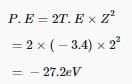All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of May Week 3 for NEET Exam
A car travelling at 36km/h-1 due North turns West in 5 seconds and maintains the same speed. What is the acceleration of the car?
- a)2√2ms-2 South West
- b)√2ms-2 South West
- c)2ms-2 North West
- d)4ms-2 North West
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A car travelling at 36km/h-1 due North turns West in 5 seconds and maintains the same speed. What is the acceleration of the car?
a)
2√2ms-2 South West
b)
√2ms-2 South West
c)
2ms-2 North West
d)
4ms-2 North West
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Initial velocity of car = 36 km/hr due north
Final velocity of car = 36 km/hr due west
magnitude of change in velocity = root[(36)^2 + (36)^2] = 36 x √2
(since velocity is a vector, so direction has to be taken into account)
Acceleration = Change in velocity/time = [36√2 x 5/18]/5 m/s^2 = 2√2 m/s^2 = 2.828 m/s^2
A particle moves in x-y plane starting from the origin in a direction making 30° angle with x-axis. Distance covered by it is 5 m. what is the position vector of the particle.- a)
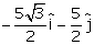
- b)
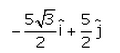
- c)
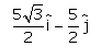
- d)
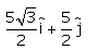
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle moves in x-y plane starting from the origin in a direction making 30° angle with x-axis. Distance covered by it is 5 m. what is the position vector of the particle.
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Ankita Menon answered |
Initial velocity = u = 20 m/s
Final velocity = v = 0 [ at maximum height , v = 0 ]
Final velocity = v = 0 [ at maximum height , v = 0 ]
Acceleration due to gravity(g) in this case , is taken as negative.
This is because , when the direction of motion of object is opposite to "g" , then value of g is taken as -ve
This is because , when the direction of motion of object is opposite to "g" , then value of g is taken as -ve
hence ,
g = -9.8 m/s²
Let's use the formula :-
[h = height ]
v² -u² = 2gh
0² - 20² = 2*-9.8*h
-400 = -19.6h
h = -400/-19.6
= 20.408 m [ approximately ]
-400 = -19.6h
h = -400/-19.6
= 20.408 m [ approximately ]
Which of the following electronic transitions requires that the greatest quantity of energy be absorbed by a hydrogen atom ?- a)n = 1 to n = 2
- b)n = 2 to n = 4
- c)n = 3 to n = 6
- d)n = 3 to n = ∞
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following electronic transitions requires that the greatest quantity of energy be absorbed by a hydrogen atom ?
a)
n = 1 to n = 2
b)
n = 2 to n = 4
c)
n = 3 to n = 6
d)
n = 3 to n = ∞
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Therefore, electronic transition (a) requires greatest quantity of energy.
A particle has an initial velocity 3 iˆ +4 jˆ and an acceleration 0.4 iˆ + 0.3 jˆ .Its speed after 10 s is- a)7 units
- b)8.5 units
- c)7√2 units
- d)10 units
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle has an initial velocity 3 iˆ +4 jˆ and an acceleration 0.4 iˆ + 0.3 jˆ .Its speed after 10 s is
a)
7 units
b)
8.5 units
c)
7√2 units
d)
10 units
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
Answer is C) 7 x (2)^1/2
Solution:
The initial velocity is given by
u = v - at
Where, v = Final Velocity, t = time taken, and a = acceleration
u = 3 i + 4 j
a = 0.4 i + 0.3 j
t = 10 s
Using initial velocity formula
3 i + 4 j = v - (0.4 i + 0.3 j) 10
v = 7 ( i + j)
Velocity is the vector quantity which is defined by both magnitude and direction but speed is scalar quantity which is defined by only magnitude.
The magnitude of v = (7^2+7^2)^1/2 = 7 x (2)^1/2
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-11) This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Which of the following is correct?- a)1H1 and 2He3 are isotopes
- b)6C14 and 7N14 are isotopes
- c)19K39 and 20Ca40 are isotones
- d)9F19 and 11Na24 are isodiaphers
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-11) This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Which of the following is correct?
a)
1H1 and 2He3 are isotopes
b)
6C14 and 7N14 are isotopes
c)
19K39 and 20Ca40 are isotones
d)
9F19 and 11Na24 are isodiaphers
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Because isotones means the same number of neutron, So, from the question, option c is right, number of neutron in k is,39-19= 20,and,the number of neutron in ca is also 40-20=20 so it is isotones.
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 - 19) This section contains 4 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)Q. The energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit of H-atom is -13.6 eV. What is the possible value of quantum number for the excited state to have energy -3.4 eV?
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 - 19) This section contains 4 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q. The energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit of H-atom is -13.6 eV. What is the possible value of quantum number for the excited state to have energy -3.4 eV?
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
For Bohr radius;
E = -13.6×Z2/ n2
For H atom, Z=1 and given energy = -3.4
So, we have, -3.4 = -13.6/n2
Or n = 2
E = -13.6×Z2/ n2
For H atom, Z=1 and given energy = -3.4
So, we have, -3.4 = -13.6/n2
Or n = 2
A body sliding on a smooth inclined plane requires 4 seconds to reach the bottom starting from rest at the top. How much time does it take to cover one-fourth distance starting from rest at the top- a)1 s
- b)2 s
- c)4 s
- d)16 s
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A body sliding on a smooth inclined plane requires 4 seconds to reach the bottom starting from rest at the top. How much time does it take to cover one-fourth distance starting from rest at the top
a)
1 s
b)
2 s
c)
4 s
d)
16 s
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
A body start from rest so, u = 0
Let total distance covered = s
Let a body moves with accerlation = a
► s = 1/2 × a× t2
► s = 1/2× a × 42
► s = 8a
The one-fourth of total distance, s' = 8a/4
= 2a
► s' = 1/2 × a × t2
► 2a / a = 1/2 × t2
► 4 = t2
► t = 2 s
Let total distance covered = s
Let a body moves with accerlation = a
► s = 1/2 × a× t2
► s = 1/2× a × 42
► s = 8a
The one-fourth of total distance, s' = 8a/4
= 2a
► s' = 1/2 × a × t2
► 2a / a = 1/2 × t2
► 4 = t2
► t = 2 s
The vector which when added to the resultant of  and
and 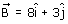 gives unit vector along x direction.
gives unit vector along x direction.- a)
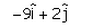
- b)
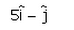
- c)
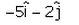
- d)
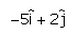
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The vector which when added to the resultant of  and
and 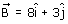 gives unit vector along x direction.
gives unit vector along x direction.
 and
and 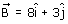 gives unit vector along x direction.
gives unit vector along x direction.a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Naveen Choudhary answered |
Time taken by first drop to cover 5 cm, u = 0
⇒ h = 1/2 gt2
⇒ 5 = 1/2 x 10 x t2
⇒ t = 1 sec
Hence interval is 0.5 sec for each drop.
Now distance fallen by second drop in 0.5 sec
⇒ h1 = 1/2 gt2
= 1/2 x 10 x (0.5)2
= 5 x 0.25
= 1.25 m
Height above the ground ( of 2nd drop) = 5 - 1.25
= 3.75 m
Find the number of waves made by a Bohr’s electron in one complete revolution in its 3rd orbit
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the number of waves made by a Bohr’s electron in one complete revolution in its 3rd orbit
