(Part - 1) Therapeutic Approaches Class 12 Psychology
Nature and Process of Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy refers to the collaborative relationship between a therapist and a client seeking treatment.
 The purpose of this relationship is to address the psychological issues faced by the client in order to bring about positive change.
The purpose of this relationship is to address the psychological issues faced by the client in order to bring about positive change.
- Psychotherapy emphasizes the significance of the interpersonal connection, which serves as the core of psychological treatment.
- The primary purpose of various psychotherapies includes:
- Boosting the client's determination for self-improvement.
- Alleviating emotional stress and strain.
- Unveiling the potential for constructive personal development.
- Adjusting behavioral patterns.
- Transforming cognitive processes.
- Augmenting self-awareness.
- Enhancing relationships and communication skills.
- Assisting in decision-making processes.
- Recognizing and evaluating life choices.
- Engaging with the social sphere in a more innovative and self-aware manner.
Therapeutic Relationship
The therapeutic relationship is a unique connection between the therapist and the client, which is not a long-term professional association, but rather a very professional one. The therapeutic relationship is composed of two elements:
- The contractual aspect of the relationship in which the client and the therapist voluntarily form a partnership aimed at resolving the client's issues.
- The limited duration of the psychotherapy.
Types of Therapies
The classification of different types of therapies, such as psychodynamic therapy, behavioral therapy, and cognitive therapy, is based on several factors. These factors include determining the cause of the client's problem, how the cause developed, the primary method of treatment, the nature of the therapeutic relationship between the client and therapist, the primary benefit to the client, and the duration of treatment.
Psychodynamic Therapy
The oldest form of therapy is Psychodynamic therapy, which was introduced by Dr. Sigmund Freud. This therapy aims to identify the sources of psychological distress and explains the structure of the psyche, including the dynamics between different components.
Methods of Eliciting Nature of Intrapsychic Conflict
- The method of Free Association is utilized in order to comprehend the client's issues. In this technique, the client is asked to recline on a couch and, once the therapeutic relationship has been established, is encouraged to speak freely without any inhibitions about whatever thoughts come to mind.
- This approach aids in comprehending the nature of the client's psyche and delving into the unconscious mind of the client.
- Dream Analysis is a technique where the client is instructed to record their dreams upon awakening. The client's dreams provide a vivid illustration of their unconscious mind and unresolved issues in their life.
Modality of Treatment
- Transference is a process in which the client begins to associate the therapist with figures from their past, usually from their childhood, as the unconscious elements are brought into consciousness through techniques like free association and dream analysis.
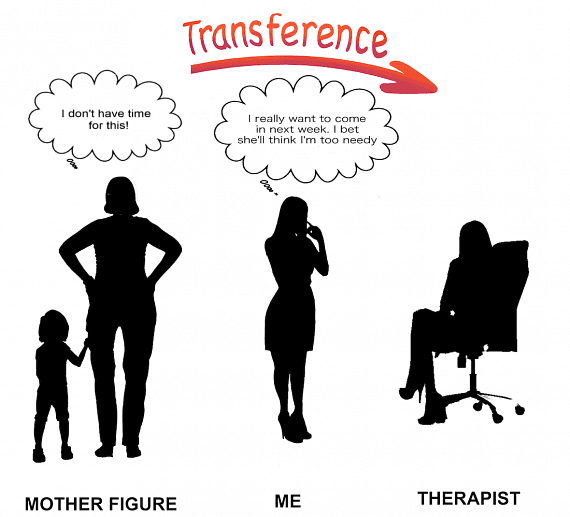 The therapist maintains a non-judgmental attitude and allows the client to continue with this process of emotional identification. This process of transference helps the therapist in understanding the unconscious conflicts of the client. The client may act out their frustrations, anger, fear, and depression towards the therapist that they harboured towards that person in the past, but could not express at that time. This is called transference neurosis. This stage is useful for the therapist in identifying the nature of intrapsychic conflicts suffered by the client. The positive transference is when the client idolizes or falls in love with the therapist and seeks their approval, while negative transference is present when the client has feelings of hostility, anger, and resentment towards the therapist.
The therapist maintains a non-judgmental attitude and allows the client to continue with this process of emotional identification. This process of transference helps the therapist in understanding the unconscious conflicts of the client. The client may act out their frustrations, anger, fear, and depression towards the therapist that they harboured towards that person in the past, but could not express at that time. This is called transference neurosis. This stage is useful for the therapist in identifying the nature of intrapsychic conflicts suffered by the client. The positive transference is when the client idolizes or falls in love with the therapist and seeks their approval, while negative transference is present when the client has feelings of hostility, anger, and resentment towards the therapist.
