UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 13th November 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Environment
Sahyadri Tiger Reserve
Source: Times of India

Why in News?
In a significant development for wildlife lovers and tourists, a new tiger has been sighted in the famous Sahyadri Tiger Reserve located in Maharashtra.
About Sahyadri Tiger Reserve:
- Location: The Sahyadri Tiger Reserve is situated in the Sahyadri Ranges of the Western Ghats in Maharashtra. It is recognized as the northernmost tiger habitat within the Western Ghats, covering approximately 741.22 square kilometers. The reserve encompasses the Koyna Wildlife Sanctuary in the north and the Chandoli National Park in the south, having been established in 2007 by merging the two areas. Central to the reserve are the Shivsagar reservoir of the Koyana River and the Vasant Sagar reservoir of the Warana River.
History
- The area's history extends back to the Maratha Empire, featuring various forts that were either constructed or seized by the first Maratha Emperor, Shivaji Bhonsle. Numerous ruins, including a legendary temple associated with the divine gift of the Bhavani Sword to Shivaji, can be found throughout the region.
Habitat
- The terrain of the Sahyadri Tiger Reserve is characterized by its undulating landscape, with steep cliffs along its western edge. A defining feature of this area is the presence of barren rocky lateritic plateaus, locally referred to as "Sadas," which are marked by minimal perennial vegetation and overhanging cliffs, as well as many fallen boulders surrounded by dense thorny shrubs.
- This reserve is unique in that it hosts a rich variety of climax and near-climax vegetation, indicating a low risk of negative anthropogenic impacts in the foreseeable future.
Flora:
- The forest ecosystem within the reserve is composed of moist evergreen, semi-evergreen, and both moist and dry deciduous vegetation types. There is a notable presence of medicinal and fruit-bearing trees, alongside commercially valuable hardwood species.
- Common floral species include:
- Anjani (Memecylon umbellatum)
- Jambhul (Syzygium cumini)
- Pisa (Actinodaphne angustifolia)
Fauna
- The dominant carnivores in the reserve include tigers, leopards, and smaller wild cat species, as well as wolves, jackals, and wild dogs.
- Large herbivores found here consist of various deer species such as Barking Deer and Sambar, along with other notable animals including the Indian Bison, Sloth Bear, Mouse Deer, Giant Indian Squirrel, and Macaque.
GS2/International Relations
A mixed report card for the IMEC
Source:The Hindu

Why in news?
The India-Middle East-Europe Corridor (IMEC), introduced at the 2023 G20 summit, is designed to reduce travel time by 40% and costs by 30%, potentially revolutionizing global shipping once operational.
What is IMEC (India-Middle East-Europe Corridor)?
- IMEC is a significant trade route connecting India, the Middle East, and Europe aimed at reducing transit times and transportation costs, officially launched in 2023 during the G20 Summit.
- It seeks to bolster regional partnerships through enhanced infrastructure, energy grids, and digital connectivity, serving as an alternative to existing maritime routes such as the Suez Canal.
What are the current challenges facing the IMEC initiative?
- Geopolitical Tensions: The escalation of the Israel-Palestine conflict in October 2023 has hindered progress on the western segment of the IMEC, causing delays in collaboration from Saudi Arabia and Jordan due to geopolitical concerns linked to Israel.
- Lack of Progress in West Asia: The ongoing conflict has slowed connectivity initiatives in West Asia, particularly impacting the northern section of the corridor, which relies on infrastructure integration and trade processes with Israel and other stakeholders.
- Incomplete Development of Additional Infrastructure: Besides basic connectivity, critical elements such as clean energy exports, undersea fiber-optic cables, and telecommunication connections are delayed, pending the restoration of stability in West Asia.
- Organizational and Logistical Framework: The lack of a central governing body, such as an IMEC secretariat, complicates streamlined cross-border trade and systematic project implementation, resulting in coordination issues among participating nations.
