Science & Technology: August 2025 Current Affairs | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
Bharat Forecast System

Why in News?
The Union Minister of State (Independent Charge) for Science and Technology, Earth Sciences recently informed the Rajya Sabha about the Bharat Forecast System, an innovative step in India’s meteorological capabilities.
Key Takeaways
- The Bharat Forecast System is an indigenously developed advanced weather forecasting system.
- It utilizes a Triangular Cubic Octahedral (TCo) dynamical grid, achieving a horizontal resolution of 6 km, enhancing precision compared to previous models.
- Real-time weather predictions are facilitated by supercomputing facilities at IITM-Pune and NCMRWF-Noida.
- The system aims to generate localized forecasts for clusters of panchayats, significantly improving predictions of extreme weather events.
Additional Details
- Development and Collaboration: The BharatFS was created by a team of scientists from Indian institutions, including IITM-Pune, with support from NCMRWF-Noida and the India Meteorological Department (IMD).
- Significance: With its enhanced resolution, the BharatFS captures local weather features, aiding farmers in crop planning, irrigation, and harvesting, while also assisting water authorities in managing reservoirs during monsoon seasons.
- The system has shown a 30% improvement in the accuracy of predicting extreme rainfall compared to previous models, reinforcing India’s meteorological services and regional leadership.
The launch of the Bharat Forecast System represents a significant upgrade in India's weather forecasting capabilities, promoting self-reliance and enabling better preparedness for extreme weather conditions.
WHO Classifies Hepatitis D as Carcinogenic
Why in News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has recently reclassified the hepatitis D virus (HDV) as carcinogenic. This decision follows an assessment by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), which was based on comprehensive data published in The Lancet Oncology.
Key Takeaways
- Hepatitis D is a serious liver infection caused by the hepatitis D virus (HDV).
- HDV requires the presence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) for its replication.
- Co-infection with HBV significantly increases the risk of severe liver damage and liver cancer.
Additional Details
- Infection Types:
- Co-infection: Occurs when a person is infected with both HDV and HBV simultaneously.
- Superinfection: Occurs when HDV infects someone who is already infected with HBV.
- Transmission: HDV can be transmitted through parenteral exposure (such as injections or blood transfusions), from mother to child, and through sexual contact.
- Diagnosis: Blood tests are used to detect HDV antibodies and HDV-RNA.
- Prevention: Key preventive measures include HBV vaccination, practicing safe blood transfusions, safe sex practices, screening, and avoiding sharing needles.
- Carcinogenicity: Co-infection with HBV and HDV can lead to a 2-6 times higher risk of developing liver cancer compared to HBV infection alone. Additionally, up to 75% of individuals may develop cirrhosis within 15 years of infection.
In conclusion, the reclassification of HDV by the WHO underscores the critical need for awareness and preventive measures against hepatitis D, especially in populations already affected by HBV.
Launch of e-Sushrut@Clinic

Why in News?
Recently, the National Health Authority (NHA) and the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) entered into a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to implement e-Sushrut@Clinic, a new initiative aimed at enhancing healthcare delivery in outpatient settings.
Key Takeaways
- e-Sushrut@Clinic is a lightweight, cloud-based Hospital Management Information System (HMIS) tailored for outpatient clinics.
- This initiative supports small and medium healthcare providers and is a vital component of the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM).
- The application is designed to facilitate easy onboarding for healthcare providers, allowing them to manage patient records efficiently.
Additional Details
- Features: The system includes modules for outpatient management, pharmacy, and nursing, providing essential functionalities at a low per-user cost.
- Healthcare providers can register on e-Sushrut@Clinic directly if they are not yet part of the Health Facility Registry (HFR) or Health Professionals Registry (HPR).
- This platform simplifies access to patient health records, telemedicine services, diagnostics, and prescriptions for both public and private clinics.
- Utilization of the AIIMS Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) for hypertension and diabetes will be available, enhancing patient care by aiding doctors in diagnosis and treatment.
The launch of e-Sushrut@Clinic represents a significant advancement in the digitization of healthcare services in India, making it easier for small and medium healthcare providers to adopt modern medical practices and improve patient outcomes.
Why India Needs a National Space Law

Why in News?
India is on the brink of a new era in space exploration, marked by significant achievements such as lunar missions, the Gaganyaan project, and the proposed Bharat Antariksh Station. However, the absence of a national space law poses a crucial challenge to the growth and regulation of this sector.
Key Takeaways
- India has made remarkable strides in space technology, but lacks a comprehensive legal framework.
- The absence of clear regulations hampers private participation and investment in the space sector.
- Internationally, countries like the U.S., Japan, and Luxembourg have established frameworks that provide legal certainty.
Additional Details
- Urgency for a National Space Law: India’s achievements in space science are impressive, yet the lack of a national legal framework may lead to accountability gaps, especially as private companies enter the field.
- Private Participation: Startups are crucial for innovation, but they face operational hurdles due to unclear licensing, foreign direct investment (FDI) rules, liability, and insurance issues.
- International Responsibility: Under the Outer Space Treaty, India is accountable for both governmental and private space activities, yet lacks a domestic framework for enforcement.
- Global Comparisons: Nations like the U.S. have laws such as the Commercial Space Launch Act that provide liability coverage and attract private investment.
- Incremental Approach: India’s cautious strategy prioritizes technical regulations before broad legislative measures, as seen in the Indian Space Policy (ISP) 2023 and the IN-SPACe Norms.
To ensure sustained growth in its space sector, India must enact a comprehensive national space law that addresses clarity, liability management, insurance, intellectual property protection, and a statutory framework for IN-SPACe. This legal framework is essential for balancing innovation with responsibility and will be pivotal for India's future as a space leader.
