NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science - Is Matter Around Us Pure
| Table of contents |

|
| Page No. 15 |

|
| Page No. 18 |

|
| Page No. 19 |

|
| Page No. 22 |

|
| Page No. 23 |

|
| Page No. 24 |

|
Page No. 15
Q1. What is meant by a substance?
Ans: A pure substance is one that is made up of only one kind of particle, either atoms or molecules. It has definite composition and distinct properties.  Examples of Pure SubstancesA pure substance consists of only one type of particle, either atoms or molecules. It has a definite composition and distinct properties. Examples include:
Examples of Pure SubstancesA pure substance consists of only one type of particle, either atoms or molecules. It has a definite composition and distinct properties. Examples include:
- Oxygen
- Carbon
In contrast, a mixture contains two or more pure substances. For instance:
- Sea water is a mixture of salt and water.
- Soil contains various organic and inorganic materials.
Key points about mixtures:
- Mixtures can be separated into their components through physical processes.
- Each component retains its own properties.
Types of mixtures include:
- Homogeneous mixtures have a uniform composition (e.g., sugar in water).
- Heterogeneous mixtures have a non-uniform composition (e.g., sand and salt).
In summary, a pure substance has consistent properties, while a mixture contains multiple substances that can vary in composition.
Q2. List the points of differences between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.
Ans: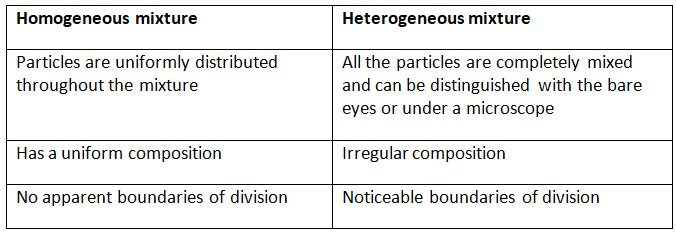
Page No. 18
Q1. Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures with examples.
Ans: The following are the differences between heterogeneous and homogenous mixtures.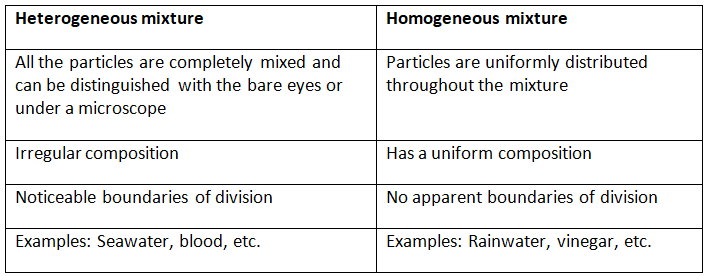
Q2. How are sol, solution and suspension different from each other?
Ans: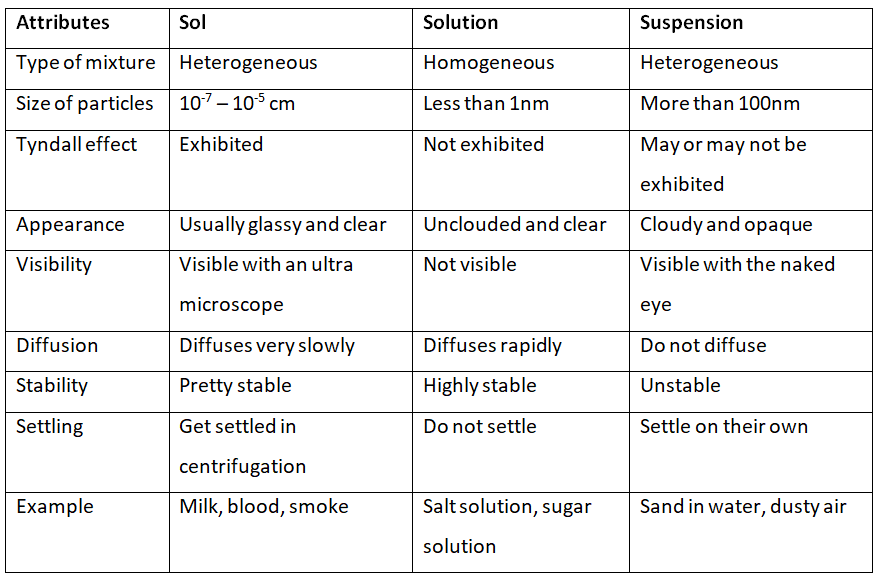
Q3. To make a saturated solution, 36g of sodium chloride is dissolved in 100 g of water at 293 K. Find its concentration at this temperature.
Ans: Mass of solute (NaCl): 36 g
Mass of solvent (H2O): 100 g
Mass of solution: 136 g (NaCl + H2O)
Concentration: Calculated as follows:
- Concentration = (Mass of solute / Mass of solution) × 100
- Concentration = (36 g / 136 g) × 100
- Concentration = 26.47%
Thus, the concentration of the solution is 26.47%.
Page No. 19
Q1. Classify the following as chemical or physical changes:
- cutting of trees,
- melting of butter in a pan,
- rusting of almirah,
- boiling of water to form steam,
- passing of electric current, through water and the water breaking down into hydrogen and oxygen gases,
- dissolving common salt in water,
- making a fruit salad with raw fruits, and
- burning of paper and wood.
Ans: The following is the classification into physical and chemical change: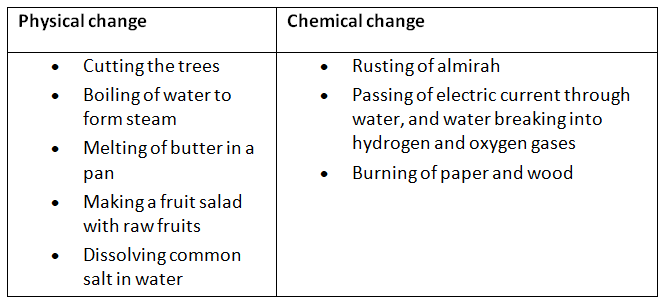
Q2. Try segregating the things around you as pure substances or mixtures.
Ans: Listed below are the classifications based on pure substances and mixtures: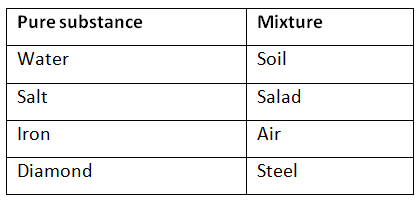