How IMEC Aims to Enhance Regional Cooperation and Economic Growth?
- Strengthening India-UAE Economic Relations: India and the UAE are enhancing bilateral trade by utilizing frameworks like the Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) and the Virtual Trade Corridor to standardize trade processes, reduce costs, and simplify logistics.
- Improving Connectivity in the East: Progress in the eastern segment, particularly between India and the UAE, is boosting trade and laying the groundwork for cooperation through standardized trade practices and increasing non-oil trade, which diversifies exports and strengthens India’s regional integration.
- Capacity Building: While awaiting resolution of regional conflicts, eastern countries, especially India, are improving port infrastructure, digitizing logistics, and developing economic zones to enhance connectivity and lower trade barriers.
- Potential for Economic Integration: Once fully operational, IMEC could connect South Asia, the Middle East, and Europe, fostering deeper economic ties, reducing costs, and creating a stable trade route to promote regional development and integration.
What are the implications of IMEC for global trade dynamics?
- Reduced Dependency on the Suez Canal: IMEC offers a strategic alternative to the Suez Canal, with the potential to decrease transit time by 40% and costs by 30%, significantly impacting global trade routes by diversifying options and lowering shipping times and expenses.
- India’s Role as a Supply Chain Alternative: By leveraging IMEC, India can improve its position in global value chains as an alternative supply chain hub, aligning with manufacturing goals and enhancing export competitiveness through better infrastructure and reduced logistics costs.
- Reshaping Trade Infrastructure: The project not only supports connectivity but also includes potential energy infrastructure and digital linkages, presenting a comprehensive trade infrastructure model that could shape future trade frameworks in the Indo-Pacific and beyond.
- Attracting Participation: The establishment of the IMEC secretariat could facilitate strategic decision-making, build empirical support for trade benefits, and attract more countries to join the corridor, potentially enhancing IMEC’s influence on international trade and cooperation.
Way forward:
- Strengthen Geopolitical Stability: It is crucial to address regional tensions, particularly in West Asia, to ensure smoother collaboration among stakeholders and to accelerate the development of the IMEC's western segment.
- Develop an IMEC Secretariat: Creating a central coordinating body will streamline operations, facilitate cross-border trade, and oversee infrastructure projects, ensuring systematic progress and attracting further global participation.
Mains PYQ:
How will I2U2 (India, Israel, UAE and USA) grouping transform India’s position in global politics?
GS2/International Relations
With Indonesia, India’s opportunity and Beijing’s eye
Source:Indian Express

Why in News?
On October 20, Indonesia experienced a significant leadership change as Prabowo Subianto, a nationalist leader, assumed the presidency. This transition raises important questions regarding the future of India-Indonesia relations.
Increased Competition with China:
- Prabowo's administration may adopt a more assertive foreign policy that seeks to utilize Indonesia's strategic position between China and India.
- The degree of this assertiveness will depend on Indonesia's ability to manage its growing economic dependency on China while maintaining its sovereignty.
Potential for Enhanced Cooperation:
- Despite the challenges posed by China's influence, India has a chance to strengthen its partnership with Indonesia.
- This cooperation could focus on defense, maritime security, and trade, leveraging Indonesia’s strategic location and resource-rich economy.
Indonesia's Relationship with China:
Strategic Balance:
- Prabowo’s choice to visit China first highlights Indonesia's pragmatic approach to balancing relations with major powers.
- Despite concerns over China’s assertiveness in the Natuna Sea, Indonesia engages with China due to its economic benefits, particularly in infrastructure and technology.
Wariness Over Chinese Influence:
- Indonesia is cautious of China's significant control over its economic assets, which opens a path for India to position itself as a partner that respects Indonesian sovereignty.
- Both nations share mutual interests in maintaining maritime security in the Indo-Pacific region.
US-Indonesian Relations:
- Prabowo's complicated history with the U.S. due to past human rights issues may drive him to explore alternative partnerships.
- This scenario presents an opportunity for India to contribute positively to regional stability.
