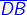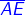Basic Geometrical Ideas Class 6 Notes Maths Chapter 4
In this chapter, several important geometric terms are included, which hold extreme importance in the later grades. The topics that are introduced not only will help students to build a foundation in geometry but will also help them to grasp the higher-level concepts in the later grades easily.
Introduction to Geometrical Ideas
The term ‘Geometry’ is the English equivalent of the Greek word "geo-metron".
"Geo" means "Earth", and "metron" means "Measurement."
Therefore, geometry means the measurement of the earth.
In our daily life, we observe and use objects having different shapes:
The ruler, pencil, and pen are straight. Balls, bangles, coins, and sun are round shaped.
Balls, bangles, coins, and sun are round shaped.
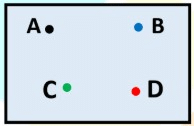
What is a Point?
- A point determines a specific location.
- They are denoted by any capital letter of the English Alphabet.
- It has no length, breadth or thickness.

We can draw a point with the tip of a sharp pencil, the tip of a compass, or the pointed end of a needle.
A point is usually represented by a small dot and is named by a single capital letter of the alphabet.
These points will be read as point A, point B and point C.
What is a Line Segment
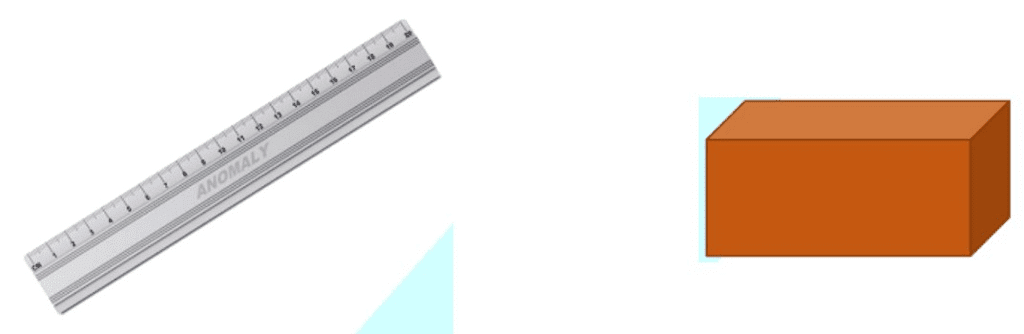
A line segment corresponds to the shortest distance between two points.
The edge of a ruler and the edge of a box are examples of line segments.
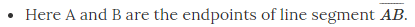
- A line segment has a fixed length.
- The line segment
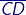 is the same as its inverse.
is the same as its inverse.
What is a Line?
- When a line segment is extended on both sides infinitely, then it is called a line. Here m is a line.
- It contains an infinite number of points on it.
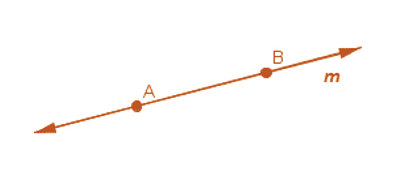
- A line is straight and extends indefinitely on both directions.
- A line segment
 extended on both sides and marked by arrows at the two ends represents a line denoted by
extended on both sides and marked by arrows at the two ends represents a line denoted by  or
or 
Example: Use the figure to name:
a) Five points
b) A-line
c) Five line segments
a) Five points are O, B, C, D and E.
b) A line:
c) Five line segments are ,,
,
,
,
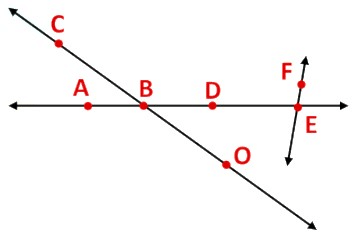
What are Intersecting and Parallel lines?
- If two lines have one common point, they are called intersecting line
- If there is a point P common to two lines
 and
and 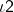 , then the twolines intersect at the point P and this point P is called the point of intersection of the given lines.
, then the twolines intersect at the point P and this point P is called the point of intersection of the given lines.
