Case Based Questions: Acids, Bases, and Salts | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Q1: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
Rahul conducted an experiment in the lab where he added sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution to a test tube containing zinc granules. He then warmed the solution and noticed bubbles forming. He passed the gas through a soap solution, collected it in an inverted test tube, and brought a burning matchstick close to it. A ‘pop’ sound was heard.
(a) Identify the gas produced and write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction. (1 mark)
(b) What is the role of NaOH in this reaction? (2 marks)
(c) Name another base that can react with zinc to produce the same gas. (1 mark)
OR
(c) Why do only some metals react with bases while others do not? (1 mark)
Ans:
(a) The gas evolved is hydrogen (H₂).
Balanced equation:
2NaOH + Zn → Na₂ZnO₂ + H₂↑
(b) NaOH acts as a strong base, reacting with zinc to form sodium zincate (Na₂ZnO₂) and hydrogen gas.
(c) Potassium hydroxide (KOH) also reacts with zinc to produce hydrogen gas.
OR
(c) Only amphoteric metals like zinc and aluminum react with bases because they can form complex salts with hydroxides.
Q2: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
A science teacher gave five unknown solutions P, Q, R, S, and T to students and asked them to test their pH using universal indicator. The results were: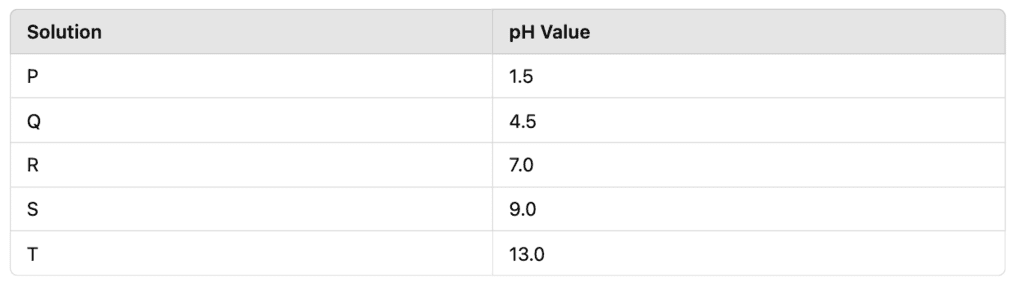
(a) Identify which solution is strongly acidic, weakly acidic, neutral, weakly basic, and strongly basic. (1 mark)
(b) Which solution has the highest concentration of H⁺ ions? Arrange them in increasing order of basicity. (2 marks)
(c) Which of these solutions could be used to neutralize an acid spill in a laboratory? (1 mark)
OR
(c) Why does a higher pH indicate a stronger base? (1 mark)
Ans:
(a)
- P = Strongly acidic
- Q = Weakly acidic
- R = Neutral
- S = Weakly basic
- T = Strongly basic
(b) Increasing order of basicity: P (1.5) < Q (4.5) < R (7.0) < S (9.0) < T (13.0)
(c) Solution T (pH 13.0) is strongly basic and can neutralize an acid spill.
OR
(c) A higher pH means a lower concentration of H⁺ ions and a higher concentration of OH⁻ ions, making it a stronger base.
Q3: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
An environmentalist explained that acid rain occurs when industrial gases like sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NO₂) dissolve in water vapor in the atmosphere, forming acids. This rain lowers the pH of soil and water bodies, harming aquatic life and plants.
(a) Identify the acids responsible for acid rain and write the balanced chemical equation for their formation. (1 mark)
(b) How does acid rain affect aquatic life and plant growth? (2 marks)
(c) Suggest one method to reduce acid rain. (1 mark)
OR
(c) How does the pH of rainwater indicate whether it is acidic or neutral? (1 mark)
Ans:
(a) Acids responsible: Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) and nitric acid (HNO₃)
Equations:
SO₂ + H₂O → H₂SO₃ (Sulfurous acid)
NO₂ + H₂O → HNO₃ (Nitric acid)
(b) Acid rain lowers soil pH, reducing nutrient availability for plants. It also makes water bodies too acidic, harming fish and aquatic organisms.
