Gametogenesis: Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
The ability of any species to reproduce is vital for its survival. While certain organisms utilize asexual reproduction, humans and other mammals depend on sexual reproduction to ensure the continuation of their species. Specialized sex cells are produced to facilitate the transmission of genetic information from parents to offspring.
What is Gametogenesis?
Gametogenesis is a biological phenomenon in which cells undergo division and maturation, transforming diploid or haploid precursor cells into fully developed haploid gametes. The process of gametogenesis involves either the meiotic division of diploid gametocytes into distinct gametes or mitosis, depending on the organism's specific biological life cycle.
In mammals and higher plants, there are two different types of gametes: male and female. These are created through specialized processes in the reproductive organs called gonads. In males, the gonads are called testes, and in females, they are called ovaries. The process of making gametes is different between males and females:
- In males, the process is called spermatogenesis. This is how sperm cells are produced in the testes.
- In females, the process is called oogenesis. This is how egg cells are produced in the ovaries.
The stages of gametogenesis are as follows:
(i) Multiplication Phase
(ii) Growth Phase
(iii) Maturation Phase
Because there are two kinds of gametes, spermatozoa and ova.
- Gametogenesis can be divided into two categories: Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis.
- The formation of spermatozoa is referred to as spermatogenesis, whereas the formation of ova is referred to as oogenesis.
- Both spermatozoa and ova are derived from extra-gonadal primordial germ cells or PGCs.
- Spermatogenesis occurs in the testicular seminiferous tubules and oogenesis occurs in the ovarian follicles. Gamete formation begins during puberty.
Spermatogenesis
The process of formation of spermatozoa in the seminiferous tubules of the testis is known as spermatogenesis. The wall of seminiferous tubules is lined by cuboidal spermatogonia (male germ cells) and columnar Sertoli cells.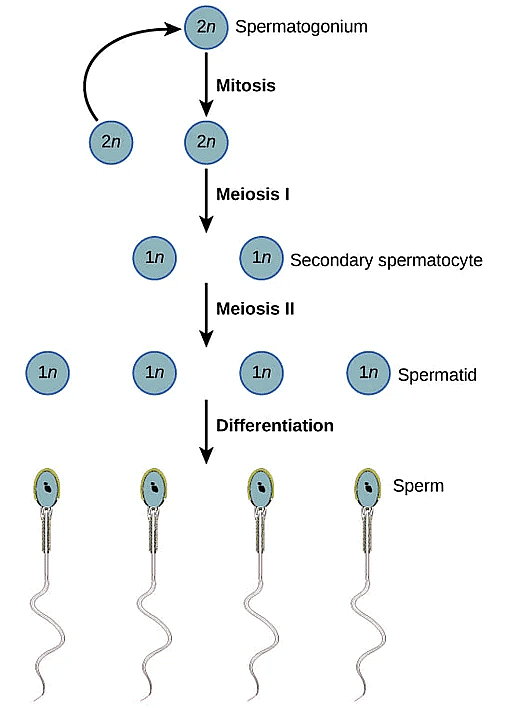
- It is divided into three phases: Multiplication phase, growth phase and maturation phase.
(A) Multiplication Phase
- Spermatogonia are derived from primordial germ cells.
- Spermatogonia present in the inside wall of seminiferous tubules multiply by mitotic divisions and increase in numbers.
(B) Growth Phase
- The cell size of primary spermatocytes increases to undergo the process of meiosis.
(C) Maturation Phase
- Each spermatogonium or primary spermatocyte is diploid and contains 46 chromosomes among which some undergo meiotic division to form two equal haploid (23) Secondary spermatocytes.
- The secondary spermatocyte undergoes 2nd meiotic division to form 4 haploid spermatids.
- At puberty, spermatids divide to form spermatozoa by the process called as spermiogeneis and after spermiogenesis, sperm heads become embedded in the Sertoli cells. Sertoli cells provide nourishment to developing sperms.
