Decimals | Quantitative Techniques for CLAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Addition of Decimals. |

|
| Subtraction of Decimals. |

|
| Converting a Decimal into Fraction. |

|
| Converting a Fraction into a Decimal |

|
| Multiplication of Decimals. |

|
| Division of Decimal |

|
Decimal Fractions and Decimals: The fractions in which the denominators are 10, 100, 1000 etc. are known as decimal fractions. Numbers written in decimal form are called decimals.
- A decimal has two parts, namely, the whole number part and the decimal part.
- The number of digits contained in the decimal part of a decimal is called the number of its decimal places.
We have 0.1 = 0.10 = 0.100 etc
Also, 0.2 = 0.20 = 0.200 etc.
- Unlike decimals may be converted into like decimals by annexing the requisite number of zeros at the end of the decimal part.
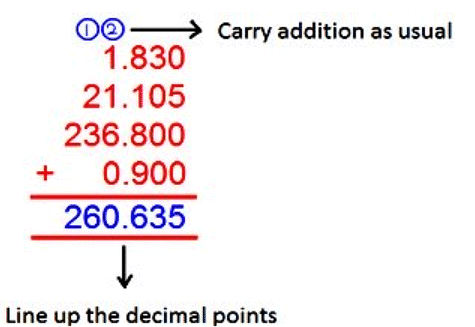
Addition of Decimals.
Step 1: Write down the decimal numbers, one number under the other number and line up the decimal points.
Step 2: Convert the given decimals to like decimals.
Step 3: Arrange the addends in such a way that the digits of the same place are in the same column.
Step 4: Add the numbers from right as we carry addition usually.
Step 5: Remember to place the decimal point down in the answer in the same place as the numbers above it.
Add the decimals:
(i) 1.83, 21.105, 236.8 and 0.9
Solution:
We have 1.83 + 21.105 + 236.8 + 0.9
Converting all the addends to like decimals
1.830 + 21.105 + 236.800 + 0.900
Arranging the addends in columns and on adding we get
Subtraction of Decimals.
Step 1: Write down the two decimal numbers, one number under the other number and line up the decimal points.
Step 2: Convert the given decimals to like decimals.
Step 3: Write the smaller decimal number under the larger decimal number in the column.
Step 4: Arrange the decimal numbers in the column in such a way that the digits of the same place are in the same column.
Step 5: Subtract the numbers in the column from the right.
Remember to place the decimal point down in the answer in the same place as the numbers above it.
Subtract the decimals:
(i) 27.59 from 31.4
Solution:
We have 27.59 from 31.4
Converting both the decimal numbers into like decimals,
31.40 - 27.59
Now arrange them in columns and subtract we get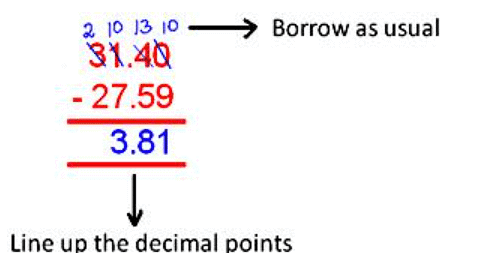
Converting a Decimal into Fraction.
Step 1: Write the given decimal without the decimal point as the numerator of the fraction.
Step 2: In the denominator write 1 followed by as many zeros as there are decimal places in the given decimal.
Step 3: Convert the above fraction into its simplest form.
Convert the following into fractions.
(i) 3.91
Solution:
Write the given decimal number without the decimal point as numerator.
In the denominator, write 1 followed by two zeros as there are 2 digits in the decimal part of the decimal number.
= 391/100
Converting a Fraction into a Decimal
a) If the denominator of the fraction is 10 or a power of 10.
- To convert a fraction having 10 in the denominator, we put the decimal point one place left of the first digit in the numerator.
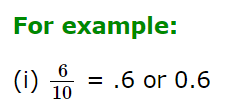
- To convert a fraction having 100 in the denominator, we put the decimal point two places left of the first digit in the numerator.
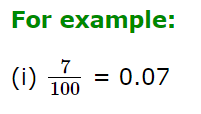
- To convert a fraction having 1000 in the denominator, we put the decimal point three places left of the first digit in the numerator.
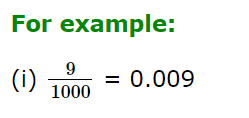
b) If the denominator is other than a power of 10
Step I Divide the num. by the den. till a non-zero remainder is obtained
Step II Put a decimal point in the dividend as well as in the quotient
Step III Put a zero on the right of the decimal point as well as on the right of the remainder
Step IV Divide again as we do in whole numbers
Step V Repeat step IV till the remainder is zero
Example 1 Convert 29/4 into a decimal fraction
Solution: On dividing we get
Example 2 Convert into a decimal fraction.
We find that in the above two examples, the process of division has terminated after a few decimal places i.e there are finite places after the decimal point. Such fractions are said to be terminating decimals.
In the case of the fractions the process of division is unending and there are infinite number of places after the decimal point. Such fractions are said to be non-terminating decimals.
Decimal representation of is 0.888 ------ or
is represented as 0.
Also
So every positive rational number is either a terminating or a non-terminating repeating decimal.
To search whether a rational number is a terminating or non-terminating repeating decimal.
If the denominator of a rational number (which is in its lowest terms) as no prime factor other than 2 or 5 or both, the rational number is a terminating decimal. Otherwise the rational number is a non-terminating repeating decimal.
Example: etc are terminating
decimals where as are non-terminating repeating decimals.
Multiplication of Decimals.
a) Multiplication of a decimal by a whole number.
To multiply a decimal by a whole number, we multiply the two numbers as if they are whole numbers. We put the decimal point in the product so that there are as many places of decimal in it as there are in the given decimal.
b) Multiplication of a decimal by 10, 100, 1000 ----- etc.
To multiply a decimal by 10, 100, 1000 etc, we have to give a jump to the decimal by one. Two or three etc places to the right
For example 2.96 x 10 = 29.6
2.96 x 100 = 296
2.96 x 1000 = 2960 etc
c) Multiplication of a decimal by a decimal
To multiply two decimals, we first multiply them as if we are multiplying two whole numbers
(ignoring the decimal points). Then the decimal is placed in the product such that it has as many decimal places as there are in multiplicand and the multiplier taken together.
For example: To find the product of 34.17 x 3.2 we first multiply 3417 by 32 and get 109344
The multiplicand and the multiplier taken together have 3 decimal places, the product should also have 3 decimal places. Hence 34.17 x 3.2 = 109.344
Division of Decimal
a) Division of decimal by a whole number is the same as for whole numbers. The decimal point in the quotient is placed just above the decimal point in the dividend.
Example:
Therefore 442.4/ 7 = 63.2
b) Division of a decimal by 10,100,1000 etc.
To divide a decimal by 10,100,1000 etc we have to give a jump to the decimal by one, two, three etc places to the left.
For example :
c) Division of a decimal by a decimal
If we want to divide 6.25 by 2.5 we write
Since the divisor has one decimal place we multiply both numerator and denominator by 10 and get
Now the problem reduces to the division of a decimal by a whole number.
Similarly
d) Division of a whole number by a decimal Convert the decimal of divisor to a whole number and divide.
|
51 videos|172 docs|73 tests
|
FAQs on Decimals - Quantitative Techniques for CLAT
| 1. What is the process for adding decimals? |  |
| 2. How do you subtract decimals? |  |
| 3. How do you convert a decimal into a fraction? |  |
| 4. How do you convert a fraction into a decimal? |  |
| 5. What is the process for multiplying decimals? |  |
