Parallel Lines
Two lines are said to be parallel if they are in the same plane and do not intersect each other.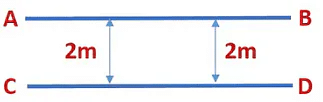


Perpendicular Lines
Two lines are said to be perpendicular when they intersect at 90 degrees (right angle).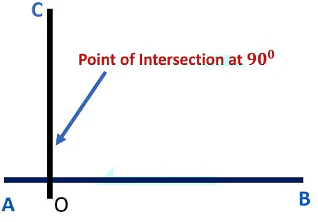
Example: Use the figure to name:
(a) Line containing point E.
(b) Line passing through A.
(c) Line on which O lies
(d) Two pairs of intersecting lines.
a) Line containing point E is
b) Line containing point A is
c) Line on which O lies
d) Two pairs of intersecting lines areand
,
and
What is a Ray?
A ray is a portion of a line. It starts at one point (called a starting point) and goes endlessly in a direction.Examples of the ray are: Beam of light from a lighthouse and sun rays.

Thus a line segment  extended endlessly in the direction from A to B, is a ray denoted by
extended endlessly in the direction from A to B, is a ray denoted by 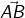

- The ray
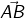 has one end (fixed) point called its initial point.
has one end (fixed) point called its initial point. - Rays
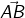 and
and 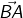 are two different rays.
are two different rays. - Ray
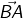 is a ray with initial point B and extends endlessly in the direction from B to A.
is a ray with initial point B and extends endlessly in the direction from B to A.
What is a curve?
Curve can be defined as the continuous movement of points in any and every direction.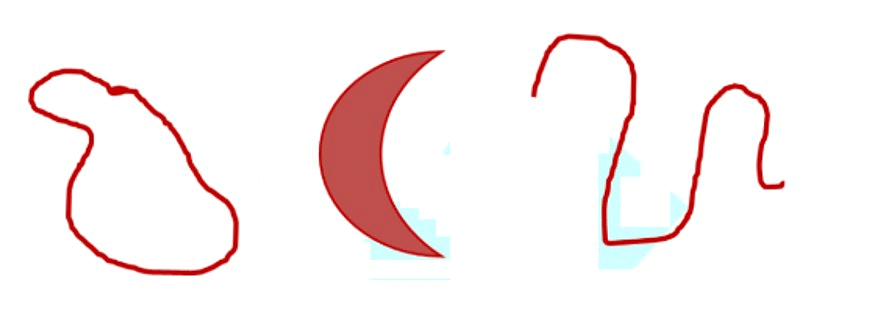
- A curve can be anything that is drawn without lifting a pencil from the paper and without using a ruler.
- ‘Curve’ means “not straight” in everyday usage.
- In mathematics, a curve can be a straight line, which is called a straight curve.

Types of Curve
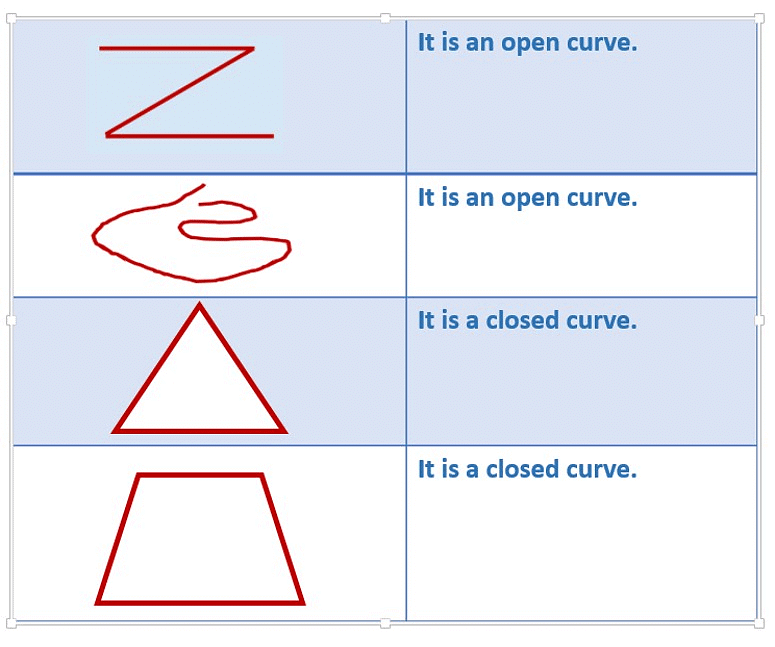
1. Simple Curve
If a curve does not cross itself, then it is called a simple curve.
