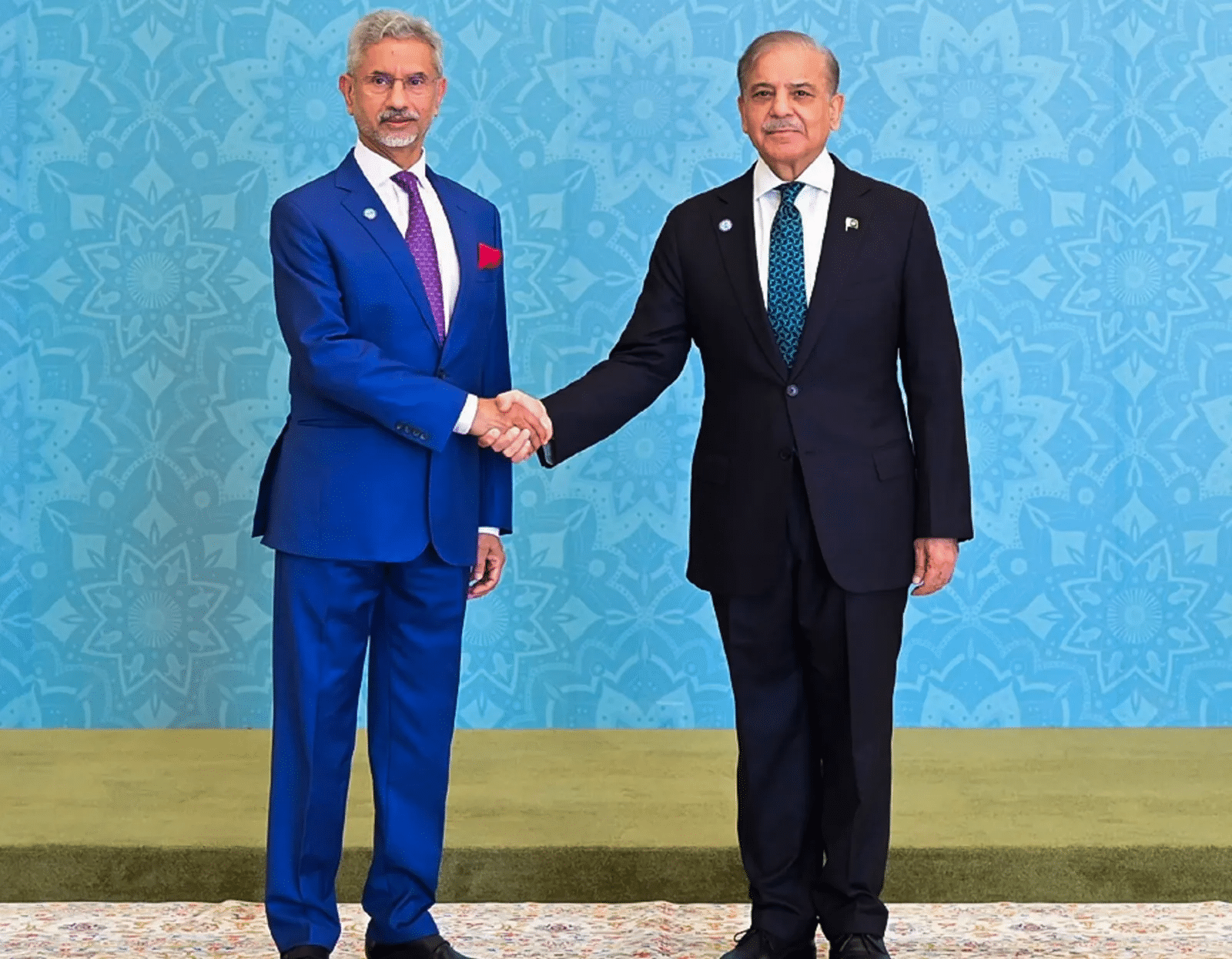
Why in news?
Recently, India’s External Affairs Minister engaged in an informal discussion with Pakistan’s Prime Minister and Foreign Minister during the SCO Council of Heads of Government meeting held in Islamabad, Pakistan.
- The tone of these exchanges was reported to be more positive compared to previous interactions.
- The Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) Council of Heads of Governments represents the second-highest decision-making body within the SCO structure.
What were the Positive Developments Between India and Pakistan at the SCO Summit?
- Avoidance of Contentious Language: Both nations refrained from using provocative language in their official statements. Notably, Pakistan did not mention sensitive topics like Kashmir, while India was careful about its references to Pakistan concerning cross-border terrorism.
- Productive Meeting: India acknowledged the Pakistani leadership for hosting a fruitful SCO meeting, indicating a constructive tone in the minister's closing remarks.
- Collaboration on Regional Issues: Discussions included trade, connectivity, energy flows, and cooperation against terrorism and extremism, focusing on collaborative efforts rather than conflict.
- Initiatives for Economic Cooperation: The summit led to proposals for an Economic Dialogue Programme aimed at boosting economic collaboration. The joint statement highlighted cooperation in green development, digital economy, trade, poverty alleviation, and renewable energy.
Why are Positive Developments Significant?
- Revocation of Article 370 (2019): India's move to strip Jammu and Kashmir of its special status in August 2019 severely affected bilateral relations. Pakistan views this as an unlawful annexation, while India regards it as an internal matter.
- Downgrade in Bilateral Relations: Following the revocation of Article 370, Pakistan downgraded diplomatic relations with India, expelling the Indian High Commissioner.
- Indus Waters Treaty: Tensions rose over the Kishanganga and Ratle hydroelectric projects, with Pakistan accusing India of treaty violations. India has sought a review of the Indus Waters Treaty, which has not been well received in Pakistan.
