International Relations: December 2024 UPSC Current Affairs | UPSC Mains: International Relations PDF Download
Celebrating Two Years of India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement Success

Why in News?
The India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (Ind-Aus ECTA) has marked two years of successful implementation, significantly enhancing economic collaboration between the two nations. As the agreement enters its third year, the Indian government is focused on maintaining this growth momentum to fulfill its Vision 2047 objective of transforming India into a developed nation.
Key Takeaways
- The ECTA has strengthened economic ties, benefitting growth, MSMEs, businesses, and employment.
- Over 90% of Australian goods exports to India will see reduced tariffs, with many becoming tariff-free.
- 96% of imports from India are now tariff-free, projected to reach 100% by 2026.
- The agreement aims for a bilateral trade target of AUD 100 billion by 2030.
Additional Details
- Impact on Trade: Bilateral merchandise trade surged from USD 12.2 billion in 2020-21 to USD 26 billion by 2022-23, indicating a robust growth trajectory.
- Sectoral Benefits: Key sectors benefiting from the ECTA include textiles, chemicals, and agriculture, with a notable increase in the export of garments to Australia.
- The agreement facilitates India's entry into the Australian market with competitive advantages over countries like Vietnam and Indonesia.
- Services Sector Expansion: Australia has committed to enhancing India's services in IT, health, education, and more, including visa opportunities for students and professionals.
Syrian Civil War and Future of Syria

Why in News?
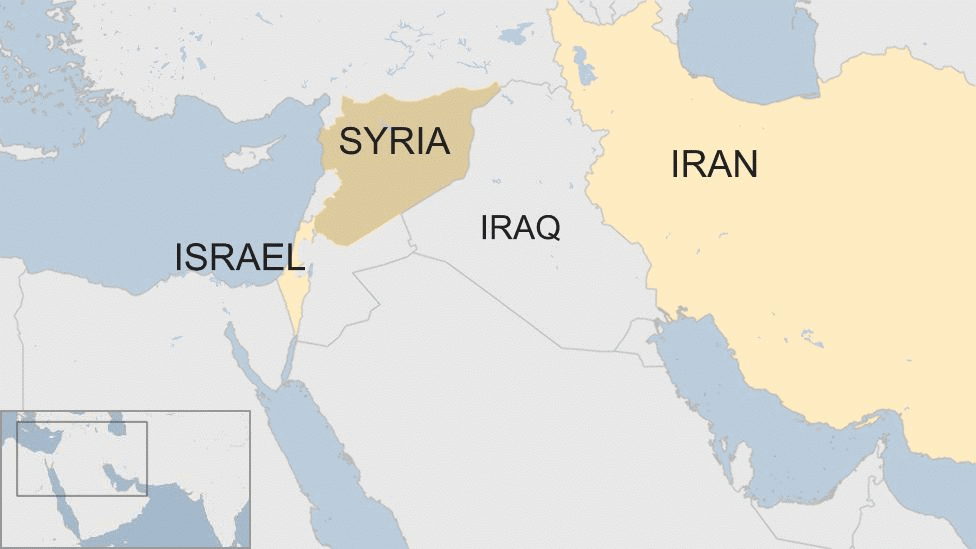
Recently, Syrian rebels, led by the Islamist militant group Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS), have claimed control of Homs, Syria’s third-largest city, marking a significant blow to President Bashar al-Assad’s regime. This development, amidst the ongoing civil war, raises concerns about the future of Syria, as it faces escalating challenges from various rebel factions.
Key Takeaways
- Syria has been under the Assad family's rule since 1971, with Bashar al-Assad succeeding his father.
- The Arab Spring protests in 2011 were met with violent repression, escalating into a civil war.
- Multiple rebel factions, including HTS and the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF), have emerged, each with different goals.
- Foreign influence is significant, with countries like Russia and Iran supporting Assad, while the US and Turkey back anti-Assad factions.
- The humanitarian crisis has led to millions of refugees, creating one of the largest displacements in modern history.
Additional Details
- Historical Context: Since 1971, Syria has been ruled by the Assad family, with authoritarian governance leading to widespread grievances among the population.
- Arab Spring Uprising: The protests against Assad in 2011 were fueled by issues like unemployment, economic inequality, and corruption.
- Rise of Rebel Factions: Various groups, including HTS and the Free Syrian Army (FSA), have sought to challenge Assad’s regime, each supported by different foreign powers.
- Foreign Influence: Countries like Russia and Iran have provided military support to Assad, while the US and Turkey have backed opposition factions, complicating the conflict.
- Future of India-Syria Relations: India maintains historical ties with Syria, emphasizing a peaceful and inclusive political process while safeguarding its interests.