Opportunities for Economic Engagement:
Energy and Mineral Resources:
- Indonesia’s vast reserves of coal, palm oil, nickel, and tin present substantial opportunities for India to fulfill its energy and mineral needs.
- This aligns with India's expanding manufacturing and electric vehicle sectors.
Infrastructure and Maritime Cooperation:
- India's current projects, such as the development of Sabang port, can be expanded to strengthen connectivity and enhance trade routes between the Nicobar Islands and Indonesia.
Services Sector Collaboration:
- India’s expertise in IT and financial services could assist Indonesia in lowering business costs and enhancing economic efficiency.
- This is particularly relevant as Indonesia seeks to modernize and diversify its economy.
Tourism and Cultural Exchange:
- With Indonesia’s rising middle class, there is potential to boost tourism and cultural exchanges that celebrate shared heritage, particularly Hindu-Buddhist traditions.
Way Forward:
Strengthen Strategic and Economic Partnerships:
- India should actively collaborate with Indonesia on joint initiatives in defense, maritime security, and infrastructure.
- This approach will utilize Indonesia's strategic location and resources to create a resilient Indo-Pacific framework that counters China’s influence.
Deepen Cultural and Economic Ties:
- Expanding collaboration in sectors like IT, energy, and tourism, while honoring shared heritage, will foster goodwill.
- This will position India as a reliable and complementary partner to Indonesia, promoting mutual growth and stability in the region.
Mains PYQ:
Indian Diaspora has an important role to play in South-East Asian countries’ economy and society. Appraise the role of Indian Diaspora in South-East Asia in this context. (UPSC IAS/2017)
GS3/Defence & Security
Long Range Land Attack Cruise Missile
Source:India Today

Why in News?
Recently, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted the maiden flight test of its Long Range Land Attack Cruise Missile (LRLACM).
About
- The Long Range Land Attack Cruise Missile is designed for launch from both mobile ground-based systems and frontline ships.
- It utilizes a universal vertical launch module, enhancing operational flexibility significantly.
- This missile can perform complex maneuvers while flying at various speeds and altitudes, demonstrating its versatility and precision.
- Equipped with advanced avionics and software, the LRLACM enhances its overall performance and reliability.
- Typically subsonic, these missiles can follow terrain-hugging flight paths, making them difficult to detect and intercept, thus providing a strategic edge in overcoming enemy defenses.
Developed by
- The LRLACM was developed by the Aeronautical Development Establishment of DRDO in Bengaluru.
- This project involved collaboration among various DRDO laboratories and Indian industries.
- Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) in Hyderabad and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) in Bengaluru acted as the Development-Cum-Production Partners.
- The Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) had previously sanctioned the LRLACM as a Mission Mode Project under the Acceptance of Necessity (AoN) procedure.
Significance
- The successful test of the missile is viewed as a significant achievement in enhancing India's defense capabilities, particularly for long-range precision strike missions.
GS2/Governance
What is the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010?
Source:Indian Express

Why in News?
The Union Ministry of Home Affairs has, for the first time, explicitly listed the reasons for denying the clearance needed under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act to receive funds from abroad.
About Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010:
- The Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010 is a law passed by Parliament to manage foreign contributions, particularly monetary donations, made by specific individuals or organizations to NGOs and other entities within India.
- This Act was originally introduced in 1976 and underwent significant amendments in 2010.
- The Act comes under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
Definition of Foreign Contribution:
- ‘Foreign Contribution’ refers to any donation, delivery, or transfer made by any foreign source, which includes:
- Any article (except gifts for personal use valued below one lakh rupees).
- Any currency, whether it is Indian or foreign.
- Any security, including foreign securities.
- This also encompasses contributions received from individuals who have obtained it from a foreign source.
- Interest accrued on foreign contributions deposited in banks is also included.
Aims and Regulations:
- The Act establishes registration requirements and spending limitations for Indian non-profit organizations receiving foreign donations.
