All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of June Week 2 for NEET Exam
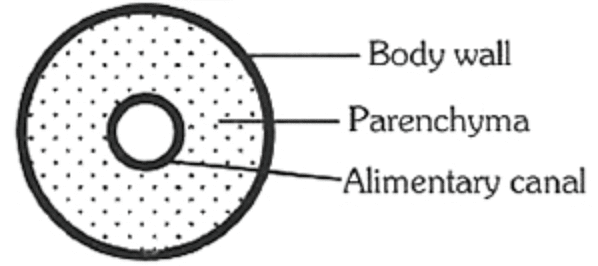
The cross-section of the body of an invertebrate is given below. Identify the animal which has this body plan.
- a)Cockroach
- b)Earthworm
- c)Roundworm
- d)Planaria
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The cross-section of the body of an invertebrate is given below. Identify the animal which has this body plan.

a)
Cockroach
b)
Earthworm
c)
Roundworm
d)
Planaria

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- It has three-layered body wall which includes ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm.
- Acoelomates lack a body cavity, and instead the space between the body wall and the digestive tract is filled with muscle fibres and loose tissue called parenchyma.
- It acts as a skeletal support, nutrient storage, motility, reserves of regenerative cells and transporting materials.
- Planaria belongs to phylum Platyhelminthes.
- These are flatworms and has acoelomate body plan.
Hence, the correct option is D.
NCERT Reference: Topic Phylum – Platyhelminthes” of chapter Animal Kingdom
Which phylum is a coelom and triploblastic animals?- a)Phylum Ctenophora
- b)Phylum Annelida
- c)Phylum Coelenterata
- d)Phylum Porifera
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which phylum is a coelom and triploblastic animals?
a)
Phylum Ctenophora
b)
Phylum Annelida
c)
Phylum Coelenterata
d)
Phylum Porifera
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Annelida are aquatic (marine and freshwater) or terrestrial, free-living, and sometimes parasitic. They are bilateral symmetric and triploblastic.
Assertion (A): Nematodes are pseudocoelomates.
Reason (R): Pseudocoelomates have a body cavity that is not fully lined with mesoderm.
- a) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- b)A is true, but R is false.
- c)A is false, but R is true.
- d)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Nematodes are pseudocoelomates.
Reason (R): Pseudocoelomates have a body cavity that is not fully lined with mesoderm.
Reason (R): Pseudocoelomates have a body cavity that is not fully lined with mesoderm.
a)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
b)
A is true, but R is false.
c)
A is false, but R is true.
d)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Nematodes, or roundworms, are indeed classified as pseudocoelomates because they possess a body cavity, known as a pseudocoel, which is not completely lined by tissue derived from mesoderm.
Which among the following is a gregarious pest?- a)Locusta
- b)Apis
- c)Laccifer
- d)Bombyx
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is a gregarious pest?
a)
Locusta
b)
Apis
c)
Laccifer
d)
Bombyx
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Locust (Locusta) is a gregarious pest belonging to phylum Arthropoda.

Fig: Image of Locust
A reptile having four chambered heart isa)Snakeb)Salamanderc)Crocodiled)LizardsCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Prakhar Maheshwari answered |
Except for crocodilians, which have a four-chambered heart, all reptiles have a three-chambered heart consisting of two atria and one ventricle.
What is the main excretory organ in insects?- a)Proboscis gland
- b)Malphighian tubules
- c)Gills
- d)Excretory pore
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the main excretory organ in insects?
a)
Proboscis gland
b)
Malphighian tubules
c)
Gills
d)
Excretory pore
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Malpighian tubule
The Malpighian tubule system is a type of excretory and osmoregulatory system found in some insects, myriapods, arachnids, and tardigrades. The system consists of branching tubules extending from the alimentary canal that absorbs solutes, water, and wastes from the surrounding hemolymph.
How is inertia used when riding a bicycle?- a)Bicycles don’t use inertia.
- b)You can stop paddling and still continue rolling forward.
- c)You must paddle harder when going up hill.
- d)You must paddle slower when going up hill.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How is inertia used when riding a bicycle?
a)
Bicycles don’t use inertia.
b)
You can stop paddling and still continue rolling forward.
c)
You must paddle harder when going up hill.
d)
You must paddle slower when going up hill.
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Due to inertia, even if we stop paddling of motion, we will continue to move forward up to a certain distance as friction will finally make us stop.
