Weekly Current Affairs (22nd to 28th February 2025) | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
Recent Controversies About Ex-Gratia Payments

Why in News?
- The recent ex-gratia compensation payments to the families of victims from the New Delhi railway station stampede have ignited considerable debate. The Ministry of Railways has provided cash payments of Rs 10 lakh to the next of kin of those who lost their lives, raising questions about the appropriateness of such cash disbursements in these situations.
Key Takeaways
- Ex-gratia payments are voluntary and made out of moral obligation, not as a legal requirement.
- There is a significant distinction between ex-gratia payments and compensation, particularly regarding liability.
- Current practices suggest that cash payments are not the standard method for disbursement in disaster situations.
Additional Details
- Ex-Gratia Payments: These payments are made voluntarily and signify a moral obligation rather than legal liability. They are often issued after tragic incidents.
- Ex-Gratia vs. Compensation: While ex-gratia payments stem from goodwill and do not admit any wrongdoing, compensation is legally mandated to cover losses caused by negligence.
- Current Practices: The Railway Board’s 2023 guidelines recommend a maximum cash disbursement of Rs 50,000 for immediate needs post-accident, emphasizing that remaining funds should be transferred via bank methods for accountability.
- Cash vs. Bank Transfers: Cash payments can be beneficial in emergencies, yet bank transfers are preferred for their transparency and traceability, as they provide a documented paper trail.
- Government Justification: Officials defended cash disbursements by highlighting the distinction between ex-gratia payments and compensation, citing previous instances of cash use due to victims' limited banking access.
- Historical Context: The Delhi government has set structured guidelines for ex-gratia payments, particularly during the Covid-19 pandemic, which included eligibility criteria and a direct benefit transfer system to ensure transparency.
In summary, the ongoing debate surrounding ex-gratia payments illustrates the complexities involved in disaster response and the government's role in providing aid to victims' families. The need for clarity and transparency in such financial disbursements remains paramount.
Cancer Care Challenges in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Acute Myeloid Leukaemia (AML) poses significant health challenges globally, especially in low and middle-income countries like India. The country faces an acute burden of AML due to late-stage diagnoses and limited access to advanced treatment options, which significantly affects patient outcomes, particularly in rural areas. Addressing these challenges is essential for enhancing survival rates among patients.
Key Takeaways
- AML is the most common type of leukaemia in adults.
- The disease involves rapid proliferation of abnormal blood cells, known as blasts.
- Diagnosis in India typically occurs at a younger age compared to high-income countries, often around age 40.
- Late-stage presentations are prevalent, leading to poorer prognoses.
Additional Details
- Barriers to Effective AML Care: Various obstacles hinder the effective management of AML in India, including disorganized referral systems and inadequate diagnostic facilities. Many patients experience delays in treatment initiation due to poor hospital infrastructure and limited access to advanced therapies. Financial constraints also significantly affect treatment access, with many patients unable to afford necessary care.
- Impact of Socioeconomic Factors: Socioeconomic status plays a crucial role in healthcare access. Patients from rural areas face additional challenges, including difficulties in traveling for treatment. Public hospitals often struggle with resource shortages, while private healthcare facilities may be financially out of reach for many.
- Government Initiatives: The Government of India has launched initiatives like the Ayushman Bharat scheme aimed at improving access to cancer care. However, there is a need for further action to enhance healthcare delivery, such as improving awareness among primary care physicians for better referrals and decentralizing diagnostic services.
- Improving Healthcare Infrastructure: Strengthening healthcare infrastructure is vital for improving outcomes in AML. This includes developing standardized treatment guidelines and increasing access to novel therapies. Policy changes should focus on including low and middle-income countries in clinical trials and ensuring the availability of quality generic medications.
- Enhancing Patient Navigation: The journey from diagnosis to treatment can be complex for AML patients. Improving access to diagnostics, expanding treatment options, and making care more affordable are essential to support patients effectively.
In conclusion, addressing the myriad challenges faced by AML patients, particularly in low and middle-income countries, is imperative. By improving healthcare infrastructure, enhancing patient navigation, and implementing effective government initiatives, we can work towards better survival outcomes for those affected by this serious disease.
27th Western Zonal Council Meeting
 Why in News?
Why in News?