- Its primary goal is to prevent foreign entities from influencing Indian electoral politics and discussions on social, political, economic, or religious matters for improper purposes.
- Contributions from Indian citizens living abroad (for example, Non-Resident Indians, or NRIs) from their personal savings through standard banking channels are not categorized as foreign contributions.
Who Can Receive Foreign Contributions?
- Any individual or organization can accept foreign contributions if:
- The person or organization has a clear cultural, economic, educational, religious, or social agenda.
- The individual must have obtained FCRA registration or prior permission from the Central Government.
- The term 'person' includes Hindu Undivided Families and companies registered under Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013.
- Foreign contributions must be utilized solely for the intended purpose, with no more than 20% of the received amount allowed for administrative expenses within a financial year.
- To receive foreign donations, the FCRA mandates that every person or NGO must establish a bank account for foreign funds in the State Bank of India, Delhi.
Registration under FCRA:
- The FCRA is applicable to all groups aiming to receive foreign donations.
- It is mandatory for all such NGOs to register under the FCRA.
- Applicants must not be fictitious or acting as benami, nor can they have been prosecuted or convicted for engaging in activities aimed at conversion through inducement or coercion from one faith to another.
- Initial registration is valid for five years and can be renewed if compliance with all requirements is maintained.
- Registered organizations may receive foreign contributions for social, educational, religious, economic, and cultural purposes.
- Registration can be revoked if any false information is found in the application.
- If an NGO's registration is canceled, it cannot re-register for three years.
- The ministry holds the authority to suspend an NGO’s registration for 180 days while an inquiry is conducted and can freeze its funds.
- All government decisions can be contested in the High Court.
GS3/Environment
COP29 Climate Summit 2024
Source:The Hindu

Why in news?
At the COP29 climate conference in Baku, countries reached a landmark decision to advance a long-delayed agreement to establish a global carbon market under the Paris Agreement. While the agreement on carbon markets is seen as a breakthrough, the critical issue of climate finance remains unresolved, with developing nations emphasising the need for an updated, substantial funding goal.
Defining COP:
- The Conference of Parties (COP) is the principal governing body of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- The UNFCCC, established in 1992, unites 198 members (197 nations plus the European Union) in addressing climate change threats.
- Each year, the COP convenes to review national emission data, assess progress, and influence global climate policy.
Key milestones of COP:
- Kyoto Protocol (1997): Adopted at COP3, it mandated emissions reductions for industrialized countries, aiming for a collective target of a 4.2% reduction by 2012 from 1990 levels.
- Copenhagen Accord (2009): Introduced at COP15, it established a 2°C warming limit and the principle of developed nations funding climate actions in vulnerable countries, although it did not result in a new binding treaty.
- Paris Agreement (2015): At COP21, this landmark agreement set a goal to limit global warming to below 2°C, ideally at 1.5°C, and introduced Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) for each country.
- Glasgow Pact (2021): COP26 resulted in the Glasgow Pact, which included commitments to reduce coal usage and phase out inefficient fossil fuel subsidies, marking the first time coal was mentioned in a UN climate agreement.
- Loss and Damage Fund (2023): COP28 initiated a fund to assist nations affected by climate disasters, addressing longstanding calls for financial aid for those most impacted by climate change.
Criticisms of COP:
- Failure to deliver climate finance: Developed nations have not fulfilled their 2009 pledge to provide $100 billion annually to developing nations.
- A 2021 UN report projected that developing countries would need $6 trillion per year through 2030 to meet climate goals, indicating a significant funding gap.
- Insufficient emission reductions: Despite emission pledges, efforts remain inadequate. The International Energy Agency's COP28 report warned that existing pledges may not prevent exceeding the critical 1.5°C warming threshold.
Agreement on Global Carbon Markets at COP29:
- Carbon market overview: The global carbon market, as outlined under Article 6 of the Paris Agreement, enables countries to trade carbon credits, which are certified reductions in carbon emissions.