- Limited Trade: After the Pulwama attack in 2019, India revoked Pakistan's Most Favoured Nation status, halting bilateral trade which previously amounted to substantial figures.
- Internal Interference: Pakistan accuses India of instigating unrest in Balochistan, while India claims that Pakistan is radicalizing youth in Kashmir.
How can Multilateral Forums Improve India-Pakistan Relations?
- Neutral Platforms for Dialogue: Multilateral forums provide neutral grounds for India and Pakistan to converse without the usual bilateral tensions, allowing for informal discussions that can help ease hostilities.
- Regional Cooperation: Both nations have previously collaborated under SAARC on regional trade agreements, and there is potential for further cooperation in areas like climate change and disaster management.
- Security Concerns: As members of the SCO’s Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS), both countries can collaborate on common security threats, even amid strained relations.
- Reducing Mistrust: International forums like the UN allow various countries to mediate constructive dialogues and potentially alleviate tensions, as seen during the Kargil conflict in 1999.
- Economic Exchanges: Collaborative projects like the Turkmenistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan-India (TAPI) Pipeline can foster cooperation even among adversarial nations.
What are the Key Facts About SCO?
- About SCO: The SCO is a permanent intergovernmental organization founded on June 15, 2001, in Shanghai, China.
- Establishment: Initially formed by six countries: Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan, evolving from the Shanghai Five mechanism.
- Objectives of the SCO: The SCO aims to enhance mutual trust among member states, promote regional peace and stability, and develop a fair international political and economic order.
- Principles of SCO: The organization is guided by the Shanghai spirit, which emphasizes mutual trust, benefit, equality, and the respect for cultural diversity.
- Decision-Making Bodies: The SCO's supreme body is the Council of Heads of States, which meets annually to discuss major issues, while the Council of Heads of Government meets yearly to strategize cooperation efforts.
- Standing Bodies: The SCO has two permanent bodies: the Secretariat in Beijing, managing daily operations, and the Executive Committee of the Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) in Tashkent, focusing on security and counter-terrorism.
- Current Membership: The SCO has 10 full members, including China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, India, Pakistan, Iran (joining in 2023), and Belarus (joining in 2024).
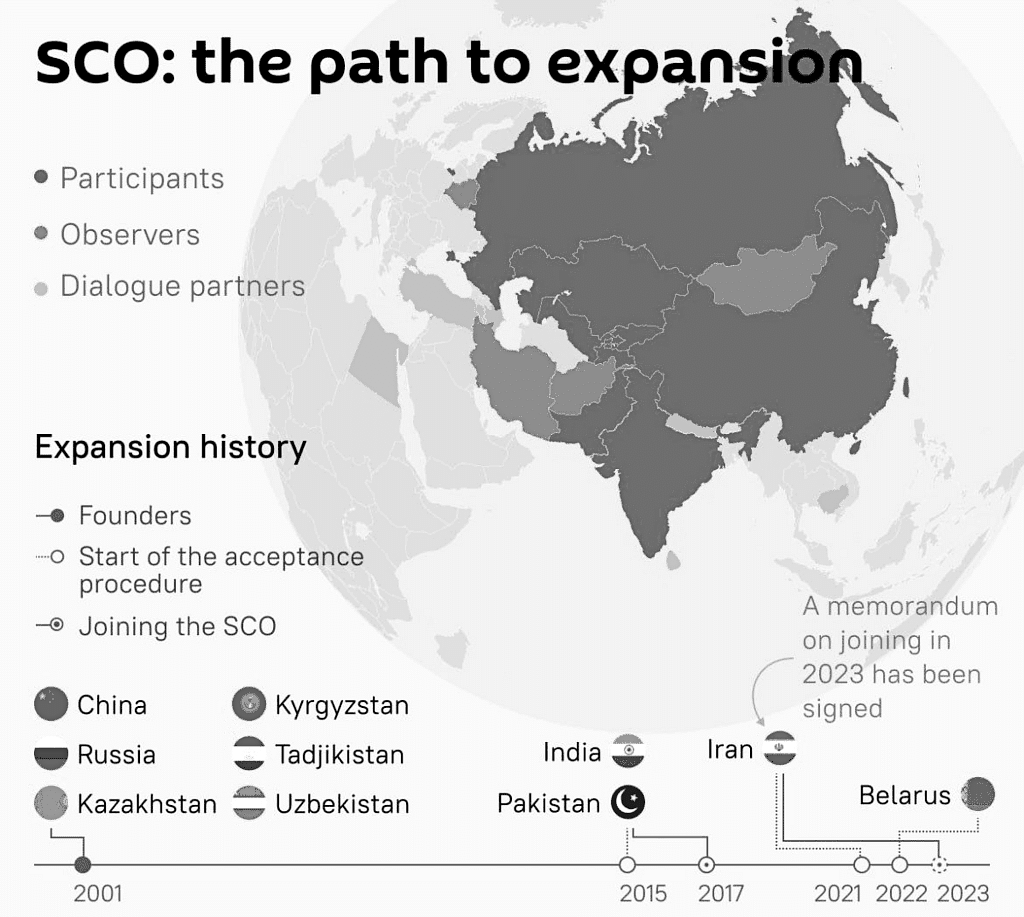
- SCO-Afghanistan Contact Group: Established in 2005 to address security and stability concerns in Afghanistan, showcasing SCO's commitment to regional security.
- Official Languages: The SCO conducts business in Russian and Chinese, facilitating communication among its members.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: The SCO maintains partnerships with organizations like the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and ASEAN, among others.