- The fall of Assad's regime is a pivotal moment in the Syrian Civil War, yet the path to peace remains uncertain. The rise of HTS and ongoing foreign influence presents challenges for Syria's future governance and stability.
- India must navigate its historical relations with Syria while ensuring the safety of its citizens and strategic interests.
India-Japan Forum 2024

Why in News?
Recently, during a meeting in New Delhi, the External Affairs Minister (EAM) of India highlighted the potential for a strategic semiconductor alliance between India and Japan.
Key Takeaways
- India and Japan are revitalizing their semiconductor industries to enhance global supply chain resilience.
- Collaboration with Taiwan aims to mitigate supply chain risks and reduce dependence on China.
- This partnership supports India's semiconductor mission and Japan's revitalization efforts, focusing on reducing strategic vulnerabilities and fostering technological autonomy.
- The cooperation aligns with broader Indo-Pacific strategies to counter Chinese dominance in critical supply chains.
Additional Details
- Quad's Growth: The EAM recognized the Trump administration (2017 to 2021) for reviving and expanding the Quad (India, Japan, Australia, US).
- The Quad's inclusive "fair share" approach to burden-sharing enhances resilience to alliance and commitment concerns, evolving into a platform for extensive intergovernmental cooperation.
- Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad): A strategic forum aimed at promoting regional security and economic cooperation in the Indo-Pacific.
- The Quad addresses regional security, counters China’s assertiveness, promotes economic growth, and improves maritime security.
- Origins: The Quad was initiated after the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami, where the US, Japan, India, and Australia provided humanitarian aid. It was formally established in 2007 but went dormant in 2008 before being revived in 2017.
- It functions through summits, joint military drills, and economic initiatives, but it lacks a formal structure like NATO.
- For India, Quad offers strategic and economic benefits, particularly in countering China and enhancing security; however, challenges include imbalanced cooperation and geopolitical tensions with China.
- The India-Japan Forum 2024 exemplifies the strengthening ties and strategic partnerships between nations in the Indo-Pacific region, particularly as they seek to enhance mutual resilience against global supply chain challenges and assertive geopolitical dynamics.
40th Charter Day of SAARC

Why in News?
On 8 December 2024, the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) celebrated its 40th Charter Day. This day is observed annually to honor the founding of SAARC.
Key Takeaways
- SAARC was established on December 8, 1985, in Dhaka, Bangladesh, with 7 founding members.
- Afghanistan became the 8th member in 2007.
- SAARC aims to promote welfare, accelerate economic growth, and enhance collaboration among member states.
Additional Details
- Origins of SAARC: The idea of regional cooperation in South Asia was first discussed in the late 1940s and early 1950s, culminating in the formal proposal by Bangladesh's President Ziaur Rahman in 1980.
- Objectives: The primary goals of SAARC include improving the quality of life in South Asia and fostering mutual trust among its members.
- Key Principles: SAARC operates on principles of sovereign equality, non-interference, and consensus-based decision-making.
- Significance of SAARC: As of 2021, SAARC represents 3% of the world's land area, 21% of the population, and 5.21% of the global economy.
Relevance of SAARC in Today’s Context
- Platform for Dialogue: Despite challenges, SAARC remains a vital platform for dialogue among South Asian countries.
- Shared Regional Solutions: The association has shown its utility during crises, coordinating efforts like the Covid-19 Emergency Fund.
- Potential for Economic Integration: With a combined GDP over USD 4 trillion, SAARC has significant untapped economic potential.
- Avoiding Overdependence on External Frameworks: SAARC enables member nations to control their development, rather than relying on external entities.
India’s Contribution to SAARC
- SAARC Summits: India has hosted three of the eighteen SAARC Summits, demonstrating its leadership role in the organization.
- Technological Cooperation: Initiatives like the National Knowledge Network and South Asian Satellite showcase India’s commitment to regional technological advancement.
- Currency Swap Arrangement: India’s establishment of a USD 400 million currency swap for SAARC members enhances financial cooperation.
- Disaster Management: India supports disaster risk management across SAARC countries through its Interim Unit for the SAARC Disaster Management Center.
- South Asian University (SAU): Established to provide educational opportunities to students from SAARC nations.
Key Challenges Facing SAARC
- Political Tensions: Bilateral conflicts, particularly between India and Pakistan, hinder cooperation.
- Low Economic Integration: Intra-regional trade is only 5% of total trade, indicating significant room for improvement.
- Asymmetric Development: India's dominance leads to mistrust among smaller nations, affecting collective action.
- Institutional Weaknesses: The requirement for unanimous agreement can stall progress on critical issues.
- External Influences: China's increasing influence through initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative complicates regional dynamics.
Way Forward
- Promoting Economic Cooperation: Accelerate the operationalization of agreements like SATIS and expand the SAARC Development Fund.