- This market aims to provide financial incentives for emission reductions, with prices determined by emission caps set by participating nations.
- Article 6 of the Paris Agreement: This article facilitates international cooperation to reduce carbon emissions, offering two pathways for trading carbon offsets.
- The first pathway, Article 6.2, allows bilateral carbon trading agreements between two countries under their own terms.
- The second pathway, Article 6.4, aims to develop a centralized, UN-managed system for both countries and companies to offset and trade carbon emissions.
Progress at COP29:
- On the first day of the global climate talks, COP29 officially adopted new operational standards for a mechanism under Article 6 of the Paris Agreement, paving the way for a global carbon market.
- This adoption of Article 6.4, achieved during the Conference of the Parties serving as the meeting of the Parties to the Paris Agreement (CMA), marks significant progress after years of delays.
- Significance of this milestone: Carbon markets are the last component of the 2015 Paris Agreement awaiting full implementation. Although further procedural steps are necessary, this agreement will enhance countries' ability to meet climate targets efficiently and affordably once operational.
Challenges Ahead at the COP29:
- Lack of consensus on climate finance: A key agenda for COP29 is to finalize the New Collective Quantified Goal (NCQG), which is a commitment by developed countries to provide funding for climate action in developing nations, replacing the unmet $100 billion target from 2020.
- However, progress has stalled, with the G77-plus China group, representing over 130 developing countries, rejecting the initial draft of the finance agreement and calling for revisions.
- Disagreements persist over the funding amount, contributors, types, and the coverage period.
- Demands of developing nations: Developing nations are asking for a minimum of $1 trillion annually starting in 2026, with G77 pushing for $1.3 trillion.
- They insist that this funding should be new, predictable, and non-debt-inducing, specifically aimed at climate action rather than being counted as investments in clean technology against existing commitments.
- Additionally, developing countries are requesting that any shortfall from the $100 billion annual goal in previous years be addressed as arrears in addition to the NCQG.
India’s Role in Shaping COP29’s Legacy:
- Call for an adequate and predictable finance mechanism: India has prioritized the NCQG, advocating for substantial financial commitments to the Global South.
- Indian negotiators stress that finance should be grant-based, low-interest, and long-term, focusing on a balanced approach to adaptation, mitigation, and addressing loss and damage.
- Emphasis on adaptation for vulnerable communities: India and its G77 allies have called for stronger support for adaptation initiatives, particularly for communities that are highly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change.
Conclusion:
- COP29 President Mukhtar Babayev highlighted that a finalized Article 6 framework could reduce the global cost of climate action by an estimated $250 billion annually through international cooperation.
- India’s NDC aims to cut emissions intensity by 45% from 2005 levels and establish an additional carbon sink of 2.5 to 3 billion tonnes by 2030.
- Effective carbon markets could play a crucial role in helping India achieve these targets.
GS3/Environment
Corpse flower
Source:CNN

Why in News?
The recent studies on the Corpse Flower (Amorphophallus titanum) have uncovered its fascinating mechanisms of heat generation and odor production, which play a crucial role in attracting pollinators through unique reproductive adaptations.
