Facts that Matter: Constitution of India | Legal Reasoning for CLAT PDF Download
1. Historical Background
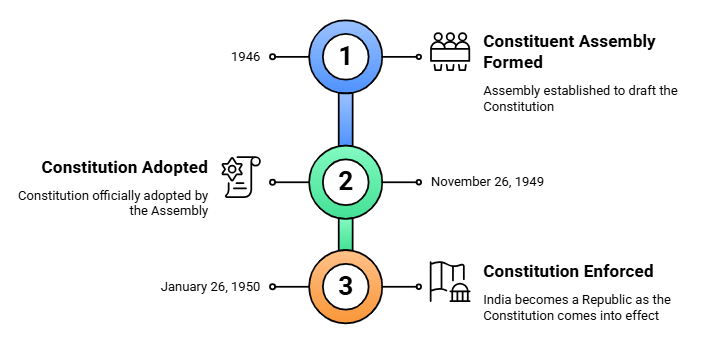
Fact 1: On which date was the Constitution of India adopted by the Constituent Assembly?
Ans: November 26, 1949
Fact 2: Who was the Chairman of the Drafting Committee of the Constitution of India, often called its chief architect?
Ans: Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
Fact 3: How long did the Constituent Assembly take to draft the Constitution of India?
Ans: 2 years, 11 months, and 18 days
Fact 4: In which year was the Constituent Assembly of India first formed to draft the Constitution?
Ans: 1946
Fact 5: Who moved the Objective Resolution in the Constituent Assembly, outlining the principles of the Constitution?
Ans: Jawaharlal Nehru
2. Salient Features
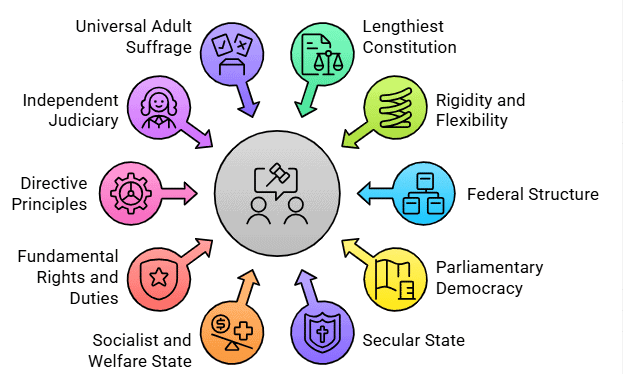
Fact 1: What is the Constitution of India often described as, due to its extensive and detailed nature?
Ans: Lengthiest Written Constitution
Fact 2: The Constitution of India is described as a blend of which two characteristics in terms of its amendment process?
Ans: Rigidity and Flexibility
Fact 3: What type of governmental structure does the Constitution establish, often described as a "Union of States" with a strong central authority?
Ans: Federal Structure with Unitary Bias
Fact 4: Which feature of the Constitution ensures that there is no state religion and all religions are treated equally?
Ans: Secular State
Fact 5: What democratic system does the Constitution of India adopt, based on the Westminster model, with a President and a Prime Minister?
