Emergence of Mahajanapadas (600-321 BC) | History(Prelims) by UPSC Toppers PDF Download
The emergence of Mahajanapadas (600-321 BC)
In the later Vedic period, the tribal organisations changed their identity and gradually shifted to the territorial identity, and the area of settlement was now regarded as janapadas or states. In the transition from tribal to monarchy, they lost the essential democratic pattern of the tribe but retained the idea of government through an assembly representing the tribes.
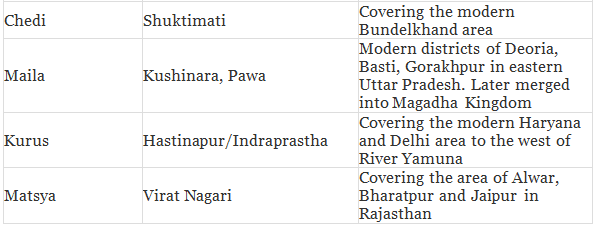
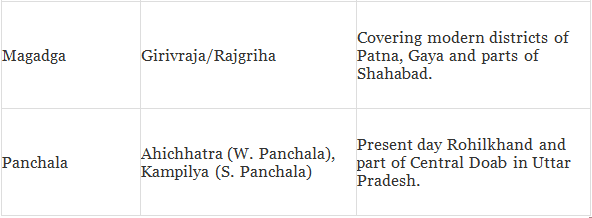
 Mahajanapadas
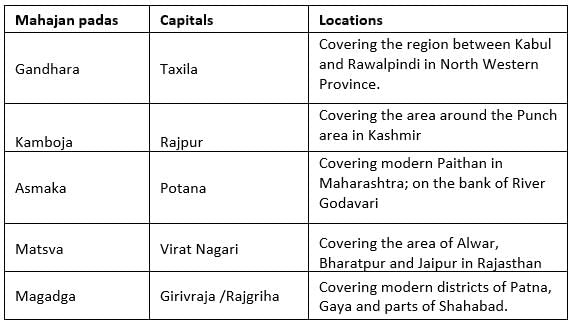
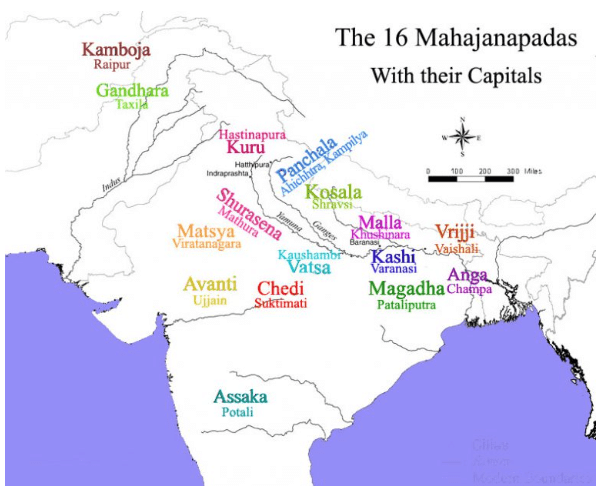
Mahajanapadas
These states consisted of either a single tribe such as Shakyas, Kolias, Malas etc. The people in the lower Ganges Valley and Delta, which were outside the Aryan pale, were not incorporated. There was, therefore, a strong consciousness of the pure land of the Aryans called Aryavarta. Each Janapada tried to dominate and subjugate other janapadas to become Mahajanapadas.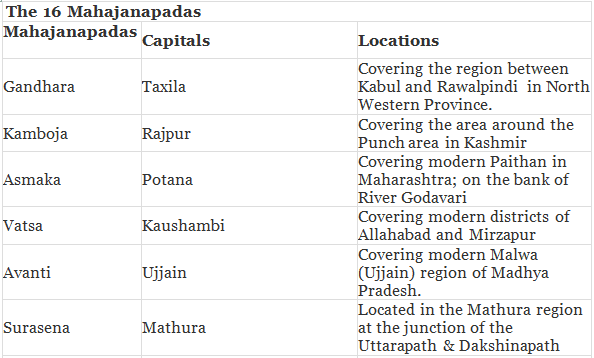

➢ Important Republics
- The kings in these states had the supreme authority. The Mahajanpadas of Vrije, Malla, Kuru, Panchal and Kamboj were republican states and so were other smaller states like Lichhavi, Shakya, Kolya, Bhagga, and Moriya. These republican states had a Gana-Parishad or an Assembly of senior and responsible citizens. This Gana-Parishad had the supreme authority in the state. All the administrative decisions were taken by this Parishad.
- Again, the republics were basically of two types:
(i) the republics comprising a single tribe like those of the Sakyas, the Kolias and the Mallas, and
(ii) the republics comprising a number of tribes or the republics of confederacy like the Vrijjis.
