Facts that Matter: Contract Law | Legal Reasoning for CLAT PDF Download
1. Introduction to Contract Law
Fact 1: Which section of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, provides the definition of a contract?
Ans: Section 2(h)
Fact 2: What does Section 2(h) of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, define a contract as?
Ans: An agreement enforceable by law
Fact 3: Which act governs the law of contracts in India?
Ans: Indian Contract Act, 1872
Fact 4: What is the purpose of the Indian Contract Act, 1872?
Ans: To regulate agreements creating legally binding obligations between parties
Fact 5: What type of agreements does the Indian Contract Act, 1872, focus on regulating?
Ans: Agreements creating legally binding obligations
2. Essentials of a Valid Contract (Section 10)
Fact 1: Which section of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, specifies the essentials of a valid contract?
Ans: Section 10
Fact 2: Under which sections of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, are a lawful offer and acceptance defined?
Ans: Sections 2(a) and 2(b)
Fact 3: Under which section of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, is lawful consideration defined?
Ans: Section 2(d)
Fact 4: Under which section are parties required to be of the age of majority, sound mind, and not disqualified by law to be competent to contract?
Ans: Section 11
Fact 5: Under which sections of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, is free consent defined?
Ans: Sections 13-22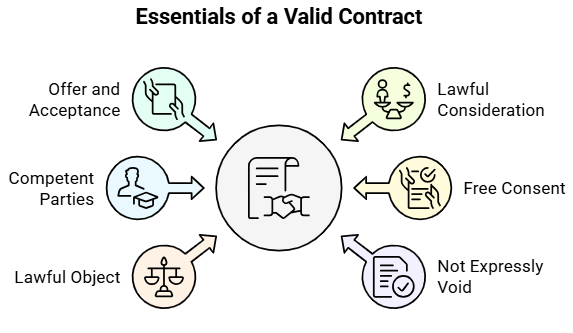
3. Key Concepts
Fact 1: Under which section of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, is an offer defined as a proposal?
Ans: Section 2(a)
Fact 2: What are the three requirements for a valid offer under the Indian Contract Act, 1872?
Ans: Must be definite, communicated, and capable of acceptance
Fact 3: What are two examples of an invitation to offer?
Ans: Price tags and advertisements
Fact 4: Under which section of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, is acceptance defined as an absolute and unqualified agreement?
Ans: Section 2(b)
Fact 5: Under which section of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, is an agreement without consideration considered void, except for specific exceptions?
Ans: Section 25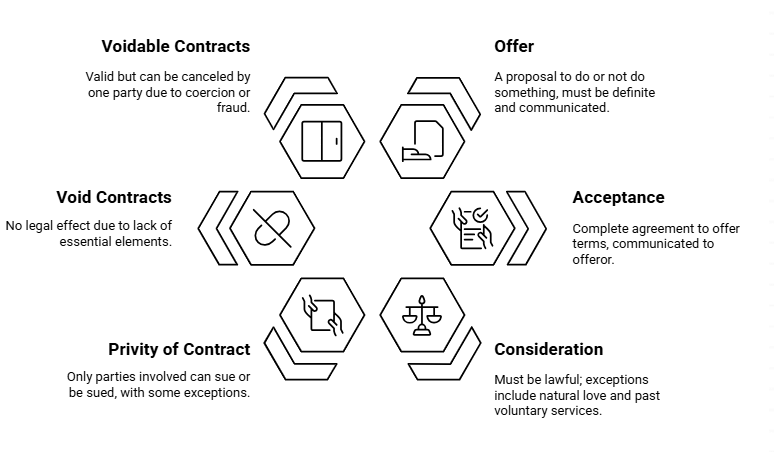
4. Types of Contracts
Fact 1: Under which section of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, are express and implied contracts defined?
Ans: Section 9
Fact 2: What type of contract is described as fully performed?
Ans: Executed contract
Fact 3: What type of contract involves a one-sided obligation, such as a reward offer?
Ans: Unilateral contract
Fact 4: Under which section of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, are contingent contracts defined?
Ans: Section 31
Fact 5: What type of contract involves mutual obligations between parties?