Orbiting Carbon Observatories (OCO) Program

Why in News?
The President of the USA has recently proposed the termination of NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatories (OCO) program, a crucial initiative for monitoring atmospheric carbon dioxide levels.
Key Takeaways
- The OCO program consists of a series of satellites specifically designed for remote sensing of Earth’s atmosphere.
- These satellites are vital for studying climate change by observing atmospheric CO2 concentrations from space.
Additional Details
- Timeline of Observatories:
- The initial OCO mission failed shortly after its launch in February 2009.
- OCO-2, launched in July 2014, was developed as a cost-effective replacement based on the original mission's design.
- In 2019, OCO-3 was launched to the International Space Station (ISS) to enhance CO2 observation capabilities.
- Importance of OCO:
- The data collected by OCO satellites have been utilized to create high-resolution maps of global plant growth.
- This information is beneficial for various sectors, including agriculture, drought monitoring, and forest management.
- Agencies like the US Department of Agriculture and private agricultural consultants use OCO data for predicting crop yields and monitoring drought conditions.
The future of the OCO program is uncertain, but its contributions to understanding climate change and supporting agricultural practices underscore its significance.
With Sci-Hub Gone, Will the ‘One Nation, One Subscription’ Scheme Step Up?

Why in News?
The recent blocking of Sci-Hub in India signifies a critical moment in the ongoing struggle between corporate publishers and the concept of open knowledge. The central issue revolves around the paradox of publicly funded research being placed behind steep paywalls. The government's One Nation One Subscription (ONOS) scheme, which allocates ₹6,000 crore, aims to make access to 13,000 journals more democratic for research institutions. However, there are significant concerns regarding its cost-effectiveness, inclusivity, and sustainability in the long term.
Key Takeaways
- The Delhi High Court's ruling against Sci-Hub is a landmark decision supporting publishers in copyright disputes.
- Publicly funded research is often monetized by private entities, which leads to exorbitant subscription costs.
- The ONOS initiative represents a large-scale attempt to bridge the knowledge access gap, yet its effectiveness remains in question.
Additional Details
- Distinctive Nature of Scientific Publishing:
- No royalties are paid to authors; researchers and peer reviewers work without compensation.
- Much of Indian scientific research is funded by taxpayers but is restricted to private access.
- Institutions face exorbitant subscription fees, with publishers justifying costs through claims of "quality control," despite significant profit margins.
- Global Controversy Around Sci-Hub:
- Sci-Hub has been ruled against for copyright infringement in various jurisdictions, including India.
- Many researchers relied on Sci-Hub for access to knowledge, especially those not affiliated with elite universities.
- Recent developments have shown a decline in Sci-Hub's relevance due to technical issues and an increase in open-access options.
- Vision of One Nation, One Subscription:
- The government plans to use ₹6,000 crore (2023-2026) for comprehensive access to 13,000 journals starting with public institutions.
- The initiative aims to provide equitable access, though private researchers may remain excluded until later phases.
The ban on Sci-Hub underscores the ongoing inequities in accessing scientific knowledge. While ONOS is a progressive step, it may only serve as a temporary solution unless accompanied by comprehensive reforms aimed at enhancing indigenous publishing capabilities, establishing national repositories, and implementing copyright retention policies. India’s goal should not merely be to alleviate symptoms of an exploitative system but to fundamentally transform knowledge into a public good.
ICRISAT's AI-based Agromet Advisory Service

Why in News?
The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT), in collaboration with the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), has launched an innovative AI-based Agromet Advisory Service aimed at enhancing agricultural practices and supporting farmers in adapting to climate change.
Key Takeaways
- The service leverages Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to deliver real-time, tailored climate advisory services.
- It focuses on providing smallholder farmers with localized, actionable weather and climate insights.
- The initiative aims to assist farmers in making critical decisions regarding sowing, irrigation, and pest management.
- Advisory services will be accessible through user-friendly digital channels, including an AI-powered WhatsApp bot.
Additional Details
- Implementation Phase: The project will initially be rolled out in Maharashtra through ICAR's Agro-Meteorological Field Units (AMFUs) targeting smallholder farmers.
- Support and Collaboration: The initiative is supported under the Government of India's Monsoon Mission III and involves several organizations, including the Central Research Institute for Dryland Agriculture (CRIDA-ICAR), the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI), the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), and the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD).
- iSAT Tool: The Intelligent Systems Advisory Tool (iSAT), previously piloted during Monsoon Mission II, is being upgraded into a fully functional AI-powered platform to transform complex climate data into personalized advisories.
This initiative is expected to significantly enhance the agricultural decision-making process for farmers, particularly in areas prone to climate variability. By providing timely and relevant insights, ICRISAT aims to serve as a model for future agricultural advisory services both nationally and internationally.