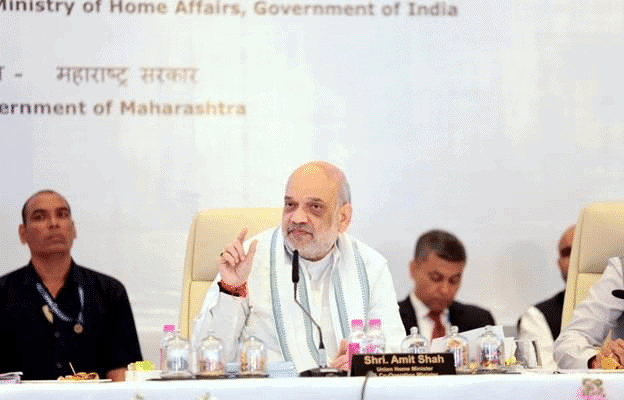
- The 27th Western Zonal Council meeting, led by Union Home Minister Amit Shah, took place in Pune, Maharashtra, on February 24, 2025. The meeting brought together Chief Ministers from Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Goa, along with the Administrator of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, and senior officials from both state and central ministries.
Key Takeaways
- Zonal Councils are essential for promoting cooperative federalism in India.
- The councils facilitate dialogue among states, addressing shared interests and enhancing regional collaboration.
- Historical context: Proposed by Jawaharlal Nehru in 1956, to mitigate linguistic conflicts post-state reorganization.
- Growth in meetings and discussions: Significant increase in the number of meetings and topics addressed since 2014.
Additional Details
- Zonal Councils: Comprise specific states and union territories, designed to foster cooperation and governance.
- Leadership Structure: Chaired by the Union Home Minister with a rotating Vice-Chairman, usually a Chief Minister of a member state.
- Functions and Roles: They serve as forums for dispute resolution, economic planning, and addressing social issues.
- Importance of the Western Region: Contributes significantly to India’s GDP and industrial operations.
- Financial Inclusion Milestone: Nearly all villages have banking facilities within 5 km, with a new target set to reduce this to 3 km.
- Malnutrition and Public Health: Ongoing concerns in prosperous Western states, necessitating urgent actions from state governments.
- Boosting Domestic Pulse Production: Efforts to reduce imports and ensure fair prices for farmers through a new mobile application.
- Key Issues Discussed: Included land transfer, mining, urban planning, and school dropout rates.
The meeting underscored the importance of cooperative federalism, with a focus on achieving 100% saturation of welfare schemes and addressing regional challenges. The Zonal Councils play a crucial role in facilitating discussions that enhance collaboration among states, aiming for balanced socio-economic development across India.
Blue-Cheeked Bee-Eater Breeding Site
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Recently, the Blue-Cheeked Bee-Eater (Merops persicus) has been confirmed to breed in peninsular India. This significant discovery occurred in the saltpans of Aandivilai, located near the Manakudy Mangroves in the Kanniyakumari district.
Key Takeaways
- The Blue-Cheeked Bee-Eater is recognized for its vibrant green plumage and distinctive blue cheek patch.
- This species has transitioned from being a passage migrant and winter visitor in India to establishing breeding grounds in Tamil Nadu.
- The population has shown signs of growth, increasing from 28 individuals at the start of the breeding season to 48 by the end of the study.
Additional Details
- Breeding Behavior: The breeding site represents the southernmost range of the Blue-Cheeked Bee-Eater in the Indian subcontinent. Researchers observed courtship behaviors and located nesting sites along the saltpans of the Pazhayar river basin.
- Threats: The Aandivilai nesting colony faces risks from habitat destruction due to development activities, as well as natural threats like flooding and erosion.
- Conservation Efforts: Experts are advocating for the protection of this critical breeding ground, which is the only known site for this species in India.
- Habitat Preferences: The Blue-Cheeked Bee-Eater prefers sub-tropical semi-desert regions with sparse trees for nesting and may nest solitarily or in small colonies.
- Seasonal Behavior: During the non-breeding season, this species adapts to various greener habitats, showcasing its resilience.
In conclusion, the establishment of breeding grounds for the Blue-Cheeked Bee-Eater in India highlights the need for effective conservation measures to protect this species and its habitat. The successful increase in population numbers underscores the importance of ongoing research and monitoring in ensuring the survival of the Blue-Cheeked Bee-Eater in its new range.
India’s Strategic Shift in Fertiliser Consumption

Why in News?
- India is currently undergoing a significant transformation in its strategy for fertiliser consumption. This shift aims to decrease dependence on imported high-analysis fertilisers such as urea, di-ammonium phosphate (DAP), and muriate of potash (MOP). The impetus for this change stems from the country's high reliance on imports for these essential fertilisers. The government has recently placed a strong emphasis on balanced fertilisation to enhance crop yield and improve nutrient absorption.
Key Takeaways
- India is heavily reliant on imported fertilisers, particularly MOP, which is 100% imported.