Ans: Bilateral contract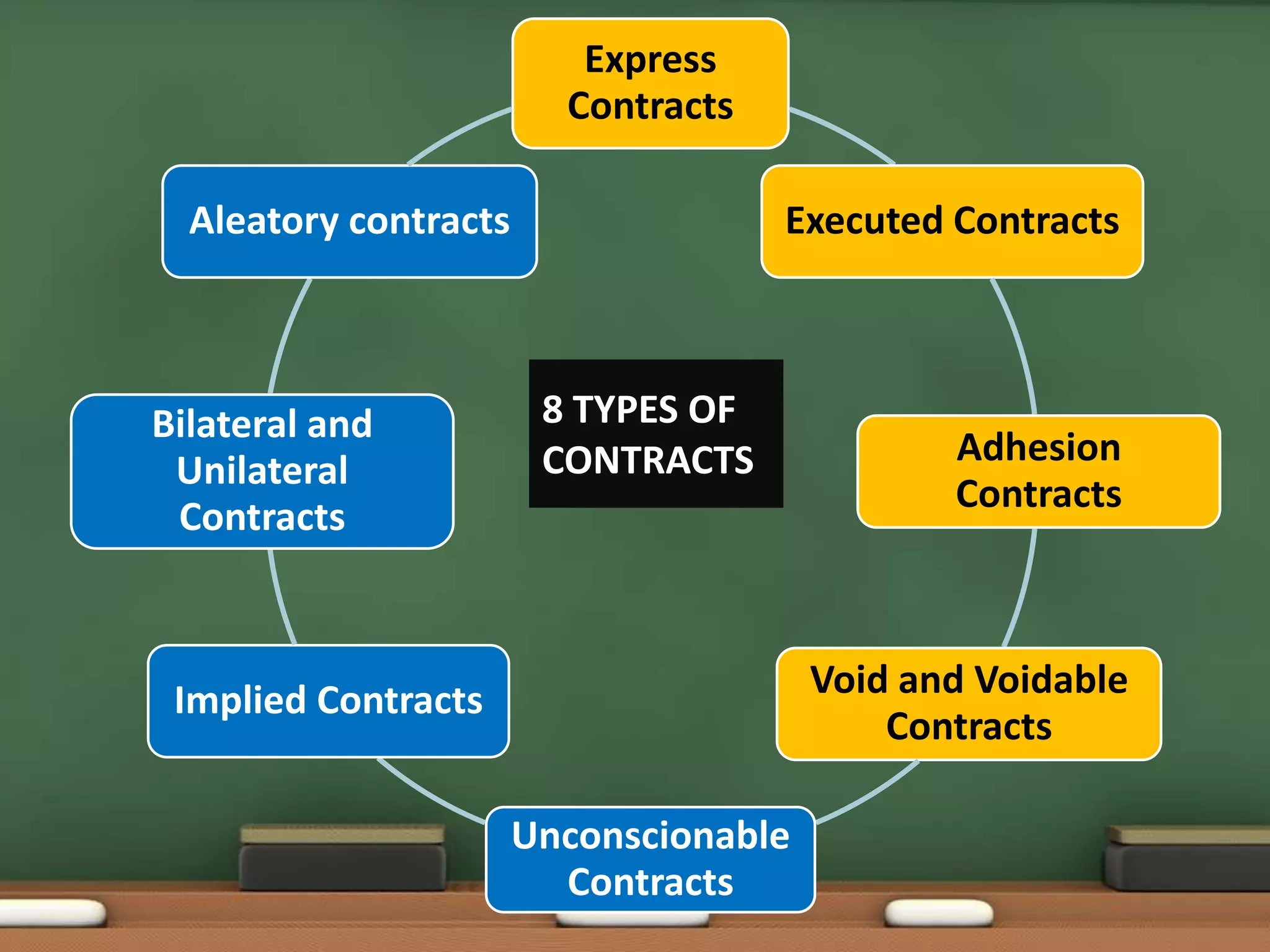
5. Vitiating Factors (Invalidating Consent)
Fact 1: Under which section of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, is coercion defined as committing or threatening an act forbidden by the IPC?
Ans: Section 15
Fact 2: Under which section of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, is undue influence defined?
Ans: Section 16
Fact 3: Under which section of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, is fraud defined as intentional misrepresentation?
Ans: Section 17
Fact 4: Under which section of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, is misrepresentation defined as an innocent or negligent false statement?
Ans: Section 18
Fact 5: Under which sections of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, are mutual and unilateral mistakes addressed?