Which among the following is oviparous?- a)Platypus
- b)Flying fox
- c)Common dolphin
- d)lephant
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is oviparous?
a)
Platypus
b)
Flying fox
c)
Common dolphin
d)
lephant
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Platypus is oviparous as it is an egg-laying mammal
Rest three are viviparous mammals.
Species going to extinct due to low reproductive rate is- a)Island sps
- b)Bald eagle
- c)Lion
- d)Giant panda
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Species going to extinct due to low reproductive rate is
a)
Island sps
b)
Bald eagle
c)
Lion
d)
Giant panda

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
Giant panda is going to extinct due to low reproductively rate. They live in mountain ranges in central china. There reproductively rate is varyless due to climatic conditions.
Two masses are in the ratio 1:5. What is ratio of their inertia?- a)1:5
- b)5:1
- c)1:25
- d)25:1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two masses are in the ratio 1:5. What is ratio of their inertia?
a)
1:5
b)
5:1
c)
1:25
d)
25:1
|
|
Sagar Goyal answered |
Force of inertia = ma
Let the masses be 1x and 5x
Force of inertia for 1st body= 1x * a
Force of inertia for 2nd = 5x * a
Ratio= x * a / 5x * a = 1:5
Which one of the following group of animals is correctly matched with its characteristics without any exception?- a)Reptila possess 3-chambered heart with incompletely divided ventricle
- b)Mammalia give birth to young ones
- c)Chordates possess a mouth with an upper and lower jaw
- d)Chondrichthyes possess cartilaginous endoskeleton
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following group of animals is correctly matched with its characteristics without any exception?
a)
Reptila possess 3-chambered heart with incompletely divided ventricle
b)
Mammalia give birth to young ones
c)
Chordates possess a mouth with an upper and lower jaw
d)
Chondrichthyes possess cartilaginous endoskeleton
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
The members of the class - Chondrichthyes are marine animals with a streamlined body and have a cartilaginous endoskeleton.
Which law is in control of a spacecraft that cruises through space at a constant speed without using any fuel?- a)Universal law of gravitation
- b)Newton’s third law
- c)Newton’s second law
- d)Newton’s first law
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which law is in control of a spacecraft that cruises through space at a constant speed without using any fuel?
a)
Universal law of gravitation
b)
Newton’s third law
c)
Newton’s second law
d)
Newton’s first law
|
|
Rajveer Kumar answered |
Given information:
- Mass of the object = 6 kg
- Three forces acting on the object:
- F1 = 20i + 30j N
- F2 = 8i - 50j N
- F3 = 2i + 2j N
To find: Acceleration of the object
Solution:
- We know that the net force acting on the object, F_net = F1 + F2 + F3
- Using vector addition, we can find the net force: F_net = (20+8+2)i + (30-50+2)j = 30i - 18j N
- Now, using Newton's second law of motion, F_net = m*a, where m is the mass of the object and a is the acceleration produced.
- Substituting the values, we get: 30i - 18j = 6*a
- Dividing both sides by 6, we get: a = (30/6)i - (18/6)j = 5i - 3j m/s^2
Therefore, the acceleration of the object is 5i - 3j m/s^2, which is option 'B'.
- Mass of the object = 6 kg
- Three forces acting on the object:
- F1 = 20i + 30j N
- F2 = 8i - 50j N
- F3 = 2i + 2j N
To find: Acceleration of the object
Solution:
- We know that the net force acting on the object, F_net = F1 + F2 + F3
- Using vector addition, we can find the net force: F_net = (20+8+2)i + (30-50+2)j = 30i - 18j N
- Now, using Newton's second law of motion, F_net = m*a, where m is the mass of the object and a is the acceleration produced.
- Substituting the values, we get: 30i - 18j = 6*a
- Dividing both sides by 6, we get: a = (30/6)i - (18/6)j = 5i - 3j m/s^2
Therefore, the acceleration of the object is 5i - 3j m/s^2, which is option 'B'.
The excretory organ of Saccoglossus is- a)Malphighian tubules
- b)Proboscis gland
- c)Gills
- d)Excretory pore
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The excretory organ of Saccoglossus is
a)
Malphighian tubules
b)
Proboscis gland
c)
Gills
d)
Excretory pore
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
A proboscis is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular mouth parts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a proboscis is an elongated nose or snout.