Ans: Parliamentary Democracy
3. Preamble
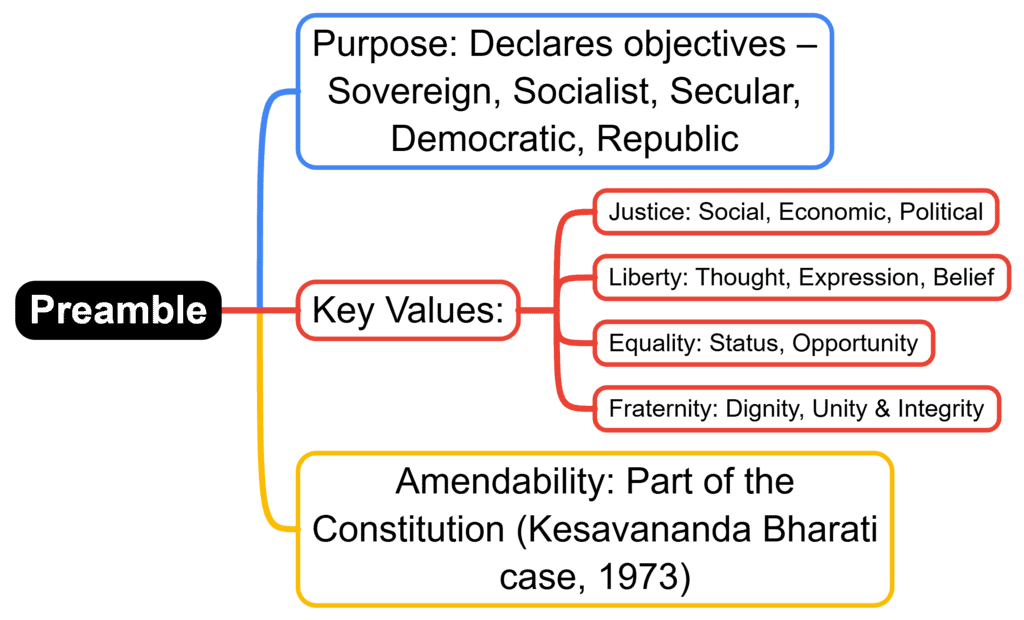
Fact 1: From which country’s Constitution is the concept of Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity in the Preamble derived?
Ans: France
Fact 2: The idea of a Democratic Republic in the Preamble was inspired by which country’s Constitution?
Ans: USA
Fact 3: From which historical document did the framers of the Preamble draw inspiration for its structure and ideals?
Ans: Objective Resolution
Fact 4: The concept of Justice—social, economic, and political—in the Preamble was influenced by which country’s revolution?
Ans: Russia
Fact 5: From which country’s Constitution did the Preamble borrow the idea of a Sovereign state free from external control?
Ans: UK
4. Parts of the Constitution
Fact 1: Which part of the Constitution contains the Fundamental Rights of citizens?
Ans: Part III
Fact 2: The part of the Constitution dealing with Directive Principles of State Policy is?
Ans: Part IV
Fact 3: Which part of the Constitution was added by the 42nd Amendment to include Fundamental Duties?
Ans: Part IVA
Fact 4: The part of the Constitution that outlines the Emergency Provisions is known as?
Ans: Part XVIII
Fact 5: Which part of the Constitution deals with the amendment process under Article 368?
Ans: Part XX
5. Schedules
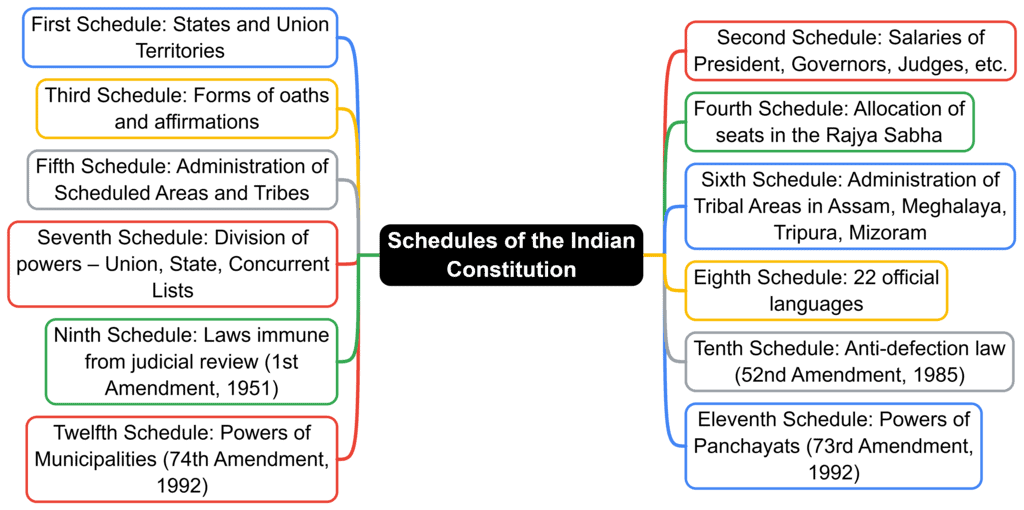
Fact 1: Which Schedule of the Indian Constitution contains the list of states and union territories of India?