Conclusion
The recent informal dialogues between India and Pakistan at the SCO meeting, marked by positive developments and constructive exchanges, illustrate the potential of multilateral platforms to encourage cooperation. By prioritizing regional collaboration and tackling common challenges, these forums could enhance bilateral relations and contribute to stability.
Mains Question
Q: Analyse how multilateral forums can reduce mistrust between India and Pakistan. How can the spirit of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) contribute to this?
Presidential Visit to Malawi and Mauritania

Why in news?
Recently, India’s President made a historic visit to Malawi and Mauritania, marking the first time an Indian leader has visited these nations.
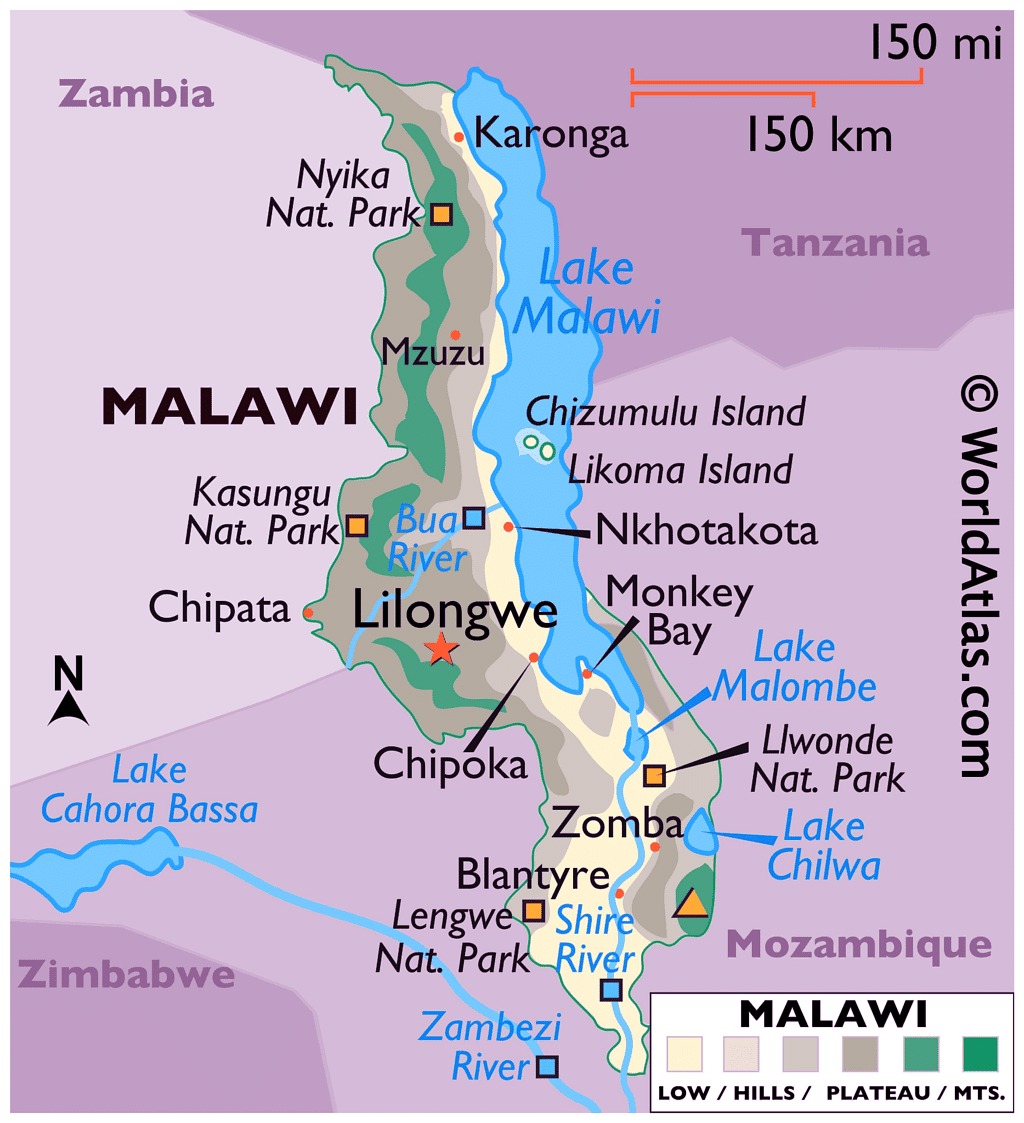
- India is recognized as the fourth-largest trading partner of Malawi, with bilateral trade reaching USD 256.41 million in the fiscal year 2021-22. Furthermore, India's total investments in Malawi exceed USD 500 million, reflecting a strong economic relationship.
- Malawi, previously known as Nyasaland, is a landlocked nation situated in southeastern Africa. In the year 2019-20, the total trade between India and Malawi was USD 94.53 million, indicating a steady growth in their economic ties.