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Number of waves = n(n - 1)/2 where n = Principal quantum number or number of orbit number of waves = 3(3 - 1)/2 = 3 * 2/2 = 3
ALTERNATIVE SOLUTIONS :
In general, the number of waves made by a Bohr electron in an orbit is equal to its quantum number.
According to Bohr’s postulate of angular momentum, in the 3rd orbit
Mur = n h/2π
Mur = 3 (h/2π) …..(i) [n = 3]
According to de Broglie relationship
λ = h/mu ….(ii)
Substituting (ii) in (i), we get
(h/λ) r = 3 (h/2π) or 3λ = 2πr
[∵ mu = h/λ]
Thus the circumference of the 3rd orbit is equal to 3 times the wavelength of electron i.e. the electron makes three revolution around the 3rd orbit.
Why are bryophytes referred to as "amphibians of the plant kingdom"?
- a)They can live both on land and in water.
- b)They can change their reproductive methods.
- c)They have adaptations for both sexual and asexual reproduction.
- d)They are capable of moving between different habitats.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Why are bryophytes referred to as "amphibians of the plant kingdom"?
a)
They can live both on land and in water.
b)
They can change their reproductive methods.
c)
They have adaptations for both sexual and asexual reproduction.
d)
They are capable of moving between different habitats.
|
|
Saranya Joshi answered |
**Answer:**
The prominent phase in the life cycle of bryophytes is the **gametophyte**. Bryophytes are non-vascular plants that include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. They have a unique life cycle that involves alternating generations of two distinct phases: the gametophyte and the sporophyte.
**Gametophyte Phase:**
The gametophyte is the dominant phase in the life cycle of bryophytes. It is the haploid (having one set of chromosomes) and gamete-producing phase. The gametophyte is the visible, leafy part of the plant that we commonly recognize as the moss or liverwort. It is the phase that carries out photosynthesis and produces the sex organs.
During the gametophyte phase, the moss or liverwort produces archegonia and antheridia. The archegonia are female sex organs that produce eggs, while the antheridia are male sex organs that produce sperm. The sperm requires water for fertilization to occur because they swim to the eggs through a film of water.
After fertilization, the zygote is formed, which develops into the sporophyte phase.
**Sporophyte Phase:**
The sporophyte phase is the diploid (having two sets of chromosomes) and spore-producing phase in the bryophyte life cycle. It is dependent on the gametophyte phase for nutrition and support.
The sporophyte phase develops from the fertilized zygote and remains attached to the gametophyte. It is a small, non-photosynthetic structure that consists of a foot, seta, and capsule. The foot is embedded in the gametophyte and absorbs nutrients. The seta is the stalk-like structure that elevates the capsule. The capsule contains sporogenous tissue, which undergoes meiosis to produce haploid spores.
When the spores are mature, the sporophyte releases them into the environment. These spores are dispersed by wind or water and, upon landing in a suitable environment, germinate to form new gametophytes. The spores give rise to protonemata, which are thread-like structures that develop into new gametophytes.
**Conclusion:**
In conclusion, the gametophyte phase is the prominent phase in the life cycle of bryophytes. It is the leafy, haploid phase that carries out photosynthesis and produces the sex organs. The sporophyte phase, although important for spore production, remains dependent on the gametophyte phase for nutrition and support.
The prominent phase in the life cycle of bryophytes is the **gametophyte**. Bryophytes are non-vascular plants that include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. They have a unique life cycle that involves alternating generations of two distinct phases: the gametophyte and the sporophyte.
**Gametophyte Phase:**
The gametophyte is the dominant phase in the life cycle of bryophytes. It is the haploid (having one set of chromosomes) and gamete-producing phase. The gametophyte is the visible, leafy part of the plant that we commonly recognize as the moss or liverwort. It is the phase that carries out photosynthesis and produces the sex organs.
During the gametophyte phase, the moss or liverwort produces archegonia and antheridia. The archegonia are female sex organs that produce eggs, while the antheridia are male sex organs that produce sperm. The sperm requires water for fertilization to occur because they swim to the eggs through a film of water.
After fertilization, the zygote is formed, which develops into the sporophyte phase.
**Sporophyte Phase:**
The sporophyte phase is the diploid (having two sets of chromosomes) and spore-producing phase in the bryophyte life cycle. It is dependent on the gametophyte phase for nutrition and support.
The sporophyte phase develops from the fertilized zygote and remains attached to the gametophyte. It is a small, non-photosynthetic structure that consists of a foot, seta, and capsule. The foot is embedded in the gametophyte and absorbs nutrients. The seta is the stalk-like structure that elevates the capsule. The capsule contains sporogenous tissue, which undergoes meiosis to produce haploid spores.
When the spores are mature, the sporophyte releases them into the environment. These spores are dispersed by wind or water and, upon landing in a suitable environment, germinate to form new gametophytes. The spores give rise to protonemata, which are thread-like structures that develop into new gametophytes.
**Conclusion:**
In conclusion, the gametophyte phase is the prominent phase in the life cycle of bryophytes. It is the leafy, haploid phase that carries out photosynthesis and produces the sex organs. The sporophyte phase, although important for spore production, remains dependent on the gametophyte phase for nutrition and support.
A particle has an initial velocity 3 iˆ +4 jˆ and an acceleration 0.4 iˆ + 0.3 jˆ .Its speed after 10 s is- a)7 units
- b)8.5 units
- c)7√2 units
- d)10 units
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle has an initial velocity 3 iˆ +4 jˆ and an acceleration 0.4 iˆ + 0.3 jˆ .Its speed after 10 s is
a)
7 units
b)
8.5 units
c)
7√2 units
d)
10 units
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
Answer is C) 7 x (2)^1/2
Solution:
The initial velocity is given by
u = v - at
Where, v = Final Velocity, t = time taken, and a = acceleration
u = 3 i + 4 j
a = 0.4 i + 0.3 j
t = 10 s
Using initial velocity formula
3 i + 4 j = v - (0.4 i + 0.3 j) 10
v = 7 ( i + j)
Velocity is the vector quantity which is defined by both magnitude and direction but speed is scalar quantity which is defined by only magnitude.
The magnitude of v = (7^2+7^2)^1/2 = 7 x (2)^1/2
Direction (Q. Nos. 12-13) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given ptions (a),(b),(c),(d)Radius of Bohr’s orbit of H-atom is 52.9 pm. An emission in H-atom starts from the orbit having radius 1.3225 nm and ends at 211.6 pm.Q. Wavelength (in nm) associated with this emission is- a)434.17nm
- b)230.20 nm
- c)144.70nm
- d)289.40 nm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 12-13) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given ptions (a),(b),(c),(d)
Radius of Bohr’s orbit of H-atom is 52.9 pm. An emission in H-atom starts from the orbit having radius 1.3225 nm and ends at 211.6 pm.
Q.
Wavelength (in nm) associated with this emission is
a)
434.17nm
b)
230.20 nm
c)
144.70nm
d)
289.40 nm
|
|
Satakshi Kumari answered |