Ans: First Schedule
Fact 2: The provisions related to the administration and control of Scheduled Areas and Scheduled Tribes are mentioned in which Schedule?
Ans: Fifth Schedule
Fact 3: Which Schedule of the Indian Constitution details the forms of oaths and affirmations for public officials like the President, Ministers, and Judges?
Ans: Third Schedule
Fact 4: The allocation of seats in the Rajya Sabha for states and union territories is outlined in which Schedule?
Ans: Fourth Schedule
Fact 5: Which Schedule of the Indian Constitution provides the list of 22 languages recognized as official languages of India?
Ans: Eighth Schedule
6. Fundamental Rights (Part III)
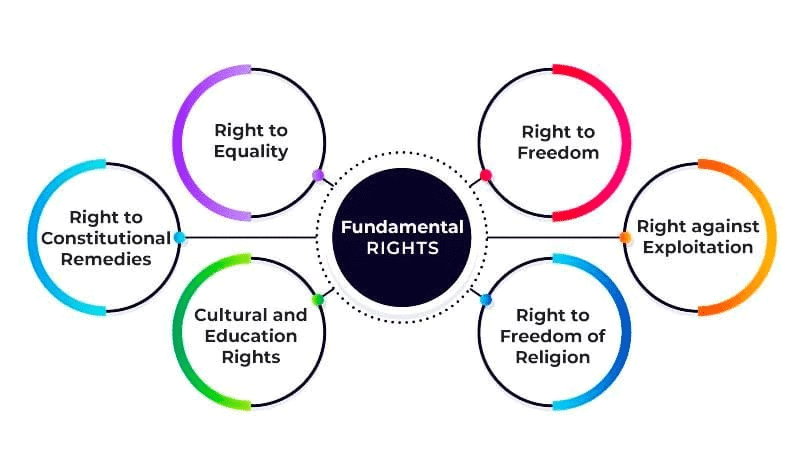
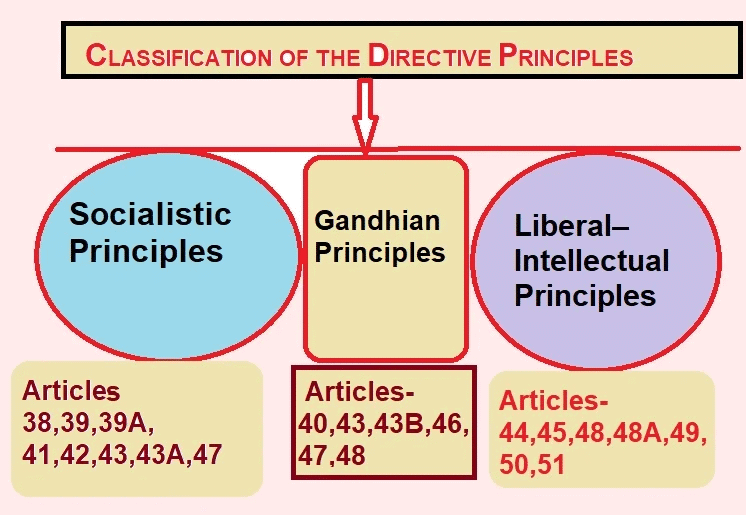
7. Directive Principles of State Policy (Part IV)
Fact 1: In which part of the Indian Constitution are the Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP) mentioned?
Ans: Part IV
Fact 2: Which article under DPSP directs the state to provide free legal aid to ensure equal justice?