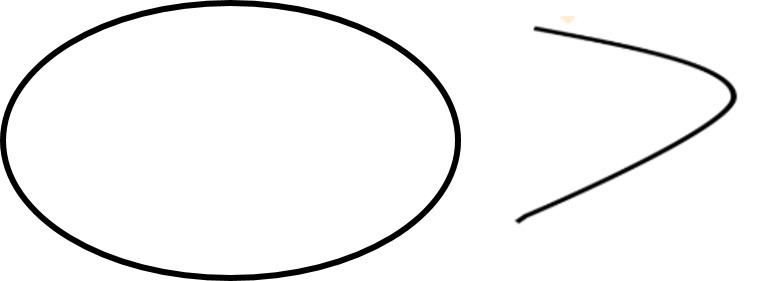
The curves shown below are not simple curves because they cross themselves.
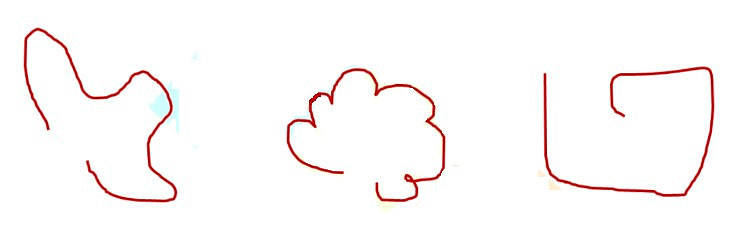
2. Open Curve
The curve which does not form a closed path is called an open curve.
In an open curve, we can find at least one point at which the curve begins or ends.
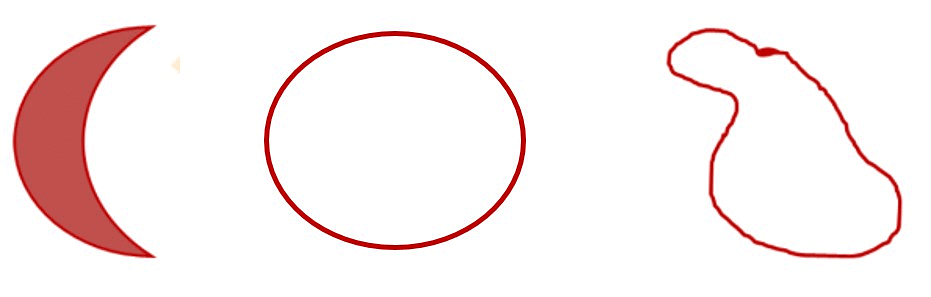
3. Closed Curve
The curve which forms a closed path is called a closed curve.
In a closed curve, we cannot find any point at which the curve begins or ends.
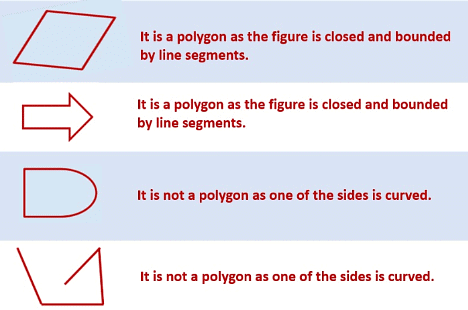
What is a Polygon?
A polygon is a closed figure formed of three or more line segments.
Examples of polygons are triangle, quadrilateral, pentagon and hexagon.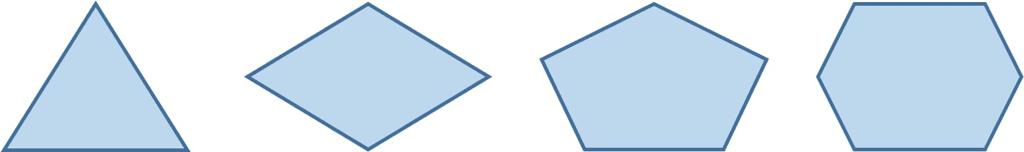
- Polygons are two-dimensional.