- Sperms are finally released from the seminiferous tubules by the process called spermiation.
- Sertoli cells form the 'blood testis barrier and protect the sperm from the immune system of the body.
- Sertoli cells function as endocrine glands. i.e. secrete three types of biochemicals:
(i) Anti Mullerian hormone: it inhibits Mullerian duct in males.
(ii) Inhibin hormone: It gives negative feedback to the pituitary gland (mainly) and hypothalamus.
(iii) Androgen Binding Protein: It concentrates testosterone in seminiferous tubules to aid spermatogenesis.
Spermatozoa are formed in the wall of the seminiferous tubules of the testes:
- The spermatogonia (type A) or germ cells (44 + X Y) divide mitotically, to give rise to more spermatogonia of type A and also spermatogonia of type B.
- The spermatogonia (type B) (44 + XY) enlarge, to form primary spermatocytes.
- The primary spermatocytes (44 + XY) now divide so that each of them forms two secondary spermatocytes. This is the first meiotic division: it reduces the number of chromosomes to half i.e 23.
- Each secondary spermatocyte has 22 + X or 22 + Y chromosomes. It divides to form two spermatids. This is the second meiotic division and this time there is no reduction in chromosome number(spermatocytogenesis).
- Each spermatid (22 + X or 22+Y) gradually changes its shape to become a spermatozoon. This process of transformation of a circular spermatid to a spermatozoon is called spermiogenesis/spermateleosis
- In human beings the maturation phase is the longest phase of spermatogenesis.
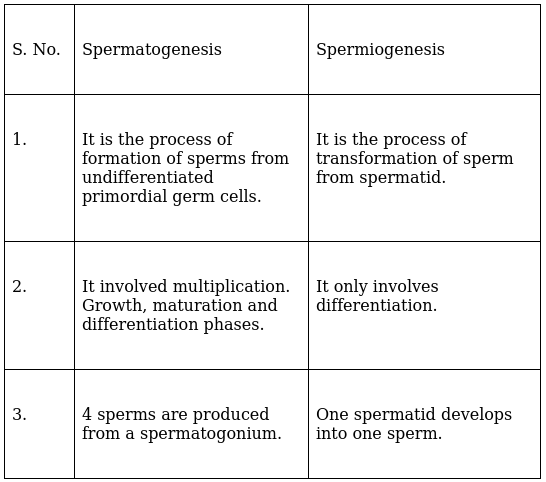 Difference between Spermatogenesis & Spermiogenesis
Difference between Spermatogenesis & Spermiogenesis
Hormonal Control of Spermatogenesis
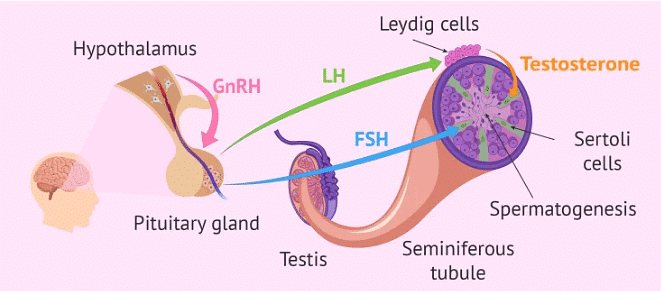
- Spermatogenesis is initiated due to an increase in gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) by the hypothalamus.
- GnRH acts on the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland to secrete luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
- LH acts on the Leydig's cells of the testes to secrete testosterone or androgens.
- FSH acts on Sertoli cells of the seminiferous tubules of the testes to secrete an androgen binding protein (ABP) and inhibin.
- ABP concentrates testosterone in the seminiferous tubules. Inhibin suppresses FSH synthesis.
- FSH acts on spermatogonia to stimulate sperm production.
