Food - Notes, Biology | General Awareness - Bank Exams PDF Download
Balanced Diet
- A balanced diet is one which contains all principal food factors, i.e., proteins, vitamins, carbohydrates, mineral salts, fats, water, etc., in correct proportion.
- This should be able to give about 3,000 calories of energy per day.

The essentials of good diet are:
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Fats
- Vitamins
- Minerals
(a) Carbohydrates:
- These are the organic compounds of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
- These produce heat and energy in the body
- Their deficiency causes loss of weight and weakness.
- These are found in rice, wheat, sugarcane, potatoes, starch in maize, etc.
(b) Proteins:
- These are complex compounds of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur.
- These build tissues of the body and repair them when torn out.
- Chief sources of proteins are milk, cheese, pulses, peanuts, fish, meat, etc.
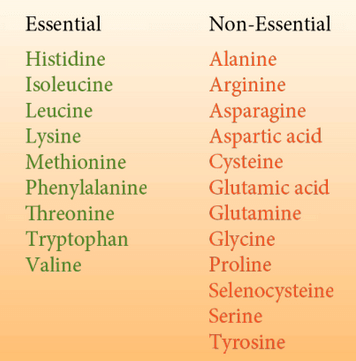
- Made up of amino acids.
Amino acids are of 2 Types :
- Essential Amino Acids : They cannot be synthesised in the body and must be taken in the diet.
- Non – Essential Amino Acids : They are synthesized in the body and do not need to be taken from outside.
Some important Proteins are:
- As Enzymes : As Catalyst in Digestion (Eg. Pepsin, Trypsin).
- As a Hormone : To regulate body functions (Eg. Insulin, Glucogon, ACTH).
- In Transport of different Substances : (Eg. Haemoglobin – Transports O2 in blood, Myoglobin – Stores O2 in muscles).
- As Contractile Proteins for Contraction in Muscles : (Eg. Actin and Myosin).
- Structural Proteins : (Eg. Collagen – Component – of Connective Tissue, Bones, Tendons, Cartilage Keratin – Component of Skin, Feathers, Nails, Hair, Horn).
- Protective Proteins : To fight infections (Eg. Gamma globulins).
- Visual Proteins : Rhodopsin and Iodopsin of rods and cones are proteins only. (Rods and Cones are the cells which are present in Retina of the eye).
Sources : Groundnuts, Soyabean, Pulses, Lean Meat, Fish, Eggs, Milk, etc.
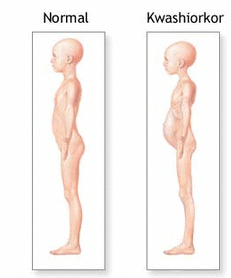
Protein deficiency causes:
Kwashiorkar :
- Due to deficiency of protein in diet.
- Kwashiorkor is most common in rural areas, especially in the sub-Saharan regions.
- Symptoms : Abdomen and feet swells (due to retention of water called oedema), Skin becomes Dark and Scaly, Enlarged Liver, Anaemia.
- Kwashiorkor usually occurs in those under 4 years of age
Marasmus :
- Deficiency of Proteins, Carbohydrates and Fats.
- Symptoms : Losing of body weight, wasting of muscles, ribs look prominent. (Oedema and skin pigmentation absent).
- In children between 6 months and 3 Years.Question for Food - Notes, BiologyTry yourself:Kwashiorkar is caused due to deficiency of ______View Solution
(c) Fats:
- These have carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
- Fat has the most calories compared to any other nutrient. Controlling fat intake is one of the most important steps in losing or maintaining weight and preventing or delaying type 2 diabetes.
- Fats are solids at room temperature. Oil refers to a fat with unsaturated fatty acid chains that is liquid at room temperature.
- They also produce heat and energy in the body and build fatty tissues.
Sources: Butter, ghee and various vegetable oils are examples of fats.
Types of fats:
(i) Unsaturated fats:
- An unsaturated fat is a fat or fatty acid in which there is at least one double bond within the fatty acid chain.
- In cellular metabolism, unsaturated fat molecules contain somewhat less energy (i.e., fewer calories) than an equivalent amount of saturated fat.
- The greater the degree of unsaturation in a fatty acid (i.e., the more double bonds in the fatty acid), the more vulnerable it is to rancidity ( When the substance containing oils and fats are exposed to air they get oxidised and become rancid due to which their smell, taste and colour change. This process is known as rancidity).