About the Corpse Flower (Titan Arum):
- Scientific Name: Amorphophallus titanum
- Common Name: Corpse Flower, Titan Arum
- Native Habitat: Found in the rainforests of western Sumatra, Indonesia
- Local Name: Bunga bangkai (where "bunga" means "flower" and "bangkai" means "corpse")
- Size: Can reach heights of 10-12 feet
- Bloom Cycle: Blooms every 5-10 years, with the flowering lasting 24-48 hours
- Structure:
- Spadix: The central column-like structure, which can grow up to 12 feet tall
- Spathe: A large, dark red petal-like structure that encases the spadix
- Corm: An underground storage organ that can weigh up to 45 kg
- Odor: Emits a strong scent reminiscent of rotting flesh to draw in pollinators, often likened to cheese, garlic, decaying fish, sweaty socks, and feces
- Odor Compounds: Contains compounds such as dimethyl trisulfide, trimethylamine, isovaleric acid, indole, and putrescine
- Thermogenesis: The spadix can heat up to 20°F above the surrounding temperature during its bloom
- Pollinators: Attracts carrion-feeding insects like flies and beetles through its scent and warmth
- Fruiting: Produces about 400 red-orange fruits, each containing two seeds
- Life Impact: The process of fruiting is energy-intensive and can sometimes lead to the plant's death
- Conservation Status: Classified as endangered, with fewer than 1,000 individuals remaining in the wild
- First Description: Initially described by the Italian botanist Odoardo Beccari in 1878
GS2/Polity
Inter-State Council
Source: The Print

Why in news?
Recently, the Union government reconstituted the Standing Committee of the Inter-State Council (ISC) and appointed the Home Minister as its chairman.
About the Inter-State Council:
- The Inter-State Council was established under Article 263 of the Constitution of India.
- Its primary purpose is to promote coordination and cooperation between the central and state governments.
- The creation of a permanent Inter-State Council was advocated by the Sarkaria Commission.
- The President has the authority to establish the council if it is deemed to be in the public interest.
- The first Inter-State Council was formed in 1990 through a presidential order.
Composition of the Inter-State Council:
- Chairman: The Prime Minister of India.
- Members:
- Chief Ministers from all states.
- Chief Ministers from Union Territories with a Legislative Assembly.
- Administrators from Union Territories without a Legislative Assembly.
- Six Cabinet Ministers from the Union Council of Ministers, nominated by the Prime Minister.
Functions of the Inter-State Council:
- The council is tasked with inquiring into and advising on disputes that may arise between states.
- It investigates and discusses subjects of common interest to some or all states, or between the Union and one or more states.
- The council makes recommendations on these subjects, particularly for improving policy and action coordination.
GS3/Science and Technology
 |
Download the notes
UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 13th November 2024
|
Download as PDF |
What is Voyager 2 Spacecraft?
Source: NASA
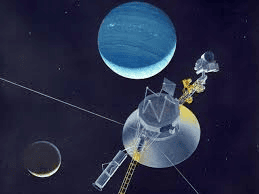
Why in News?
Nearly four decades after NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft made its historic flyby of Uranus, scientists have uncovered new revelations about the ice giant's peculiar magnetic field.
About Voyager 2 Spacecraft:
- It is an unmanned space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, shortly before its sister craft, Voyager 1.
- Primary mission:
- The mission was to explore the outer planets of our solar system, including Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, along with their moons, and then proceed on an interstellar mission.
- It remains the only spacecraft to have visited both Uranus and Neptune.
- Voyager 2 carries a Golden Record, which is a phonograph record featuring sounds and images from Earth, meant to communicate with any potential extraterrestrial civilizations it may encounter.
Firsts:
- Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft to have conducted close-range studies of all four of the solar system's giant planets.
- It discovered a 14th moon of Jupiter.
- It was the first human-made object to fly past Uranus.
- During its encounter with Uranus, Voyager 2 identified 10 new moons and two new rings.
- It was also the first human-made object to fly by Neptune.
- At Neptune, Voyager 2 found five moons, four rings, and a notable feature known as the "Great Dark Spot."
After completing its primary mission, Voyager 2 continued its journey into interstellar space, where it is still transmitting data about the interstellar medium and the heliosphere.
- It is the second spacecraft to enter interstellar space.
- On December 10, 2018, Voyager 2 joined its twin, Voyager 1, as one of the only human-made objects to reach the space between the stars.
- Currently, it is the second most distant human-made object from Earth, surpassed only by Voyager 1.
GS3/Defence & Security
Kanchanjunga Express collision was ‘accident-in-waiting
Source:Indian Express

Why in news?