Ans: Sections 20-22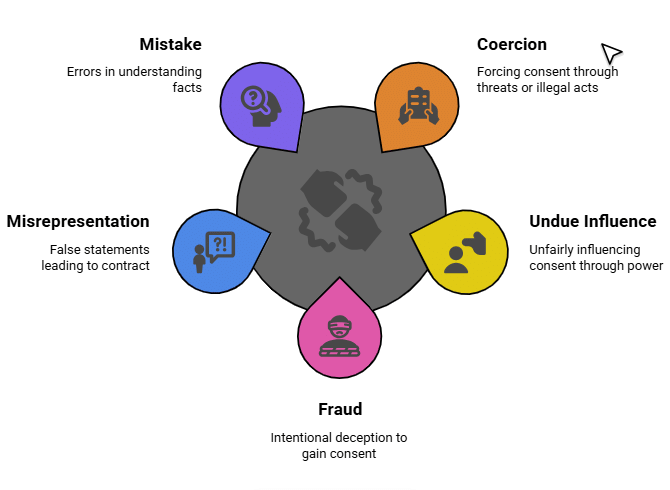
6. Void and Illegal Agreements
Fact 1: Under which sections of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, are void agreements addressed?
Ans: Sections 24-30
Fact 2: What is one example of a void agreement under the Indian Contract Act, 1872?
Ans: Agreements without lawful consideration or object
Fact 3: What is another example of a void agreement under Sections 24-30 of the Indian Contract Act, 1872?
Ans: Agreements in restraint of marriage
Fact 4: What type of agreements are considered uncertain under the Indian Contract Act, 1872?
Ans: Uncertain or wagering agreements
Fact 5: What is an example of an illegal agreement under the Indian Contract Act, 1872?
Ans: Contracts to commit a crime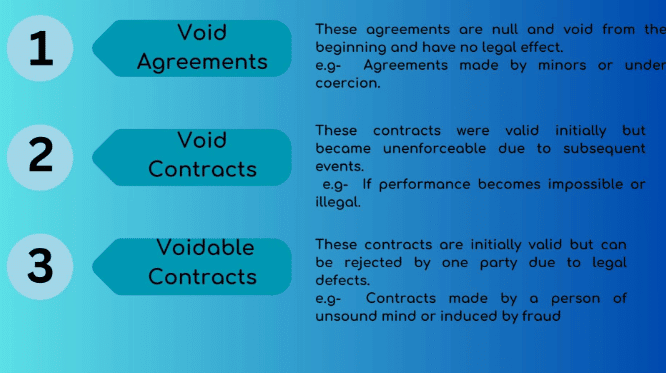
7. Performance and Discharge of Contracts
Fact 1: Under which sections of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, is the performance of contracts?
Ans: Sections 37-55
Fact 2: What is one method of discharging a contract under the Indian Contract Act, 1872?
Ans: By performance
Fact 3: Under which section of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, is impossibility of performance?
Ans: Section 56
Fact 4: What is one example of discharge by operation of law under the Indian Contract Act, 1872?
Ans: Insolvency
Fact 5: What is another example of discharge by operation of law under the Indian Contract Act, 1872?
Ans: Death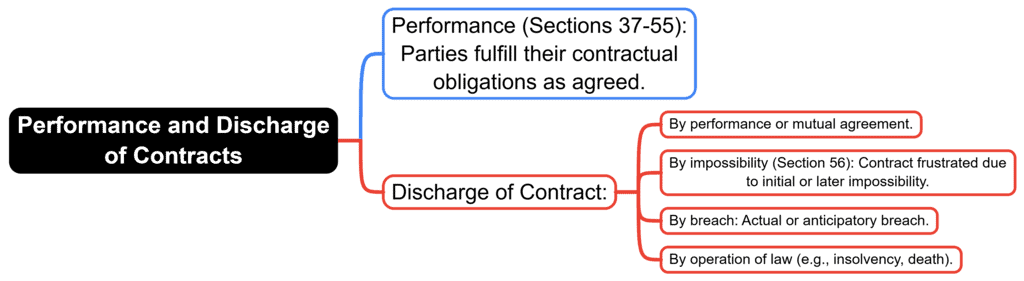
8. Breach and Remedies (Sections 73-75)
Fact 1: Under which sections of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, are breach and remedies addressed?
Ans: Sections 73-75
Fact 2: Under which section of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, are damages for breach of contract provided?
Ans: Section 73
Fact 3: What type of damages are described as direct and natural consequences under the Indian Contract Act, 1872?
Ans: Ordinary damages
Fact 4: What type of damages are awarded when there is no actual loss under the Indian Contract Act, 1872?
Ans: Nominal damages
Fact 5: What is an example of a contract where specific performance might be ordered under the Indian Contract Act, 1872?
