Science and Technology: December 2024 Current Affairs | Current Affairs & General Knowledge - CLAT PDF Download
The Environmental Impact of Space Activities

Why in News?
The increasing use of space technologies for climate monitoring and other essential functions has raised significant concerns regarding their environmental effects, particularly related to satellite interference and orbital debris.
Key Takeaways
- As of September 2024, there have been approximately 6,740 rocket launches resulting in 19,590 satellites being placed into orbit.
- Out of the satellites launched, around 13,230 remain in space, with 10,200 still functioning.
Additional Details
- Climate Footprint: This term refers to the total amount of greenhouse gases (GHGs) emitted into the atmosphere due to human activities. It serves as a measure of how much a specific activity contributes to global warming and climate change.
- Environmental Impact of Space Activities:
- Emissions of Greenhouse Gases: Every rocket launch releases carbon dioxide, black carbon, and water vapor, which contribute to global warming.
- Black Carbon’s Role: Black carbon can absorb sunlight 500 times more effectively than carbon dioxide, significantly amplifying the warming effect.
- Growing Commercial Launches: The increasing frequency of rocket launches exacerbates the cumulative emissions' impact on the climate.
- Ozone Layer Depletion: Certain rocket propellants can deplete the ozone layer at high altitudes, increasing ultraviolet radiation exposure on Earth and affecting atmospheric circulation.
- Harmful Satellite Debris: When satellites burn up upon re-entry, they can release "satellite ash" that disrupts atmospheric composition and climate patterns.
Concerns about Orbital Debris
- Orbital debris, or space junk, consists of defunct satellites, spent rocket stages, and fragments from satellite break-ups in low Earth orbit (LEO).
- Scale of the Problem:
- Over 650 fragmentation events have been recorded.
- The total mass of all objects in orbit exceeds 13,000 tonnes.
- Debris travels at speeds up to 29,000 km/hr, posing a significant threat.
The presence of non-functional objects in orbit constitutes a form of pollution and increases the risk of collisions, which generate even more debris.
Risks to Space Missions
- Satellite Damage: High-speed collisions can destroy crucial satellite components essential for communication and climate monitoring.
- Increased Costs: Satellite operators must invest in shielding technologies and costly maneuvers to avoid collisions.
- Threat to the ISS: The International Space Station frequently adjusts its orbit to evade debris, highlighting risks to human missions.
Barriers to Space-Sector Sustainability
- Absence of Clear Guidelines: The space sector lacks comprehensive international regulations to control emissions and manage debris.
- Insufficient International Cooperation: Collaboration through organizations like COPUOS is essential to establish binding sustainability standards.
- India aims to contribute to long-term space sustainability by implementing debris-free space missions by 2030, ensuring compliance with international guidelines.
Measures for Sustainable Space Exploration
- Adoption of Reusable Rockets: Companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin are working on reusable rockets to reduce manufacturing waste and costs.
- Transition to Cleaner Fuels: Cleaner alternatives such as liquid hydrogen can help reduce harmful emissions, though their production may rely on non-renewable energy.
- Use of Biodegradable Materials: Designing satellites with biodegradable materials could prevent long-term debris accumulation.
Innovative Strategies in Malaria Prevention
Why in News?
Recent advancements in malaria prevention have shifted focus from genetically modified mosquitoes to genetically modified malaria-causing parasites. This innovative approach aims to enhance immune system priming during the liver stage of the parasite's life cycle, potentially leading to more effective vaccines.
Key Takeaways
- The focus of malaria prevention is moving towards genetically modified parasites instead of mosquitoes.
- This new method enhances immune system priming in the liver, which may lead to improved vaccine efficacy.
- Trial results indicate a significant difference in protection levels between modified parasites.
- Traditional methods require much higher exposure for similar protection levels.
Additional Details
- Genetically Modified Parasites: Malaria-causing parasites have been genetically altered to study behaviors that can prevent diseases or deliver treatments. These modifications are designed to prime the immune system in the liver, effectively stopping the disease before the parasites enter the bloodstream.
- Infection symptoms from malaria typically appear only after the parasites transition from the liver to the bloodstream, making early intervention crucial for effective prevention.
- Immune Priming: This process occurs when a host enhances its immune defenses following an initial exposure to pathogens, leading to better protection during subsequent infections.
- Trial Efficacy: In trials, 89% of participants exposed to late-arresting genetically modified parasites (specifically P. falciparum) were protected from malaria, compared to only 13% for early-arresting parasites.
- Early-arresting parasites are killed on day 1 of entering the liver, while late-arresting parasites are eliminated on day 6, demonstrating a marked difference in efficacy.
- Traditional methods such as radiation-sterilized mosquitoes and radiation-attenuated sporozoites require up to 1,000 mosquito bites for comparable protection levels.
Axiom-4 Mission
Why in News?