Read the given statements and select the correct options.
Statement 1: Bryophytes play a significant role in plant succession on bare rocks and soil.
Statement 2: They contribute to the breakdown of rocks and enrich the soil, making it more suitable for higher plants.
- a)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement is the correct explanation of statement 1.
- b)Both statement 1 and 2 are correct but statement is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
- c)Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
- d)Both statement 1 and 2 are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct options.
Statement 1: Bryophytes play a significant role in plant succession on bare rocks and soil.
Statement 2: They contribute to the breakdown of rocks and enrich the soil, making it more suitable for higher plants.
a)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement is the correct explanation of statement 1.
b)
Both statement 1 and 2 are correct but statement is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
c)
Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
d)
Both statement 1 and 2 are incorrect.
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Bryophytes are known as 'amphibians of plane kingdom' because they are adapted to land as well as water habitats. In their vegetative structure, bryophytes, have become adapted to land. But they depend on water for sexual reproduction because the swimming habit is retained by their sperms.
Ionisation energy of He+ is 19.6x10-18 J atom -1. The energy of the first stationary state (n = 1)of Li2+ is- a)4.41 x 10-16 J atom-1
- b)-4 .41 x 10-17 J atom-1
- c)-2.20 x 10 -15J atom-1
- d)8. 82 x 10-17J atom-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Ionisation energy of He+ is 19.6x10-18 J atom -1. The energy of the first stationary state (n = 1)of Li2+ is
a)
4.41 x 10-16 J atom-1
b)
-4 .41 x 10-17 J atom-1
c)
-2.20 x 10 -15J atom-1
d)
8. 82 x 10-17J atom-1
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Ionisation energy = - Energy of the electron
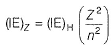
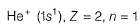
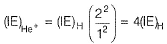
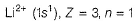
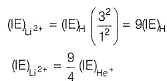
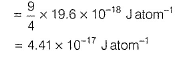