The Commissioner of Railway Safety (CRS) identified the Kanchanjunga Express-goods train collision in West Bengal, which occurred in June 2024, as a result of "lapses at multiple levels." These lapses involved both station staff and officials at divisional and zonal railway levels. The CRS described the event as an "accident-in-waiting," emphasizing that the failure to manage train operations during automatic signal failures was a significant contributing factor. To avert future incidents of this nature, the CRS urged the urgent implementation of the KAVACH automatic train-protection system.
About
- The CRS operates as a statutory body, led by the Chief Commissioner of Railway Safety.
- It is responsible for the safety of rail travel and operations as outlined in the Railways Act, 1989.
- Investigating serious train accidents is a core responsibility of the CRS, which also makes recommendations to the government.
- Headquarters: Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh.
- Nodal Ministry: The CRS operates independently of the Ministry of Railways and is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Civil Aviation (MoCA) to avoid conflicts of interest.
On June 17, a tragic collision occurred in the Darjeeling district of West Bengal, approximately 11 km from New Jalpaiguri station. A Sealdah-bound Kanchanjunga Express from Agartala was rear-ended by a goods train within the Katihar Division of the Northeast Frontier Railway (NFR).
Causes of the Accident
- The report highlighted critical failures in operational protocol as key contributors to the Kanchanjunga Express-goods train collision. The primary causes included:
- Issuance of a flawed authority letter allowing passage through defective automatic signals without speed guidance.
- Lack of a caution order and inadequate counseling for loco pilots and station masters.
- Insufficient safety equipment, such as walkie-talkies, which hampered communication and led to misunderstandings.
- The CRS classified the incident as an "Error in train working," holding the station master, station superintendent, chief loco inspector, and traffic inspector accountable.
Communication Failures and Safety Violations
- The flawed authority letter misled the loco pilot into maintaining sectional speed despite defective signals.
- The letter was unsigned by the train manager, resulting in unawareness of the signal issues.
- Communication was further hindered by the absence of walkie-talkies, limiting effective interaction among the loco pilot, train manager, and station master.
- The CRS ruled out factors such as intoxication, negligence, or excessive speed by the loco pilot as contributors.
Systemic Signal Failures and Safety Concerns
- Repeated failures of automatic signals within the Katihar Division raised significant concerns regarding operational safety.
- Since January 2023, the division experienced 275 signal failures, highlighting severe reliability issues with the automatic signaling system.
- Over the past five years, there were 208 dangerous signal-passing incidents, of which 12 resulted in collisions.
- The CRS criticized the limitations of current preventive measures and called for enhancements in collaboration with the Research Design and Standards Organisation (RDSO) and Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs).
Recommendations for Safety Enhancements
- The CRS stressed the urgent need for implementing the KAVACH automatic train-protection system.
- Additional recommendations included:
- Prioritizing crashworthiness features in passenger coaches, beginning with the last two coaches on all trains and retrofitting existing coaches during major servicing.
- Accelerating the installation of Crew Voice and Video Recording Systems (CVVRS) in locomotives to improve communication monitoring among train personnel.
Conclusion
- The CRS concluded that improved adherence to safety protocols, clear communication guidelines, and timely availability of equipment could have prevented this "accident-in-waiting."
Disciplinary Actions Initiated
- Following the CRS report, the Ministry of Railways has initiated disciplinary actions against employees found responsible for the accident.
Amendments to Rules and Procedures
- The Ministry has revised the General and Subsidiary Rules (G&SR) to prevent future lapses.
- Changes to the formats of books and forms related to automatic block section working have been implemented to eliminate ambiguities and ensure clear instructions for signal failure situations.
Safety Equipment Procurement and Replacement
- To address equipment shortages, the Ministry has ensured:
- Procurement and replacement of all defective walkie-talkie sets.
- Confirmation of no current shortages in safety equipment across Northeast Frontier (N.F.) Railway.
