Q1: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
A teacher demonstrated an experiment in class where she took different samples of iron, copper, sulfur, and graphite. She performed the following tests:
- Striking the samples with a hammer to test malleability.
- Drawing them into wires to check ductility.
- Testing their ability to conduct electricity by connecting them to a circuit.
- Observing their appearance before and after rubbing with sandpaper to check for metallic lustre.
(a) Identify which of the given substances are metals and non-metals based on tests done and also give observation table. (1 mark)
(b) From above samples which non-metal is a good conductor of electricity? (2 marks)
(c) Name two metals that are poor conductors of heat. (1 mark, )
Ans:
(a) Iron and copper = Metals, Sulfur and graphite = Non-metals (based on malleability, ductility, and conductivity).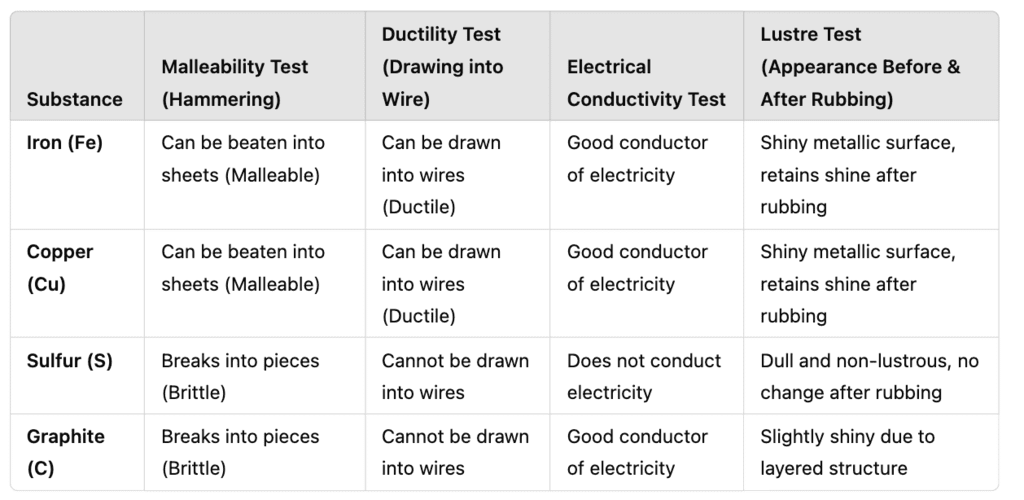
(b) Graphite is a good conductor of electricity because it has free-moving electrons in its layered structure.
(c) Lead and mercury are poor conductors of heat.
Q2: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
Riya conducted an experiment where she burned magnesium ribbon and sulfur powder in separate test tubes and dissolved the products in water. She then tested both solutions with red and blue litmus papers.
- Magnesium oxide turned red litmus blue.
- Sulfur dioxide turned blue litmus red.
(a) Identify the nature of the products formed when magnesium and sulfur burn in oxygen. (1 mark)
(b) Write the balanced chemical equations for both reactions. (2 marks)
(c) Name a metal oxide that shows both acidic and basic properties. (1 mark)
OR
(c) What happens when sodium is exposed to air? (1 mark)
Ans:
(a) Magnesium oxide (MgO) is basic, and sulfur dioxide (SO₂) is acidic.
(b) Balanced equations:
- Magnesium: 2Mg + O₂ → 2MgO
- Sulfur: S + O₂ → SO₂
(c) Aluminium oxide (Al₂O₃) and zinc oxide (ZnO) are amphoteric oxides (show both acidic and basic properties).
OR
(c) Sodium reacts violently with oxygen, forming sodium oxide (Na₂O) and must be stored in kerosene to prevent accidental ignition.
Q3: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
Aryan added sodium, calcium, and iron to separate beakers containing cold water. He observed that:
- Sodium reacted violently, producing heat and gas.
- Calcium reacted moderately, forming bubbles and a cloudy solution.
- Iron did not react with cold water.
(a) Identify the gases evolved in these reactions. (1 mark)
(b) Write the balanced equations for the reaction of sodium and calcium with water. (2 marks)
(c) Why does iron not react with cold water but react with steam? (1 mark)
OR
(c) Why is calcium stored in an air-tight container? (1 mark)
Ans:
(a) Hydrogen (H₂) gas is evolved in all reactions.
(b) Balanced equations:
- 2Na + 2H₂O → 2NaOH + H₂
- Ca + 2H₂O → Ca(OH)₂ + H₂
(c) Iron does not react with cold water but reacts with steam because of its low reactivity to form iron oxide and hydrogen gas.
Equation: 3Fe + 4H₂O → Fe₃O₄ + 4H₂
OR
(c) Calcium reacts with air and moisture to form calcium hydroxide, so it must be stored in airtight containers.
Q4: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
A student placed an iron nail in a beaker containing copper sulfate (CuSO₄) solution. After some time, he observed that the blue color faded, and a reddish-brown deposit appeared on the nail.
(a) Identify the reaction taking place. (1 mark)
(b) Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction. (2 marks)
(c) What would happen if a copper wire was placed in iron sulfate (FeSO₄) solution? (1 mark)
OR
(c) Arrange the metals Fe, Cu, and Zn in order of reactivity. (1 mark)
Ans:
(a) This is a displacement reaction, where a more reactive metal (iron) displaces a less reactive metal (copper).
(b) Balanced equation: Fe + CuSO₄ → FeSO₄ + Cu
(c) No reaction occurs because copper is less reactive than iron.
OR
(c) Reactivity order: Zn > Fe > Cu.
Q5: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
A teacher demonstrated an experiment where she placed iron nails in three test tubes:
- Test Tube A: Contained only water.
- Test Tube B: Contained boiled distilled water with oil.
- Test Tube C: Contained anhydrous calcium chloride (dry air).
After a few days, the nails in Test Tube A rusted, but those in B and C did not.
(a) Identify the test tube in which iron nail will rust and state conditions required for rusting. (1 mark)
(b) Write the balanced chemical equation for rusting of iron. (2 marks)
(c) Name one method to prevent rusting. (1 mark)
OR
(c) Why does oil prevent rusting? (1 mark)
Ans:
(a) In Test Tube A nail will start to rust and Rusting requires both oxygen and water.
(b) Balanced equation:
4Fe + 3O₂ + 6H₂O → 4Fe(OH)₃ → Fe₂O₃·xH₂O (rust)
(c) Galvanization (coating iron with zinc) prevents rusting.
OR
(c) Oil prevents rusting by forming a protective layer that blocks water and oxygen from reaching the iron surface.





