ISRO Conducts Air Drop Test for Gaganyaan
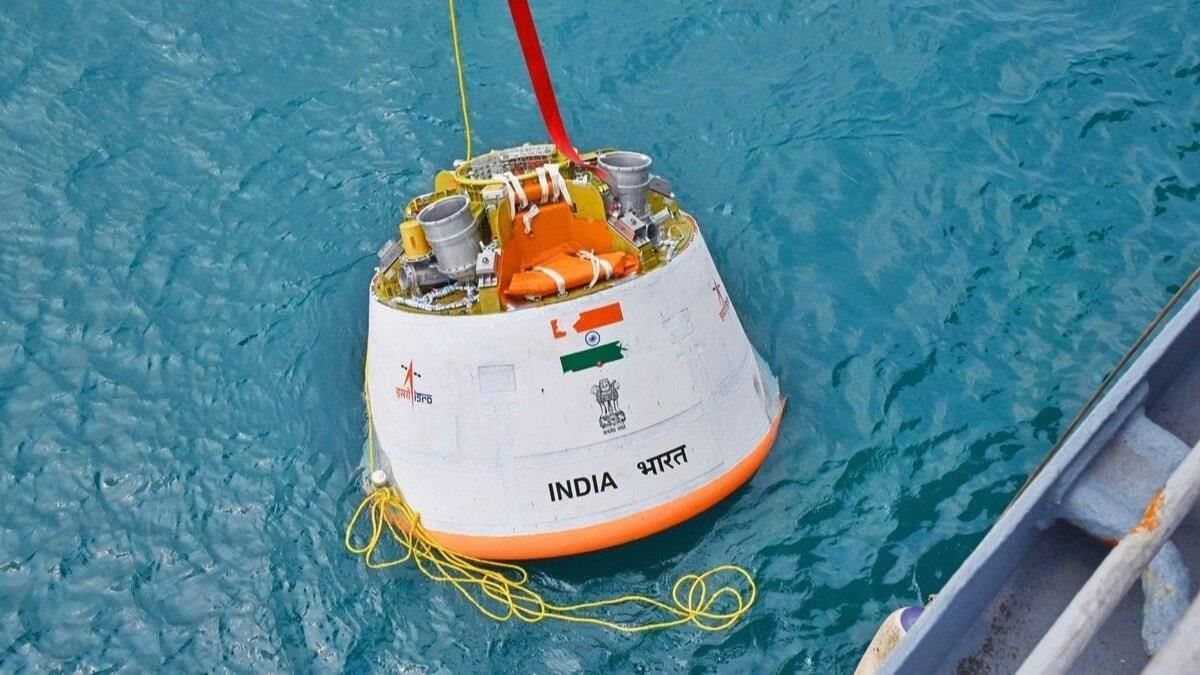

Why in News?
ISRO has successfully conducted its first Integrated Air Drop Test (IADT-1), a significant milestone for the Gaganyaan human spaceflight mission. This test involved the release of a five-tonne dummy crew capsule from a helicopter to assess its parachute-based deceleration system, which is essential for ensuring safe splashdown. The successful execution of this test validates critical safety mechanisms necessary for ensuring astronaut survival during re-entry and landing. The first uncrewed mission is anticipated by late 2025, while India’s inaugural crewed spaceflight is planned for 2027.
Key Takeaways
- The IADT-1 test simulates the final phase of a spacecraft's return to Earth.
- Parachute deployment and module safety during splashdown were evaluated.
- Upcoming missions include the first uncrewed launch (Gaganyaan-1) planned for late 2025.
Additional Details
- Integrated Air Drop Test (IADT): This test simulates a launch pad abort scenario, allowing engineers to assess critical systems such as parachute deployment during emergencies and performance during partial parachute failure. However, it cannot fully replicate the actual re-entry conditions, which necessitate further sub-orbital or orbital testing.
- Purpose of IADT-1: Conducted to evaluate the parachute-based deceleration system, an uncrewed capsule was dropped from 3 km altitude with parachutes designed to deploy in a specific sequence, ultimately slowing the capsule to approximately 8 m/s prior to splashdown.
- The test confirmed the crew module's orientation and recovery process during splashdown, ensuring astronaut safety.
The Gaganyaan mission represents a critical step in India's long-term human spaceflight objectives, aiming to send Indian astronauts to low-earth orbit by 2027. To achieve this, ISRO is executing a series of rigorous tests to validate essential safety and mission systems, including the upcoming Test Vehicle Abort Mission-2 (TV-D2), scheduled for the third quarter of 2025, which will simulate a more complex abort scenario.
Lunar Module Launch Vehicle (LMLV)
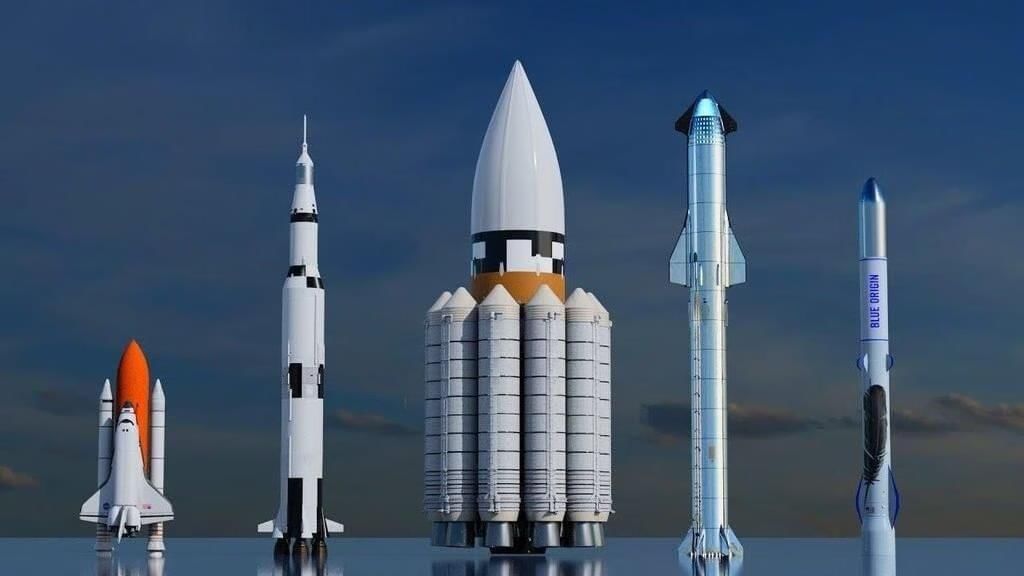 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is in the process of developing its heaviest rocket to date, the Lunar Module Launch Vehicle (LMLV), aimed at enhancing India's capabilities in space exploration.