In some animal groups, the body is found divided into compartments with serial repetition of at least some organs. This characteristic feature is called- a)Segmentation
- b)Metagenesis
- c)Metamerism
- d)Metamorphosis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In some animal groups, the body is found divided into compartments with serial repetition of at least some organs. This characteristic feature is called
a)
Segmentation
b)
Metagenesis
c)
Metamerism
d)
Metamorphosis
|
|
Santunu Pradhan answered |
Metamerism
How many chambers are there in camel’s stomach?Identify the animal given below. Mention its phylum.
- a)1 chamber, Ascidia and phylum Chordata
- b)3 Chamber, Spongilla and phylum Porifera
- c)3 chambers, Euspongia and phylum Porifera
- d)4 chamber, Aurelia and phylum Coelenterata
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many chambers are there in camel’s stomach?Identify the animal given below. Mention its phylum.
a)
1 chamber, Ascidia and phylum Chordata
b)
3 Chamber, Spongilla and phylum Porifera
c)
3 chambers, Euspongia and phylum Porifera
d)
4 chamber, Aurelia and phylum Coelenterata

|
Shiksha Academy answered |
Euspongia, which belongs to the phylum Porifera, is commonly known as a sponge. Sponges are some of the simplest and most primitive animals in the animal kingdom.
Hence, the correct option is C.
NCERT Reference: Topic: Phylum – Porifera” of chapter Animal Kingdom
NCERT Reference: Topic: Phylum – Porifera” of chapter Animal Kingdom
Which group of chordates possesses sucking and circular mouth without jaws?- a)ClassChondrichthyes
- b)Class Cyclostomata
- c)Class Osteichthyes
- d)Both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which group of chordates possesses sucking and circular mouth without jaws?
a)
ClassChondrichthyes
b)
Class Cyclostomata
c)
Class Osteichthyes
d)
Both (b) and (c)
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Class-Cyclostomata is comprised of, the living jawless fishes. Their mouth is circular and lack jaws, hence they are also called agnathans. It is surrounded by tentacles (e.g., lampreys and hellish). These also presses retractable teeth.
For alkali metals, which one of the following trends is INCORRECT?
- a)Hydration energy: Li > Na > K > Rb
- b)Ionization energy: Li > Na > K > Rb
- c)Atomic size: Li < Na < K < Rb
- d)Density: Li < Na < K < Rb
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For alkali metals, which one of the following trends is INCORRECT?
a)
Hydration energy: Li > Na > K > Rb
b)
Ionization energy: Li > Na > K > Rb
c)
Atomic size: Li < Na < K < Rb
d)
Density: Li < Na < K < Rb
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Density: Li < Na < K < Rb.
The density of K is lower than that of Na. Thus, option D is incorrect. The correct trend is
Li < K < Na < Rb
The density of K is lower than that of Na. Thus, option D is incorrect. The correct trend is
Li < K < Na < Rb
Animals which possess cleidoic egg exhibit- a)External fertilisation and external development
- b)External fertilisation and internal development
- c)Internal fertilisation and internal development
- d)Internal fertilisation and external development
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Animals which possess cleidoic egg exhibit
a)
External fertilisation and external development
b)
External fertilisation and internal development
c)
Internal fertilisation and internal development
d)
Internal fertilisation and external development
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Cleidoic eggs are laid by reptiles & birds. These eggs have protective shell which is porous to air and may be flexible or calcareous (hard). Birds and reptiles exhibit internal fertilization and laid eggs contain all the food the embryo needs for external development.
Silk produced by Antheraea Mylitta is called- a)Eri silk
- b)Muga silk
- c)Mysore silk
- d)Tasar silk
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Silk produced by Antheraea Mylitta is called
a)
Eri silk
b)
Muga silk
c)
Mysore silk
d)
Tasar silk
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Tropical Tasar: Tasar (Tussah) is copperish colour, coarse silk mainly used for furnishings and interiors. It is less lustrous than mulberry silk, but has its own feel and appeal. Tasar silk is generated by the silkworm, Antheraea mylitta which mainly thrive on the food plants Asan and Arjun.
14 elements after actinium is called
a) Lanthanides
b) Actinides
c) D-block elements
d) P block elements
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
14 elements after actinium is called Actinides.
Air bladder is absent in- a)Sea horse
- b)Shark
- c)Flying fish
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Air bladder is absent in
a)
Sea horse
b)
Shark
c)
Flying fish
d)
All of the above
|
|
Roshni Tiwari answered |
Explanation:
Air bladder is a gas-filled sac that helps fish to maintain buoyancy in water. However, not all fish have air bladders. The correct answer to the given question is option B, i.e., shark, as sharks do not have air bladders.
