Indian Society and Social Issues: June 2025 Current Affairs | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
India Slips to 131st in Global Gender Gap Index 2025: Progress and Challenges

Why in News?
The World Economic Forum has recently released the Global Gender Gap Report 2025, revealing that India has fallen to the 131st position out of 148 countries. This marks a decline of two places from its previous rank of 129th in 2024. Published on June 12, 2025, the report indicates that India ranks among the lowest in South Asia for gender parity, with a parity score of 64.1%. The findings highlight both incremental improvements in certain areas and ongoing challenges, particularly in political empowerment.
Key Takeaways
- India ranks 131st out of 148 countries in the Global Gender Gap Index 2025.
- The country shows improvements in economic participation and educational attainment.
- Significant decline in political empowerment, with reduced female representation in leadership roles.
- Bangladesh made significant gains, improving its rank to 24th globally.
- Iceland maintains its top position for the 16th consecutive year.
Additional Details
- Global Gender Gap Index: This index evaluates countries based on four key dimensions: Economic Participation and Opportunity, Educational Attainment, Health and Survival, and Political Empowerment. It measures gender-based disparities and tracks progress over time.
- India saw the most notable improvement in Economic Participation, achieving a 0.9 percentage point increase to 40.7%. However, the labor force participation rate remained stagnant at 45.9%.
- In the Education sector, India achieved near parity with a score of 97.1%, driven by higher female literacy rates and improved tertiary education enrollment.
- The decline in Political Empowerment is concerning, with female representation in Parliament falling from 14.7% in 2024 to 13.8% in 2025.
- Globally, women constitute 41.2% of the workforce yet occupy only 28.8% of leadership positions, indicating a critical gap in decision-making roles.
The findings of the Global Gender Gap Index 2025 underline the need for stronger institutional actions and gender-sensitive policies to improve India's standing in gender parity. Despite some progress, the country faces significant challenges, particularly in political representation, which requires immediate attention.
UNFPA State of World Population 2025
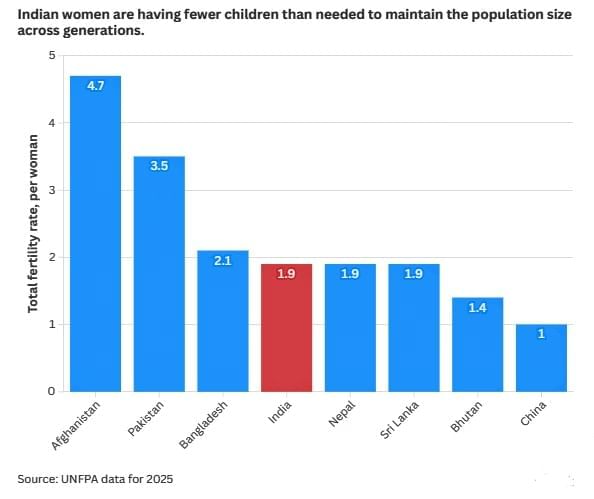
Context
India’s population has reached an estimated 146.39 crore by April 2025, according to the United Nations report titled “State of the World Population 2025: The Real Fertility Crisis..
India’s Status as per the 2025 Report
- Current Population Status: India is the world’s most populous country with 146.39 crore people, surpassing China (141.61 crore).
- The population is expected to peak at 170 crore before beginning to decline in approximately 40 years.
- Decline in Fertility Rate: TFR is now 1.9, below the replacement level of 2.1. Among the states that had fertility rates higher than the national average were Bihar (2.98), Meghalaya (2.9), Uttar Pradesh (2.35), Jharkhand (2.26), and Manipur (2.2).
Demographic Composition:
- Working-age population (15–64 years):68%
- Children (0–14 years):24%
- Youth (10–24 years):26%
- Elderly (65+ years):7% (expected to rise)
What is the Real Fertility Crisis?
- The real fertility crisis lies not in overpopulation or underpopulation, but in the inability of individuals to achieve their reproductive goals.
- It calls for reproductive agency —the freedom to make informed choices regarding sex, contraception, and family planning.
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
- The average number of children born to a woman during her childbearing years.
- A TFR of 2.1 is considered the replacement level needed to maintain a stable population.
Reasons for Population Decline
- Access to Reproductive Healthcare: Contraceptive use and maternal health services have expanded.
- Female Education & Empowerment: Increased female literacy and workforce participation delay childbirth.
- Urbanization: Urban lifestyles reduce family size due to cost and space constraints.
- Economic Uncertainty: Rising cost of living and job instability discourage large families.
Significance of the Population decline
- Population Stabilization:. TFR of 2.0 indicates India is approaching population stabilization, which can ease pressure on natural resources, public services, and the environment.
- Improved Maternal health: Fewer childbirths per woman, coupled with delayed age of marriage, lead to reduced maternal mortality, better child care, and healthier families.
- Women Empowerment: Lower fertility rates reflect higher education levels, workforce participation, and greater autonomy among women, leading to better social and economic outcomes.
What are the concerns?
- Ageing Population: rise in the elderly population will increase the dependency on the working population, demanding increased focus on pension, healthcare, and social welfare systems.
- Potential for Skewed Sex Ratios: In certain areas, fertility reduction without tackling gender bias can exacerbate sex-selective practices, leading to imbalanced sex ratios.
- Demographic Imbalance: States with vast fertility differences, potentially leading to interstate migration, cultural shifts, and resource strain in low-TFR states.
Global scenario
- In Japan the median age is over 48 years. This has led to prolonged economic stagnation, shrinking workforce, and increased public spending on pensions and healthcare.
- China’s one-child policy, enforced from 1979 to 2015, significantly lowered the birth rate, leading to a rapidly aging population.
- South Korea has one of the world’s lowest fertility rates, at 0.78 as of 2022.
Concluding remarks
India stands at a demographic crossroads. The decline in fertility is a testament to social progress in education, healthcare, and gender empowerment.
However, as the focus shifts from population control to reproductive rights and demographic balance, India must prepare for a future that balances economic productivity, social support systems, and individual reproductive choices.
|
164 videos|798 docs|1153 tests
|
FAQs on Indian Society and Social Issues: June 2025 Current Affairs - General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce
| 1. What is the Global Gender Gap Index, and how is it calculated? |  |
| 2. What factors contributed to India's decline to the 131st position in the Global Gender Gap Index? |  |
| 3. How does the Global Gender Gap Index impact policy-making in India? |  |
| 4. What are some key challenges faced by women in India that affect their standing in the Global Gender Gap Index? |  |
| 5. What initiatives has the Indian government implemented to improve gender equality and address the issues highlighted in the Global Gender Gap Index? |  |





