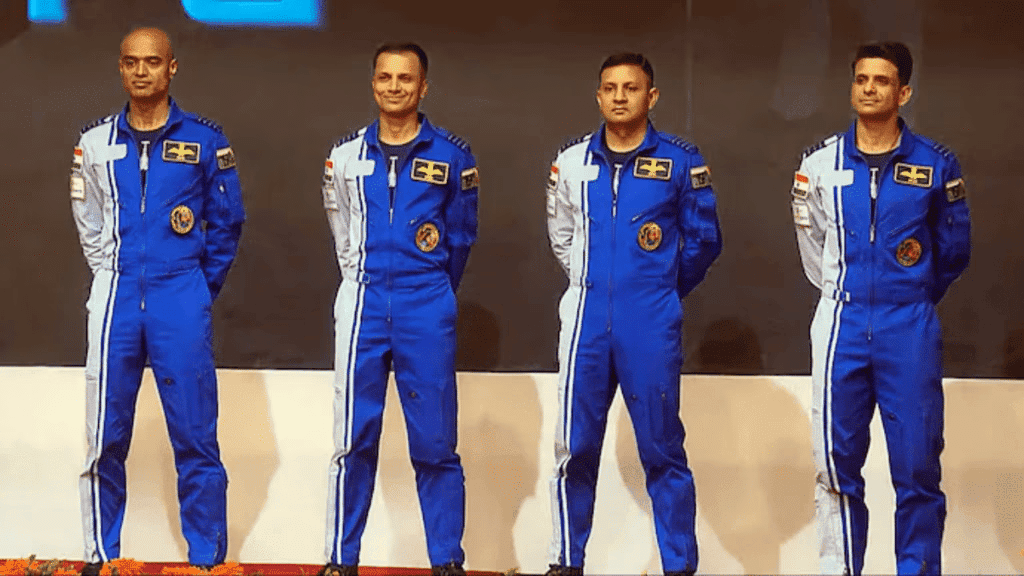
Recently, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) announced that two Indian astronauts selected for the Axiom-4 mission, which is set to launch in 2024, have successfully completed the initial phase of their training. The astronauts are Prime-Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla and Backup-Group Captain Prasanth Balakrishnan Nair.
Key Takeaways
- The Axiom-4 mission is a private spaceflight to the International Space Station (ISS) operated by Axiom Space.
- It will utilize the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft, which is reusable and designed for transporting astronauts.
- This mission marks the fourth collaboration with NASA, following Axiom Missions 1, 2, and 3.
Additional Details
- Axiom Mission 4 (Ax-4): This mission aims to enable commercial space initiatives such as space tourism and to demonstrate the viability of commercial space stations for research and business.
- International Collaboration: The mission emphasizes global cooperation in space exploration by featuring a diverse multinational crew, thereby strengthening international partnerships.
- Research and Development: It will support scientific experiments in microgravity, focusing on areas like materials science and biology, which could lead to significant breakthroughs.
- Mission Duration: The expected duration is 14 days, during which the crew will conduct experiments, technology demonstrations, and educational outreach aboard the ISS.
- Commercial Space Station Development: Axiom-4 is part of Axiom Space's vision to create the first commercial space station, transitioning from current ISS operations to an independent orbital platform.
- Significance for India: This mission represents a crucial collaboration between India and NASA, enhancing India's presence in space exploration and fostering the development of human spaceflight capabilities.
ecDNA Challenging Genetics Principles
Why in the News?
A recent study published in Nature has revealed that extrachromosomal DNA (ecDNA) is found in about 50% of cancer types. It plays a crucial role in how tumors develop and their genetic diversity.
What is ecDNA?
- ecDNA refers to extrachromosomal DNA, which is a small, circular form of DNA located in the cell nucleus, distinct from normal chromosomes.
- It forms when DNA fragments detach from chromosomes, typically due to damage or mistakes during cell division.
- ecDNA can carry additional copies of oncogenes, which are genes that encourage cancer growth.
- Though it was previously considered unimportant, new research indicates that it significantly impacts cancer.
How ecDNA Contributes to Cancer and Drug Resistance
- Promotes Tumor Growth: ecDNA includes extra copies of oncogenes that enable cancer cells to grow more rapidly and aggressively.
- Increases Drug Resistance: The additional oncogenes make it tougher to treat cancer with standard medications as they generate more harmful proteins.
- Accelerates Tumor Evolution: ecDNA allows cancer cells to change quickly, enhancing their resistance to treatments like chemotherapy and helping tumors to continue growing even with medication.
How ecDNA Challenges Genetics Laws
- Mendel’s Law states that genes on different chromosomes are inherited independently, meaning they are passed on randomly to the next generation.
- However, ecDNA contradicts this principle by grouping genes together and passing them on as a cluster during cell division.
- This process enables cancer cells to easily inherit advantageous genes, promoting faster tumor growth.
- Unlike regular chromosomes, which are distributed randomly during cell division, ecDNA is inherited as a package.
- This mechanism provides cancer cells with an advantage by ensuring they receive beneficial genetic combinations that aid in cancer growth and resistance to treatments.
Global Cooperation in Space Debris Management

What is Space Debris?