Key Takeaways
- The LMLV is designed primarily for lunar exploration and aims to support India's first human mission to the Moon by 2040.
- This rocket will replace the Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV) plan and will aid in the development of India's space station program.
- It will be as tall as a 40-storey building, significantly larger than the current LVM-3 model.
Additional Details
- Payload Capacity: The LMLV can carry up to 80 tonnes to Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and 27 tonnes to the Moon, making it suitable for human-rated spacecraft.
- Design:The vehicle is a partially reusable super heavy-lift rocket that consists of three stages:
- The first two stages utilize liquid propellants.
- The third stage operates on cryogenic propellant.
- It features strap-on boosters that are taller than the entire LVM-3 rocket and a total of 27 engines in the first stage (core plus boosters).
- Timeline: The LMLV is expected to be completed by 2035, demonstrating ISRO's commitment to advancing India's long-term space exploration goals.
Future missions planned using the LMLV include:
- Human Lunar Mission (2040 target): The LMLV will be capable of carrying crew modules weighing 18-20 tonnes for India's inaugural astronaut landing on the Moon.
- Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS): The LMLV will facilitate the deployment of heavy modules for India's planned five-module space station by 2035.
- Lunar Cargo Missions: It can transport approximately 27 tonnes to the Moon, aiding in logistics and infrastructure development on the lunar surface.
- Deep Space Exploration: The heavy-lift capacity of the LMLV could support interplanetary missions in the 2040s, extending beyond lunar initiatives.
In light of these developments, the LMLV is poised to significantly enhance India's position in global space exploration.
Reforming the Steel Framework

Why in News?
The Prime Minister's speech on Independence Day 2025 marked a significant shift towards focusing on frontier technologies, including semiconductors, clean energy, artificial intelligence (AI), quantum computing, and defense indigenization. This speech acknowledged the bureaucratic inertia and regulatory challenges that continue to impede India's technological ambitions.
Key Takeaways
- The Prime Minister emphasized the need for India to develop capabilities in critical areas such as semiconductors and electric vehicles (EVs).
- India aims to reduce dependency on imports within two decades.
- India is currently the largest per capita data consumer globally, surpassing China and the US.
Additional Details
- Current Technological Landscape: India has established strengths in mid-tech sectors, particularly in fintech, data access, and digitization. Key cities like Bengaluru and Hyderabad are emerging as high-tech hubs.
- Import Dependency: Despite advancements, India heavily relies on imports for semiconductors and defense hardware, highlighting the need for self-reliance.
- Bureaucratic Challenges: The colonial legacy of bureaucratic structures prioritizes control over innovation, with rigid frameworks inhibiting progress. Efforts for reform, including the Veerappa Moily Committee's recommendations, have not been fully realized.
- Importance of Reforms: Regulatory and judicial reforms are critical to eliminate persistent red tape and improve the investment climate, particularly in high-tech sectors.
- International Comparisons: Countries like the US and China showcase models where political leadership can effectively drive national interests, contrasting with India's bureaucratic hurdles.
- Vision for Viksit Bharat@2047: For India to become a deep-tech powerhouse, it must undergo significant governance restructuring alongside financial investments.
In conclusion, India's aspirations in deep-tech must align with necessary institutional reforms. The Prime Minister's 2025 address highlighted the need to address bureaucratic bottlenecks as part of the broader goal of achieving Atmanirbhar Bharat. The upcoming centenary of the UPSC in 2026 presents a unique opportunity to reshape governance to meet India's 2047 objectives.
India’s Aquanauts to Lead Deep-Sea Exploration under Samudrayaan
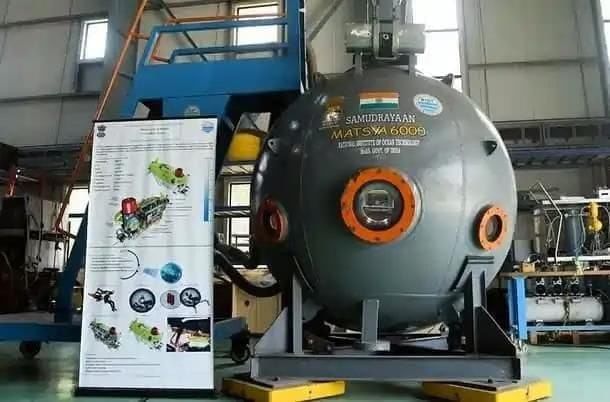

Why in News?
Recently, two Indian aquanauts, Cdr (Retd) Jatinder Pal Singh and R Ramesh, completed training dives aboard the French vessel Nautile, achieving depths of 5,002 and 4,025 metres in the Atlantic Ocean. These dives are preparatory steps for India's ambitious Samudrayaan project, which aims to send three humans to a depth of 6,000 metres by 2027. This initiative parallels how Axiom-4 supports the Gaganyaan mission, providing crucial insights for enhancing India's deep-sea exploration capabilities.
Key Takeaways
- The Samudrayaan mission aims for deep-ocean exploration, reaching 6,000 metres.
- Matsya-6000 is the crewed submersible being developed for this mission.
- India's deep-sea exploration aligns with its Blue Economy Vision.
Additional Details
- Samudrayaan Mission: This mission is part of India's Deep Ocean Mission, approved in 2021, with a budget of ₹4,077 crore over five years. Its goals include developing technologies for deep-sea mining and underwater vehicles.
- Matsya-6000: This submersible is designed to carry three aquanauts to depths of 6,000 metres. It is shaped like a large fish and contains a 2.1-metre diameter personal sphere for the crew, ensuring life support for 12-hour missions.