Ans: Property contracts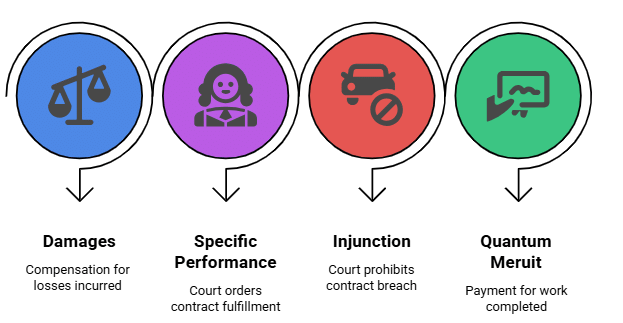
9. Quasi-Contracts (Sections 68-72)
Fact 1: Under which sections of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, are quasi-contracts covered?
Ans: Sections 68-72
Fact 2: What is the purpose of quasi-contracts under the Indian Contract Act, 1872?
Ans: To prevent unjust enrichment
Fact 3: Under which section of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, is the supply of necessaries to a minor considered a quasi-contract?
Ans: Section 68
Fact 4: Under which section of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, is payment by an interested person considered a quasi-contract?
Ans: Section 69
Fact 5: Under which section of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, is the finder of goods considered a quasi-contract?
Ans: Section 71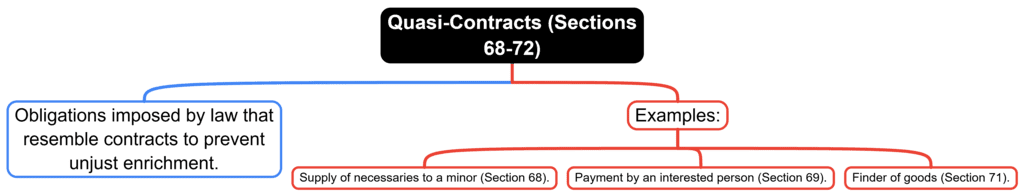
10. Key Legal Maxims
Fact 1: What is the Latin term for the maxim meaning "Agreements must be honored"?
Ans: Pacta Sunt Servanda
Fact 2: What is the Latin term for the maxim meaning "No one can give what they do not have"?
Ans: Nemo Dat Quod Non Habet
Fact 3: What is the Latin term for the maxim meaning "No action arises from an illegal cause"?
Ans: Ex Turpi Causa Non Oritur Actio
Fact 4: Which legal maxim means "Agreements must be honored"?
Ans: Pacta Sunt Servanda
Fact 5: Which legal maxim means "No action arises from an illegal cause"?
Ans: Ex Turpi Causa Non Oritur Actio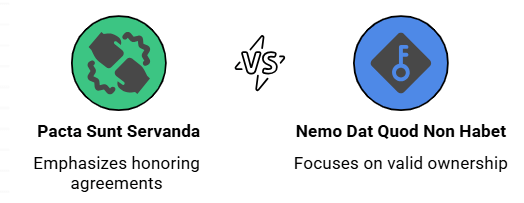
11. Landmark Case Laws
Fact 1: In which year was the case Balfour v. Balfour decided?
Ans: 1919
Fact 2: In which year was the case Mohori Bibee v. Dharmodas Ghose decided?
Ans: 1903
Fact 3: In which year was the case Hadley v. Baxendale decided?
Ans: 1854
Fact 4: In which year was the case Carlill v. Carbolic Smoke Ball Co. decided?
Ans: 1893
Fact 5: Which case established that a minor’s contract is void?
Ans: Mohori Bibee v. Dharmodas Ghose (1903)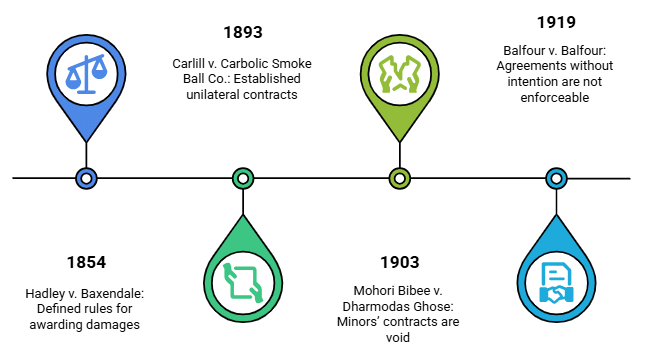
|
63 videos|174 docs|38 tests
|
FAQs on Facts that Matter: Contract Law - Legal Reasoning for CLAT
| 1. What are the essentials of a valid contract as per Section 10? |  |
| 2. What are vitiating factors that can invalidate consent in a contract? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between void and illegal agreements? |  |
| 4. What remedies are available for breach of contract under Sections 73-75? |  |
| 5. What are quasi-contracts and how do they function? |  |





