In Lyman series, shortest wavelength of H-atom appears at x m, then longest wavelength in Balmer series of He+ appear at- a)
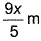
- b)
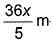
- c)
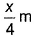
- d)
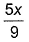
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In Lyman series, shortest wavelength of H-atom appears at x m, then longest wavelength in Balmer series of He+ appear at
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
For the spectral line in H -atom and H -like species (one electron)
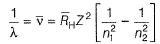
For Lyman series
For shortest wavelength (maximum wave number) n2 → ∞
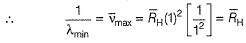

For longest wave length (minimum wave number), n2 = (n1, + 1).
For Balmer series, n1 = 2
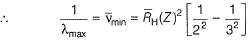
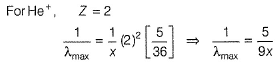
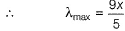
For Lyman series
For shortest wavelength (maximum wave number) n2 → ∞
For longest wave length (minimum wave number), n2 = (n1, + 1).
For Balmer series, n1 = 2
Question:
Read the following statements about the life cycle of a moss and identify the number of incorrect statements: - The predominant stage of the life cycle of a moss is the gametophyte.
- The protonema stage is the second stage of the gametophyte, which develops from the leafy stage.
- The leafy stage develops from the secondary protonema as a lateral bud.
- The leafy stage is attached to the soil through multicellular and branched rhizoids.
How many of the above statements are incorrect?
- a)One
- b)Two
- c)Three
- d)Four
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question:
Read the following statements about the life cycle of a moss and identify the number of incorrect statements:
Read the following statements about the life cycle of a moss and identify the number of incorrect statements:
- The predominant stage of the life cycle of a moss is the gametophyte.
- The protonema stage is the second stage of the gametophyte, which develops from the leafy stage.
- The leafy stage develops from the secondary protonema as a lateral bud.
- The leafy stage is attached to the soil through multicellular and branched rhizoids.
How many of the above statements are incorrect?
a)
One
b)
Two
c)
Three
d)
Four
|
|
Prasenjit Ghosh answered |
Incorrect Statements in the Life Cycle of a Moss:
1. The protonema stage is the second stage of the gametophyte, which develops from the leafy stage.
- This statement is incorrect. The protonema stage is actually the first stage of the gametophyte, not the second stage. It develops from the germinated spore and eventually gives rise to the leafy stage.
2. The leafy stage develops from the secondary protonema as a lateral bud.
- This statement is incorrect. The leafy stage actually develops from the primary protonema, not the secondary protonema. It emerges from the protonema as a lateral bud, eventually forming the leafy structure of the moss plant.
3. The leafy stage is attached to the soil through multicellular and branched rhizoids.
- This statement is correct. The leafy stage of a moss is indeed attached to the soil through multicellular and branched rhizoids, which help anchor the plant and absorb water and nutrients from the environment.
Therefore, there are two incorrect statements in the given list regarding the life cycle of a moss.
1. The protonema stage is the second stage of the gametophyte, which develops from the leafy stage.
- This statement is incorrect. The protonema stage is actually the first stage of the gametophyte, not the second stage. It develops from the germinated spore and eventually gives rise to the leafy stage.
2. The leafy stage develops from the secondary protonema as a lateral bud.
- This statement is incorrect. The leafy stage actually develops from the primary protonema, not the secondary protonema. It emerges from the protonema as a lateral bud, eventually forming the leafy structure of the moss plant.
3. The leafy stage is attached to the soil through multicellular and branched rhizoids.
- This statement is correct. The leafy stage of a moss is indeed attached to the soil through multicellular and branched rhizoids, which help anchor the plant and absorb water and nutrients from the environment.
Therefore, there are two incorrect statements in the given list regarding the life cycle of a moss.
The embryonic development in bryophytes takes place in the- a)protonema
- b)sporangium
- c)antheridium
- d)archegonium
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The embryonic development in bryophytes takes place in the
a)
protonema
b)
sporangium
c)
antheridium
d)
archegonium
|
|
Gayatri Basu answered |
Embryonic development in bryophytes takes place in the archegonium.
The archegonium is a multicellular structure found in bryophytes, which are a group of non-vascular plants including mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. It is the female reproductive organ and is responsible for the production and protection of the female gametes, or eggs.
Embryonic development in bryophytes refers to the process by which a zygote, formed by the fusion of a sperm and an egg, develops into a mature sporophyte. This process occurs within the archegonium.
Here is a detailed explanation of the embryonic development in bryophytes:
1. Fertilization: In bryophytes, the male gametes, or sperm, are produced in antheridia, which are male reproductive organs. The sperm are released into the environment and need water to swim to the archegonium. Once the sperm reaches the archegonium, it fertilizes the egg, resulting in the formation of a zygote.
2. Zygote Development: After fertilization, the zygote starts to develop within the archegonium. The archegonium provides a protective environment for the developing embryo. It nourishes the embryo and provides it with the necessary nutrients for growth.
3. Embryo Formation: As the zygote develops, it undergoes cell divisions and differentiation. The archegonium nurtures the developing embryo by supplying it with nutrients and water. The embryo grows within the archegonium and gradually develops into a multicellular structure known as a sporophyte.
4. Sporophyte Maturation: The sporophyte continues to grow within the archegonium until it becomes mature. The mature sporophyte consists of a stalk-like structure called a seta and a capsule, or sporangium, at the top. The sporangium contains spores, which are reproductive cells that can grow into new gametophytes.
5. Spore Release: When the sporophyte is mature, the sporangium releases spores into the environment. These spores are dispersed by wind or water and can germinate to form new gametophytes, starting the cycle again.
In summary, the embryonic development in bryophytes takes place in the archegonium. The archegonium provides a protected environment for the growth and development of the zygote into a mature sporophyte. This process is essential for the reproduction and survival of bryophytes.
The archegonium is a multicellular structure found in bryophytes, which are a group of non-vascular plants including mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. It is the female reproductive organ and is responsible for the production and protection of the female gametes, or eggs.
Embryonic development in bryophytes refers to the process by which a zygote, formed by the fusion of a sperm and an egg, develops into a mature sporophyte. This process occurs within the archegonium.
Here is a detailed explanation of the embryonic development in bryophytes:
1. Fertilization: In bryophytes, the male gametes, or sperm, are produced in antheridia, which are male reproductive organs. The sperm are released into the environment and need water to swim to the archegonium. Once the sperm reaches the archegonium, it fertilizes the egg, resulting in the formation of a zygote.
2. Zygote Development: After fertilization, the zygote starts to develop within the archegonium. The archegonium provides a protective environment for the developing embryo. It nourishes the embryo and provides it with the necessary nutrients for growth.
3. Embryo Formation: As the zygote develops, it undergoes cell divisions and differentiation. The archegonium nurtures the developing embryo by supplying it with nutrients and water. The embryo grows within the archegonium and gradually develops into a multicellular structure known as a sporophyte.
4. Sporophyte Maturation: The sporophyte continues to grow within the archegonium until it becomes mature. The mature sporophyte consists of a stalk-like structure called a seta and a capsule, or sporangium, at the top. The sporangium contains spores, which are reproductive cells that can grow into new gametophytes.
5. Spore Release: When the sporophyte is mature, the sporangium releases spores into the environment. These spores are dispersed by wind or water and can germinate to form new gametophytes, starting the cycle again.
In summary, the embryonic development in bryophytes takes place in the archegonium. The archegonium provides a protected environment for the growth and development of the zygote into a mature sporophyte. This process is essential for the reproduction and survival of bryophytes.
Read the following statements and select the incorrect ones:(a) Mosses have an elaborate mechanism of spore dispersal.
(b) In liverworts, the haploid free-living sporophyte is formed by spore germination.
(c) Vegetative reproduction in Polytrichum occurs by budding in the secondary protonema.
(d) Marchantia is a heterosporous bryophyte.
(e) Growth of bog moss ultimately fills ponds and lakes with soil
- a)(a), (b) and (c)
- b)(d) and (e) only
- c)(b) and (d) only
- d)All except (a)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements and select the incorrect ones:
(a) Mosses have an elaborate mechanism of spore dispersal.
(b) In liverworts, the haploid free-living sporophyte is formed by spore germination.
(c) Vegetative reproduction in Polytrichum occurs by budding in the secondary protonema.
(d) Marchantia is a heterosporous bryophyte.
(e) Growth of bog moss ultimately fills ponds and lakes with soil
(b) In liverworts, the haploid free-living sporophyte is formed by spore germination.
(c) Vegetative reproduction in Polytrichum occurs by budding in the secondary protonema.
(d) Marchantia is a heterosporous bryophyte.
(e) Growth of bog moss ultimately fills ponds and lakes with soil
a)
(a), (b) and (c)
b)
(d) and (e) only
c)
(b) and (d) only
d)
All except (a)