- Challenges: The mission faces significant challenges such as developing a pressure-resistant vessel and maintaining a livable environment for the aquanauts.
- Health and Safety: Aquanauts must undergo rigorous physical conditioning and manage food and water intake carefully during missions.
- Communication: Traditional communication methods fail underwater; thus, India is developing an acoustic telephone system for reliable communication.
The Samudrayaan Mission positions India among a select group of nations, including the United States, Russia, China, Japan, and France, with advanced capabilities in deep-sea exploration. This initiative not only aims to explore the largely uncharted deep ocean, which holds vast reserves of resources, but also supports India's vision of achieving a Viksit Bharat.
ICMR Introduces ‘CEREBO’ to Diagnose Brain Injury
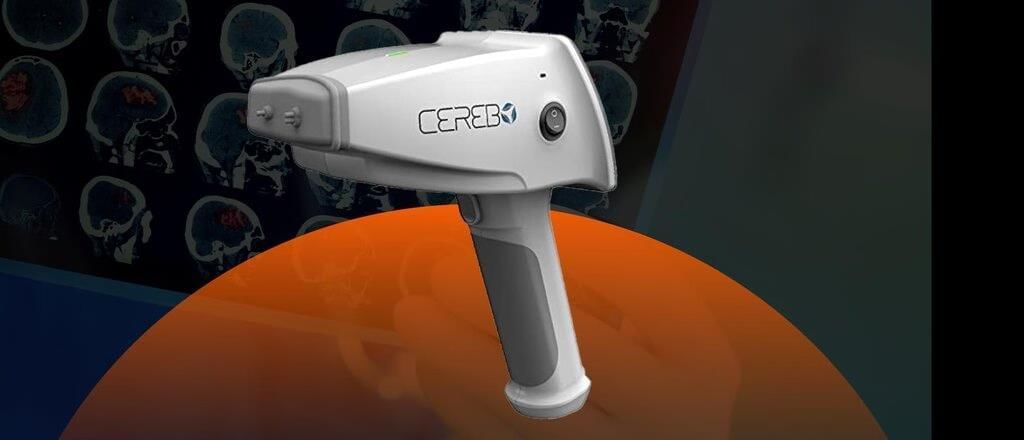

Why in News?
The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has launched an innovative, indigenous device named CEREBO. This portable tool is designed for the rapid and radiation-free diagnosis of traumatic brain injuries (TBI), particularly aimed at enhancing healthcare access in emergency and rural settings.
Key Takeaways
- CEREBO is a handheld device that allows for quick diagnosis of brain injuries.
- It is developed using near-infrared spectroscopy and machine learning algorithms.
- The device is user-friendly, requiring minimal training for operation.
- It can detect intracranial bleeding and oedema in under a minute.
- The introduction of CEREBO aims to address the high mortality and morbidity rates associated with head injuries in India.
Additional Details
- CEREBO: A portable, non-invasive diagnostic tool that is radiation-free and safe for use on infants and pregnant women.
- Development and Collaboration: The device was developed through a collaborative effort involving ICMR, AIIMS Bhopal, NIMHANS Bengaluru, and others, ensuring clinical validation and regulatory approvals.
- Significance: CEREBO addresses the lack of accessibility to advanced imaging facilities in rural areas, reducing costs and improving speed in diagnosis.
- Public Health Impact: Early detection through this device can significantly reduce mortality rates and improve recovery outcomes for TBI patients.
In conclusion, CEREBO represents a significant advancement in the diagnosis and management of traumatic brain injuries in India. By providing a cost-effective and efficient alternative to traditional imaging methods, it aims to enhance emergency healthcare responses, particularly in underserved regions.
CANCER AI & TECHNOLOGY CHALLENGE (CATCH) Grant Program

Why in News?
The IndiaAI Independent Business Division (IBD) has partnered with the National Cancer Grid (NCG) to launch the Cancer AI & Technology Challenge (CATCH) Grant Program. This initiative aims to enhance cancer care through innovative AI solutions across India.
Key Takeaways
- The CATCH Grant Program supports the development of AI-driven solutions for cancer screening, diagnostics, and treatment support.
- Grants of up to ₹50 lakh will be awarded to selected teams comprising technology innovators and clinical institutions.
- Successful pilot projects may qualify for additional scale-up grants of up to ₹1 crore.
- The program encourages joint applications from clinical and technical leads.
Additional Details
- Grants: The program will provide funding of up to ₹50 lakh per project, co-funded by IndiaAI and NCG, to support the deployment of AI solutions in the NCG hospital network.
- Focus Areas: The challenge will prioritize high-impact categories such as AI-enabled screening, diagnostics, clinical decision support, patient engagement, operational efficiency, research, and data curation.
- Eligibility: Applicants can include startups, health technology companies, academic institutions, and public or private hospitals. Joint applications are encouraged.
- Responsible AI: The program will emphasize ethical AI development, clinical validation, and readiness for deployment in the Indian healthcare context.
This initiative is a significant step towards integrating AI technologies in healthcare, aiming for a transformative impact on cancer care across India.
What is Pneumococcal Disease?
Why in News?
Pneumococcal disease has gained attention due to the recent launch of Pfizer's next-generation 20-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV20) in India. This vaccine aims to protect against 20 serotypes of pneumococcus, which are responsible for a significant proportion of pneumococcal diseases.
Key Takeaways
- Pneumococcal disease encompasses a variety of illnesses caused by the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- The disease can lead to mild infections, such as ear infections, as well as severe conditions like pneumonia and meningitis.
- Young children and the elderly are particularly vulnerable to pneumococcal infections, especially in developing regions.