- Resolving Political Conflicts: Implement mediation mechanisms and promote Track-II diplomacy to ease tensions.
- Leveraging Sub-regional Groupings: Utilize initiatives like BBIN and BIMSTEC to supplement SAARC's objectives.
- Combating Non-traditional Security Threats: Enhance cooperation on counter-terrorism and intelligence-sharing.
- Reform Institutional Mechanisms: Consider moving to a weighted voting system to facilitate decision-making.
- Encouraging Youth Participation: Foster student exchanges and development programs that utilize the region's youthful population.
BRICS Nations Explore Alternative Currencies
Why in News?
- At the 16th BRICS summit in October 2024, member countries talked about using more local currencies in trade or creating a new BRICS currency to lessen dependence on the US dollar.
- In response, US President-elect Donald Trump warned that BRICS nations could face 100% import tariffs if they support a currency to replace the US dollar as the main global reserve currency.
- India confirmed its strong economic relationship with the US, stating it does not plan to undermine the US dollar.
Why are BRICS Nations Exploring Alternative Currencies?
- Reducing Transaction Costs: Using local currencies can lower transaction costs by avoiding the need for other foreign currencies, which makes trading more efficient among BRICS countries.
- Dominance of the Dollar: The US dollar is involved in over 90% of global trade and is crucial for international reserves. Heavy reliance on the dollar means countries are affected by US monetary policies, potentially causing economic instability.
- Many BRICS countries, especially those from the Global South, find it hard to access major currencies like the dollar, which affects their ability to import goods and trade internationally. Using local currencies can help them grow their markets and improve trade within the group.
- Political Motivations: Countries are also looking to local currencies to avoid the impact of US financial sanctions. For instance, the US has blocked Russia and Iran from the SWIFT system, pushing them to find alternatives for trade.
- Geopolitical Reasons: Nations such as Brazil and Russia want more independence from US influence by promoting currencies like the yuan and rouble or even considering a unified BRICS currency.
- As countries like China grow, they become important trading partners, encouraging the use of alternative currencies for trade.
Trade in Local Currencies
- China's Approach: China has encouraged the use of its currency through bilateral currency swap agreements, like its trade with Ethiopia.
- A bilateral currency swap agreement is when two central banks agree to exchange a specific amount of one currency for another.
- China's barter trade model allows it to trade goods with African countries using local currencies, which are then converted to renminbi supporting its currency's international use.
- Southern Africa: The South African Rand is important for trade in the Southern African Customs Union, where countries like Namibia, Botswana, Lesotho, and Eswatini use it alongside their currencies.
- India-Russia: Due to US sanctions, India and Russia have started trading in their local currencies (the rupee and rouble), with 90% of their bilateral trade now in these currencies or others.
What are the Potential Risks of Moving Away from the US Dollar?
- Chinese Domination: Reducing reliance on the US dollar raises concerns about increased Chinese economic power. China wants a larger role for the yuan in global trade, especially with other BRICS nations.
- Implementation Challenges: Creating a BRICS currency or using local currencies faces issues, such as banking concerns due to US sanctions, which makes large-scale adoption difficult.
- Many BRICS currencies are not widely used globally, which limits their effectiveness for trade.
- Countries that export more than they import may struggle to get foreign currencies for trade, complicating the use of local currencies.
- Liquidity Issues: The US dollar is very liquid and widely accepted, while alternatives may not have the same level of acceptance, making international transactions harder.
- Volatility and Exchange Rate Risks: Countries may face increased exchange rate instability during the shift away from the dollar, especially if they have less stable financial markets. This can disrupt trade and investment.
What are the Potential Impacts of a 100% US Tariff on BRICS Imports?
- Impact on Global Trade: Such tariffs could push BRICS nations to increase trade among themselves, speeding up the move away from the dollar.
- This could lead to more trade with non-US markets, reducing US influence on global trade and possibly increasing the use of other reserve currencies like the Australian dollar and Chinese renminbi.
- Impact on the US: A 100% tariff on BRICS imports could hurt the US economy by raising import costs, potentially driving imports to third-party countries.
- This situation could lead to higher prices for American consumers without significantly boosting US manufacturing.
- BRICS nations might respond with their own tariffs on US goods, escalating trade tensions and affecting global trade dynamics.
- The US's economic strength is linked to the dollar's role in trade. Increased use of alternatives could weaken its financial power and require the US to adjust to a more diverse global market.
What are India's Initiatives to Improve Trade in Local Currencies?
- Internationalizing the Rupee: In 2022, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) allowed trade invoicing and payments in Indian rupees, particularly with Russia, as a response to US sanctions.
- Initiatives like digital payment systems such as UPI aim to promote the use of the rupee internationally.
|
88 videos|123 docs
|
















