(Part - 2) Social Influence and Group Processes Class 12 Psychology
| Table of contents |

|
| Compliance |

|
| Obedience |

|
| Co-operation and Competition |

|
| Social Identity |

|
| Intergroup Conflict: Nature and Causes |

|
| Conflict Resolution Strategies |

|
Compliance
Compliance refers to the act of changing one's behavior or attitude in response to a direct request from another person or group.
 Compliance can be influenced by various factors, including the nature of the request, the social context in which the request is made, and the characteristics of the person making the request.
Compliance can be influenced by various factors, including the nature of the request, the social context in which the request is made, and the characteristics of the person making the request.
There are several techniques that people may use to increase compliance with their requests. These include:
- Foot-in-the-door technique: This involves making a small request first, and then following up with a larger request. The idea is that people are more likely to comply with the larger request if they have already agreed to the smaller one.
- Door-in-the-face technique: This involves making a very large request first, which is likely to be rejected, and then following up with a smaller, more reasonable request. The idea is that people are more likely to comply with the smaller request if they feel that they have already rejected a larger one.
- Lowballing: This involves making an attractive offer at first, but then changing the terms of the offer after the person has already committed to it. The idea is that people are more likely to comply with the changed terms because they have already committed to the initial offer.
- Social proof: This involves providing evidence that other people have already complied with the request. The idea is that people are more likely to comply if they see that others have already done so.
- Authority: This involves appealing to a person's respect for authority or expertise. The idea is that people are more likely to comply if they feel that the person making the request has legitimate authority or expertise.
Compliance can have both positive and negative effects, depending on the nature of the request and the context in which it is made. Compliance can be a useful tool for achieving social goals, such as promoting health behaviors or reducing prejudice. However, compliance can also be used to perpetuate harmful behaviors or attitudes, such as conformity to oppressive social norms.
Obedience
- Obedience refers to the act of following the instructions or orders of someone perceived as an authority figure. This can involve complying with demands that are unethical, immoral, or in violation of one's personal beliefs or values.
- The most famous study of obedience is the Milgram experiment, conducted in the early 1960s by psychologist Stanley Milgram. In the study, participants were asked to administer electric shocks to a "learner" in another room whenever they made a mistake on a memory task. The shocks were not real, but the participants did not know this. The "learner" was an actor who would scream and protest as the shocks increased in intensity. Despite this, many participants continued to administer shocks, even when the "learner" begged them to stop.
- Milgram's study demonstrated the power of authority figures to influence people's behavior, even in situations where that behavior goes against their moral beliefs. The study has been criticized for ethical reasons, as it involved deception and the potential for psychological harm to participants.
- Other research has shown that obedience can be influenced by factors such as the perceived legitimacy of the authority figure, the immediacy of the consequences of disobedience, and the presence of others who are also obeying.
- Obedience can have both positive and negative effects. On the one hand, obedience can help to maintain social order and facilitate cooperation within groups. On the other hand, blind obedience to authority can lead to unethical or harmful behavior, such as the perpetuation of unjust laws or the participation in acts of violence or oppression.
- Obedience is a complex phenomenon that has been studied extensively in psychology. While obedience can be a useful tool for achieving social goals, it can also have negative consequences when it leads to the perpetuation of harmful behaviors or attitudes.
Co-operation and Competition
- Cooperation and competition are two important concepts that describe the ways in which individuals interact with each other in social situations.
- Cooperation refers to the act of working together towards a common goal or objective. In cooperative situations, individuals may share resources, knowledge, or skills to achieve a mutually beneficial outcome. Cooperation can foster positive relationships, build trust, and promote social cohesion.
- Competition, on the other hand, refers to the act of striving against others to achieve a desired outcome. In competitive situations, individuals may engage in behaviors such as strategic thinking, self-promotion, or aggression to gain an advantage over others. Competition can lead to feelings of rivalry, hostility, and mistrust.
- Cooperation and competition can coexist in many social situations. For example, in team sports, players may compete against each other to win a game, but also cooperate with each other to achieve that goal. In business, companies may compete with each other for customers and profits, but may also cooperate on joint ventures or initiatives that benefit both parties.
- Research has shown that cooperation and competition can have both positive and negative effects on individuals and society. Cooperation can lead to greater social harmony, trust, and well-being, while competition can lead to stress, anxiety, and inequality. Both cooperation and competition can also influence the development of social norms, values, and identities.
- Cooperation and competition are two important concepts in psychology that describe the ways in which individuals interact with each other in social situations. While both cooperation and competition can have positive and negative effects, they can also coexist and complement each other in many situations.
Social Identity
- Social identity refers to the part of an individual's self-concept that is derived from their membership in various social groups. Social identity is based on shared characteristics or experiences that define a particular group, such as race, ethnicity, gender, religion, nationality, or occupation.