 Hormonal Control of Spermatogenesis
Hormonal Control of Spermatogenesis
Attempt this test to check your knowledge of Spermatogenesis: Spermatogenesis
Structure of Sperm
Around 200-300 million sperms are ejaculated at once.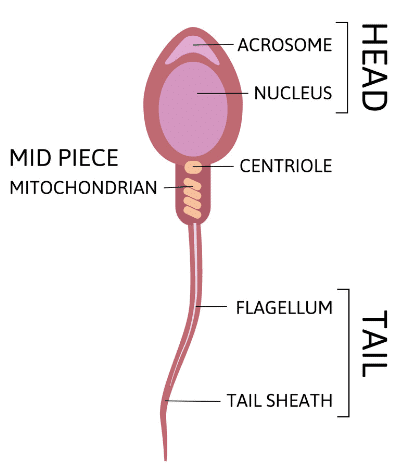 Structure of Sperm
Structure of Sperm
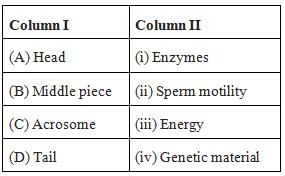
- The Head contains acrosome apically, which contains enzymes that facilitate the entry of sperm into the ovum. It is followed by an elongated nucleus (haploid).
- The middle piece has multiple mitochondria that provide energy for the movement of sperms.
- The tail is a flagellum that protrudes out of the cell body and is responsible for the vigorous motility of sperms. The tail helps sperm in swimming so that they can reach the ovum.
- Secretions from the epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicle, and prostate are required for sperm maturation and motility.
- For normal fertility, 60% sperms must have normal shapes and 40% sperms must show vigorous motility.
 |
Test: Gametogenesis
|
Start Test |
Oogenesis
- The process of formation of a mature female gamete is called Oogenesis.
- Like spermatogenesis oogenesis process also can be divided into three stages :
(A) Multiplication Phase
(B) Growth Phase
(C) Maturation Phase
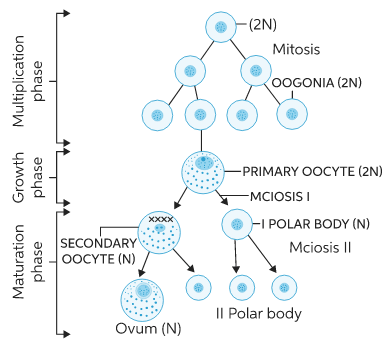 Phases of Oogenesis
Phases of Oogenesis
(A) Multiplication Phase
- During the embryonic development stage primordial germ cells or gamete mother cells repeatedly divide by mitosis to form a large number of diploid oogonia in each foetal ovary, no more oogonia are formed and added after birth.
- This process completes in the embryo stage of females in most higher animals.
(B) Growth Phase
- Like spermatogenesis, in this process oogonia grows in size and forms primary oocytes.
- The growth phase is the longest phase in oogenesis in oviparous animals.
- During the growth phase the size of the egg increases many times.
(C) Maturation Phase
- It is the longest phase in humans.
- In contrast to males the initial steps in egg production occur prior to birth. By the time the foetus is 25 weeks old, all the oogonia that she will ever produce are already formed by mitosis. These diploid cells develop into primary oocytes, begin the first steps of the first meiotic division, proceed up to diplotene (prophase-I) and then stop any further development.
- Each primary oocyte is surrounded by a layer of granulosa cells called the primary follicle.
- These primary follicles are surrounded by more layers of granulosa cells and a new theca called the secondary follicle.
- Secondary follicle then transforms to tertiary follicle characterised by fluid filled cavity called antrum.
- The oocytes within the tertiary follicle grow much larger and complete meiosis I, forming a large secondary oocyte and a small polar body that receives a very little amount of cytoplasm but one full set of chromosomes.
- First polar body may undergo degeneration due to a lack of cytoplasm or may divide.
- Whereas the secondary oocyte proceeds as far as the metaphase stage of meiosis II. However, it then stops advancing any further, it awaits the arrival of the spermatozoa for completion of the second meiotic division.