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Correct answer: 3. (b) and (d) only
Explanation:
- Statement (b) is incorrect because liverworts have a haploid gametophyte and a diploid sporophyte. The sporophyte is not free-living and does not form by spore germination.
- Statement (d) is incorrect because Marchantia is not a heterosporous bryophyte; it is a homosporous liverwort.
- Statement (a) is correct; mosses do have an elaborate mechanism of spore dispersal.
- Statement (c) is correct; vegetative reproduction in Polytrichum occurs by budding in the secondary protonema.
- Statement (e) is correct; bog moss growth can contribute to the formation of peatlands by filling ponds and lakes with soil.
Peat, obtained from Sphagnum moss, is used as- a)fuel
- b)manure
- c)corrosive
- d)both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Peat, obtained from Sphagnum moss, is used as
a)
fuel
b)
manure
c)
corrosive
d)
both (a) and (b)
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Peat consists of deposits of vegetable matter which have accumulated in bogs and swamps and slowly decomposed, becoming somewhat carbonised and compacted. It is dark brown in colour. Peat is built by Sphagnum moss, for this reason, Sphagnum is called peat moss. Peat is used as fuel and manure.
Consider the following statements regarding bryophytes:I. Bryophytes are also called amphibians of the plant kingdom because they are dependent on water for sexual reproduction.II. They play an important role in plant succession on bare rocks.III. They lack true roots, stem or leaves.IV. The sex organs in bryophytes are multicelluar.V. They produce biflagellate zoospres.VI. Archegonium is flask-shaped and produces a single egg.The number of corrected statements is- a)3
- b)4
- c)5
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements regarding bryophytes:
I. Bryophytes are also called amphibians of the plant kingdom because they are dependent on water for sexual reproduction.
II. They play an important role in plant succession on bare rocks.
III. They lack true roots, stem or leaves.
IV. The sex organs in bryophytes are multicelluar.
V. They produce biflagellate zoospres.
VI. Archegonium is flask-shaped and produces a single egg.
The number of corrected statements is
a)
3
b)
4
c)
5
d)
6
|
|
Nandita Rane answered |
Corrected Statements:
I. Bryophytes are also called amphibians of the plant kingdom because they are dependent on water for sexual reproduction.
- This statement is correct. Bryophytes, like amphibians, require water for the fertilization of their gametes.
II. They play an important role in plant succession on bare rocks.
- This statement is correct. Bryophytes are pioneer plants that colonize bare rocks and help in soil formation, paving the way for other plant species.
III. They lack true roots, stem or leaves.
- This statement is correct. Bryophytes lack true vascular tissues and have simple structures that function in a manner similar to roots, stems, and leaves.
IV. The sex organs in bryophytes are multicellular.
- This statement is correct. Bryophytes have multicellular sex organs called archegonia and antheridia.
V. They produce biflagellate zoospores.
- This statement is incorrect. Bryophytes produce haploid spores, not zoospores.
VI. Archegonium is flask-shaped and produces a single egg.
- This statement is correct. The archegonium in bryophytes is flask-shaped and produces a single egg.
Therefore, out of the given statements, 5 are correct.
I. Bryophytes are also called amphibians of the plant kingdom because they are dependent on water for sexual reproduction.
- This statement is correct. Bryophytes, like amphibians, require water for the fertilization of their gametes.
II. They play an important role in plant succession on bare rocks.
- This statement is correct. Bryophytes are pioneer plants that colonize bare rocks and help in soil formation, paving the way for other plant species.
III. They lack true roots, stem or leaves.
- This statement is correct. Bryophytes lack true vascular tissues and have simple structures that function in a manner similar to roots, stems, and leaves.
IV. The sex organs in bryophytes are multicellular.
- This statement is correct. Bryophytes have multicellular sex organs called archegonia and antheridia.
V. They produce biflagellate zoospores.
- This statement is incorrect. Bryophytes produce haploid spores, not zoospores.
VI. Archegonium is flask-shaped and produces a single egg.
- This statement is correct. The archegonium in bryophytes is flask-shaped and produces a single egg.
Therefore, out of the given statements, 5 are correct.
‘Hartree’ is the atomic unit of energy and is equal to- a)-13 .6 eV atom-1
- b)-27.2 eV atom -1
- c)+13.6 eV atom -1
- d)+27.2 eV atom-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
‘Hartree’ is the atomic unit of energy and is equal to
a)
-13 .6 eV atom-1
b)
-27.2 eV atom -1
c)
+13.6 eV atom -1
d)
+27.2 eV atom-1

|
Prasenjit Pillai answered |
The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr’s orbit in the H-atom is
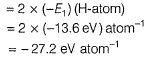
This energy is defined as an atomic unit of energy called HARTREE.
This energy is defined as an atomic unit of energy called HARTREE.
How do mosses primarily reproduce vegetatively?- a) By seeds
- b) By bulbs
- c) By fragmentation and budding
- d) By spores
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How do mosses primarily reproduce vegetatively?
a)
By seeds
b)
By bulbs
c)
By fragmentation and budding
d)
By spores
|
|
Sanaya Mishra answered |
Understanding Moss Reproduction
Mosses, as non-flowering plants, primarily reproduce through vegetative methods, specifically via fragmentation and budding. This allows them to spread and colonize new areas effectively.
Methods of Vegetative Reproduction
- Fragmentation:
- Mosses can break into smaller pieces, where each fragment can grow into a new individual. This process often occurs naturally when environmental conditions are favorable, or through physical disturbances.
- Budding:
- In some moss species, small outgrowths or buds can form on the parent plant. These buds eventually detach and develop into new moss plants. Budding is a form of asexual reproduction, allowing for rapid population increases.
Advantages of Vegetative Reproduction
- Rapid Colonization:
- Mosses can quickly occupy new habitats, as each fragment or bud can establish itself independently.
- Genetic Uniformity:
- Since the offspring are clones of the parent, they are well-adapted to the same environment. This can be beneficial in stable habitats.
Comparison with Other Methods
- Seeds:
- Mosses do not reproduce by seeds; they primarily use spores for sexual reproduction.
- Bulbs:
- Bulb formation is not a characteristic of mosses; it is more common in certain flowering plants.
In conclusion, the correct answer to how mosses primarily reproduce vegetatively is by fragmentation and budding, making option 'C' the right choice. This reproductive strategy plays a crucial role in the survival and distribution of mosses in various ecosystems.
Mosses, as non-flowering plants, primarily reproduce through vegetative methods, specifically via fragmentation and budding. This allows them to spread and colonize new areas effectively.
Methods of Vegetative Reproduction
- Fragmentation:
- Mosses can break into smaller pieces, where each fragment can grow into a new individual. This process often occurs naturally when environmental conditions are favorable, or through physical disturbances.
- Budding:
- In some moss species, small outgrowths or buds can form on the parent plant. These buds eventually detach and develop into new moss plants. Budding is a form of asexual reproduction, allowing for rapid population increases.
Advantages of Vegetative Reproduction
- Rapid Colonization:
- Mosses can quickly occupy new habitats, as each fragment or bud can establish itself independently.
- Genetic Uniformity:
- Since the offspring are clones of the parent, they are well-adapted to the same environment. This can be beneficial in stable habitats.
Comparison with Other Methods
- Seeds:
- Mosses do not reproduce by seeds; they primarily use spores for sexual reproduction.
- Bulbs:
- Bulb formation is not a characteristic of mosses; it is more common in certain flowering plants.
In conclusion, the correct answer to how mosses primarily reproduce vegetatively is by fragmentation and budding, making option 'C' the right choice. This reproductive strategy plays a crucial role in the survival and distribution of mosses in various ecosystems.
What is the predominant stage of the moss life cycle?- a) Sporophyte stage
- b) Protonema stage
- c) Gametophyte stage
- d) Leafy stage
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the predominant stage of the moss life cycle?
a)
Sporophyte stage
b)
Protonema stage
c)
Gametophyte stage
d)
Leafy stage