Ans: Article 39A
Fact 3: From which country’s constitution was the concept of DPSP borrowed?
Ans: Ireland
Fact 4: Which article of DPSP promotes the state to secure a uniform civil code for all citizens?
Ans: Article 44
Fact 5: Are the Directive Principles of State Policy enforceable by courts, unlike Fundamental Rights?
Ans: No, they are non-justiciable.
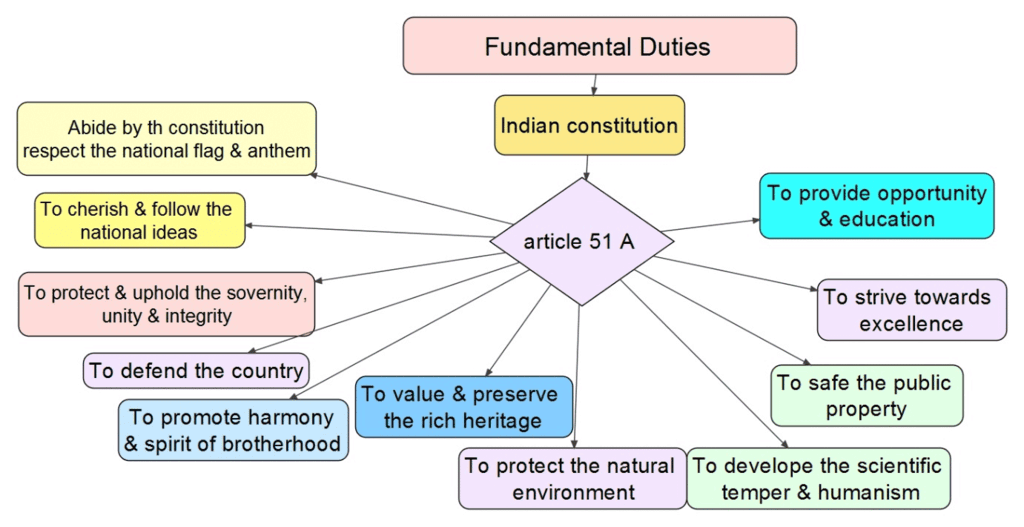
8. Fundamental Duties (Part IVA)
Fact 1: In which part of the Indian Constitution are the Fundamental Duties listed?
Ans: Part IV-A
Fact 2: Which article specifies the Fundamental Duties of Indian citizens?
Ans: Article 51A
Fact 3: From which country’s constitution were the Fundamental Duties inspired?
Ans: Soviet Union (USSR)
Fact 4: In which year were the Fundamental Duties added to the Indian Constitution through the 42nd Amendment?
Ans: 1976
Fact 5: How many Fundamental Duties are currently listed in the Indian Constitution?
Ans: 11
9. Judiciary
Fact 1: Which part of the Indian Constitution deals with the establishment and functioning of the Supreme Court?
Ans: Part V
Fact 2: Under which article can the Supreme Court issue writs to protect Fundamental Rights?
Ans: Article 32
Fact 3: What is the retirement age for a Supreme Court judge in India?
Ans: 65 years
Fact 4: Which article provides for the establishment of High Courts in states?
Ans: Article 214
Fact 5: From which country’s constitution was the concept of judicial review in India primarily borrowed?
Ans: United States
10. Key Amendments
Fact 1: Which amendment introduced the Ninth Schedule to protect land reform laws from judicial review?
Ans: 1st Amendment, 1951
Fact 2: Which amendment, known as the "Mini-Constitution," added the words "Socialist" and "Secular" to the Preamble?
Ans: 42nd Amendment, 1976
Fact 3: Which amendment removed the Right to Property as a Fundamental Right and made it a legal right under Article 300A?
Ans: 44th Amendment, 1978
Fact 4: Which amendments introduced the Panchayati Raj system and urban local bodies for grassroots governance?