- They are bounded by straight lines, and the shapes are closed.
- Minimum three line segments are required to make a closed figure, thus a triangle is a polygon with a minimum of three sides.
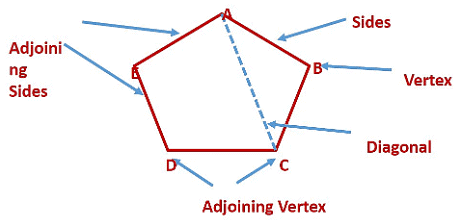
- The line segments forming a polygon are called its sides.
- The meeting point of a pair of sides is called a vertex.
- Any two sides with a common endpoint are called the adjacent sides of the polygon.
- The endpoints of the same side of a polygon are called the adjacent vertices.

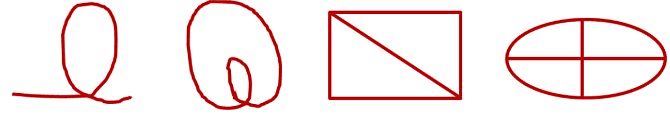
Example: Classify the following curves as
(i) Open
(ii) Closed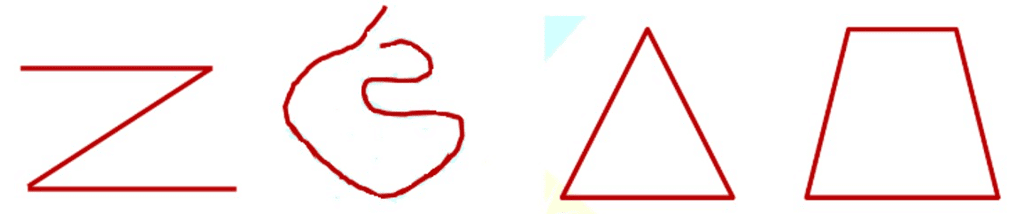
Answer:
Example: Consider the given figure and answer the questions:
(a) Is it a curve?
(b) Is it closed?
(a) Yes, it is a curve because a curve is drawn without lifting the pencil from the paper and without using a ruler.
(b) Yes, it is closed because the curve forms a closed path.
Example: Illustrate, if possible, each one of the following with a rough diagram:
(a) A closed curve that is not a polygon.
(b) An open curve made up entirely of line segments.
(c) A polygon with two sides.
Answer:
a) A closed curve that is not a polygon.b) An open curve made up entirely of line segments.
c) A polygon with two sides cannot be drawn as minimum three line segments are required to make a polygon.
What is an Angle?
An angle is made up of two rays starting from a common endpoint.
- The two rays forming the angle are called the arms or the sides of the angle.
- The common endpoint is the vertex of the angle.
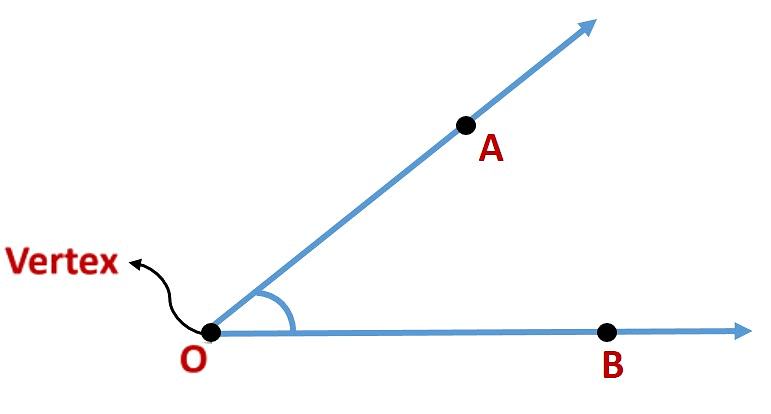
Here, angle is formed by the rays 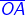 and
and  .The name of the angle is ∠AOB or ∠BOA, keeping the vertex in the
.The name of the angle is ∠AOB or ∠BOA, keeping the vertex in the
middle.