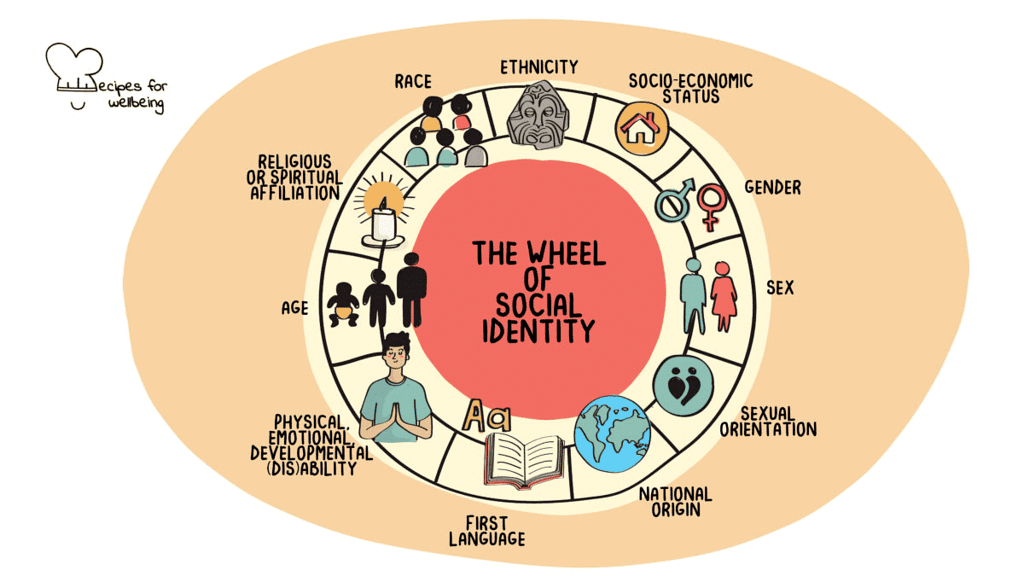
- Social identity can have a powerful influence on an individual's attitudes, beliefs, and behavior. When people identify strongly with a particular group, they may experience a sense of belonging, pride, and loyalty towards that group. This can lead to positive outcomes such as increased self-esteem, social support, and a sense of purpose or meaning in life.
- However, social identity can also lead to negative outcomes such as prejudice, discrimination, and conflict between groups. This occurs when individuals see their own group as superior to others and engage in behaviors that undermine or exclude members of other groups. Such negative outcomes can have serious consequences for both the individuals involved and society as a whole.
- Research has shown that social identity can be influenced by a range of factors, including individual differences such as personality traits and cognitive processes, as well as social and cultural factors such as social norms and media representations. Social identity can also change over time, as individuals move in and out of different groups or as the characteristics of the group itself change.
- Social identity is an important concept in psychology that describes the way in which an individual's self-concept is shaped by their membership in social groups. Social identity can have both positive and negative effects on individuals and society, and understanding the factors that influence social identity can help to promote greater understanding and acceptance between different groups.
Intergroup Conflict: Nature and Causes
- Intergroup conflict refers to conflicts that occur between different groups of people, based on factors such as race, ethnicity, religion, nationality, or political ideology. Intergroup conflict can have serious consequences for individuals and society, including discrimination, violence, and social polarization.
- There are many factors that can contribute to intergroup conflict. One important factor is social identity, which refers to the way in which an individual's self-concept is shaped by their membership in social groups. When individuals identify strongly with a particular group, they may perceive members of other groups as a threat to their own group's interests and engage in behaviors that reinforce their group's superiority. This can lead to prejudice, discrimination, and conflict between groups.
- Another factor that can contribute to intergroup conflict is perceived threat. When members of a group perceive a threat to their own group's interests, such as economic or political competition, they may respond with hostility towards members of other groups. This can lead to a spiral of escalating conflict, as each group perceives the other as a greater threat and responds with increasingly aggressive behaviors.
- Cognitive factors can also contribute to intergroup conflict. For example, people tend to form stereotypes about members of other groups, which can lead to negative attitudes and behaviors towards those individuals. This can also lead to a self-fulfilling prophecy, where members of the stereotyped group respond to negative treatment with further negative behaviors, reinforcing the stereotype.
- Social and cultural factors, such as social norms, media representations, and historical events, can also contribute to intergroup conflict. For example, when certain groups are portrayed in a negative light in the media or when historical events create long-standing tensions between groups, this can reinforce negative attitudes and behaviors towards those groups.
- Intergroup conflict is a complex phenomenon that is influenced by a range of factors, including social identity, perceived threat, cognitive biases, and social and cultural factors. Understanding the causes of intergroup conflict can help to promote greater understanding and cooperation between different groups, and ultimately reduce the negative consequences of intergroup conflict for individuals and society.
Conflict Resolution Strategies
Conflict resolution strategies refer to the various methods and techniques that can be used to manage and resolve conflicts between individuals or groups. Conflict resolution strategies can be used in a wide range of contexts, including personal relationships, work environments, and social and political conflicts.Here are some common conflict resolution strategies:
- Compromise: This strategy involves finding a middle ground where both parties can compromise on their needs and interests. This can involve each party giving up something in order to reach a mutually acceptable solution.
- Collaboration: This strategy involves working together to find a solution that satisfies the needs and interests of both parties. This can involve brainstorming and problem-solving together to find a win-win solution.
- Accommodation: This strategy involves one party making concessions or accommodations to the other in order to resolve the conflict. This can be effective when one party has more power or when the conflict is relatively minor.
- Avoidance: This strategy involves avoiding the conflict altogether, either by walking away from the situation or by delaying the conflict until a later time when emotions may have cooled down.
- Competition: This strategy involves attempting to win the conflict at all costs, often by using aggressive or confrontational tactics. This strategy can be effective in situations where there is a clear winner and loser, but it can also escalate the conflict and damage relationships.
- Mediation: This strategy involves bringing in a neutral third party to help facilitate communication and negotiation between the parties. This can be effective when the parties are unable to resolve the conflict on their own.
Conflict resolution strategies are an important tool for managing and resolving conflicts between individuals or groups. By understanding and using these strategies effectively, individuals can improve their communication and negotiation skills and promote greater understanding and cooperation between different parties.
FAQs on (Part - 2) Social Influence and Group Processes Class 12 Psychology
| 1. What is the difference between compliance and obedience? |  |
| 2. How do social identity and intergroup conflict influence group processes? |  |
| 3. What are some common conflict resolution strategies in group settings? |  |
| 4. How does cooperation and competition impact group dynamics? |  |
| 5. What are the natural causes of intergroup conflict? |  |