- Urea production satisfies 85% of domestic demand but depends on imported liquefied natural gas.
- DAP is predominantly imported, with the rupee's depreciation complicating import costs.
- High-analysis fertilisers are nutrient-dense but often do not meet the comprehensive nutrient needs of crops.
- Ammonium phosphate sulphate (APS) is gaining popularity as a cost-effective alternative to DAP.
Additional Details
- Import Dependency: The majority of India's fertilisers are imported, with MOP sourced entirely from countries like Canada and Russia. This heavy reliance poses challenges, especially with fluctuating currency values.
- High Analysis vs Balanced Fertilisation: While high-analysis fertilisers contain concentrated nutrients (e.g., urea with 46% nitrogen), balanced fertilisation is essential for optimal crop growth, incorporating secondary nutrients and micronutrients.
- Emergence of APS: APS is being promoted as a viable alternative to DAP, containing 20% nitrogen, 20% phosphorous, and 13% sulphur. It is considered a more economical option for farmers as it uses less phosphoric acid.
- Market Trends: Sales of APS have increased by over 32%, while DAP sales are on the decline. This shift is influenced by short supply and high import costs of DAP.
- Government Policies: The Government of India has established a maximum retail price for DAP, making imports less viable. The lower price of APS encourages its adoption among farmers, influenced by government subsidy policies.
The outlook for the fiscal year 2024-25 is optimistic, with expectations of increased sales in NPKS complex fertilisers driven by APS. There is a concerted effort to further promote complex fertilisers to minimize the use of high-analysis products, ultimately aiming to enhance nutrient use efficiency among farmers.
Ex INS Guldar Transformed Into Underwater Museum

Why in News?
- The Indian Navy has recently transferred Ex INS Guldar, a decommissioned Landing Ship Tank (Medium), to the Maharashtra Tourism Development Corporation Limited (MTDC). This initiative represents a groundbreaking effort in India to convert a retired naval vessel into an underwater museum and artificial reef. The handover occurred in Karwar, with MTDC taking responsibility for the vessel on an ‘as is where is’ basis. The project aims to promote marine conservation while offering new opportunities for local communities.
Key Takeaways
- Ex INS Guldar was commissioned into the Indian Navy on December 30, 1985.
- The ship served primarily in the Eastern Naval Command until 1995 and later in the Andaman and Nicobar Command until its decommissioning on January 12, 2024.
- Over its 39 years of service, Ex INS Guldar participated in numerous operations and conducted over 490 beaching operations.
Additional Details
- Environmental and Economic Benefits: The project enhances marine conservation efforts by creating artificial reefs that support diverse marine life, providing shelter and contributing to thriving ecosystems. This initiative is also expected to generate livelihood opportunities for coastal communities through underwater tourism.
- Diving Training Opportunities: The project will facilitate diving training for the Indian Navy at the scuttled site, enhancing the Navy’s operational capabilities while promoting marine tourism in the region.
- Other Marine Museums in India: Previously, India has transformed other naval vessels into museums, such as INS Kursura in Vishakhapatnam, which serves as an underwater museum. INS Vikrant operated as a museum before being recommissioned in 2022, and INS Cuddalore has also been converted into an underwater museum, further enriching India’s maritime heritage.
This initiative not only preserves the legacy of Ex INS Guldar but also contributes significantly to marine conservation efforts and local economic development through tourism and training.
What is AI Singularity?
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have sparked significant discussions regarding its potential future effects on society. Elon Musk, a prominent voice in this debate, has raised alarms about the risks of AI exceeding human intelligence, predicting that superintelligent AI could emerge as soon as 2025. This concept, referred to as AI singularity, marks a critical moment where machines could self-enhance beyond human oversight. The discourse surrounding AI singularity has gained momentum among scientists and technology leaders.
Key Takeaways
- AI singularity is the hypothetical point when AI surpasses human intelligence.
- The concept was first put forth by mathematician John von Neumann.
- There is a divide in predictions about when this may happen, with some, like Ray Kurzweil, projecting 2045, while Musk suggests it may be sooner.
Additional Details
- Current AI Developments: AI technology is evolving rapidly, with machine learning models beginning to exhibit self-improvement capabilities. However, fully autonomous superintelligent AI remains a theoretical concept. The emphasis is currently on responsible AI development, addressing ethical implications, and creating regulatory frameworks to manage these advancements.
- Concerns and Risks: Experts voice significant concerns regarding the potential dangers of superintelligent AI. In 2023, over 33,700 AI researchers signed an open letter advocating for a pause on the development of AI models exceeding OpenAI's GPT-4, citing serious risks to society and humanity. Critics warn that AI could undermine human value and present existential threats.