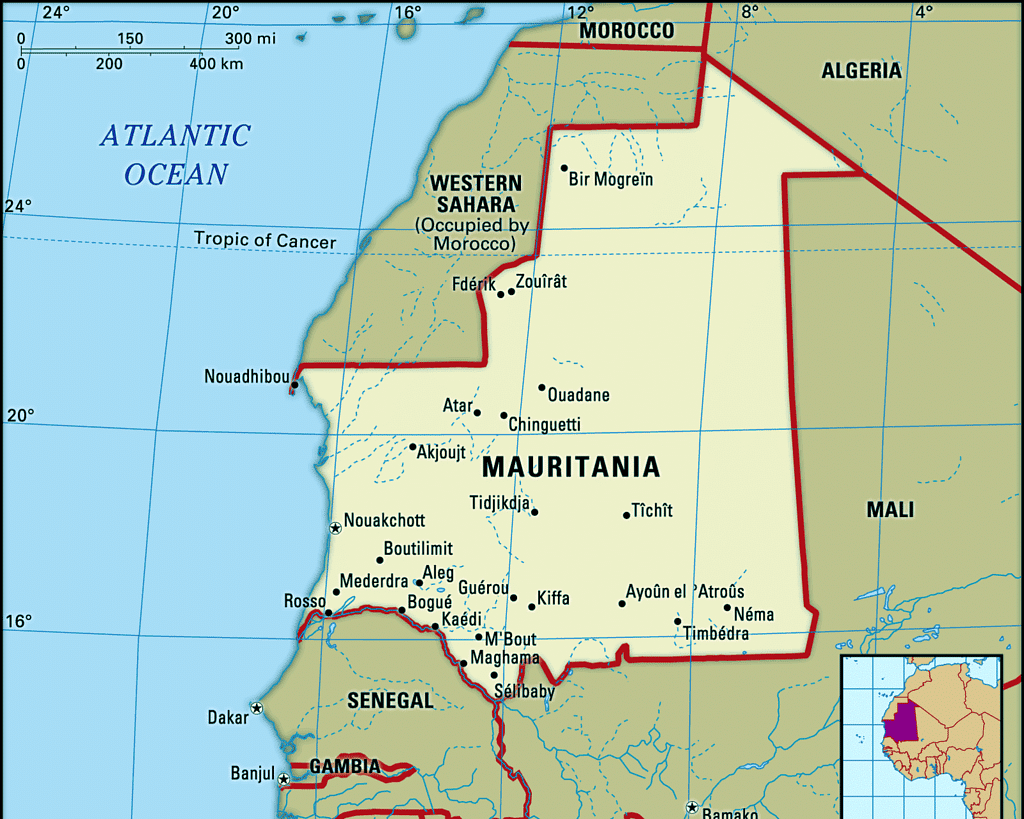
- Mauritania, located in western Africa along the Atlantic Ocean, is home to the Indigenous Berber people and the Moors. In June 2021, India established its diplomatic mission in Nouakchott, the capital city of Mauritania, which signifies India's commitment to strengthening relations with the country.
India-Bhutan Relations
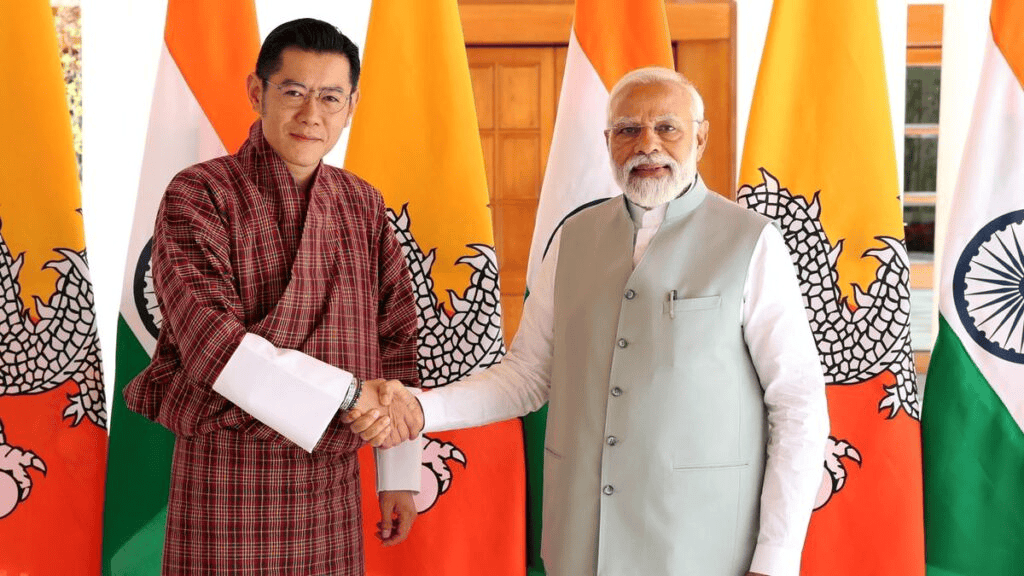

Why in news?
Recently, the Prime Minister of Bhutan made an official visit to India, resulting in extensive discussions and the signing of various agreements between the two nations. The relationship between India and Bhutan is characterized by deep-rooted trust, goodwill, and shared values that manifest at all levels of interaction. This enduring partnership is vital for mutual prosperity and regional stability in South Asia.
Key Highlights of the India-Bhutan Bilateral Talks
- Petroleum Agreement: A new agreement was established for the supply of petroleum products, ensuring a consistent and reliable supply from India to Bhutan, thereby enhancing economic collaboration in the hydrocarbon sector.
- Food Safety Collaboration: The Food and Drug Authority of Bhutan and India's Food Safety and Standards Authority (FSSAI) signed an agreement aimed at improving food safety measures, which will facilitate trade by ensuring adherence to safety standards and lowering compliance costs.
- Energy Efficiency and Conservation: An MoU was signed focused on energy efficiency and conservation, highlighting a commitment to sustainable practices. India plans to support Bhutan in improving household energy efficiency and promoting the use of energy-saving appliances.
- Border Dispute Resolution: The visit coincided with ongoing negotiations between China and Bhutan regarding their border dispute, which affects regional security, particularly in the Doklam area. Recent agreements also aim to address these border tensions.