|
Infinity Academy answered |
In the life cycle of a moss, the predominant stage is the gametophyte stage. This stage consists of two main stages: the protonema stage and the leafy stage. The protonema stage is the first stage, developing directly from a spore, while the leafy stage develops from the secondary protonema as a lateral bud. The gametophyte stage bears the sex organs and is crucial for the reproductive cycle of mosses.
Read the given statements and select the correct options.
Statement 1: Each sperm of moss has two flagella.
Statement 2: Water is essential for fertilization is mosses.
- a)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement is the correct explanation of statement 1.
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
- c)Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
- d)Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct options.
Statement 1: Each sperm of moss has two flagella.
Statement 2: Water is essential for fertilization is mosses.
Statement 1: Each sperm of moss has two flagella.
Statement 2: Water is essential for fertilization is mosses.
a)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement is the correct explanation of statement 1.
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
c)
Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
d)
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
|
|
Mansi Gupta answered |
Statement 1: Each sperm of moss has two flagella.
Statement 2: Water is essential for fertilization in mosses.
Explanation:
The correct answer is option 'B' - Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
1. Importance of Water in Moss Fertilization:
- Mosses are non-vascular plants that reproduce through the process of fertilization.
- In order for fertilization to occur in mosses, water is essential.
- Mosses require a moist environment for the male and female gametes to come in contact with each other.
- The presence of water is necessary for the sperm to swim from the male reproductive structure (antheridium) to the female reproductive structure (archegonium) where fertilization takes place.
- Water acts as a medium for the movement of sperm and facilitates the union of gametes, leading to fertilization.
2. Flagella in Moss Sperm:
- Mosses are unique in that they have swimming sperm, unlike most other plants where fertilization occurs through passive pollen transfer.
- The sperm of mosses are flagellated, meaning they possess whip-like structures called flagella that enable them to move in a liquid environment.
- Each sperm of moss possesses two flagella, which provide the necessary motility for the sperm to swim through the water to reach the egg for fertilization.
- The flagella help the sperm to navigate in the water towards the female reproductive structure and increase the chances of successful fertilization.
Explanation of the Correct Answer (Option B):
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct, as moss sperm do have two flagella and water is indeed essential for fertilization in mosses. However, statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
Statement 1 simply states a fact about moss sperm having two flagella, whereas statement 2 provides the reason behind the requirement of water for fertilization in mosses. The two statements are related but not interdependent on each other.
Statement 2: Water is essential for fertilization in mosses.
Explanation:
The correct answer is option 'B' - Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
1. Importance of Water in Moss Fertilization:
- Mosses are non-vascular plants that reproduce through the process of fertilization.
- In order for fertilization to occur in mosses, water is essential.
- Mosses require a moist environment for the male and female gametes to come in contact with each other.
- The presence of water is necessary for the sperm to swim from the male reproductive structure (antheridium) to the female reproductive structure (archegonium) where fertilization takes place.
- Water acts as a medium for the movement of sperm and facilitates the union of gametes, leading to fertilization.
2. Flagella in Moss Sperm:
- Mosses are unique in that they have swimming sperm, unlike most other plants where fertilization occurs through passive pollen transfer.
- The sperm of mosses are flagellated, meaning they possess whip-like structures called flagella that enable them to move in a liquid environment.
- Each sperm of moss possesses two flagella, which provide the necessary motility for the sperm to swim through the water to reach the egg for fertilization.
- The flagella help the sperm to navigate in the water towards the female reproductive structure and increase the chances of successful fertilization.
Explanation of the Correct Answer (Option B):
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct, as moss sperm do have two flagella and water is indeed essential for fertilization in mosses. However, statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
Statement 1 simply states a fact about moss sperm having two flagella, whereas statement 2 provides the reason behind the requirement of water for fertilization in mosses. The two statements are related but not interdependent on each other.
Question: Identify the incorrect statement regarding liverworts- a)Liverworts typically grow in moist, shady habitats such as the banks of streams, marshy ground, and damp soil.
- b)The plant body of a liverwort is thalloid and dorsiventral, as seen in Marchantia.
- c)Asexual reproduction in liverworts occurs through the fragmentation of thalli or the formation of gemmae.
- d)The sporophyte in liverworts is differentiated into a foot, seta, and rhizoid.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question: Identify the incorrect statement regarding liverworts
a)
Liverworts typically grow in moist, shady habitats such as the banks of streams, marshy ground, and damp soil.
b)
The plant body of a liverwort is thalloid and dorsiventral, as seen in Marchantia.
c)
Asexual reproduction in liverworts occurs through the fragmentation of thalli or the formation of gemmae.
d)
The sporophyte in liverworts is differentiated into a foot, seta, and rhizoid.
|
|
Sounak Saini answered |
Incorrect Statement Analysis
The correct answer is option 'D', which states: "The sporophyte in liverworts is differentiated into a foot, seta, and rhizoid." This statement is incorrect due to the following reasons:
Structure of Liverwort Sporophyte
- Unlike true mosses and higher plants, the sporophyte of liverworts is not well-differentiated.
- In liverworts, particularly in the thalloid forms like Marchantia, the sporophyte consists mainly of a foot that anchors it to the gametophyte and a capsule where spores are produced.
- There is no seta (stalk) present as seen in more advanced plants.
Comparison with Other Bryophytes
- In contrast, in mosses, the sporophyte is clearly differentiated into a foot, seta, and capsule.
- The absence of a seta in liverworts signifies their simpler structure compared to other bryophytes.
Summary of Liverwort Characteristics
- Habitat: Liverworts thrive in moist, shady environments such as stream banks and damp soils.
- Plant Body: The plant body is typically thalloid and dorsiventral, as observed in Marchantia.
- Asexual Reproduction: Asexual reproduction occurs through fragmentation and the formation of gemmae, which are specialized structures for asexual propagation.
In conclusion, option 'D' is incorrect because liverworts do not possess a differentiated sporophyte structure akin to that of mosses, making it clear that their sporophyte is simpler and lacks a seta.
The correct answer is option 'D', which states: "The sporophyte in liverworts is differentiated into a foot, seta, and rhizoid." This statement is incorrect due to the following reasons:
Structure of Liverwort Sporophyte
- Unlike true mosses and higher plants, the sporophyte of liverworts is not well-differentiated.
- In liverworts, particularly in the thalloid forms like Marchantia, the sporophyte consists mainly of a foot that anchors it to the gametophyte and a capsule where spores are produced.
- There is no seta (stalk) present as seen in more advanced plants.
Comparison with Other Bryophytes
- In contrast, in mosses, the sporophyte is clearly differentiated into a foot, seta, and capsule.
- The absence of a seta in liverworts signifies their simpler structure compared to other bryophytes.
Summary of Liverwort Characteristics
- Habitat: Liverworts thrive in moist, shady environments such as stream banks and damp soils.
- Plant Body: The plant body is typically thalloid and dorsiventral, as observed in Marchantia.
- Asexual Reproduction: Asexual reproduction occurs through fragmentation and the formation of gemmae, which are specialized structures for asexual propagation.
In conclusion, option 'D' is incorrect because liverworts do not possess a differentiated sporophyte structure akin to that of mosses, making it clear that their sporophyte is simpler and lacks a seta.
Read the following statements about liverworts and identify the number of incorrect statements: - The plant body of liverworts is leafy with tiny leaf-like appendages arranged in three rows on the stem-like structures.
- Liverworts are typically found growing on bark of trees and deep in the woods.
- Gemmae are green, multicellular, asexual buds that develop in gemma cups located on the thalli.
- During sexual reproduction, male and female sex organs are produced only on different thalli in liverworts.
How many of the above statements are incorrect?- a)None
- b)One
- c)Two
- d)Three
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements about liverworts and identify the number of incorrect statements:
- The plant body of liverworts is leafy with tiny leaf-like appendages arranged in three rows on the stem-like structures.
- Liverworts are typically found growing on bark of trees and deep in the woods.
- Gemmae are green, multicellular, asexual buds that develop in gemma cups located on the thalli.
- During sexual reproduction, male and female sex organs are produced only on different thalli in liverworts.
How many of the above statements are incorrect?
a)
None
b)
One
c)
Two
d)
Three