The interior of the angle is bounded by the arms of an angle.
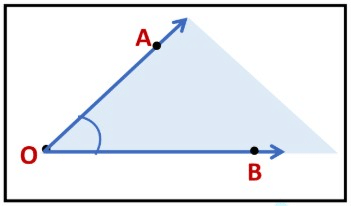
The exterior of the angle is the region that lies outside the angle.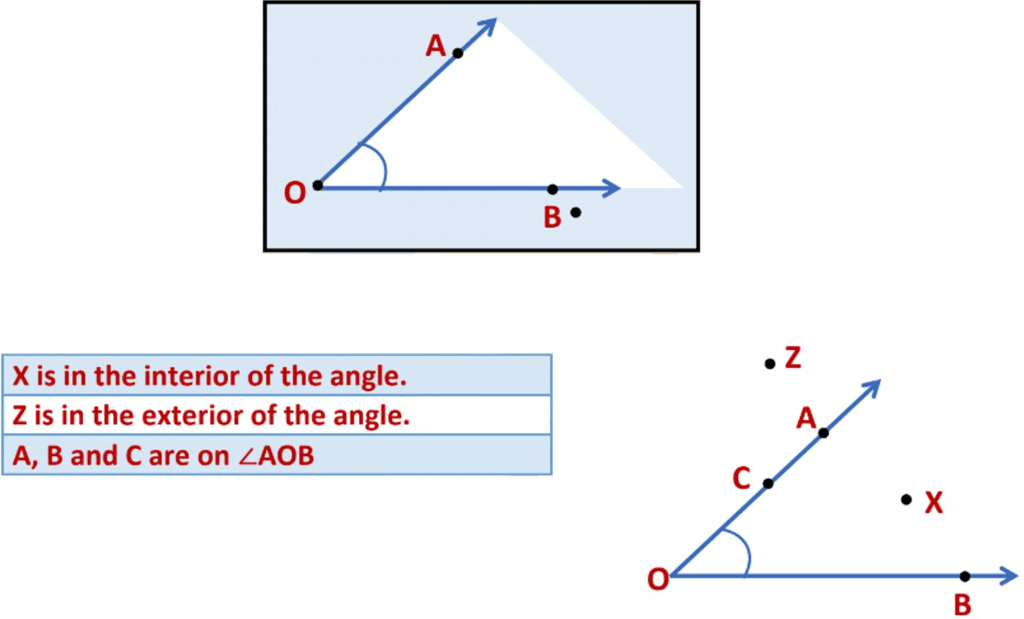
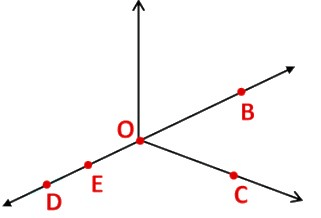
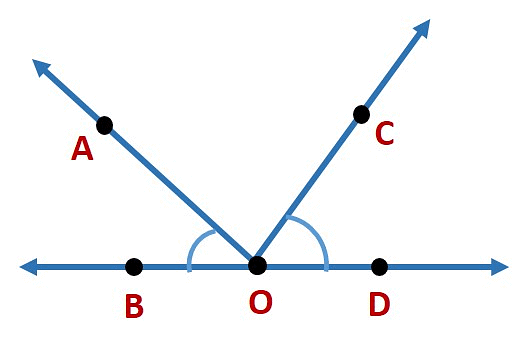
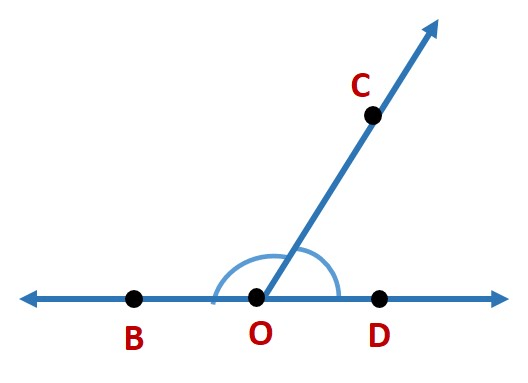
Example: In the given diagram, name the point(s)
(a) In the interior of ∠DOE
(b) In the exterior of ∠EOF
(c) On ∠EOF
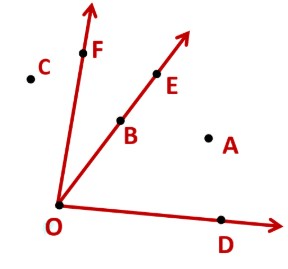
(a)Point in the interior of ∠DOE is A.
