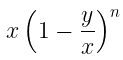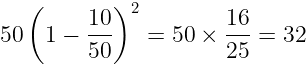- Mixture: The new product obtained by mixing two or more ingredients in a certain ratio is called a mixture of those particular ingredients.
- Alligation: It is a method of solving arithmetic problems related to mixtures of ingredients. This rule enables us to find the ratio in which two or more ingredients at the given price must be mixed to produce a mixture of the desired price.

Rule of Alligation
Alligation is a rule that enables us to find the ratio in which two or more ingredients at the given price must be mixed to produce a mixture of the desired price.
There are two types of methods used in alligation.
(a) Alligation Method 1
The rule also helps to find out the mean or average value of mixture when the prices of two or more ingredients which may be mixed together and the ratio in which they are mixed are given.
When two ingredients at given prices are known, then the ratio in which these two are mixed to obtain a mixture of known price is given by: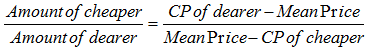
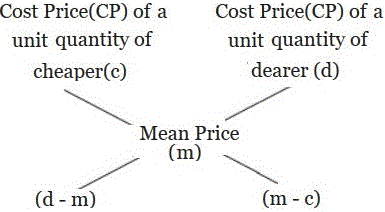 Hence, Amount of Cheaper: Amount of dearer = (D – M) : (M – C)
Hence, Amount of Cheaper: Amount of dearer = (D – M) : (M – C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Note:
(1) This method can be used when per cent, per hour, per km, per kg etc are being compared
(2) The CP of the unit quantity of the mixture is called the mean price (M)
Example 1: In what ratio, wheat at Rs 6.20 per kg be mixed with wheat at Rs 7.20 per kg, so that the mixture is worth Rs 6.50 per kg?
Sol.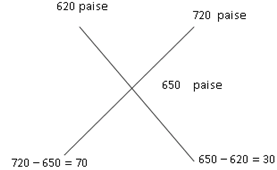 Required ratio is 70 : 30 or 7 : 3
Required ratio is 70 : 30 or 7 : 3
Example 2: In what ratio Rice worth Rs 30 per kg should be mixed with rice worth Rs 32.5 per kg so that on selling the mixture at Rs 34.10 per kg, the profit is 10%.
Sol. Cost price of rice so that the profit is 10% when SP is 34.10 = 34.10 x (100/110) = Rs 31
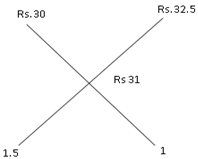
The ratio in which rice is to be mixed is 1.5:1 Or 3:2
Example 3: The mixture of a certain quantity of milk with 16 litres of water is worth 0.75 per litre. If pure milk is worth 2.25 per litre, how much milk is there in the mixture?
Sol. Cost of water is Rs 0 per litre.
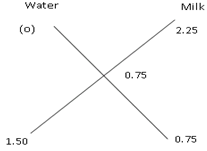
Water : Milk = 1.50 : 0.75 = 2 : 1
⇒ Quantity of milk 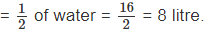
(b) Alligation Method 2: Repeated Dilution
This is used to calculate pure quantity left after 'n' number of processes of repeated replacement is done on the pure quantity. Suppose, a container contains 'x' units of a liquid from which 'y' units are taken out and replaced by water.
After 'n' operations quantity of pure will be: 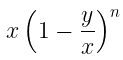
Example 4: A container contains 50 litres of milk. From this container, 10 litres of milk was taken out and replaced by water. This process is repeated one more time.
How much milk is now left in the container?
Sol. Units of milk in the container, x = 50 L
Units of milk to be replaced, y = 10 L
number of process of repeated replacement = 2
Applying the Replacement Method: Amount of milk after 2 operations =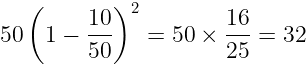
Practice Question
Question for Mixture And Alligation
Try yourself:A container contains 40 liters of milk. From this container, 4 liters of milk were taken out and replaced by water. This process was repeated further two times. How much milk is now contained by the container?
Explanation
Assume that a container contains x of liquid from which y units are taken out and replaced by water.
After n operations, the quantity of pure liquid = x(1 - y/x)n
Hence milk now contained by the container = 40(1 - 4/40)3 = 40(1 - 1/10)3 = 40 × 9/10 × 9/10 × 9/10 = 29.16
Report a problem
Question for Mixture And Alligation
Try yourself:A vessel is filled with liquid, 3 parts of which are water and 5 parts syrup. How much of the mixture must be drawn off and replaced with water so that the mixture may be half water and half syrup?
Explanation
Suppose the vessel initially contains 8 litres of liquid.
Let x litres of this liquid be replaced with water.
Quantity of water in new mixture = (3 – 3x/8 + x) litre
Quantity of syrup in new mixture = (5 – 5x/8) litres
So (3 – 3x/8 + x) = (5 – 5x/8) litres
⇒ 5x + 24 = 40 – 5x
⇒ 10x = 16
⇒ x = 8/5 .