- Approximately one million children die from pneumococcal disease annually worldwide.
Additional Details
- Pneumococcus: This bacterium is encapsulated and possesses a polysaccharide capsule, which is crucial for its virulence.
- Transmission: Pneumococci are primarily spread through direct contact with respiratory secretions from infected individuals or healthy carriers.
- Treatment: Management typically involves the use of antibiotics, while vaccines can significantly lower the risk of infection, particularly in at-risk populations.
- Resistance Issues: There is a growing concern regarding pneumococcal resistance to antimicrobial treatments, which poses a serious public health challenge.
In conclusion, pneumococcal disease remains a critical global health issue, and the introduction of effective vaccines like PCV20 is essential for reducing its impact, especially among vulnerable groups.
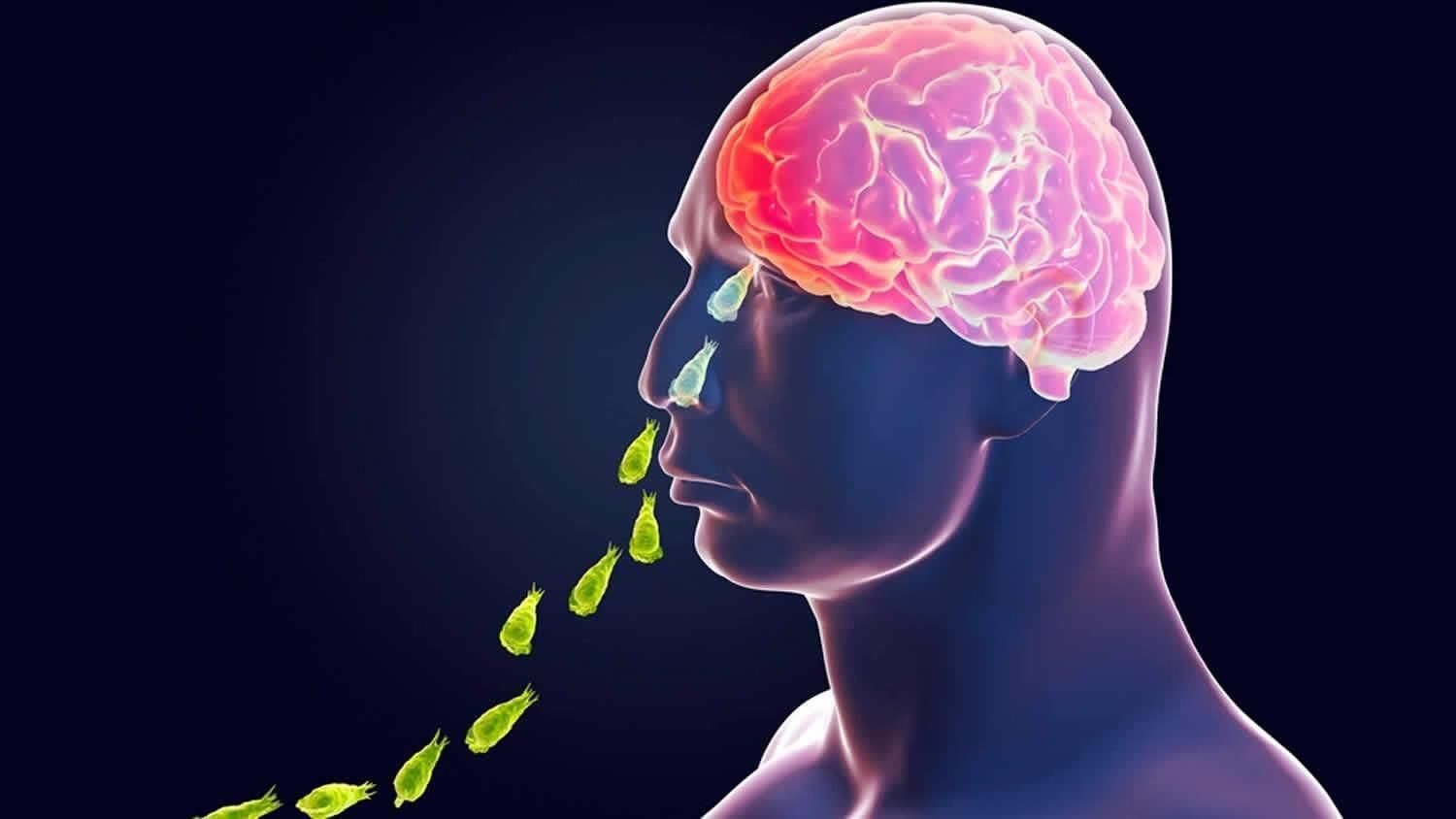
Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM)
Why in News?
Kerala’s health department has issued an alert in Kozhikode district following three consecutive cases of the rare and highly fatal disease known as Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM).
Key Takeaways
- PAM is caused by the amoeba Naegleria fowleri, often referred to as the "brain-eating amoeba."
- This infection thrives in warm freshwater environments, with optimal temperatures reaching up to 46°C (115°F).
Additional Details
- Entry Point: The amoeba typically enters the body through the nose during swimming or other water-related activities, subsequently traveling through the olfactory nerve to the brain.
- Impact: Once in the brain, the amoeba destroys brain tissue and causes severe swelling, leading to significant neurological damage.
- Transmission: PAM is not communicable from person to person.
- Symptoms: Initial symptoms include headache, fever, nausea, and vomiting, which can progress to stiff neck, confusion, seizures, hallucinations, coma, and ultimately death.