(b) Points in the exterior of ∠EOF is C, A and D.
(c) Points on ∠EOF is E, B, O and F.
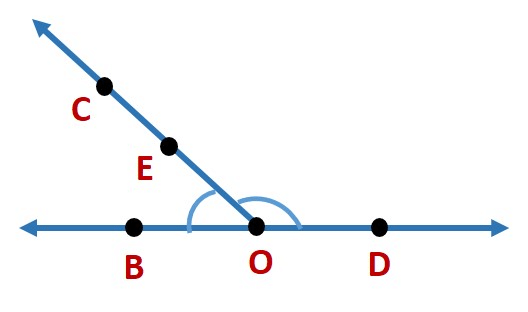
Example: Draw rough diagrams of two angles such that they have
(a) One point in common.
(b) Two points in common.
(c) Three points in common.
(d) Four points in common.
(e) One ray in common.
(a) One point in common
∠AOB and ∠COD have only one point in common, i.e. O
(b) Two points in common
∠BOC and ∠COD have two points in common, i.e. O and C
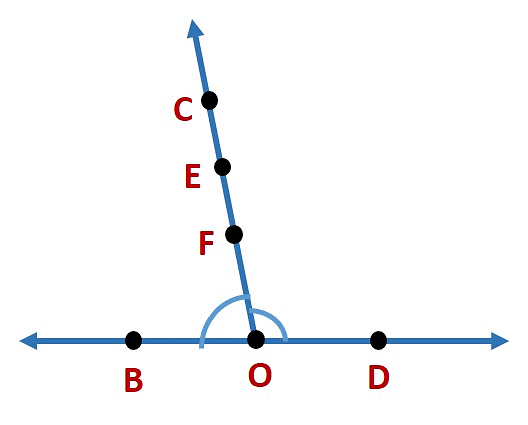
(c) Three points in common
∠BOC and ∠COD have three points in common, i.e. O, E and C.
(d) Four points in common
∠BOC and ∠COD have four points in common, i.e. O, C, E and F.