- Bhutan's Regional Economic Hub in Gelephu: Bhutan plans to develop a regional economic hub in Gelephu, known as the "Gelephu Mindfulness City," which emphasizes sustainable practices and aims to foster connectivity and regional development.
Significance of Bhutan for India
- Strategic Importance: Bhutan's geographical position as a buffer state between India and China is crucial for India's security. India has provided considerable support in defense and infrastructure, which has helped maintain Bhutan's sovereignty.
- Economic Importance: India is Bhutan's largest trading partner, significantly contributing to its economy through hydropower development, which is pivotal for Bhutan's revenue generation.
- Cultural Importance: The cultural ties between India and Bhutan are strong, with many Bhutanese studying in India and a shared Buddhist heritage that fosters mutual respect and understanding.
- Environmental Importance: Bhutan's commitment to remaining carbon-neutral aligns with India's support in areas like renewable energy and forest conservation.
Challenges in India-Bhutan Relations
- China's Growing Influence: The increasing presence of China, especially near the disputed border, poses challenges for India, which has historically been Bhutan's closest ally.
- Border Disputes: While the India-Bhutan border is generally peaceful, recent incursions by Chinese forces have raised concerns, particularly highlighted during the 2017 Doklam standoff.
- Hydropower Projects: There are growing concerns in Bhutan regarding the terms of certain hydropower projects with India, which some perceive as overly favorable to India.
- Trade Issues: Despite being Bhutan's major trading partner, trade imbalances exist, with Bhutan importing significantly more from India than it exports, leading to calls for better access to Indian markets.
Way Forward
- India can further support Bhutan's economic growth through investments in infrastructure, tourism, and other sectors, enhancing self-reliance and job creation.
- Promoting cultural exchanges will deepen understanding and appreciation of each nation’s heritage.
- Facilitating visa-free travel could enhance regional cooperation and people-to-people connections.
- Joint efforts in strategic cooperation can help address mutual security concerns, including combating terrorism and drug trafficking.
16th BRICS Summit & India-China Border Agreement
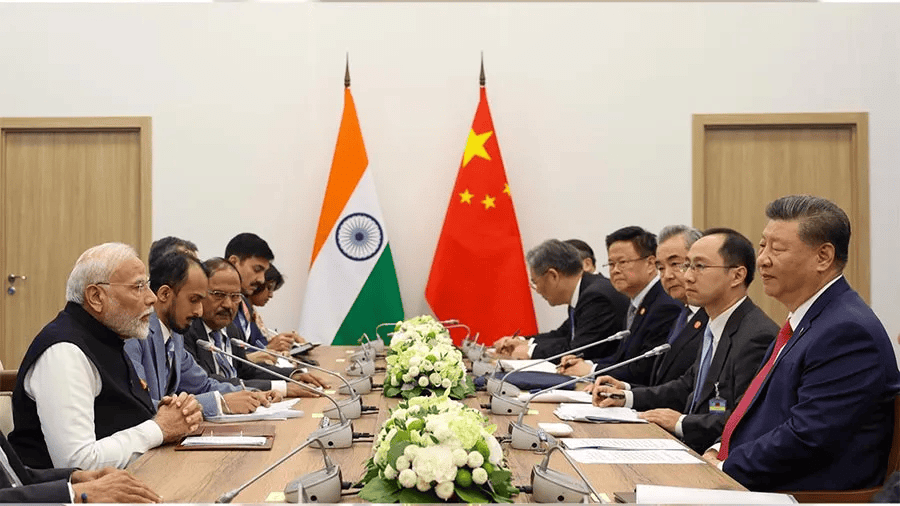

Why in News?
Recently, the 16th BRICS Summit took place in Kazan, Russia. On the sidelines of this summit, India’s Prime Minister welcomed the recent agreement with China aimed at achieving "complete disengagement and resolution" of border disputes that have been ongoing since 2020. This marks their first bilateral meeting since the tensions escalated in 2020.
Key Highlights of the Summit
- New Members Participation: The summit highlighted the involvement of new member countries, showcasing the growing influence and diversity within the BRICS+ alliance.
- Focus on Multilateralism: Leaders discussed ways to enhance multilateralism, combat terrorism, promote economic growth, pursue sustainable development, and address issues affecting the Global South.
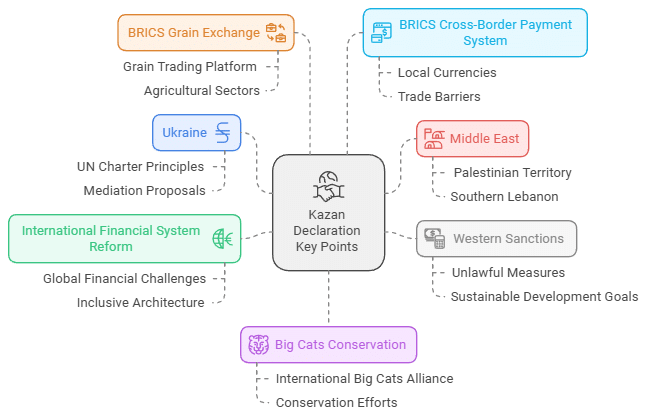
Kazan Declaration
Stand on Geopolitical Conflicts
- On Ukraine: Leaders emphasized the need for a peaceful resolution through dialogue and diplomacy.
- On West Asia Crisis: There was a strong expression of concern regarding the humanitarian crisis in the Gaza Strip and West Bank, condemning the loss of civilian lives and damage to infrastructure due to Israeli attacks in Southern Lebanon.