Reasons why sharks do not have an air bladder are:
1. Buoyancy control: Sharks have a special organ called the liver that is filled with oil. This oil is less dense than water and provides buoyancy to the shark, allowing it to stay afloat.
2. Depth control: Unlike bony fish that have a swim bladder to adjust their depth in water, sharks are able to control their depth by swimming. They can swim at different angles to adjust their depth in water.
3. Adaptation to environment: Sharks have evolved to live in their environment, and their body shape and buoyancy control mechanisms have adapted to suit their needs.
Therefore, it can be concluded that while some fish have air bladders to maintain buoyancy in water, sharks have evolved different mechanisms to control their buoyancy and depth in water.
Air bladder is a gas-filled sac that helps fish to maintain buoyancy in water. However, not all fish have air bladders. The correct answer to the given question is option B, i.e., shark, as sharks do not have air bladders.
Reasons why sharks do not have an air bladder are:
1. Buoyancy control: Sharks have a special organ called the liver that is filled with oil. This oil is less dense than water and provides buoyancy to the shark, allowing it to stay afloat.
2. Depth control: Unlike bony fish that have a swim bladder to adjust their depth in water, sharks are able to control their depth by swimming. They can swim at different angles to adjust their depth in water.
3. Adaptation to environment: Sharks have evolved to live in their environment, and their body shape and buoyancy control mechanisms have adapted to suit their needs.
Therefore, it can be concluded that while some fish have air bladders to maintain buoyancy in water, sharks have evolved different mechanisms to control their buoyancy and depth in water.
The scientific name of Asian tiger mosquito- a)Aedes aegypti
- b)Aedes albolineatus
- c)Aedes taeniorhynchus
- d)Aedes albopictus
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The scientific name of Asian tiger mosquito
a)
Aedes aegypti
b)
Aedes albolineatus
c)
Aedes taeniorhynchus
d)
Aedes albopictus
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
The Asian tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) is a small black and white mosquito, about 1/4-inch long.
The phylum in which adults exhibit radial symmetry and larva exhibit bilateral symmetry is- a)Phylum Arthropoda
- b)Phylum Echinodermata
- c)Phylum Annelida
- d)Phylum Aschelminthes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The phylum in which adults exhibit radial symmetry and larva exhibit bilateral symmetry is
a)
Phylum Arthropoda
b)
Phylum Echinodermata
c)
Phylum Annelida
d)
Phylum Aschelminthes
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Symmetry is an attribute of an organism showing regularity in body parts on a plane or around an axis. In Phylum Echinodermata, the adult echinoderms are radially symmetrical but the larvae are bilaterally symmetrical.
A particle of mass M, originally at rest is subjected to a force whose direction is constant but whose magnitude varies with the time according to the relation
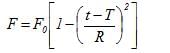
where F0 and T are constant. The force acts only for the time interval 2T. Find the velocity v of the particle after time 2T.
- a)F0/3M
- b)4F0/3M
- c)F0/2M
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle of mass M, originally at rest is subjected to a force whose direction is constant but whose magnitude varies with the time according to the relation
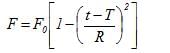
where F0 and T are constant. The force acts only for the time interval 2T. Find the velocity v of the particle after time 2T.
where F0 and T are constant. The force acts only for the time interval 2T. Find the velocity v of the particle after time 2T.
a)
F0/3M
b)
4F0/3M
c)
F0/2M
d)
none of the above

|
R L Sharma answered |
I think this statement is said by Aristotle as every body is in the natural state of rest. and it get in the state of motion ony when some external force is applied on it.
A particle of mass 'm' original at rest, is subjected to a force whose direction is constant but whose magnitude varies with according to the relation
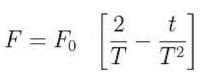 Where F0 and T are constant.
Where F0 and T are constant.
Then speed of the particle after a time 2T is:
- a)
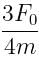
- b)
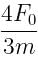
- c)
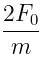
- d)
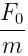
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle of mass 'm' original at rest, is subjected to a force whose direction is constant but whose magnitude varies with according to the relation
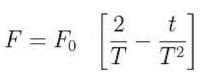
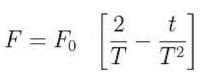
Where F0 and T are constant.