Page No. 22
Exercises
Q1. Which separation techniques will you apply for the separation of the following?
(a) Sodium chloride from its solution in water.
(b) Ammonium chloride from a mixture containing sodium chloride and ammonium chloride.
(c) Small pieces of metal in the engine oil of a car.
(d) Different pigments from an extract of flower petals.
(e) Butter from curd.
(f) Oil from water.
(g) Tea leaves from tea.
(h) Iron pins from sand.
(i) Wheat grains from husk.
(j) Fine mud particles suspended in water.
Ans: (a) In water, sodium chloride in its solution can be separated through the process of evaporation (as well as crystallization).
(b) The sublimation technique is appropriate as ammonium chloride supports sublimation.
(c) Tiny metal pieces in the engine oil of a car can be filtered manually.
(d) Chromatography can be used to separate different pigments from an extract of flower petals.
(e) The technique of churning can be applied to separate butter from curd. It is based on the concept of difference in density.
(f) To separate oil from water, which are two immiscible liquids which vary in their densities, using a funnel can be an effective method.
(g) Tea leaves can be manually separated from tea using simple filtration methods.
(h) Iron pins can be separated from sand either manually or with the use of magnets as the pins exhibit strong magnetic quality, which can be a key characteristic taken into consideration.
(i) The differentiating property between husk and wheat is that there is a difference in their mass. If treated with a small amount of wind energy, a remarkable variation in the moving distance is noticed. Hence, to separate them, the sedimentation/winnowing procedure can be applied.
(j) Due to the property of water, sand or fine mud particles tend to sink in the bottom as it is denser, provided they are undisturbed. Through the process of sedimentation/decantation, water can be separated from fine mud particles, as the technique is established on obtaining clear water by tilting it out.
Page No. 23
Q2. Write the steps you would use for making tea. Use the words solution, solvent, solute, dissolve, soluble, insoluble, filtrate and residue.
Ans: Steps for Making Tea
- Heat a cup of milk, which acts as the solvent.
- Add tea powder or leaves, the solute, to the boiling milk.
- Observe that the tea powder remains insoluble while boiling.
- Add sugar to the boiling solution and stir.
- Sugar, being a solute, is soluble in the milk.
- Continue stirring until the sugar completely dissolves, achieving saturation.
- Once the raw smell of tea leaves disappears, remove the solution from heat.
- Filter the mixture to separate the tea powder, which becomes the residue.
- The liquid that passes through is the filtrate, containing the dissolved sugar and milk.
Q3. Pragya tested the solubility of three different substances at different temperatures and collected the data as given below (results are given in the following table, as grams of substance dissolved in 100 grams of water to form a saturated solution).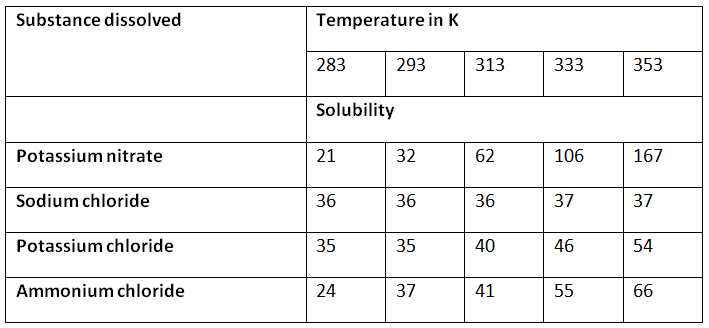