- On Western Sanctions: The summit underscored the negative impact of unlawful unilateral coercive measures, including illegal sanctions, on the global economy, international trade, and the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- On BRICS Grain Exchange: Discussions were held regarding the establishment of a grain trading platform within BRICS, with future expansions potentially including other agricultural sectors.
- Financial Integration Support: The summit highlighted the need for enhanced financial integration among member nations, emphasizing the importance of trade in local currencies and facilitating smooth cross-border payments. India’s UPI was noted as a successful model for this initiative.
- On Big Cats: There was support for conservation efforts aimed at protecting endangered species, particularly big cats, with India proposing the creation of an International Big Cats Alliance. BRICS countries were encouraged to collaborate further on these conservation efforts.
What is BRICS?
About: Initially formed informally during a meeting among Brazil, Russia, India, and China (BRIC) at the G8 Outreach Summit in 2006, BRICS now includes South Africa, making it a group of nine countries: Brazil, China, Egypt, Ethiopia, India, Iran, Russia, South Africa, and the UAE. The inaugural BRIC summit was held in Yekaterinburg, Russia, in 2009, and the New Development Bank (NDB) was established in 2014.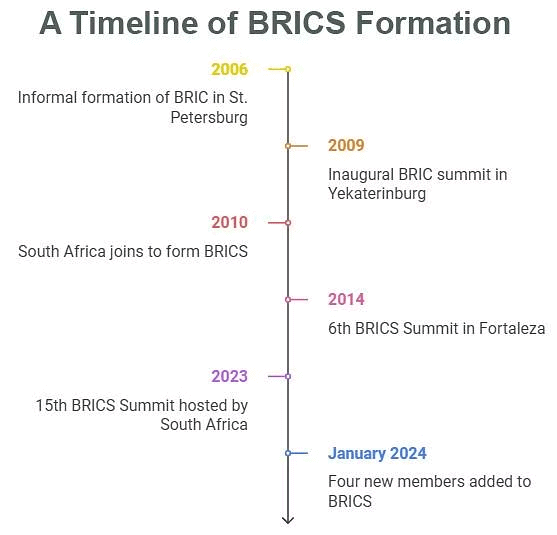
- Significance: As of August 2023, the BRICS contributes 40% of the world's population which controls 26% of the global GDP.
Why BRICS Matters?
- Engagement of Non-Western Countries with Russia: The Kazan Summit underscored the acknowledgment of Russia's strategic importance by non-Western nations, particularly regarding its role as a key supplier of weapons and energy.
- BRICS as a Cohesive Institution: Despite its diverse membership, BRICS has shown effective management and collaboration through annual summits and the establishment of the NDB, which has funded projects worth USD 30 billion since 2015.
- Emergence as an Influential Bloc: BRICS has gained importance in global politics, raising concerns in the West about its potential to compete with Western-led institutions like the G20. While primarily focused on economic issues, BRICS also tackles political challenges, advocating for fair representation in international organizations.
- The Kazan Declaration: This document reflects BRICS's collective desire to reform existing international frameworks, seeking to enhance its representation and influence globally.
What are the Challenges Related to the BRICS?
- Countering the Dollar: Despite efforts to create a multipolar financial system, BRICS faces significant challenges, particularly in promoting non-dollar currency transactions and the limited progress of the NDB compared to the World Bank.
- Geopolitical Contradictions: The diversity of new members presents complexities, as some maintain alliances with the US while others, like Iran, oppose it. This could hinder BRICS’s ability to maintain a unified agenda.
- Decision-Making Difficulties: The expansion of BRICS might complicate decision-making processes, as achieving consensus among more members could become increasingly challenging, reminiscent of the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) and Group of 77 (G77)
- Way Forward: It is essential to establish clear, shared objectives among member countries, focusing on cooperation in trade, technology, and security. Engaging in initiatives that bolster collaboration in supply chains, energy, food security, and financial resilience is also crucial.
Mains Question
Q: How do the developments from the recent BRICS summit, particularly the India-China bilateral meeting, impact regional stability and international relations?
United Nations Day 2024

Why in news?
United Nations Day is observed annually on October 24 to commemorate the anniversary of the UN Charter's enactment in 1945, which occurred in the aftermath of World War II. This day serves to enhance public awareness regarding the objectives and accomplishments of the United Nations.
What is the UN Charter?
Background:
- The UN Charter was signed on June 26, 1945, during the UN Conference on International Organization in San Francisco and officially came into effect on October 24, 1945.
- India ratified the UN Charter on October 30, 1945, and is one of its founding members.
- The League of Nations, established in 1919 under the Treaty of Versailles, is considered the predecessor of the UN, aimed at fostering international collaboration and securing peace.
About:
- The Charter serves as the fundamental document of the UN and is a binding instrument of international law for UN Member States.
- It delineates essential principles of international relations, emphasizing equal rights among nations and prohibiting the use of force between states.
- Since its inception, the Charter has been amended three times: in 1963, 1965, and 1973.
Significance:
- The UN's primary focus includes maintaining international peace and security, delivering humanitarian aid, protecting human rights, and enforcing international law.
- For over 75 years, the UN has played a pivotal role in fostering international cooperation, peace, and development.
What are the Different Organs of the UN?
- General Assembly: The UN General Assembly (UNGA) is the primary policy-making body of the UN, comprising all Member States, facilitating a platform for multilateral discussions on a wide range of international issues as per the UN Charter. Each of the 193 Member States has an equal vote within the Assembly.
- The UN Security Council: This council includes 15 members, comprising five permanent members (China, France, Russia, the UK, and the USA) and ten non-permanent members who serve two-year terms. India has held a non-permanent seat on the UNSC eight times.