Then speed of the particle after a time 2T is:
Then speed of the particle after a time 2T is:
a)
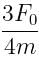
b)
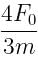
c)
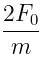
d)
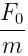

|
Cstoppers Instructors answered |
Given:
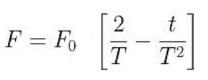
Speed of the particle after a time 2T,
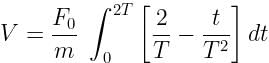
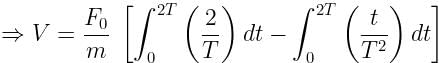
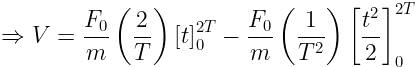
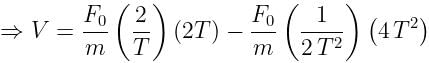
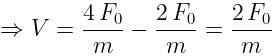
The order of Decreasing radius isa)Van der Waals’radius > Metallic radius > Covalent radiusb)Covalent radius Van der Waals’radiusc)Metallic radius > Van der Waals’radius > Covalent radiusd)Van der Waals’radius > Covalent radius > Metallic radiusCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Raghav Chakraborty answered |
vanderwaal radius > Metallic radius > Covalent radius.
Metalloids show the properties of- a)properties that are characteristic of both metals and viscous liquids
- b)properties that are characteristic of both metals and plastics
- c)properties that are characteristic of both metals and nonmetals
- d)properties that are characteristic of both metals and gases
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Metalloids show the properties of
a)
properties that are characteristic of both metals and viscous liquids
b)
properties that are characteristic of both metals and plastics
c)
properties that are characteristic of both metals and nonmetals
d)
properties that are characteristic of both metals and gases

|
Janhavi Banerjee answered |
Metalloids shows both the properties of metals as well as non metals.
Which of the following will have the most negative electron gain enthalpy and which one the least negative? P, S, Cl, F.- a)Cl, P
- b)P,Cl
- c)P,S
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following will have the most negative electron gain enthalpy and which one the least negative? P, S, Cl, F.
a)
Cl, P
b)
P,Cl
c)
P,S
d)
none
|
|
Sinjini Pillai answered |
**Answer:**
The electron gain enthalpy is the energy released when an atom gains an electron to form a negative ion. It is a measure of the tendency of an atom to accept an electron.
To determine which element will have the most negative electron gain enthalpy and which one will have the least negative, we need to consider the factors that influence electron gain enthalpy.
1. **Nuclear charge**: The greater the nuclear charge, the stronger the attraction for the incoming electron, resulting in a more negative electron gain enthalpy.
2. **Atomic size**: The smaller the atomic size, the closer the valence electrons are to the nucleus, resulting in a stronger attraction for the incoming electron and a more negative electron gain enthalpy.
Considering these factors, we can analyze the elements given in the options:
a) Cl, P: Chlorine (Cl) has a higher nuclear charge than Phosphorus (P), so it will have a greater attraction for the incoming electron. Additionally, chlorine is smaller in size compared to phosphorus. Therefore, chlorine will have the most negative electron gain enthalpy, and phosphorus will have a less negative electron gain enthalpy.
b) P, Cl: As mentioned above, chlorine (Cl) has a higher nuclear charge and is smaller in size compared to phosphorus (P). Therefore, chlorine will have a more negative electron gain enthalpy, and phosphorus will have a less negative electron gain enthalpy.
c) P, S: Sulfur (S) has a higher nuclear charge and is smaller in size compared to phosphorus (P). Therefore, sulfur will have a more negative electron gain enthalpy, and phosphorus will have a less negative electron gain enthalpy.
d) None: The answer cannot be "none" since we have already determined that chlorine will have the most negative electron gain enthalpy.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'A': Cl will have the most negative electron gain enthalpy, and P will have the least negative electron gain enthalpy.
The electron gain enthalpy is the energy released when an atom gains an electron to form a negative ion. It is a measure of the tendency of an atom to accept an electron.
To determine which element will have the most negative electron gain enthalpy and which one will have the least negative, we need to consider the factors that influence electron gain enthalpy.
1. **Nuclear charge**: The greater the nuclear charge, the stronger the attraction for the incoming electron, resulting in a more negative electron gain enthalpy.
2. **Atomic size**: The smaller the atomic size, the closer the valence electrons are to the nucleus, resulting in a stronger attraction for the incoming electron and a more negative electron gain enthalpy.