So, part of the mixture replaced = (8/5 x 1/8) = 1/5
Report a problem
Question for Mixture And Alligation
Try yourself:Tea worth Rs. 126 per kg and Rs. 135 per kg are mixed with a third variety of tea in the ratio 1:1:2. If the mixture is worth Rs. 153 per kg, what is the price of the third variety per kg?
Explanation
Tea worth Rs. 126 per kg and Rs. 135 per kg are mixed in the ratio 1:1
So their average price = (126 + 135) / 2 = Rs.130.5
Hence let’s consider that the mixture is formed by mixing two varieties of tea.
one at Rs. 130.50 per kg and the other at Rs. x per kg in the ratio 2 : 2, i.e., 1 : 1.
Now let’s find out x.
By the rule of alligation, we can write as
(x – 153) : 22.5 = 1 : 1
⇒ x – 153 = 22.50
⇒ x = 153 + 22.5 = 175.5
Report a problem
Question for Mixture And Alligation
Try yourself:A can contains a mixture of two liquids A and B is the ratio 7:5. When 9 liters of the mixture are drawn off and the can is filled with B, the ratio of A and B becomes 7:9. How many liters of liquid A were contained by the can initially?
Explanation
Suppose the can initially contain 7x and 5x of mixtures A and B respectively.
Quantity of A in mixture left = 7x – (7/12 x 9) = 7x – 21/4 litres.
Quantity of B in mixture left = 5x – (5/12 x 9) = 5x – 15/4 litres
(7x – 21/4) / [(5x – 15/4) +9] = 7/9
⇒ (28x – 21) / (20x + 21) = 7/9
⇒ 52x – 189 = 140x + 147
⇒ 112x = 336
⇒ x = 3.
So, the can contain 21 litres of A.
Report a problem
Question for Mixture And Alligation
Try yourself:Two vessels A and B contain spirit and water in the ratio 5 : 2 and 7 : 6 respectively. Find the ratio in which these mixture be mixed to obtain a new mixture in vessel C containing spirit and water in the ration 8 : 5 ?
Explanation
Let Cost Price(CP) of the 1-litre spirit be Rs.1
Quantity of spirit in 1-litre mixture from vessel A = 5/7
Cost Price(CP) of 1 litre mixture from vessel A = Rs. 5/7
Quantity of spirit in 1 litre mixture from vessel B = 7/13
Cost Price(CP) of 1 litre mixture from vessel B = Rs. 7/13
Quantity of spirit to be obtained in 1 litre mixture from vessel C = 8/13
Cost Price(CP) of 1 litre mixture from vessel C = Rs. 8/13 = Mean Price
By the rule of alligation,
Mixture from Vessel A : Mixture from Vessel B = 1/13 : 9/91 = 7 : 9 = Required Ratio
Report a problem
Question for Mixture And Alligation
Try yourself:8 litres are drawn from a cask full of wine and is then filled with water. This operation is performed three more times. The ratio of the quantity of wine now left in cask to that of the water is 16 : 65. How much wine did the cask originally hold?
Explanation
Let the initial quantity of wine = x litre
After a total of 4 operations, quantity of wine = x(1 - y/x)n = x(1 - 8/x)4
Given that after a total of 4 operations, the ratio of the quantity of wine left in cask to that of water = 16 : 65
Hence we can write as [x(1 - 8/x)4] / x = 16/81
(1-8/x)4 = (2/3)4
(1 - 8/x) = 2/3
3(x - 8) = 2x
x = 24
Report a problem
Question for Mixture And Alligation
Try yourself:A dishonest milkman professes to sell his milk at cost price but he mixes it with water and thereby gains 25%. The percentage of water in the mixture is:
Explanation
Let C.P. of 1 litre milk be Re. 1
Then, S.P. of 1 litre of mixture = Re. 1, Gain = 25%.
C.P. of 1 litre mixture = Re.(100/125 x 1) = 4/5
By the rule of alligation,
Ratio of milk to water = 4/5 : 1/5 = 4 : 1.
Hence, percentage of water in the mixture = (1/5 x 100)% = 20%
Report a problem
Question for Mixture And Alligation
Try yourself:A jar full of whiskey contains 40% alcohol. A part of this whisky is replaced by another containing 19% alcohols and now the percentage of alcohol was found to be 26%. The quantity of whisky replaced is:
Explanation
Concentration of alcohol in 1st Jar = 40%
Concentration of alcohol in 2nd Jar = 19%
After the mixing, Concentration of alcohol in the mixture = 26%
By the rule of alligation,
ratio of 1st and 2nd quantities = 7 : 14 = 1 : 2
Report a problem

 Hence, Amount of Cheaper: Amount of dearer = (D – M) : (M – C)
Hence, Amount of Cheaper: Amount of dearer = (D – M) : (M – C) View Answer
View Answer 
Required ratio is 70 : 30 or 7 : 3