- Space debris, also called space junk, includes any unused or discarded objects made by humans in space.
- These can be large items like defunct satellites or smaller pieces like fragments and paint flakes that come off rockets.
- The majority of space debris is made up of materials from rocket launches and inactive satellites.
- Most of this debris is found in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), which is within 2,000 kilometers of Earth, while some can be found in higher orbits like the Geostationary Orbit at 35,786 kilometers above the equator.
Sources of Space Debris
- According to the ESA's Space Environment Report 2022, there are over 30,000 pieces of space debris tracked regularly.
- About 200,000 pieces of micro debris (1 to 10 cm in size) exist, with millions of even smaller fragments.
- There are around 34,000 objects larger than 10 cm.
- As of 2022, there were about 6,718 active satellites in orbit, an increase of nearly 2,000 from the previous year.
Causes of Space Debris
The rise in space debris is largely due to increased human activities in space, particularly:
- Launching objects into space: The number of satellites being sent into orbit has rapidly increased. For example, SpaceX's Starlink satellites make up half of all active satellites.
- Abandoned satellites: Many satellites become inactive after their missions end, adding to the space junk.
- Approximately 3,000 decommissioned satellites are currently in space, according to the Natural History Museum.
- Anti-satellite tests: Countries like the USA, China, and India have conducted tests that intentionally destroy their satellites, creating debris. For instance, China's 2007 test increased trackable debris by 25%.
- Growing expansion: The space industry is expanding, with significant investments in exploration from both public and private sectors.
- Long-lasting debris: Debris from satellites in LEO might eventually fall back to Earth, but debris at higher altitudes can stay in orbit much longer.
- Fragmentation: Collisions, explosions, and decay often break debris into smaller pieces, which contributes to the growing problem.
Threats and Challenges from Space Debris
While space debris is not an immediate disaster, it poses serious risks and challenges:
- Satellite danger: Debris can collide with working satellites, causing damage or destruction. The Russian Cosmos-1275 satellite was damaged by debris in 1981, and in 2013, the U.S. GOES-13 satellite was destroyed.
- Kessler Syndrome: More debris raises the chances of collisions, which can lead to a chain reaction making Earth's orbit unusable.
- Limitations on future activities: The issue may reduce available orbital slots, complicating new missions.
- Space station risks: Space debris threatens the safety of astronauts on space stations. NASA has had to adjust the ISS's orbit 32 times since 1999 to avoid debris.
- Space pollution: The accumulation of debris raises environmental concerns for future explorations.
- International tensions: As more countries engage in space activities, disputes over responsibility for debris and damages may arise.
Space Debris Removal Initiatives
Addressing space debris is crucial for the safety of active satellites and sustainable space operations:
International Initiatives:
- Space Industry Debris Mitigation Recommendations: Operators of LEO spacecraft should aim for a post-mission disposal success rate of 95-99%.
- Collision Avoidance Measures: Operators should use technology to minimize collision risks with debris.
- Data Sharing: Space agencies should share satellite movement data to improve traffic management in orbit.
- Incentives for Long-Term Missions: Insurance organizations could promote sustainable practices in space activities.
- Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC): Formed in 1993, this international body coordinates efforts regarding space debris.
- Committee on Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS): A UN committee created in 1958 for governing space exploration.
- Clean Space Initiative: Launched by the ESA in 2012 to ensure a sustainable space environment.
- Clearspace-1: The first mission planned to remove debris from orbit is set for launch in 2026.
- Liability Convention of 1972: This convention holds launching states liable for damages caused by their space objects.
- Remove DEBRIS: A program focused on demonstrating technologies for removing space debris.
- Outer Space Treaty: Established guidelines for activities in space since 1967.
India's Initiatives for Space Debris Removal
India is taking steps to tackle space debris:
- ISRO System for Safe & Sustainable Operations Management (IS4OM): Launched in 2022, this system ensures the safety of space assets and monitors potential collision threats.
- Project Netra: An early warning system by ISRO to detect space debris and threats to Indian satellites, capable of tracking objects as small as 10 cm.
- Collision Avoidance Manoeuvres: In 2022, ISRO performed 21 maneuvers to avoid collisions.
- ISRO SSA Control Centre: Established in 2020 to coordinate space situational awareness activities in India.
Measures Needed to Tackle Space Debris
Addressing space debris is a complex issue requiring combined efforts:
- Enhanced awareness: Improving observation technology and tracking models for better monitoring of space debris.
- Improved coordination: Establishing new methods to manage increasing traffic in orbit.
- Minimizing space debris growth: Encouraging the use of reusable launch vehicles to reduce new debris.
- Debris mitigation and active removal: Collecting and moving non-functional debris to lower orbits for faster deorbiting. Technologies like harpoons and lasers are being considered for capturing debris.
- Adherence to international guidelines: Space operators should follow guidelines for debris mitigation more closely.
|
125 videos|815 docs|33 tests
|
|
125 videos|815 docs|33 tests
|



