- Progression: Most cases lead to death within 1-18 days post symptom onset, as noted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- Diagnosis and Treatment: Diagnosis is challenging due to its rarity and is confirmed via a Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) test of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). PAM is often misdiagnosed as bacterial or viral meningitis, and there is no universally effective treatment. Management typically involves a combination of drugs such as amphotericin B, azithromycin, fluconazole, rifampin, miltefosine, and dexamethasone, as per CDC guidelines.
Awareness and prompt identification of PAM are crucial due to the rapid progression and high fatality rate associated with this disease. It is important for healthcare providers to consider PAM in patients presenting with neurological symptoms, especially in areas where the amoeba is prevalent.
Understanding Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)
Why in News?
Recently, there has been an alarming increase in cases of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) in Gaza, a condition that can lead to full-body paralysis in severe instances.
Key Takeaways
- GBS is a rare autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the peripheral nervous system.
- It commonly affects individuals aged 30 to 50 and can manifest at any age.
- The syndrome may follow a viral or bacterial infection, vaccination, or major surgery.
Additional Details
- What is Guillain-Barré Syndrome? GBS, also known as acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (AIDP), affects the part of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord, which controls muscle movement and sensory signals.
- Symptoms: Initial symptoms often include an unknown fever, followed by progressive weakness and other nervous system-related issues that intensify over hours, days, or weeks. While some patients may only experience mild weakness, others can suffer from severe paralysis, potentially affecting their ability to breathe independently.
- Treatment: There is currently no known cure for GBS. However, various treatment options can alleviate symptoms and expedite recovery. Most individuals recover completely, although recovery may take several years, with many regaining the ability to walk within six months of the onset of symptoms.
In summary, while Guillain-Barré syndrome is a serious condition that poses significant challenges, awareness and prompt medical intervention can aid in recovery and improve outcomes for affected individuals.
ClassGPT: How AI is Reshaping Campuses

Why in News?
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in higher education has sparked a debate surrounding its benefits and challenges. With students increasingly turning to AI for various academic tasks, institutions are compelled to reassess their policies to foster originality and critical thinking while embracing technological advancements.
Key Takeaways
- High student and faculty usage of AI tools.
- Concerns about academic integrity and critical thinking.
- Varied institutional responses to AI integration.
- Global perspectives on AI's role in education.
Additional Details
- AI Usage Among Students: A recent survey from IIT Delhi (2024) revealed that four out of five students utilize AI tools frequently, with some opting for premium subscriptions.
- Faculty Engagement: Approximately 77% of educators reported using AI for tasks such as summarizing papers and drafting communications.
- Student Motivations: Students find AI beneficial for simplifying complex concepts, summarizing material, creating mind maps, and simulating scenarios.
- Concerns Raised: Issues include mathematical inaccuracies, flawed debugging, and inadequate context handling, leading to questions about originality and academic integrity.
- Institutional Innovations: Various Indian institutions are experimenting with AI in their curricula, introducing workshops, and reevaluating assessment methods to incorporate AI responsibly.
- Global Trends: In countries like the USA, Australia, and the UK, educational institutions are adapting their policies to integrate AI while emphasizing transparency and ethical use.
In conclusion, as generative AI becomes an integral part of classrooms in India, the focus must shift from whether to ban or allow its use to how it can be effectively regulated and ethically integrated into learning environments. The future of education will depend on finding a balance that promotes critical thinking while leveraging the advantages of AI technology.
Maryam Mirzakhani New Frontiers Prize
Why in News?
Indian mathematician Dr. Rajula Srivastava has been awarded the Maryam Mirzakhani New Frontiers Prize for her innovative research in harmonic analysis and number theory.
Key Takeaways
- Dr. Rajula Srivastava's affiliation includes the Hausdorff Center for Mathematics, University of Bonn, and Max Planck Institute of Mathematics, Germany.
- The prize recognizes early-career women mathematicians for their significant contributions to the field.
About the Indian Laureate: Dr. Rajula Srivastava
- Field of Work: Dr. Srivastava focuses on simplifying complex mathematical functions using advanced mathematical tools.
- Her research involves exploring how certain numbers can approximate specific points on curved shapes in higher dimensions.
About the Maryam Mirzakhani New Frontiers Prize
- Purpose: This award aims to honor and encourage early-career women mathematicians (within two years of PhD completion) for their exceptional research contributions.
- Named After: The prize is named in honor of Maryam Mirzakhani, the first woman and first Iranian to receive the Fields Medal, renowned for her work on geometry and Riemann surfaces.
- Established: The prize was initiated in November 2019 by the Breakthrough Prize Foundation.
- Prize Amount: $50,000, which may be shared among multiple recipients in a given year.
- Eligibility: Women mathematicians who have recently completed their PhD (within 2 years) and demonstrated exceptional promise and innovation in mathematical research.
Other Important Prizes in Mathematics
- Fields Medal: Awarded every four years to mathematicians under 40, it is regarded as the most prestigious global mathematics award, established in 1936.
- Abel Prize: Instituted by the King of Norway in 2001, this annual award recognizes lifetime achievements in mathematics and is often considered the closest equivalent to the Nobel Prize in this field.
- Wolf Prize in Mathematics: Awarded annually since 1978 by the Wolf Foundation in Israel, it honors exceptional accomplishments across all branches of mathematics and is ranked just below the Fields and Abel Prizes in prestige.
In popular culture, a recent film titled "The Man Who Knew Infinity" is based on the biography of the renowned mathematician S. Ramanujan.
Biologics & Biosimilars: The Next Frontier in Affordable Medicines
Source: Science Direct
Why in News?
The emergence of biologics and biosimilars is revolutionizing modern medicine, moving beyond traditional small molecule drugs. These complex therapies offer targeted treatments that can significantly impact healthcare.
Key Takeaways
- Biologics are large, complex drugs derived from living organisms.