- UN Economic and Social Council: Comprising 54 members elected by the UNGA, ECOSOC is the principal body for coordinating economic, social, and environmental policy discussions and recommendations.
- Trusteeship Council: This council was established to oversee the administration of trust territories as they moved toward becoming sovereign nations.
- International Court of Justice: The ICJ is the sole international court that resolves disputes between the 193 UN Member States.
- It can adjudicate two types of cases: "contentious cases," which are legal disputes between states, and "advisory proceedings," which provide advisory opinions on legal questions referred to it by UN bodies and specialized agencies.
- Secretariat: The Secretary-General is appointed by the UNGA upon the recommendation of the Security Council and acts as the chief administrative officer of the organization.
What are the Challenges Related to the UN?
- Power Alignments: The UN grapples with power disparities between affluent and developing nations, complicating its ability to achieve its objectives and undermining impartiality in addressing global challenges.
- Security and Terrorism: The organization faces dynamic security threats, including terrorism and ideological conflicts, necessitating a broader approach that encompasses issues like human security, poverty, and disease, alongside traditional security concerns.
- Peacekeeping: Modern peacekeeping operations encounter obstacles, especially in internal conflicts where warring parties often disregard UN neutrality. The challenge is to shift from traditional peacekeeping to effective peace observation using quickly deployable teams.
- Human Rights Challenges: The UN aims to establish and reinforce national human rights institutions, particularly in post-conflict nations, ensuring adherence to international standards for the long-term protection and promotion of human rights.
- Financial Constraints and Arrears: The UN struggles with financial instability due to delays in member states' assessed contributions, affecting its operational capabilities and ability to meet global commitments.
What are the Proposals to Reform the UN?
- Expanding Permanent Membership & Inclusive Representation: Proposals to increase the number of permanent members beyond the P5 and to reassess veto powers could lead to a more representative and democratic Security Council.
- This expansion would potentially provide underrepresented regions, particularly in Africa, with a greater voice in decision-making processes.
- Reducing Inefficiencies in Administrative Processes: Simplifying the UN's administrative procedures and minimizing bureaucratic obstacles could greatly enhance its operational efficiency.
- India's Role in UN Reform: India has shown a steadfast commitment to global peace, security, and development through its active participation in UN peacekeeping missions and humanitarian efforts.
- The country advocates for a permanent seat on the Security Council, arguing that this would render the Council more representative and responsive to the challenges of the 21st century.
Mains Question
Q: What are the main challenges faced by the UN in fulfilling its objectives? Analyze the proposed reforms to enhance its effectiveness.
UNIFIL Mission
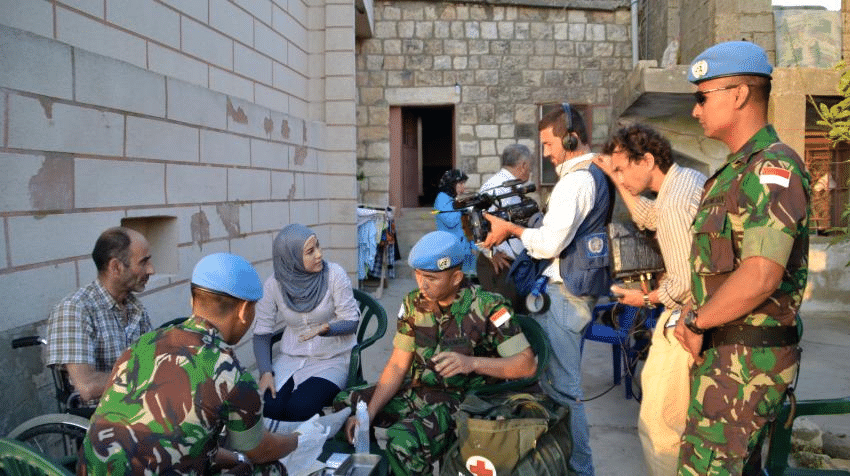

Why in news?
India is worried about the safety of UN peacekeepers in south Lebanon after they were shot at by Israeli forces. There are 600 Indian soldiers among the peacekeepers, who are part of the UN peacekeeping mission. These soldiers are stationed along the 120-km Blue Line, which is the border between Israel and Lebanon.
What is UNIFIL (United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon)?
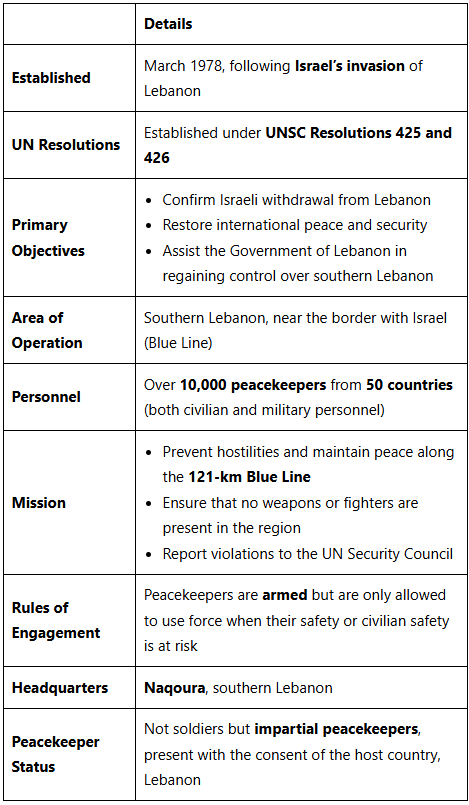
Significance of UNIFIL
- Conflict Prevention: UNIFIL keeps an eye on the Blue Line to stop any fights from getting worse between Israel and Lebanon.