(c) Reducing industrial emissions of SO₂ and NO₂ by using scrubbers in factories can help.
OR
(c) If rainwater has a pH below 5.6, it is acidic. A pH of 7.0 indicates neutral rainwater.)
Q4: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
A student found a white crystalline powder at home, commonly used for cooking. He tested its pH and found it to be slightly basic. When he heated it, it released a gas that turned lime water milky.
(a) Identify the substance and write the reaction that takes place upon heating. (1 mark)
(b) Why does the gas turn lime water milky? (2 marks)
(c) What are two common uses of this substance? (1 mark)
OR
(c) Why is this substance used as an antacid? (1 mark)
Ans:
(a) The substance is baking soda (NaHCO₃).
Reaction on heating:
2NaHCO₃ → Na₂CO₃ + H₂O + CO₂↑
(b) The gas carbon dioxide (CO₂) reacts with lime water (Ca(OH)₂) to form calcium carbonate (CaCO₃), which appears as a white precipitate.
Equation:
Ca(OH)₂ + CO₂ → CaCO₃ (white ppt) + H₂O
(c) Uses:
- Used in baking to make cakes and bread fluffy.
- Used in fire extinguishers.
OR
(c) It is used as an antacid because it neutralizes excess stomach acid, providing relief from acidity.
Q5: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
Riya was testing the pH of different salt solutions and found that one solution turned red litmus blue and had a pH of 10.5. She concluded that this salt was derived from a strong base and a weak acid.
(a) Identify the salt and write its dissociation reaction in water. (1 mark)
(b) Explain why the salt solution is basic in nature. (2 marks)
(c) What would be the expected pH of a salt formed from a strong acid and a strong base? (1 mark)
OR
(c) Why does ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl) solution show acidic properties? (1 mark)
Ans:
(a) The salt is sodium carbonate (Na₂CO₃).
Dissociation reaction:
Na₂CO₃ → 2Na⁺ + CO₃²⁻
(b) The carbonate ion (CO₃²⁻) hydrolyzes in water, producing OH⁻ ions, making the solution basic.
(c) A salt from a strong acid and a strong base (e.g., NaCl) has a neutral pH (around 7.0).
OR
(c) NH₄Cl comes from a strong acid (HCl) and a weak base (NH₄OH), making it acidic in nature.
Q6: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
A doctor used a white powder to make a cast for a patient’s fractured hand. The powder was mixed with water and quickly hardened into a solid. Later, the doctor explained that this substance is commonly used for making molds, sculptures, and smooth wall surfaces.
(a) Identify the substance and write its chemical formula. (1 mark)
(b) Write the chemical reaction that occurs when it is mixed with water. (2 marks)
(c) Why should this substance be stored in a moisture-proof container? (1 mark)
OR
(c) What is the role of temperature in the formation of this substance? (1 mark)
Ans:
(a) The substance is Plaster of Paris (POP).
Chemical formula: CaSO₄·½H₂O
(b) Reaction with water:
CaSO₄·½H₂O + 1½H₂O → CaSO₄·2H₂O
(Plaster of Paris) → (Gypsum - hard solid)
(c) POP absorbs moisture and gets converted to gypsum, making it unusable.
OR
(c) POP is formed by heating gypsum at 373K; excess heating makes it anhydrous, losing its setting property.
Q7: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
A chemical industry produces three important products: chlorine, hydrogen, and sodium hydroxide by passing electricity through brine (NaCl solution). These products are used in various industries, including paper, textiles, and water purification.
(a) Identify the process and write the balanced chemical equation. (1 mark)
(b) Name one use of each product formed in this process. (2 marks)
(c) Why is this process called the chlor-alkali process? (1 mark)
OR
(c) Which product of this process is used in disinfecting drinking water? (1 mark)
Ans:
(a) The process is called the Chlor-Alkali Process.