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Correct answer: Two
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect because the tiny leaf-like appendages are arranged in two rows, not three.
- Statement 4 is incorrect because male and female sex organs can be produced either on the same or on different thalli in liverworts.
Radius of Bohr’s orbit of H-atom is 52.9 pm. An emission in H-atom starts from the orbit having radius 1.3225 nm and ends at 211.6 pm.Q.
Spectral line appears in .......... region.- a)UV
- b)Visible
- c)near IR
- d)far IR
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Radius of Bohr’s orbit of H-atom is 52.9 pm. An emission in H-atom starts from the orbit having radius 1.3225 nm and ends at 211.6 pm.
Q.
Spectral line appears in .......... region.
Spectral line appears in .......... region.
a)
UV
b)
Visible
c)
near IR
d)
far IR

|
Ishaan Menon answered |
Emission (n2 = 5 to n1 = 2) is called Balmer series and appears in visible region.
Energy of the electron in nth orbit is given by E 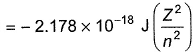 Wavelength of light required to excite an electron in an H-atom from level n = 1 to n = 2 will be (h = 6.62 x 10-34 J s ; c = 3.0 x 108ms -1)[AIEEE 2012]
Wavelength of light required to excite an electron in an H-atom from level n = 1 to n = 2 will be (h = 6.62 x 10-34 J s ; c = 3.0 x 108ms -1)[AIEEE 2012]- a)1.216x 10-7 m
- b)2.816x 10-7 m
- c)6.500x 10-7 m
- d)8.500x 10-7 m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Energy of the electron in nth orbit is given by E 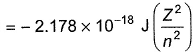 Wavelength of light required to excite an electron in an H-atom from level n = 1 to n = 2 will be (h = 6.62 x 10-34 J s ; c = 3.0 x 108ms -1)
Wavelength of light required to excite an electron in an H-atom from level n = 1 to n = 2 will be (h = 6.62 x 10-34 J s ; c = 3.0 x 108ms -1)
[AIEEE 2012]
a)
1.216x 10-7 m
b)
2.816x 10-7 m
c)
6.500x 10-7 m
d)
8.500x 10-7 m
|
|
Jyoti Aiims Aspirant answered |
An electron in H-atom in its ground state absorbs 1.5 times as much as energy as the minimum required for its escape from the atom Q. Thus, kinetic energy given to the emitted electron is
Q. Thus, kinetic energy given to the emitted electron is- a)20.4 eV
- b)34.0 eV
- c)-20.4 eV
- d)-34.0 eV
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An electron in H-atom in its ground state absorbs 1.5 times as much as energy as the minimum required for its escape from the atom
Q. Thus, kinetic energy given to the emitted electron is
a)
20.4 eV
b)
34.0 eV
c)
-20.4 eV
d)
-34.0 eV

|
Krish Saha answered |
E1 = Energy of H-atom in the ground state = 13.6 eV
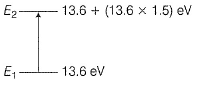
Energy absorbed = (13.6 x 1.5) = 20.4 eV
E2 = Energy of the excited state
= 13.6+ 20.4= 34.0 eV
ΔE = KE = (E2 - E1)
= 34.0 - 13.6 = 20.4 eV
Energy absorbed = (13.6 x 1.5) = 20.4 eV
E2 = Energy of the excited state
= 13.6+ 20.4= 34.0 eV
ΔE = KE = (E2 - E1)
= 34.0 - 13.6 = 20.4 eV
The kinetic energy of an electron in the second Bohr orbit of a hydrogen atom is (a0 is Bohr radius)[AIEEE 2012]- a)
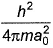
- b)
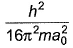
- c)
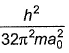
- d)
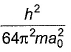
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The kinetic energy of an electron in the second Bohr orbit of a hydrogen atom is (a0 is Bohr radius)
[AIEEE 2012]
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
The kinetic energy of an electron in the second Bohr orbit of s H atom is [a0 is Bohr radius],