➢ Difference between Republics and Monarchies
- In republics, every tribal oligarch claimed a share in revenues from peasants. In the monarchies, the king claimed to be the sole recipient of such revenues.
- In the tribal oligarchy or republic, each raja (tribal oligarch) was free to maintain his own little army under his Senapati. In a monarchy, the king maintained his regular standing army. He did not permit any other armed forces within his boundaries.
- Republics functioned under the leadership of the oligarchic assemblies, while a monarchy functioned under the individual leadership of the king.
- The Brahmanas had a considerable influence on the monarchial administration, while they were relegated to the background in the republics.
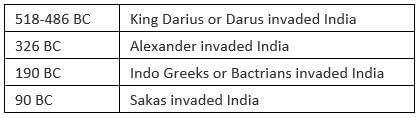
➢ Alexander Invasion
- In the fourth century BC, the Greeks and the Iranians fought for the supremacy of the world. The Greek ruler Alexander conquered not only Asia Minor and Iraq but also Iran. From Iran, he marched to India, obviously attracted by its great wealth. Alexander conquered principalities one by one. Among the rulers of these territories, two were well-known: Ambhi, the prince of Taxila, and Porus whose kingdom lay between the Jhelum and the Chenab.
- After the conquest of Iran, Alexander moved on to Kabul, from where he marched India through the Khyber Pass. Ambhi, the ruler of Taxila, readily submitted to the invader, augmented his army and replenished his treasure.
Alexander Invasion
- Alexander remained in India for 19 months (326-325 BC), which were full of fighting. He had barely any time to organize his conquest. Still, he made some arrangements. Most of the conquered states were restored to their rulers who submitted to his authority. But his own territorial possessions were divided into three parts, which were placed under three Greek governors.
➢ Alexander Invasion
- Alexander marched to India through the Khyber Pass in 326 BC
- His advance was checked on the bank of the Beast because of the mutiny of his soldiers
- In 325 BC, he began his home guard journey.
- In 324 BC, he reached Susa in Persia and died the next year.
➢ Persian Invasion
- The Achaemenid rulers of Iran, who expanded their empire at the same time as the Magadhan kings, took advantage of the political disunity on the northwest frontier. The Iranian ruler, Darius, penetrated into northwest India in 518 BC and annexed Punjab, west of the Indus, and Sindh.
 The Persian Invasion
The Persian Invasion
- He divided the province in the 20th Strappy, which was considered to be the richest and the most populous province of the Persian empire. According to Herodotus, Punjab and Sindh satrapy (province) were the twentieth in the Persian empire.
- It was considered to be the richest and the most popular province of the Persian empire. Its annual tribute amounted to 360 Euboic talents of gold dust.
- The Kharosthi script was used on the north-western frontier from then until about the 4th century AD. On the eve of Alexander's invasion, the hold of Persian emperors on their Indian provinces had become weak.

➢ Effects of Persian Invasion
- Introduction into India the Araminc form of writing, which later developed into the Kharosthi alphabet.
- Promotion of Indo-Iranian trade
- Geographical exploration of the Indus and the Arabian Sea, leading to opening of a new water route.
- Fusion of Iranian/Persian features in the Mauryan art.
- Impact of Buddhism on the Zoroastrian religion of ancient Persia.
➢ Effects of Greek Invasion
- The Greek invasion of India opened the trade route between north-west and Wester India
- Eastwards trade went through the Ganga delta to the coast of Northern Burma and south along the east coast.
- Guilds (Shreni) came into existence
- Money was introduced. Punch-marked coins in gold and silver and of copper cast have been discovered.
- Introduction of money facilitated the trade.
- Divided his army during the last expedition at Patala and appointed Niyarkas as head of Navy.
- Opening up of four distinct routes between India & Greek by land sea paving way for increased trade and cultural contacts between the two regions.
- Establishments of more Greek settlements in north-western region
- Ashokan pillars were also influenced by Greek Art.
- Establishment of the coast and search for harbours from the mouth of the Indus to that of the Euphrates.
- Promotion to expansion of the Mauryan empire in north-west India due to destruction of local powers by Alexander
- India and Greek established trade contact.
- Coins of India non inscribed on 'Uluk Model' of the Greeks
- Many Greek scholars came to India with Alexander and wrote on Indian history which are relevant in constructions of contemporary socio-religious aspects.
1. Alexander Invasion
2. King Darius
3. Sakas
4. Indo Greeks
|
32 videos|98 docs|135 tests
|
FAQs on Emergence of Mahajanapadas (600-321 BC) - History(Prelims) by UPSC Toppers
| 1. What are Mahajanapadas and when did they emerge? |  |
| 2. How many Mahajanapadas were there? |  |
| 3. What led to the emergence of Mahajanapadas? |  |
| 4. What was the significance of Mahajanapadas in ancient India? |  |
| 5. What was the impact of Mahajanapadas on the social and economic life of people? |  |