Balanced equation:
2NaCl + 2H₂O → 2NaOH + Cl₂ + H₂
(b) Uses of products:
- NaOH: Used in soap and paper industries.
- Cl₂: Used for water purification.
- H₂: Used in making ammonia for fertilizers.
(c) This process is called Chlor-Alkali because it produces chlorine (Chlor) and sodium hydroxide (Alkali).
OR
(c) Chlorine gas (Cl₂) is used in disinfecting drinking water.
Q8: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
Reema was conducting an experiment where she tested different household substances using turmeric, red litmus, blue litmus, and phenolphthalein. She observed:
- Lemon juice turned blue litmus red
- Soap solution turned turmeric paper red
- Milk had no effect on any indicator
- Phenolphthalein remained colorless in vinegar but turned pink in baking soda solution
(a) Identify which substances are acidic, basic, and neutral. (1 mark)
(b) Explain why turmeric changes color in a basic solution but not in an acidic one. (2 marks)
(c) What would happen if we add lemon juice to baking soda solution? (1 mark)
OR
(c) Why do some indicators like phenolphthalein change color only in bases? (1 mark)
Ans:
(a)
- Lemon juice = Acidic
- Soap solution = Basic
- Milk = Neutral
- Baking soda = Basic
(b) Turmeric is yellow in acids and neutral solutions but turns red in bases due to the reaction with OH⁻ ions.
(c) Lemon juice (acid) reacts with baking soda (base), leading to neutralization and the evolution of carbon dioxide gas (CO₂).
OR
(c) Phenolphthalein is colorless in acids but pink in bases because it reacts only with OH⁻ ions.)
Q9: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
Ravi’s mother complained of acidity and stomach pain after eating spicy food. The doctor prescribed an antacid containing magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)₂), which helped her feel better. The doctor explained that too much HCl in the stomach can cause discomfort.
(a) Why does an antacid help in relieving acidity? (1 mark)
(b) Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between magnesium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid. (2 marks)
(c) Why does milk of magnesia act as a better antacid than baking soda? (1 mark)
OR
(c) Why is pH important in digestion? (1 mark)
Ans:
(a) Antacids like magnesium hydroxide neutralize excess stomach acid (HCl), relieving acidity.
(b) Balanced equation:
Mg(OH)₂ + 2HCl → MgCl₂ + 2H₂O
(c) Milk of magnesia (Mg(OH)₂) is a mild base and does not disturb the stomach’s natural pH, whereas baking soda (NaHCO₃) may cause excess CO₂ formation, leading to bloating.
OR
(c) The stomach maintains a pH of 1.5-3.5 to activate digestive enzymes like pepsin, which require an acidic environment.
Q10: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
In a factory visit, students observed the manufacture of a white crystalline solid used for removing hardness of water. The guide explained that this compound is a hydrated salt, which forms a solution with a pH greater than 7.
(a) Identify the compound and write its chemical formula. (1 mark)
(b) Write the reaction for the formation of this compound from sodium carbonate. (2 marks)
(c) Why does this compound help in removing water hardness? (1 mark)
OR
(c) What happens when this compound is heated strongly? (1 mark)
Ans:
(a) The compound is washing soda (sodium carbonate decahydrate, Na₂CO₃·10H₂O).
(b) Formation reaction:
Na₂CO₃ + 10H₂O → Na₂CO₃·10H₂O
(c) Washing soda removes water hardness by precipitating calcium and magnesium ions as insoluble carbonates.
OR
(c) On strong heating, it loses water of crystallization and becomes anhydrous sodium carbonate (Na₂CO₃).
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Case Based Questions: Acids, Bases, and Salts - Science Class 10
| 1. What are acids and bases, and how do they differ from each other? |  |
| 2. What is the pH scale, and why is it important for acids and bases? |  |
| 3. What are some common examples of acids, bases, and salts found in everyday life? |  |
| 4. How do neutralization reactions work between acids and bases? |  |
| 5. What safety precautions should be taken when handling acids and bases? |  |






