Enhanced Staff Training and Counselling
- Comprehensive training and counseling sessions have been conducted for frontline railway personnel, including:
- Station masters, loco pilots, loco inspectors, and train managers, to reinforce operational safety and adherence to updated protocols.
GS3/Defence & Security
HAWK Missile
Source: Money Control

Why in News?
It is up to the United States to decide what to do with Taiwan's decommissioned HAWK anti-aircraft missiles, the island's Defence Minister said recently.
Overview of HAWK Missile:
- The HAWK (Homing All the Way Killer) MIM-23 is an all-weather, low-to-medium altitude ground-to-air missile system.
- Developed by the American defense firm Raytheon, it was initially intended for aircraft destruction but later adapted to intercept missiles in flight.
- Entered service in 1960, the missile has undergone extensive upgrades to remain effective over the years.
- Although it was replaced by the MIM-104 Patriot in U.S. Army service by 1994, it continued to be used by some military branches until its final phase-out in 2002.
- The last user in the U.S. military was the US Marine Corps, which transitioned to the FIM-92 Stinger, a man-portable infrared-guided missile.
- The HAWK missile has seen widespread export and continues to be utilized by various nations, including NATO allies and countries across Asia and the Middle East.
Guidance System:
- It employs a Semi-Active Radar Homing (SARH) guidance system, allowing it to track and engage targets effectively.
Launch and Propulsion:
- Transported and launched from the M192 towed triple-missile launcher, the HAWK is powered by a dual-thrust motor that features both a boost phase for initial launch and a sustain phase for ongoing flight.
Operational Capability:
- Notably, the HAWK can engage multiple targets at the same time and operates effectively in various weather conditions.
- Despite its capabilities, the system is generally viewed as outdated when compared to more modern missile defense systems like the Patriot missile system.
GS3/Environment
What are Comb Jellies?
Source:Times of India
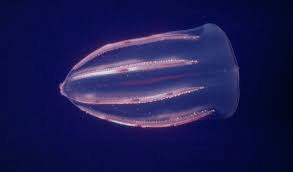
Why in News?
Comb jellies, scientifically known as ctenophore Mnemiopsis leidyi, have recently been studied for their remarkable ability to revert to earlier life stages, effectively defying aging.
About Comb Jellies:
- They are transparent, gelatinous invertebrates that inhabit the waters of the world's oceans.
- Considered one of the oldest multicellular animal groups, comb jellies may have existed for over 500 million years.
- Currently, there are between 100 and 150 recognized species, with the most familiar ones found near coastal areas.
Description
- Comb jellies are colorful and simple invertebrates that belong to the family Ctenophora.
- While species vary in size, the average length of a comb jelly is about four inches.
- They are named for their eight rows of cilia, which are fused together and resemble combs, aiding in their movement through water.
- These creatures are the largest known animals that utilize cilia for locomotion.
- Comb jellies possess two long, trailing tentacles that spread out to form a net-like structure, which helps them capture prey.
- The tentacles function as sticky lines, efficiently trapping food and drawing it towards their bodies.
- Structurally, comb jellies consist of two primary cell layers: the outer epidermis and the inner gastrodermis, with a gelatinous mesoderm in between.
- Many species exhibit bioluminescence, producing a beautiful blue or green glow when stimulated, such as by touch.
- They are carnivorous and opportunistic feeders, consuming a variety of organisms that drift into their vicinity.
- Unlike jellyfish, their close relatives, comb jellies lack stinging tentacles and pose no harm to humans.
|
39 videos|4566 docs|979 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 13th November 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the Sahyadri Tiger Reserve and its significance in India? |  |
| 2. What are the key objectives of the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010? |  |
| 3. What is the Long Range Land Attack Cruise Missile (LRLACM) and its purpose? |  |
| 4. What are the main agenda topics expected to be discussed at COP29 Climate Summit 2024? |  |
| 5. What was the Kanchanjunga Express collision, and what were its implications? |  |

