Considering these factors, we can analyze the elements given in the options:
a) Cl, P: Chlorine (Cl) has a higher nuclear charge than Phosphorus (P), so it will have a greater attraction for the incoming electron. Additionally, chlorine is smaller in size compared to phosphorus. Therefore, chlorine will have the most negative electron gain enthalpy, and phosphorus will have a less negative electron gain enthalpy.
b) P, Cl: As mentioned above, chlorine (Cl) has a higher nuclear charge and is smaller in size compared to phosphorus (P). Therefore, chlorine will have a more negative electron gain enthalpy, and phosphorus will have a less negative electron gain enthalpy.
c) P, S: Sulfur (S) has a higher nuclear charge and is smaller in size compared to phosphorus (P). Therefore, sulfur will have a more negative electron gain enthalpy, and phosphorus will have a less negative electron gain enthalpy.
d) None: The answer cannot be "none" since we have already determined that chlorine will have the most negative electron gain enthalpy.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'A': Cl will have the most negative electron gain enthalpy, and P will have the least negative electron gain enthalpy.
Which of the following statements is false?- a)Alkali metals form covalent bonds with oxygen.
- b)Alkali metals have relatively low first ionization energies
- c)Alkali metals forms oxides that act as basic anhydrides.
- d)Alkali metals usually have a +1 oxidation state
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is false?
a)
Alkali metals form covalent bonds with oxygen.
b)
Alkali metals have relatively low first ionization energies
c)
Alkali metals forms oxides that act as basic anhydrides.
d)
Alkali metals usually have a +1 oxidation state
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Lithium, sodium and potassium all react vigorously with water. Hydrogen gas bubbles off and, in the case of potassium, this burns with a lilac flame. The metal hydroxide is formed which is a strong alkali. Alkali metals need to be stored under oil to prevent them reacting with the oxygen and water vapour in the air.
Read the following statements:
i) Spider and mosquito possess compound eye
ii) Jelly fishes possess cnidoblasts but comb-jellies lack them.
iii) All animals having true coelom are characterized by the presence of bilateral symmetry usually, tube-within-tube body plan, presence of mesoderm and true segmentation
iv) The animals of the phylum Porifera have originated from colonial protozoans.
Which of the above statements are correct?- a)i, ii, iv
- b)iii, iv
- c)i, iii
- d)ii, iii
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements:
i) Spider and mosquito possess compound eye
ii) Jelly fishes possess cnidoblasts but comb-jellies lack them.
iii) All animals having true coelom are characterized by the presence of bilateral symmetry usually, tube-within-tube body plan, presence of mesoderm and true segmentation
iv) The animals of the phylum Porifera have originated from colonial protozoans.
Which of the above statements are correct?
i) Spider and mosquito possess compound eye
ii) Jelly fishes possess cnidoblasts but comb-jellies lack them.
iii) All animals having true coelom are characterized by the presence of bilateral symmetry usually, tube-within-tube body plan, presence of mesoderm and true segmentation
iv) The animals of the phylum Porifera have originated from colonial protozoans.
Which of the above statements are correct?
a)
i, ii, iv
b)
iii, iv
c)
i, iii
d)
ii, iii

|
Stepway Academy answered |
i) Spider and mosquito possess compound eyes. The eyes of most insects, which are composed of many light-sensitive elements, each having its own reflective system and each forming a portion of an image.
ii) Jelly fishes possess cnidoblasts but comb-jellies lack them. Cnidoblasts are features of Coelenterata (Cnidaria) and comb-jellies come under the phylum Ctenophora.
iii) All animals with a true coelom usually exhibit bilateral symmetry, a tube-within-tube body plan, presence of mesoderm, and true segmentation.
iv) The animals of the phylum Porifera have indeed originated from colonial protozoans.
Thus, the correct statements are i, ii, and iv. The answer is Option A.
ii) Jelly fishes possess cnidoblasts but comb-jellies lack them. Cnidoblasts are features of Coelenterata (Cnidaria) and comb-jellies come under the phylum Ctenophora.
iii) All animals with a true coelom usually exhibit bilateral symmetry, a tube-within-tube body plan, presence of mesoderm, and true segmentation.
iv) The animals of the phylum Porifera have indeed originated from colonial protozoans.
Thus, the correct statements are i, ii, and iv. The answer is Option A.