Select the option that correctly identifies A, B and C in the given figure of female thallus of Marchantia.
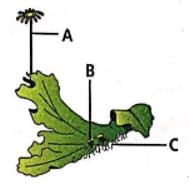
- a)A-Antheridiophore, B-Gemma cup, C-Rhizoids
- b)A-Antheridiophore, B-Rhizoids, C-Gemma cup
- c)A - Archegoniophore, B-Gemma cup, C-Rhizoids
- d)A - Archegoniophore, B-Rhizoids, C-Gemma cup
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the option that correctly identifies A, B and C in the given figure of female thallus of Marchantia.


a)
A-Antheridiophore, B-Gemma cup, C-Rhizoids
b)
A-Antheridiophore, B-Rhizoids, C-Gemma cup
c)
A - Archegoniophore, B-Gemma cup, C-Rhizoids
d)
A - Archegoniophore, B-Rhizoids, C-Gemma cup
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Sexually Marchantia is dioecious with sex organic borne on stalked upright receptacles or gametophoers. Gametophore of male thallus is called Antheridiophce having a stalk and a 8 lobed male receptacle. Gametophce of female thallus is called archegoniphore. Its receptacle has nine cylindrical processes or rays.
Direction (Q. Nos. 14 and 15) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.Q. Match the equation in Column I with the name type in Column II.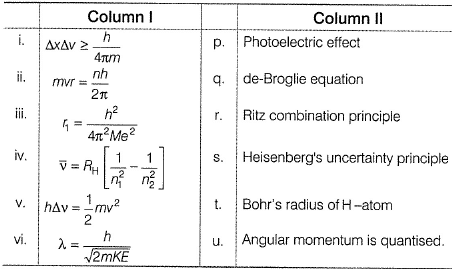
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 14 and 15) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q. Match the equation in Column I with the name type in Column II.
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Ashwini Khanna answered |
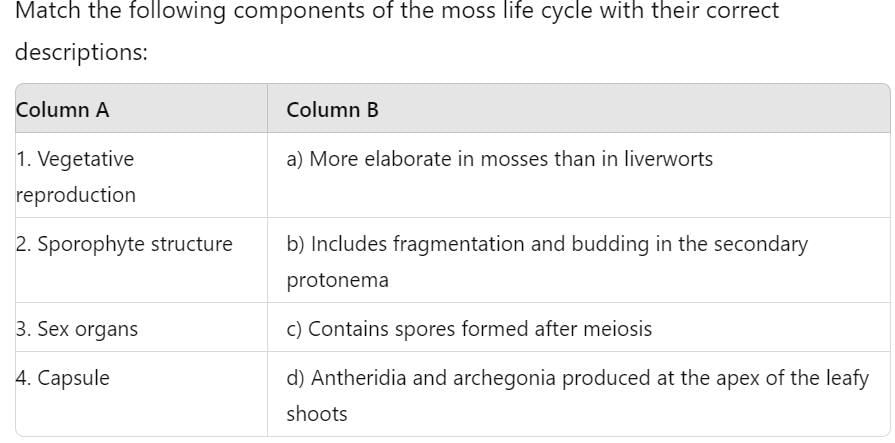
- a)1-b, 2-d, 3-c, 4-a
- b)1-c, 2-a, 3-b, 4-d
- c)1-a, 2-b, 3-d, 4-c
- d)1-b, 2-a, 3-d, 4-c
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

a)
1-b, 2-d, 3-c, 4-a
b)
1-c, 2-a, 3-b, 4-d
c)
1-a, 2-b, 3-d, 4-c
d)
1-b, 2-a, 3-d, 4-c

|
Lead Academy answered |
Correct Matching:
- Vegetative reproduction - b) Includes fragmentation and budding in the secondary protonema
- Sporophyte structure - a) More elaborate in mosses than in liverworts
- Sex organs - d) Antheridia and archegonia produced at the apex of the leafy shoots
- Capsule - c) Contains spores formed after meiosis
Explanation:
- Vegetative reproduction in mosses occurs by fragmentation and budding in the secondary protonema.
- The sporophyte in mosses is more complex compared to liverworts, consisting of a foot, seta, and capsule.
- Sex organs (antheridia and archegonia) are located at the apex of the leafy shoots.
- The capsule of the sporophyte contains spores, which are released through an elaborate dispersal mechanism.
A particle is projected with a velocity v so that its range on a horizontal plane is twice the greatest height attained If g is acceleration due to gravity, then its range is- a)
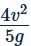
- b)

- c)
- d)
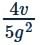
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle is projected with a velocity v so that its range on a horizontal plane is twice the greatest height attained If g is acceleration due to gravity, then its range is
a)
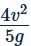
b)

c)
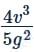
d)
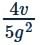

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Let the range be R and the maximum height be H. Given that R = 2H.
Range formula: R = (v2 sin 2θ) / g
Maximum height formula: H = (v2 sin2 θ) / (2g)
Given:
R = 2H
=> (v2 sin 2θ) / g = 2 × (v2 sin2 θ) / (2g)
=> sin 2θ = sin2 θ
Using sin 2θ = 2 sin θ cos θ, we get:
2 sin θ cos θ = sin2 θ
=> 2 cos θ = sin θ
=> tan θ = 2
Substitute tan θ = 2 to find sin 2θ:
sin 2θ = 2 sin θ cos θ
Using tan θ = 2, let sin θ = 2k and cos θ = k for some k.
Since sin2 θ + cos2 θ = 1:
(2k)2 + k2 = 1
4k2 + k2 = 1
5k2 = 1
k = 1/√5
So sin θ = 2/√5, cos θ = 1/√5.
sin 2θ = 2 × (2/√5) × (1/√5) = 4/5.
Therefore, range R = (v2 × 4/5) / g = 4v2 / 5g.
Chapter doubts & questions for May Week 3 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of May Week 3 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup