CTET & State TET Exam > CTET & State TET Notes > Social Studies & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams > Mind Map: India After Independence
Mind Map: India After Independence | Social Studies & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET PDF Download
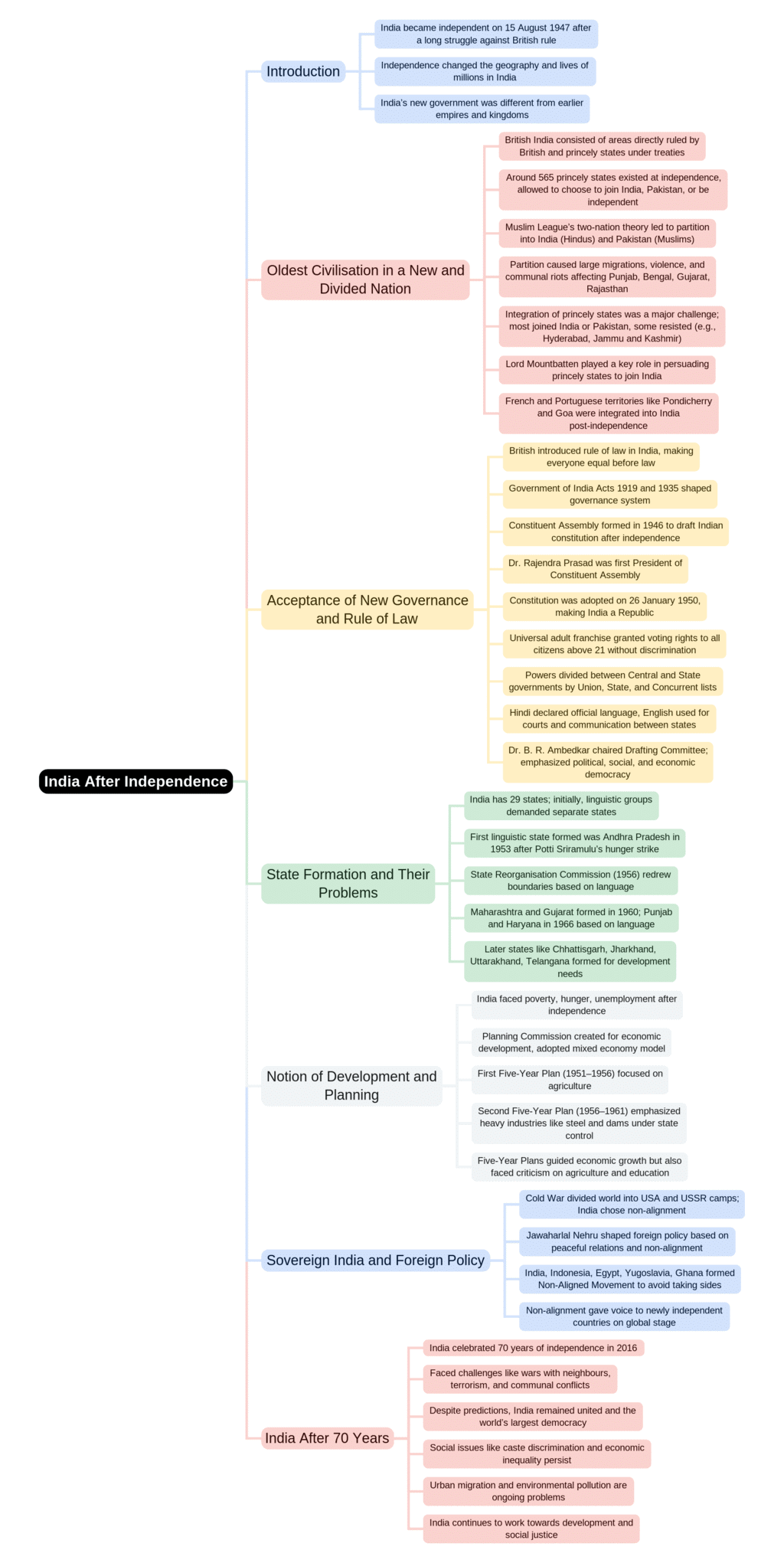
The document Mind Map: India After Independence | Social Studies & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET is a part of the CTET & State TET Course Social Studies & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams.
All you need of CTET & State TET at this link: CTET & State TET
|
75 videos|320 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: India After Independence - Social Studies & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET
| 1. What were the major challenges faced by India immediately after independence? |  |
Ans. After gaining independence, India faced several significant challenges, including political instability, communal violence, and the refugee crisis due to the partition. The newly formed nation had to address the integration of princely states, establish a democratic government, and ensure social and economic development. Moreover, there were issues related to poverty, illiteracy, and the need for land reforms to support agrarian communities.
| 2. How did the Indian Constitution address the diverse needs of its population? |  |
Ans. The Indian Constitution, adopted in 1950, was designed to accommodate the country's diversity. It established a framework for a secular, democratic state while ensuring individual rights and freedoms. The Constitution includes provisions for social justice, affirmative action for marginalized communities, and the protection of cultural and linguistic diversity. It aimed to unite the nation while respecting its varied cultural backgrounds.
| 3. What role did economic planning play in India's development post-independence? |  |
Ans. Economic planning became a cornerstone of India's development strategy after independence. The government established Five-Year Plans to outline priorities for economic growth, focusing on industrialization, agriculture, and infrastructure development. The emphasis was on self-reliance and reducing dependence on foreign aid. This approach aimed to promote balanced regional development and uplift various sectors of the economy.
| 4. How did India address social issues such as caste and gender inequality after independence? |  |
Ans. India undertook various measures to combat social issues like caste and gender inequality. The Constitution abolished "untouchability" and promoted equality before the law. Legislative measures, such as the Hindu Succession Act and the Dowry Prohibition Act, were enacted to improve women's rights. Social reforms aimed at empowering marginalized communities were also implemented, alongside public awareness campaigns to challenge deep-rooted societal norms.
| 5. What were the key milestones in India's foreign policy after independence? |  |
Ans. India's foreign policy post-independence was characterized by non-alignment, promoting peace, and fostering cooperation with other nations. Key milestones included participation in the Bandung Conference, which emphasized solidarity among newly independent nations, and the establishment of diplomatic relations with various countries. India also played a critical role in the formation of the Non-Aligned Movement, seeking to provide an alternative to the Cold War divisions.
Related Searches
