The sequence of ionic mobility in aqueous solution is - a)K+ > Na+ > Rb+ > Cs+
- b)Cs+ > Rb+ > K+ >Na+
- c)Rb+ > K+> Cs+ > Na+
- d)Na+ > K+ >Rb+ >Cs+
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The sequence of ionic mobility in aqueous solution is
a)
K+ > Na+ > Rb+ > Cs+
b)
Cs+ > Rb+ > K+ >Na+
c)
Rb+ > K+> Cs+ > Na+
d)
Na+ > K+ >Rb+ >Cs+
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Smaller the size of cation, higher will be the hydration and its effective size will increase and hence mobility in aqueous solution will decrease. Larger size ions have more ionic mobility due to less hydration. Thus the degree of hydration of M+ ions decreases from Li+ to Cs+. Consequently the radii of the hydrated ion decreases from Li+ to Cs+. Hence the ionic conductance of these hydrated ions increases from Li+ to Cs+
For the four successive transition elements (Cr, Mn, Fe and Co), the stability of + 2 oxidation state will be there in which of the following order? (At. nos. Cr = 24, Mn = 25, Fe = 26, Co = 27)- a)Fe > Mn > Co > Cr
- b)Mn > Fe > Cr > Co
- c)Cr > Mn > Co > Fe
- d)Co > Mn > Fe > Cr
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For the four successive transition elements (Cr, Mn, Fe and Co), the stability of + 2 oxidation state will be there in which of the following order? (At. nos. Cr = 24, Mn = 25, Fe = 26, Co = 27)
a)
Fe > Mn > Co > Cr
b)
Mn > Fe > Cr > Co
c)
Cr > Mn > Co > Fe
d)
Co > Mn > Fe > Cr

|
Gaurav Saini answered |
Mn has most stable +2 stable because Mn+2 had d5 configuration which is most stable.
Dust can be removed out of a blanket using- a)Law of inertia
- b)Newton’s second law of motion
- c)Newton’s third law of motion
- d)Newton’s law of gravitation
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Dust can be removed out of a blanket using
a)
Law of inertia
b)
Newton’s second law of motion
c)
Newton’s third law of motion
d)
Newton’s law of gravitation
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
When a blanket is bitten with a stick or something then particles of blanket come into motion while dust particles remains in rest thus comes out which shows law of inertia.
Match each item in Column I with one item in Column II and choose your answer from the codes given below.
Column I | Column II
I. Placoid Scales | 1. Chondrichthyes
II. Ctenoid scales | 2. Osteichthyes
III. Ectoparasites | 3. Hemichordata
IV. Proboscis gland | 4. Cyclostomata
Codes:- a)1 2 3 4
- b)2 1 4 3
- c)2 1 3 4
- d)1 2 4 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Column I | Column II
I. Placoid Scales | 1. Chondrichthyes
II. Ctenoid scales | 2. Osteichthyes
III. Ectoparasites | 3. Hemichordata
IV. Proboscis gland | 4. Cyclostomata
Codes:
a)
1 2 3 4
b)
2 1 4 3
c)
2 1 3 4
d)
1 2 4 3
|
|
Sinjini Choudhury answered |
Understanding the Matchings
In this question, we need to match items from Column I with their respective classifications or characteristics from Column II. Here’s an explanation of each item:
Placoid Scales
- These are the scales found in Chondrichthyes, which include sharks and rays.
- Placoid scales are tooth-like structures that provide protection and help reduce turbulence while swimming.
Ctenoid Scales
- These scales are characteristic of Osteichthyes, or bony fish.
- Ctenoid scales have a comb-like edge and are more flexible compared to other types of scales, providing better movement in water.
Ectoparasites
- Ectoparasites are organisms that live on the outside of a host, often feeding on its blood or tissues.
- An example of ectoparasites includes certain species of leeches and lice, which are commonly associated with Hemichordata and other marine organisms.
Proboscis Gland
- This gland is primarily found in Cyclostomata, which includes lampreys and hagfish.
- The proboscis gland is used for feeding and attachment to hosts, particularly in parasitic species.
Matching Codes
- Based on the definitions and classifications:
- I. Placoid Scales → 1. Chondrichthyes
- II. Ctenoid Scales → 2. Osteichthyes
- III. Ectoparasites → 4. Cyclostomata
- IV. Proboscis Gland → 3. Hemichordata
Correct Answer Explanation
The correct matching is represented by option D (1 2 4 3), indicating:
- Placoid Scales are associated with Chondrichthyes (1).
- Ctenoid Scales are associated with Osteichthyes (2).
- Ectoparasites are linked to Cyclostomata (4).
- Proboscis Gland corresponds with Hemichordata (3).