- Entry of the sperm restarts the cell cycle breaking down MPF (Metaphase promoting factor and turning on the APC (Anaphase promoting complex). Completion of meiosis II converts the secondary oocyte into a fertilised egg or zygote (and also a second polar body).
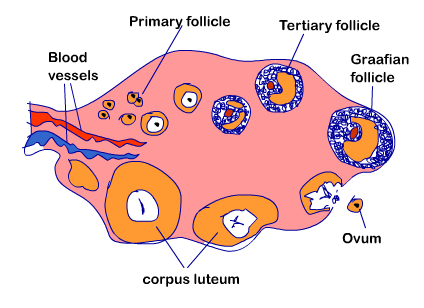 Image showing development of Follicle
Image showing development of Follicle
Ovulation
- The tertiary follicle in the ovary changes into mature follicle or Graaffian follicle.
- The secondary oocyte forms a new membrane called zona pellucida.
- The Graafian follicle ruptures to release the secondary oocyte from the ovary by the process called Ovulation.
- In humans, the ovum is released from the ovary in the secondary oocyte stage.
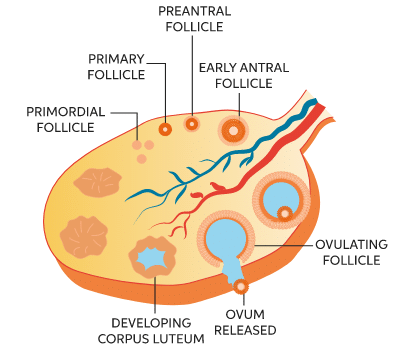 Process of Ovulation
Process of Ovulation
- In humans, ovulation occurs about 14 days before the onset of the next menstruation. Ovulation is induced by LH.
- The maturation of the ovum is completed in the mother's Fallopian tube usually after the sperm has entered the secondary oocyte during fertilisation.
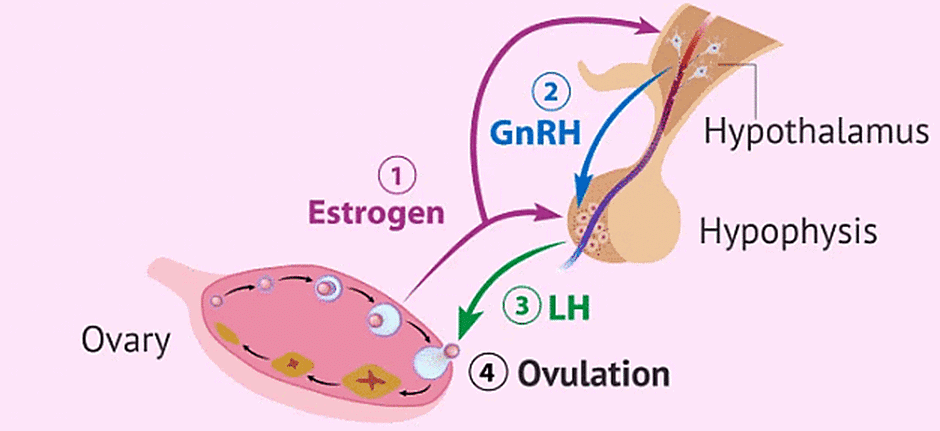
Hormonal Control of Oogenesis
- GnRH secreted by the hypothalamus stimulates the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland to secrete LH and FSH.
- FSH stimulates the growth of Graafian follicles and also the development of egg/oocyte within the follicle to complete the meiosis I to form a secondary oocyte.
- FSH also stimulates the formation of estrogens.
- LH induces the rupture of the mature Graafian follicle and thereby the release of secondary oocytes. Thus LH causes ovulation.
- In brief ovulation in human beings may be defined as the release of the secondary oocyte from the Graafian follicle.
- The remaining part of the Graafian follicle is stimulated by LH to develop into corpus luteum ("yellow body").
- The rising level of progesterone inhibits the release of GnRH, which in turn, inhibits the production of FSH, LH and progesterone.