Ans: 73rd & 74th Amendments, 1992
Fact 5: Which amendment introduced the Goods and Services Tax (GST) by adding Articles 246A and 279A?
Ans: 101st Amendment, 2016

11. Landmark Doctrines and Cases
Fact 1: Which case established the "Basic Structure Doctrine," stating that certain features of the Constitution cannot be amended?
Ans: Kesavananda Bharati v. State of Kerala (1973)
Fact 2: Which doctrine ensures that the judiciary can strike down laws that violate Fundamental Rights, as established in the Minerva Mills case?
Ans: Doctrine of Judicial Review
Fact 3: Which case introduced the "Doctrine of Pith and Substance" to determine the true nature of a law in legislative competence disputes?
Ans: State of Bombay v. F.N. Balsara (1951)
Fact 4: Which landmark case expanded the scope of Article 21 to include the Right to Privacy as a Fundamental Right?
Ans: Justice K.S. Puttaswamy v. Union of India (2017)
Fact 5: Which case established the "Doctrine of Harmonious Construction" to resolve conflicts between Fundamental Rights and DPSP?
Ans: Re Kerala Education Bill (1957)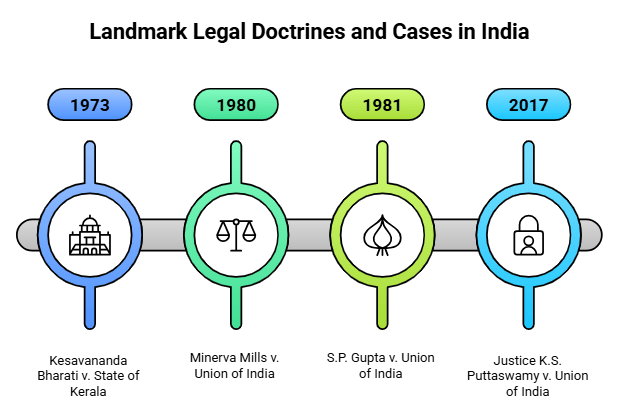
12. Emergency Provisions
Fact 1: Under which article can a National Emergency be declared due to war, external aggression, or armed rebellion?
Ans: Article 352
Fact 2: Which type of emergency, also known as President’s Rule, can be imposed in a state if its constitutional machinery fails?
Ans: State Emergency under Article 356
Fact 3: Which article allows the suspension of Fundamental Rights (except Articles 20 and 21) during a National Emergency?
Ans: Article 359
Fact 4: From which country’s constitution were the precautionary emergency provisions of India primarily borrowed?
Ans: Germany (Weimar Constitution)
Fact 5: Which amendment made it mandatory for a National Emergency to be approved by both Houses of Parliament within one month?
Ans: 44th Amendment, 1978

13. Miscellaneous Facts
Fact 1: How many languages are recognized as official languages of India in the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution?
Ans: 22
Fact 2: Who administers the Union Territories of India, as per Article 239 of the Constitution?
Ans: The President through an Administrator
Fact 3: Which schedule of the Indian Constitution contains provisions related to the Anti-Defection Law to prevent political defections?
Ans: Tenth Schedule
Fact 4: What status does the Right to Property hold after the 44th Amendment of the Indian Constitution?
Ans: It is a legal right under Article 300A, not a Fundamental Right
Fact 5: Which article of the Constitution defines the Finance Commission, responsible for recommending the distribution of taxes between the Union and States?
Ans: Article 280
|
63 videos|175 docs|37 tests
|
FAQs on Facts that Matter: Constitution of India - Legal Reasoning for CLAT
| 1. What is the significance of the Preamble in the Constitution of India? |  |
| 2. What are the Fundamental Rights enshrined in Part III of the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 3. How do the Directive Principles of State Policy in Part IV differ from Fundamental Rights? |  |
| 4. What is the role of the Judiciary in the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 5. What are some key amendments made to the Indian Constitution? |  |
