(a) What mass of potassium nitrate would be needed to produce a saturated solution of potassium nitrate in 50 grams of water at 313 K?
(b) Pragya makes a saturated solution of potassium chloride in water at 353 K and leaves the solution to cool at room temperature. What would she observe as the solution cools? Explain.
(c) Find the solubility of each salt at 293 K. Which salt has the highest solubility at this temperature?
(d) What is the effect of change of temperature on the solubility of a salt?
Ans: (a) Given:
Mass of potassium nitrate required to produce a saturated solution in 100 g of water at 313 K = 62g
To find:
Mass of potassium nitrate required to produce a saturated solution in 50 g of water =?
Required amount = 62 x 50/100 = 31
Hence, 31 g of potassium nitrate is required.
(b) The solubility of potassium chloride in water is decreased when a saturated solution of potassium chloride loses heat at 353 K. Consequently, Pragya would observe crystals of potassium chloride, which would have surpassed its solubility at low temperatures.
(c) As per the given data, that is
Solubility of potassium nitrate at 293K = 32 g
Solubility of sodium chloride at 293K = 36 g
Solubility of potassium chloride at 293K = 35 g
Solubility of ammonium chloride at 293K = 37g
We can observe from this data that ammonium chloride has the highest solubility at 293K.
(d) Effect of change of temperature on the solubility of salts:
The table clearly depicts that the solubility of the salt is dependent upon the temperature and increases with an increase in temperature. With this, we can infer that when a salt arrives at its saturation point at a specific temperature, there is a propensity to dissolve more salt through an increase in the temperature of the solution.
Q4. Explain the following, giving examples.
(a) Saturated solution
(b) Pure substance
(c) Colloid
(d) Suspension
Ans: (a) Saturated solution: It is the state in a solution at a specific temperature when a solvent is no longer soluble without an increase in temperature. Example: Excess carbon leaves off as bubbles from a carbonated water solution saturated with carbon.
(b) Pure substance: A substance is said to be pure when it comprises only one kind of molecule, atom or compound without adulteration with any other substance or any divergence in the structural arrangement. Examples: Sulphur, diamonds etc.
(c) Colloid: A Colloid is an intermediate between solution and suspension. It has particles of various sizes that range between 2 to 1000 nanometers. Colloids can be distinguished from solutions using the Tyndall effect. Tyndall effect is defined as the scattering of light (light beam) through a colloidal solution. Examples: Milk and gelatin.
(d) Suspension: It is a heterogeneous mixture that comprises solute particles that are insoluble but are suspended in the medium. These particles that are suspended are not microscopic but visible to bare eyes and are large enough (usually larger than a micrometer) to undergo sedimentation.