- Antioxidants can protect unsaturated fat from lipid oxidation.
(ii) Saturated fats:
- A saturated fat is a fat in which all the fatty acids have single bonds.
- Most animal fats are saturated whereas the fats of plants and fish are generally unsaturated.
- Many experts recommend a diet low in saturated fat.
- Saturated fats are popular with manufacturers of processed foods because they are less vulnerable to rancidity and are, in general, more solid at room temperature than unsaturated fats.
(d) Vitamins:

- These are a group of substances that are essential in small quantities for normal functions of the body.
- Their deficiency causes sickness and improper development of body.
- At present six of these are recognised as essential to human nutrition.
- These are A, B, C, D, E and K. The richest sources of vitamins are green vegetables, milk, fruits, eggs, etc.
Vitamins are classified into two groups depending upon their solubility in water or fat. These are:
(i) Fat soluble vitamins:
Vitamins which are soluble in fat and oils but insoluble in water are kept in this group. These are vitamins A, D, E and K. They are stored in liver and adipose (fat storing) tissues.(ii) Water soluble vitamins:
- B group vitamins and vitamin C are soluble in water so they are grouped together.
- Water soluble vitamins must be supplied regularly in diet because they are readily excreted in urine and cannot be stored (except vitamin B12) in our body.
Types of vitamins:
1. Vitamin A:
- It increases resistance to infection and tones up the whole system.
- Its deficiency causes night blindness, disorders of skin, stomach growth and respiratory diseases.
- It is found in milk, butter, egg-yolk, ghee, carrot, cod-liver oil, etc.
2. Vitamin B:
- It is present in cereals, peas and beans.
- It protects the body from nerve diseases such as beri-beri, pellagra, etc., and it cures pernicious anaemia, degeneration of sex glands and enlargement of liver and adrenals.
- Vitamin B1 is also called thiamine.
3. Vitamin C:
- It is also called Ascorbic Acid.
- It ensures healthy teeth, bones and protects the body against scurvy.
- It is present in fresh vegetables, orange, lemon, lettuce, tomato, cabbage, turnip, potato and mango
4. Vitamin D:
- It is present in milk, butter, ghee, cod-liver oil, yolk of eggs and it is also produced under the skin by the rays of the sun.
- It promotes bone promotion and prevents rickets.
5. Vitamin E:
- It has vital influence on organs to reproduction.
- Its absence causes sterility.
- It is present in the germinating wheat.
- It is also called Alpha-tecopherol.
6. Vitamin K:
- It help in the clotting of blood.
- Its absence cause haemorrhage.
- It is found in fish, oats and wheat.Question for Food - Notes, BiologyTry yourself:____ called Ascorbic Acid.View Solution
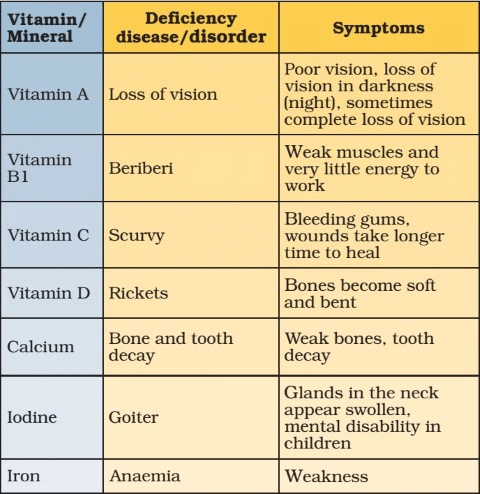
Deficiency Diseases
- A person may be getting enough food to eat, but sometimes the food may not contain a particular nutrient. If this continues over a long period of time, the person may suffer from its deficiency.
- Deficiency of one or more nutrients can cause diseases or disorders in our body. Diseases that occur due to lack of nutrients over a long period are called deficiency diseases.
Question for Food - Notes, BiologyTry yourself:What helps in blood cloting?
View Solution
Water
- It serves to dissolve food when digested and aids absorption.
- It helps in removing waste matters from the body.
- It also helps in circulation of blood.
|
365 videos|701 docs|149 tests
|
FAQs on Food - Notes, Biology - General Awareness - Bank Exams
| 1. What is a balanced diet? |  |
| 2. Why is a balanced diet important? |  |
| 3. What are the components of a balanced diet? |  |
| 4. How can one achieve a balanced diet? |  |
| 5. What are the consequences of an imbalanced diet? |  |

