What is a Triangle?
A triangle is a three-sided polygon. It is the polygon with the least number of sides. It is denoted by the symbol ∆.
We see many triangle-shaped objects in our daily life.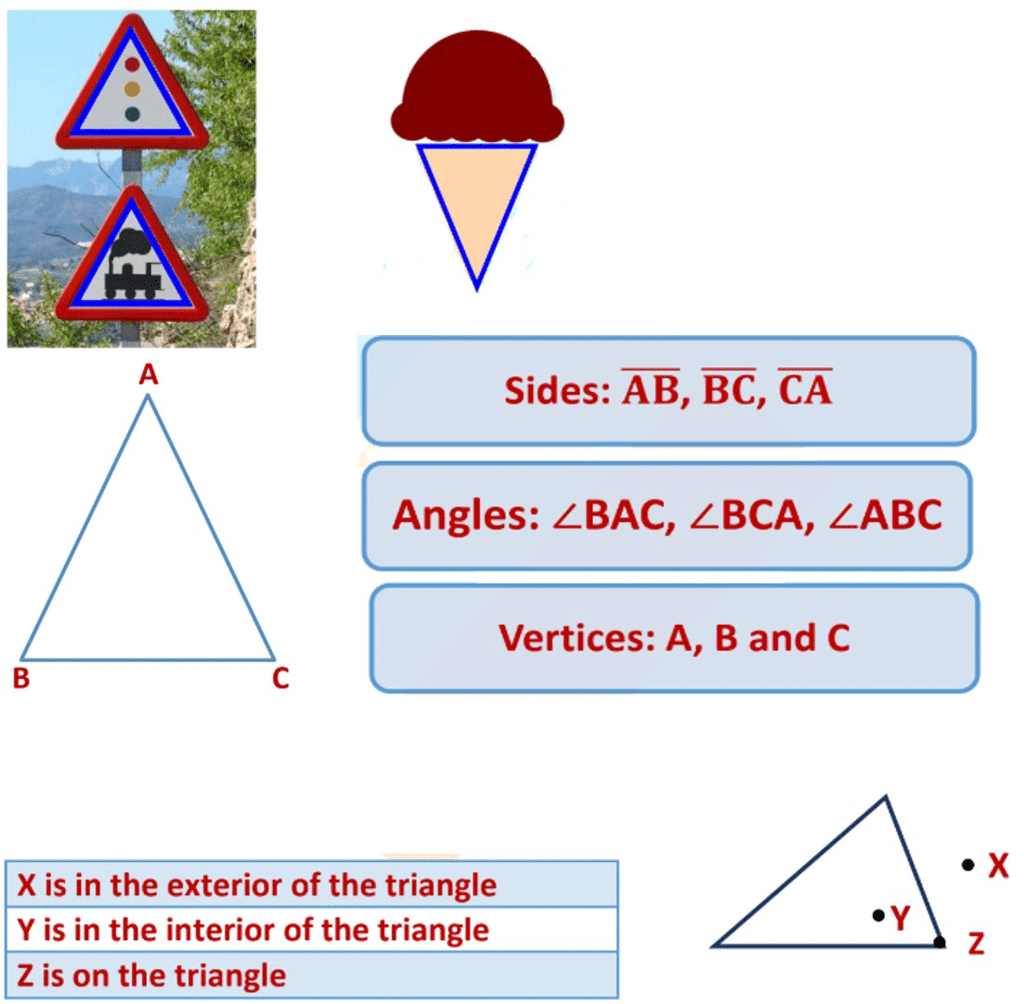 Example:
Example:
Draw a rough sketch of a triangle ABC. Mark a point P in its interior and a point Q in its exterior. Is the point A in its exterior or in its interior?
Point A is not in the interior or exterior of ∆ ABC as it is a vertex (a point where two line segments meet).
What is a Quadrilateral?
A four-sided polygon is a quadrilateral. It has 4 sides and 4 angles.
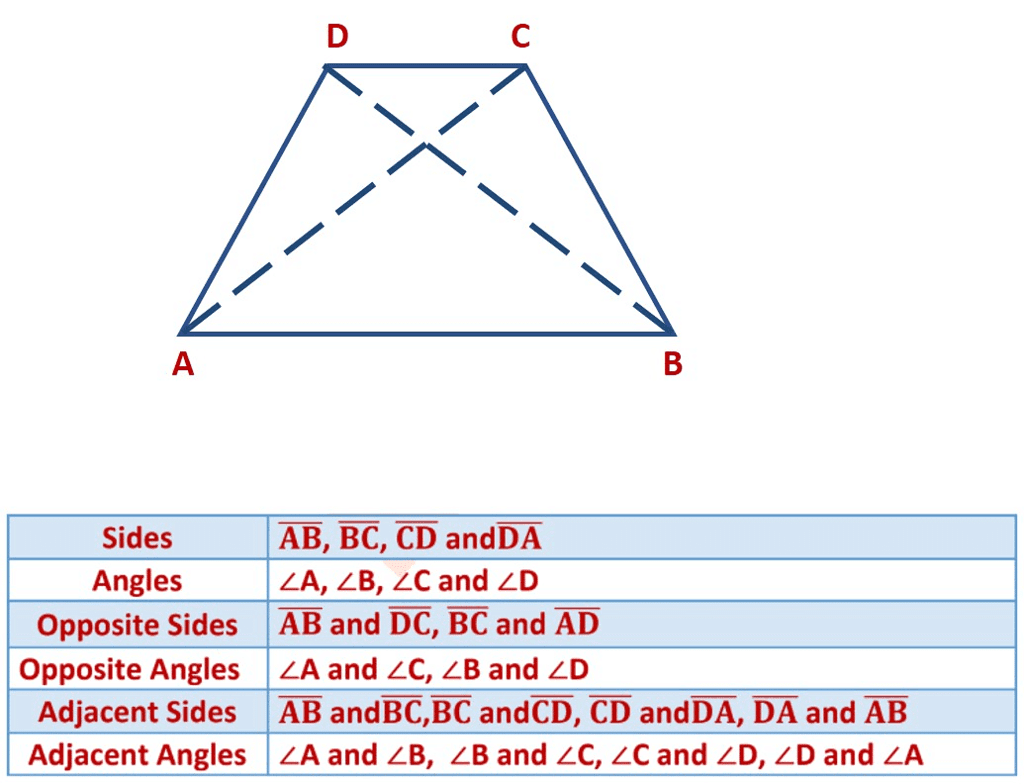
Example: Draw a rough sketch of a quadrilateral PQRS.