- Resistance occurs when the process of transference is encountered. The client may resist the process of transference because it brings to light unconscious conflicts and wishes, causing discomfort. The client may oppose the progress of therapy to prevent the recall of painful memories. Resistance can be conscious, such as when the client deliberately withholds information, or unconscious, such as when the client becomes silent during therapy or recalls trivial details without the emotional context. The therapist addresses resistance by repeatedly confronting the patient about it and uncovering the underlying emotions like anxiety, fear, or shame that cause the resistance.
- Interpretation is a crucial element in bringing about change in psychotherapy. There are two types of analytical techniques used in interpretation. The first technique, confrontation, involves the therapist pointing out a particular aspect of the client's psyche that needs to be faced. The second technique, clarification, involves the therapist highlighting important details about a vague or confusing event, thus bringing it into sharp focus.
- Interpretation is considered to be the highest point of psychoanalysis and is a subtle process. The therapist uses the unconscious material that has been revealed through free association, dream interpretation, transference, and resistance to help the client become aware of the conflicts and psychic contents that have caused certain symptoms and conflicts. Interpretation may focus on intrapsychic conflicts or childhood deprivations.
- Working through refers to the process of repeatedly using confrontation, clarification, and interpretation in psychotherapy. This process helps the patient to gain a better understanding of themselves, the source of their problems, and to integrate the uncovered material into their psyche or sense of self.
- Insight is the result of the process of working through, which involves the repeated use of confrontation, clarification, and interpretation to bring unconscious memories and conflicts to the conscious level. As the client gains more insight, they come to understand themselves better intellectually and emotionally, and gain an understanding of their conflicts and problems. There are two types of insight: intellectual insight and emotional insight, which involves accepting and changing one's irrational reactions to past events. Insight marks the end of therapy, and a psychologically healthy client emerges, free of past conflicts, defense mechanisms, and physical symptoms.
Behavior Therapy
Behavior Therapies center on the idea that psychological distress stems from problematic thinking or behavior patterns. The primary emphasis is on the client's current thinking and behaviors, and the past is only relevant for comprehending the root cause of the client's maladaptive behavior. Unlike Psychodynamic Therapy, the past is not relived in Behavior Therapies.
Method of Treatment
- Behavioral Analysis is used to identify maladaptive behaviors, as well as the factors that cause and maintain them.
- Antecedent factors are the causes of the problematic behavior, while maintaining factors are those that keep it going.
- Once these factors are identified, treatment options can be determined. These may include antecedent operations, in which the therapist controls the causal factors, or establishing operations, in which the reinforcement value of the consequences is increased or decreased.
Techniques of Behavioral Therapy
Here are some paraphrased explanations of various techniques used in behavioral therapy:
- Aversive Conditioning: This technique involves pairing an undesirable behavior with an unpleasant consequence in order to create an association between the two. This technique is often used in rehabilitation centers.
- Positive Reinforcement: This technique involves rewarding an adaptive behavior in order to increase the frequency of that behavior.
- Negative Reinforcement: This technique involves removing or avoiding a painful stimulus in the environment in order to increase the frequency of an adaptive behavior.
Unwanted behaviour can be reduced and wanted behaviour can be increased simultaneously through differential reinforcement.
- Positive reinforcement for the wanted behaviour and negative reinforcement for the unwanted behaviour attempted together may be one such method.
- The other method is to positively reinforce the wanted behaviour and ignore the unwanted behaviour. This latter method is less painful and equally effective.
The wanted behaviour of politely asking to be taken to the cinema increases and the unwanted behaviour of crying and sulking decreases. - Systematic desensitisation is a technique introduced by Wolpe for treating phobias or irrational fears.
The client is interviewed to elicit fear-provoking situations and together with the client, the therapist prepares a hierarchy of anxiety-provoking stimuli with the least anxiety-provoking stimuli at the bottom of the hierarchy.
The therapist relaxes the client and asks the client to think about the least anxiety-provoking situation. The client is asked to stop thinking of the fearful situation if the slightest tension is felt.
The principle of reciprocal inhibition operates here. This principle states that the presence of two mutually opposing forces at the same time inhibits the weaker force.
- Modelling is the procedure wherein the client learns to behave in a certain way by observing the behaviour of a role model or the therapist who initially acts as the role model.
Vicarious learning, i.e., learning by observing others, is used, and through a process of rewarding small changes in behaviour, the client gradually learns to acquire the behaviour of the model.
FAQs on (Part - 1) Therapeutic Approaches Class 12 Psychology
| 1. What are some common therapeutic approaches used in psychotherapy? |  |
| 2. How does the nature of psychotherapy differ from the process of psychotherapy? |  |
| 3. How do the humanities and arts play a role in psychotherapy? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of meaningful therapeutic approaches used in psychotherapy? |  |
| 5. How can individuals determine which type of therapy is best for them? |  |






