Q5. Classify each of the following as a homogeneous or heterogeneous mixture.
soda water, wood, air, soil, vinegar, filtered tea.
Ans: The following is the classification of the given substances into homogenous and heterogenous mixtures.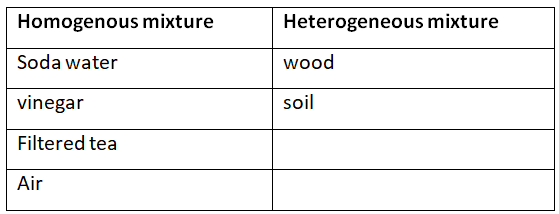
Q6. How would you confirm that a colorless liquid given to you is pure water?
Ans: We can confirm if a colorless liquid is pure by setting it to boil. If it boils at 100°C, it is said to be pure. But if there is a decrease or increase in the boiling point, we infer that water has added impurities and, hence not pure.
Page No. 24
Q7. Which of the following materials fall in the category of a “pure substance”?
(a) Ice
(b) Milk
(c) Iron
(d) Hydrochloric acid
(e) Calcium oxide
(f) Mercury
(g) Brick
(h) Wood
(i) Air
Ans: The following substances from the above-mentioned list are pure substances:
- Iron
- Ice
- Hydrochloric acid
- Calcium oxide
- Mercury
Q8. Identify the solutions among the following mixtures.
(a) Soil
(b) Seawater
(c) Air
(d) Coal
(e) Soda water
Ans: The following are the solutions from the above-mentioned list of mixtures:
- Sea water
- Air
- Soda water
Q9. Which of the following will show the “Tyndall effect”?
(a) Salt solution
(b) Milk
(c) Copper sulphate solution
(d) Starch solution
Ans: Milk and starch solution demonstrate the Tyndall effect because they are colloidal solutions. In these solutions, light is scattered, making its path visible.
- The Tyndall effect occurs when light passes through a colloid.
- Colloidal solutions contain particles that are small enough to scatter light.
- Examples of colloids include milk and starch solutions.
Q10. Classify the following into elements, compounds, and mixtures.
(a) Sodium
(b) Soil
(c) Sugar solution
(d) Silver
(e) Calcium carbonate
(f) Tin
(g) Silicon
(h) Coal
(i) Air
(j) Soap
(k) Methane
(i) Carbon dioxide
(m) Blood
Ans: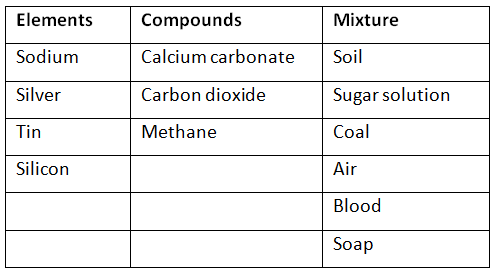
Q11. Which of the following are chemical changes?
(a) Growth of a plant
(b) Rusting of iron
(c) Mixing of iron filings and sand
(d) Cooking of food
(e) Digestion of food
(f) Freezing of water
(g) Burning of a candle
Ans: Among the options listed, the following are considered chemical changes:
- Rusting of iron
- Cooking of food
- Digestion of food
- Burning of a candle
The growth of a plant is a complex process involving both chemical and physical changes, while mixing iron filings and sand and freezing water are not chemical changes.
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science - Is Matter Around Us Pure
| $1. What is a pure substance and how is it different from a mixture? |  |
| $2. What are the different methods to separate mixtures? |  |
| $3. How can we determine whether a substance is a homogeneous or heterogeneous mixture? |  |
| $4. What is the significance of the term 'colloid' in the context of mixtures? |  |
| $5. Why is it important to study the properties of matter and mixtures? |  |





