- Civilian Protection: The mission works to protect civilians and helps with humanitarian efforts in areas affected by conflict.
- Support for Lebanon: UNIFIL assists the Lebanese government in establishing its authority in the southern region, working alongside the Lebanese Armed Forces.
SCO Summit 2024
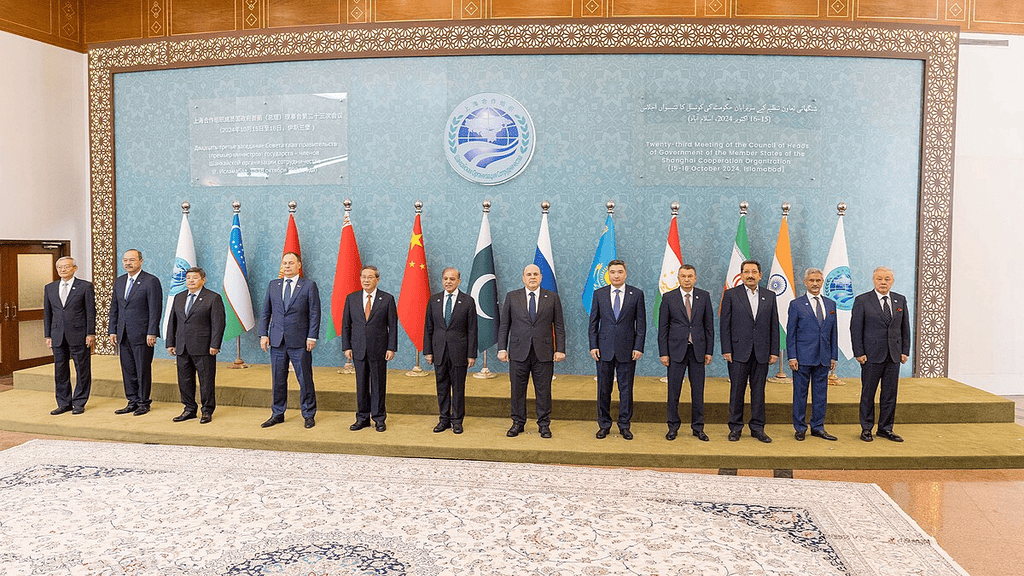

Why in news?
- The heads of government meeting of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) included India, Pakistan, China, Russia, and six other member countries.
- External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar travelled to Islamabad for this meeting, marking his first visit in nine years.
Key Takeaways
- India is the only SCO member that opposes China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) due to issues of territorial sovereignty.
- The SCO's joint statement reaffirmed support for China's BRI.
- The summit included criticism of Western sanctions on Russia and Iran, which were seen as damaging to global trade and economic relations.
- Discussions between India and Pakistan hinted at a possible revival of cricket ties, though it is still early.
- Regarding Pakistan, the External Affairs Minister stated, “If activities across borders involve terrorism, extremism, and separatism, they are unlikely to promote trade, energy flows, connectivity, and people-to-people exchanges.”
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO)
- The SCO originated from the Shanghai Five, formed in 1996 from discussions about border issues and demilitarization between four former USSR republics and China.
- The original members were Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Tajikistan.
- The group was renamed the SCO after Uzbekistan joined in 2001.
- The main goal is to boost regional cooperation to combat terrorism, separatism, and extremism in Central Asia.
Members
- Current members include China, Russia, India, Pakistan, Iran, Belarus, and the four Central Asian countries: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.
- Observer status is granted to Afghanistan and Mongolia.
- The official languages of the SCO are Russian and Chinese.
Structure
- The highest decision-making body is the Council of Heads of States (CHS), which meets annually.
- The organization has two key offices: the Secretariat in Beijing and the Executive Committee of the Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) in Tashkent.
Significance for India
- Regional Security: The SCO provides a platform to address security challenges, including terrorism, separatism, and extremism, which are vital issues for India given its geographical and political context.
- Economic Cooperation: The organization promotes economic collaboration among member states, enhancing trade and investment opportunities for India, especially with Central Asian countries.
- Geopolitical Influence: India’s membership in the SCO helps increase its influence in Central Asia and counteracts the presence of China and Pakistan in the region.
- Central Asia: The SCO is particularly significant for India as it emphasizes Central Asia, a region where India wants to strengthen ties, despite facing challenges in outreach.
- Recently, India has held dialogues with Central Asian leaders to show its commitment to partnership, and the External Affairs Minister's visit to Islamabad aimed to reinforce that message.
Challenges
- China-Pakistan Axis: The strong relationship between China and Pakistan within the SCO complicates India’s strategic position, sometimes limiting its influence in regional security discussions.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Ongoing border disputes and geopolitical tensions with China and Pakistan affect India’s ability to engage constructively in SCO discussions.
- Focus on Security over Economic Development: The SCO's emphasis on security issues can overshadow economic and developmental cooperation, which are important for India’s interests in the region.
|
88 videos|124 docs
|
FAQs on International Relations: October 2024 UPSC Current Affairs - UPSC Mains: International Relations
| 1. How would a direct conflict between Israel and Iran impact India's security interests? |  |
| 2. What are the implications of the Jamaican Prime Minister's visit to India for bilateral relations? |  |
| 3. What outcomes can be expected from the Maldives' President's state visit to India? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the 10 Point Plan for India-ASEAN relations? |  |
| 5. How has the India-Canada diplomatic row affected bilateral trade and relations? |  |
