Draw its diagonals.
Name them.
Is the meeting point of the diagonals in the interior or exterior of the quadrilateral?
The two diagonals are PR and QS. Diagonal PR and diagonal QS meet at point T which is in the interior of the quadrilateral PQRS.
What is a Circle?
A circle is a simple closed curve which is not a polygon. We see many things that are round: a clock, a bangle, and a coin.
Parts of a circle
Here is a circle with center O. A, P, B, and M are points on the circle.
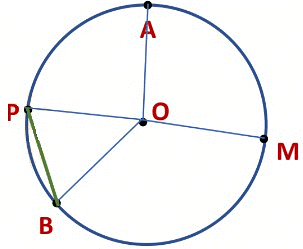

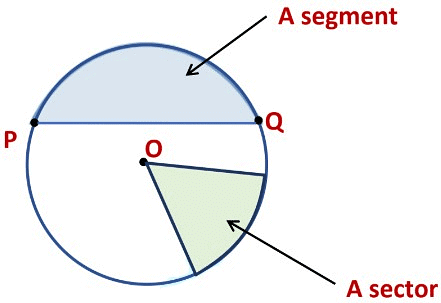

Example: From the figure, identify:
(a) The center of circle
(b) Three radii
(c) A diameter
(d) A chord
(e) Two points in the interior
(f) A point in the exterior
(g) A sector
(h) A segment
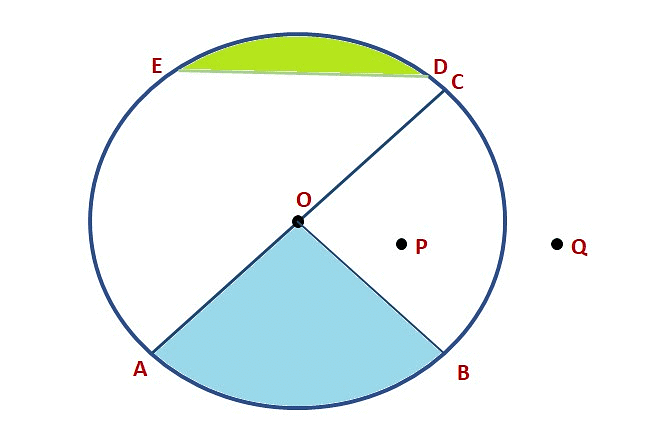
(a) O is the center of the circle.
(d) ED is a chord
(b) OA, OB and OC are the three radii
(c) AC is the diameter of the circle
(e) O and P are the two points in the interior.
(f) Q is the point in the exterior
(g) OAB (shaded portion) is a sector
(h) ED (shaded portion) is a segment
|
30 videos|120 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Basic Geometrical Ideas Class 6 Notes Maths Chapter 4
| 1. What is the difference between a point and a line segment? |  |
| 2. How are intersecting lines different from parallel lines? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of a ray in geometry? |  |
| 4. Can a curve be considered a straight line? |  |
| 5. How many sides does a polygon have? |  |