- Potential Benefits: Despite the risks, there are optimistic perspectives on AI singularity. Proponents argue that it could lead to revolutionary scientific advancements, enabling AI to automate complex problem-solving and transform fields such as medicine, environmental sustainability, and space exploration.
- Regulatory Efforts and Market Growth: As AI technology continues to advance, governments and industry leaders are exploring regulations to mitigate unintended consequences. The AI market, currently valued at $100 billion, is projected to grow to $2 trillion by 2030, highlighting the urgent need for effective governance in AI development.
- Public Perception and Awareness: The public discourse surrounding AI singularity is becoming increasingly vital. Figures like Musk underscore the importance of caution and readiness, with his warnings about a potential “Terminator” future resonating with many, stressing the need to consider the societal implications of advanced AI.
In summary, the concept of AI singularity raises important questions about the future of artificial intelligence and its role in society. As developments continue, it is crucial to balance innovation with ethical considerations and regulatory frameworks to ensure a safe trajectory for AI advancements.
CISF Training Centre Renamed in Honor of Rajaditya Chola
Why in News?
- The Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) has officially renamed its Recruits Training Centre located in Arakkonam to honor Rajaditya Cholan, a significant figure in Tamil history. This renaming, which took effect on February 24, 2025, serves to commemorate Rajaditya, a Chola prince who lost his life in the historic Battle of Thakkolam in 949 CE. This battle was a crucial moment in the ongoing conflict between the Cholas and the Rashtrakutas, and Rajaditya's legacy continues to inspire pride in Tamil heritage.
Key Takeaways
- The CISF Training Centre in Arakkonam is now named after Rajaditya Cholan.
- Rajaditya was a prominent figure in the Chola dynasty who died in the Battle of Thakkolam.
- His legacy is significant in Tamil history, symbolizing bravery and cultural pride.
Additional Details
- Rajaditya Cholan: The son of Parantaka I, Rajaditya was a notable warrior in the Chola dynasty. He was honored with the title ‘Yanaimel Thunjiya Devar’, translating to ‘The king who died on the back of an elephant’. His valor and contributions are immortalized in Tamil literature.
- The Battle of Thakkolam: This battle took place in 949 CE between the Chola and Rashtrakuta armies, where Rajaditya led the Chola forces. Despite their valiant efforts, he was fatally wounded, marking a significant event in Tamil history.
- Rajaditya was also an effective administrator who oversaw northern Chola territories, promoting agricultural and socio-cultural advancements.
- His legacy inspires future generations of Tamil leaders and is celebrated in various cultural references, including the famous Tamil novel “Ponniyin Selvam” by Kalki Krishnamurthy.
In conclusion, the renaming of the CISF Training Centre represents not only a tribute to Rajaditya Cholan’s bravery but also serves as a reminder of the rich historical and cultural heritage of the Tamil people. His contributions to the Chola dynasty and Tamil literature continue to resonate today.
Chinese Alligator Population Crisis
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Chinese alligator (Alligator sinensis), a small crocodilian species native to eastern China, is critically endangered. Its survival is threatened by human activities and a lack of awareness about its plight. Urgent conservation efforts are needed to protect this unique reptile as its habitat dwindles.
Key Takeaways
- The Chinese alligator is endemic to freshwater wetlands in eastern China.
- Only about 200 individuals are left, primarily in southeastern Anhui Province.
- It is classified as Critically Endangered by the IUCN and is a global conservation priority.
Additional Details
- Current Status: Historically widespread across the middle and lower Yangtze and Yellow River basins, the population has drastically declined due to agricultural expansion.
- Conservation Measures: The species was designated as a Class I Endangered Species in 1972, and the National Chinese Alligator Reserve was established in 1982 to protect the remaining population.
- Research Findings: A recent survey revealed that fewer than half of local residents could identify alligators, and many were unaware of the population decline.
- Human Impacts: Habitat disturbance and potential poisoning from contaminated prey pose significant threats to the alligator's survival, particularly from unsustainable agricultural practices.
- Conservation Strategies: Effective conservation efforts require educational outreach to raise awareness, monitoring human threats, and implementing captive breeding programs to bolster the wild population.
In conclusion, the future of the Chinese alligator hinges on ongoing research, education, and collaboration with local communities to adapt conservation strategies to changing human activities and landscapes.
Soyabean Market Trends and Government Procurement Challenges
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Indian soyabean market is currently facing significant challenges despite government efforts to stabilize the situation. As of February 2025, the central government has procured 20 lakh tonnes of soyabean; however, wholesale prices have not shown expected movements, raising concerns about the effectiveness of the current procurement strategies.