Significance of Oogenesis
- One oogonium produces one ovum and three polar bodies.
- Polar bodies have a small amount of cytoplasm. It helps to retain a sufficient amount of cytoplasm in the ovum which is essential for the development of the early embryo. The formation. of polar bodies maintains half the number of chromosomes in the ovum.
- During meiosis the first crossing over takes place which brings about variation.
- Oogenesis occurs in various organisms. Therefore, it supports the evidence of basic relationships among the organisms.
Done learning about Oogenesis? Attempt this test to check how much you have learned:
Test-Oogenesis
 |
Download the notes
Gametogenesis: Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis
|
Download as PDF |
Difference Between Male Sperm & Female Egg
Similarities in Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis
- Both processes consist of three main phases, viz., multiplication, growth and maturation phases.
- In the multiplication phase, the primordial germ cells of testes and ovaries proliferate mitotically, forming numerous gametogonia (spermatogonia/oogonia) in both processes.
- In the growth phase, the cells accumulate food reserves and grow to primary gametocytes (spermatocytes/oocytes) in both processes.
- Maturation phase in both processes comprises two successive divisions, first meiotic and second meiotic, resulting in the formation of secondary gametocytes and gametes respectively.
Differences in Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis
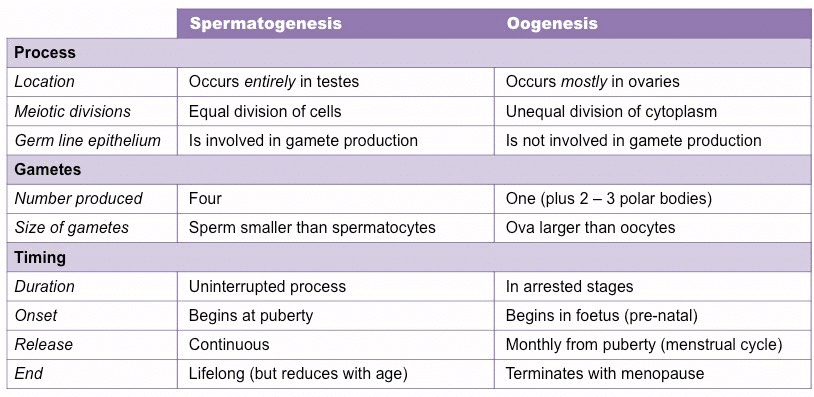
In this document you have learnt the following:
- The primary sex organs – the testis in males and the ovaries in females – produce gametes, i.e., sperms and eggs, through a process known as gametogenesis.
- The process of formation of spermatozoa in the seminiferous tubules of the testis is known as spermatogenesis. The wall of seminiferous tubules is lined by cuboidal spermatogonia (male germ cells) and columnar Sertoli cells.
- Spermatogenesis is initiated due to an increase in gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) by the hypothalamus.
- Secretions from the epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicle, and prostate are required for sperm maturation and motility.
- Oogenesis occurs in various organisms. therefore, it supports the evidence of basic relationships among the organisms.
- The process of formation of a mature female gamete is called Oogenesis.
- The tertiary follicle in the ovary changes into mature follicle or Graaffian follicle.
- The secondary oocyte forms a new membrane called zona pellucida.
- The Graafian follicle ruptures to release the secondary oocyte from the ovary by the process called Ovulation.
- Similarities between spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
- Differences between spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
Attempt this test based completely on NCERT:
Test: Gametogenesis
|
78 videos|279 docs|174 tests
|
FAQs on Gametogenesis: Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is the difference between spermatogenesis and oogenesis? |  |
| 2. How long does spermatogenesis take to complete compared to oogenesis? |  |
| 3. What factors can affect the process of gametogenesis in both males and females? |  |
| 4. How does the process of spermatogenesis differ from oogenesis in terms of gamete production? |  |
| 5. What are the main stages involved in both spermatogenesis and oogenesis? |  |




