- Biosimilars are near-identical copies of biologics, available after the original patent expires.
- Regulatory reforms are essential for improving access to affordable medicines in India.
Additional Details
- Small Molecule Drugs:These are low molecular weight compounds that are chemically synthesized. They are characterized by:
- Fixed structures that are chemically stable.
- Ease of replication and patent protection.
- High costs during patent protection, followed by significantly reduced prices post-expiry (e.g., Sovaldi dropped from $84,000 to $1,000).
- Biologics:These are large, intricate drugs created from living cells or organisms. Examples include:
- Insulin (~5,800 daltons)
- Remicade (~150,000 daltons)
- Biosimilars: These are close replicas of biologics but are not identical due to their complex production processes. They provide lower-cost alternatives to biologics after patent expiration.
- Regulation and Reform:
- Current regulations require costly trials for biosimilars, including animal and clinical trials, unlike generic drugs.
- Countries like the UK and USA are reducing the burden of animal trials, promoting innovations like organ-on-chip and human models.
- India still adheres to older regulatory norms, although waivers are under review, and clinical trials remain mandatory.
- Significance for India:
- Access to generic small molecules has transformed Indian healthcare.
- Affordable biosimilars could similarly enhance treatment for chronic and rare diseases.
- Regulatory reform is critical to lowering costs, speeding up access, and expanding healthcare coverage.
In summary, as biologics and biosimilars continue to evolve, they present both challenges and opportunities for healthcare systems, particularly in India, where regulatory changes could pave the way for more affordable treatment options.
Darwin Tree of Life (DToL) Project
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Darwin Tree of Life (DToL) project is nearing the completion of its first phase, aiming to sequence the genomes of a significant number of species across Britain and Ireland.
Key Takeaways
- The project targets the sequencing of genomes from 70,000 species of eukaryotic organisms.
- It is part of the larger Earth BioGenome Project, which endeavors to sequence all complex life on Earth.
- The initiative employs advanced DNA sequencing technologies and computational tools to analyze genetic diversity.
Additional Details
- Eukaryotes: These are organisms with complex cells that have a defined nucleus. They include multi-cellular organisms such as protists, plants, animals, and fungi.
- Eukaryotic cells feature a nuclear membrane that encases the nucleus, which holds well-defined chromosomes.
- These cells also contain various organelles, such as mitochondria (responsible for cellular energy production) and the Golgi apparatus.
- Reproductive methods in eukaryotes include asexual reproduction through mitosis and sexual reproduction via meiosis and gamete fusion.
This collaborative effort involves ten partners specializing in biodiversity, genomics, and analytical methods, all working together to deepen our understanding of life's genetic diversity.
Seabuckthorn: The Wonder Plant of Cold Deserts
Why in News?
The seeds of seabuckthorn and buckwheat cultivated in the cold desert of Ladakh are currently part of experiments aboard the International Space Station conducted by NASA's Crew-11 mission.
Key Takeaways
- Seabuckthorn is often referred to as the 'Wonder Plant', 'Ladakh Gold', 'Golden Bush', or 'Gold Mine' of cold deserts.
- This plant species thrives in extreme temperatures and is notably drought-resistant.
Additional Details
- Distribution: Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) is found across Europe and Asia, particularly in the Himalayan region of India, where it grows above the tree line in dry areas like Ladakh and Spiti.
- Characteristics: The plant produces small orange or yellow berries that are sour yet rich in vitamins, especially vitamin C. It can endure temperatures ranging from -43°C to 40°C and retains its berries during winter, making it resilient in harsh climates.
- Uses: Traditionally, every part of the seabuckthorn plant—fruit, leaves, twigs, roots, and thorns—has been utilized for various purposes such as medicine, nutritional supplements, fuel, and fencing. Furthermore, its berries provide food for numerous bird species during periods of food scarcity.
- The leaves serve as a protein-rich fodder for animals in cold desert regions, including sheep, goats, donkeys, cattle, and double-humped camels.
In summary, the seabuckthorn plant is not only vital for its ecological benefits but also holds significant cultural and nutritional value in the regions it grows, making it a key subject of study in space and terrestrial environments.
Charge-Coupled Device
Why in News?
The charge-coupled device (CCD) is a groundbreaking electronic component that has had a profound impact on various technological fields, particularly in imaging systems.
Key Takeaways
- A CCD converts light into electrical signals using an array of capacitors.
- It consists of an integrated circuit made up of small picture elements known as pixels.
- The device operates on the principle of the photoelectric effect to generate images.
Additional Details
- Functionality: Each pixel in a CCD acts as a light sensor, collecting photons and converting them into electrical charges. These charges are sequentially transferred across the device to create a digital image.
- Photoelectric Effect: When light hits the CCD, it generates electron-hole pairs in the semiconductor material. This process produces a small group of electrons that corresponds to the intensity of light received by the pixel.
- The sequential transfer mechanism of charges resembles passing buckets of water, allowing for precise imaging results.
CCDs have revolutionized digital imaging, replacing traditional film in cameras and enabling high-quality imaging in various fields such as medicine and astronomy. Their ability to capture detailed images has made them indispensable in today’s technology landscape.
|
164 videos|798 docs|1153 tests
|
FAQs on Science & Technology: August 2025 Current Affairs - General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce
| 1. What are ionic liquids and what are their potential applications? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of chalkiness in rice? |  |
| 3. How does the 'CEREBO' system introduced by ICMR diagnose brain injuries? |  |
| 4. What is the Bharat Forecast System and its relevance? |  |
| 5. Why has the WHO classified Hepatitis D as carcinogenic? |  |





