Key Takeaways
- The Government of India has a procurement target of 30 lakh tonnes but has only achieved 14.71 lakh tonnes as of February 2025.
- Prices of soyabean have consistently traded below the Minimum Support Price (MSP) of Rs 4,892 per quintal.
- Market prices in Latur, Maharashtra, have declined unexpectedly, suggesting a disconnect between government procurement efforts and market realities.
Additional Details
- Current Procurement Status: The procurement process involves sub-agents who directly purchase from farmers, ensuring immediate payments. Despite this, prices have not risen as anticipated.
- Price Dynamics: The soyabean marketing year runs from September to October. Prices fell from Rs 5,220 in September to Rs 4,511 in November, with a slight recovery to Rs 4,872 in December.
- Market Reactions: Traders have expressed that the prices may not recover soon, especially with government stocks still available.
- Export Considerations: Indian soyameal prices are currently at $380 per tonne, higher than Argentina's $360 per tonne, but there are doubts about the impact of increased exports on domestic prices.
- Future Outlook: Analysts believe that a major price correction in the wholesale market is unlikely until government stocks are depleted. Suggestions have been made to include soyabean in the public distribution system to stabilize prices.
In conclusion, the current state of the soyabean market in India reflects a complex interaction between government procurement efforts and actual market dynamics. Without strategic adjustments, the anticipated price recovery may remain elusive.
Indian Government Proposes Tax Revenue Cuts for States
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Government of India is contemplating a reduction in the federal tax revenues allocated to states. This significant proposal will be submitted to the Finance Commission of India, which is crucial in overseeing tax distribution and fiscal relations between the central and state governments. The recommendations from this commission are anticipated by October 31, 2025, and will be mandatory for implementation.
Key Takeaways
- States currently receive 41% of tax revenues, a rise from 20% in 1980.
- A proposed reduction to 40% could generate approximately Rs 35,000 crore (around $4.03 billion) for the federal government.
- India's fiscal deficit is projected at 4.8% of GDP for 2024-25.
Additional Details
- Current Tax Revenue Distribution: The increase in states’ share from 20% to 41% has been driven by the rising fiscal demands of state governments, primarily for social infrastructure such as health and education.
- Financial Implications: The cabinet is expected to approve the proposed tax cuts by March 2025, which could necessitate adjustments in state budgets due to diminished federal support.
- Impact of GST: The introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in July 2017 has restricted states' capacity to independently raise revenue, making them increasingly dependent on federal allocations.
- Conditional Grants: The federal government may introduce conditions for federal grants to states, potentially curbing states' abilities to provide cash handouts for political benefits.
In summary, the proposed tax revenue cuts could significantly alter the financial landscape for Indian states, compelling them to reassess their spending priorities and budget allocations. This shift is expected to have broad implications for governance and public welfare initiatives across the country.
Aadhaar Good Governance Portal Launch
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has introduced the Aadhaar Good Governance portal on February 28, 2025. This innovative platform is designed to streamline the approval process for Aadhaar authentication requests, contributing to a broader initiative aimed at enhancing the ease of living for citizens and improving service accessibility.
Key Takeaways
- The portal facilitates efficient submission and approval of Aadhaar authentication requests.
- It aligns with the goal of improving transparency and inclusivity in public services.
Additional Details
- Legislative Changes: The portal's launch follows recent amendments to the Aadhaar (Targeted Delivery of Financial and Other Subsidies, Benefits and Services) Act, 2016, which were notified in January 2025. These amendments expand the usage of Aadhaar for various public interest services, thereby enhancing service delivery.
- Digital Economy Impact: Aadhaar serves as a globally recognized digital identity. It has been utilized over a billion times by more than a billion Indians in the past decade, significantly contributing to the growth of India's digital economy and facilitating resident-centric services.
- Benefits for Users: The amendments allow Aadhaar number holders to access services across multiple sectors, including healthcare, hospitality, e-commerce, and education. Service providers can leverage Aadhaar for customer onboarding, e-KYC verification, and employee attendance tracking.
- User Guidance: The Aadhaar Good Governance portal will offer comprehensive guidance for entities seeking authentication, including Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for application and onboarding. Future updates may involve the integration of face authentication in customer-facing applications.
In conclusion, the Aadhaar Good Governance portal represents a significant advancement in the efficiency and accessibility of public services in India, reinforcing the government's commitment to enhancing citizen services through technology.
|
164 videos|800 docs|1155 tests
|
