Thus, option D accurately matches each item from Column I to Column II.
In this question, we need to match items from Column I with their respective classifications or characteristics from Column II. Here’s an explanation of each item:
Placoid Scales
- These are the scales found in Chondrichthyes, which include sharks and rays.
- Placoid scales are tooth-like structures that provide protection and help reduce turbulence while swimming.
Ctenoid Scales
- These scales are characteristic of Osteichthyes, or bony fish.
- Ctenoid scales have a comb-like edge and are more flexible compared to other types of scales, providing better movement in water.
Ectoparasites
- Ectoparasites are organisms that live on the outside of a host, often feeding on its blood or tissues.
- An example of ectoparasites includes certain species of leeches and lice, which are commonly associated with Hemichordata and other marine organisms.
Proboscis Gland
- This gland is primarily found in Cyclostomata, which includes lampreys and hagfish.
- The proboscis gland is used for feeding and attachment to hosts, particularly in parasitic species.
Matching Codes
- Based on the definitions and classifications:
- I. Placoid Scales → 1. Chondrichthyes
- II. Ctenoid Scales → 2. Osteichthyes
- III. Ectoparasites → 4. Cyclostomata
- IV. Proboscis Gland → 3. Hemichordata
Correct Answer Explanation
The correct matching is represented by option D (1 2 4 3), indicating:
- Placoid Scales are associated with Chondrichthyes (1).
- Ctenoid Scales are associated with Osteichthyes (2).
- Ectoparasites are linked to Cyclostomata (4).
- Proboscis Gland corresponds with Hemichordata (3).
Thus, option D accurately matches each item from Column I to Column II.
One of the following options is not used for explaining atomic radius- a)coordinate radius
- b)covalent radius
- c)van der waals’radius
- d)metallic radius
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the following options is not used for explaining atomic radius
a)
coordinate radius
b)
covalent radius
c)
van der waals’radius
d)
metallic radius
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Atomic radius
The distance from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost shell containing electrons.
or
The distance from the centre of the nucleus to the point up to which the density of the electron cloud is maximum.
Types of atomic radii
1) Covalent radius
2) Van der waals radius
3)Metallic radius
Metagenesis refers to?
Options:- a)The presence of different morphic forms
- b)Alternation of generation between asexual and sexual phases of an organism
- c)Occurrence of a drastic change in the form during post-embryonic development
- d)Presence of a segmented body and parthenogenic mode of reproduction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Options:
a)
The presence of different morphic forms
b)
Alternation of generation between asexual and sexual phases of an organism
c)
Occurrence of a drastic change in the form during post-embryonic development
d)
Presence of a segmented body and parthenogenic mode of reproduction
|
|
Shivani Kulkarni answered |
Alternation of generation between asexual and sexual phases of an organism
Metagenesis refers to the phenomenon of alternation of generation between asexual and sexual phases of an organism. This term is commonly used in the context of certain invertebrates, such as jellyfish, where the life cycle involves both sexual and asexual reproduction.
Explanation:
- In metagenesis, the organism goes through both sexual and asexual phases during its life cycle.
- The asexual phase typically involves reproduction by budding or fragmentation, leading to the formation of new individuals.
- The sexual phase involves the production of gametes, which fuse to form a zygote that develops into a new organism.
- This alternating pattern of reproduction allows for genetic variation and adaptation to different environmental conditions.
- Metagenesis is a unique reproductive strategy that ensures the survival and success of certain organisms in their respective habitats.
In conclusion, metagenesis is an intriguing biological phenomenon that showcases the diversity and complexity of reproductive strategies in nature.
Metagenesis refers to the phenomenon of alternation of generation between asexual and sexual phases of an organism. This term is commonly used in the context of certain invertebrates, such as jellyfish, where the life cycle involves both sexual and asexual reproduction.
Explanation:
- In metagenesis, the organism goes through both sexual and asexual phases during its life cycle.
- The asexual phase typically involves reproduction by budding or fragmentation, leading to the formation of new individuals.
- The sexual phase involves the production of gametes, which fuse to form a zygote that develops into a new organism.
- This alternating pattern of reproduction allows for genetic variation and adaptation to different environmental conditions.
- Metagenesis is a unique reproductive strategy that ensures the survival and success of certain organisms in their respective habitats.
In conclusion, metagenesis is an intriguing biological phenomenon that showcases the diversity and complexity of reproductive strategies in nature.
Which of the following statements correctly describes the presence of the notochord in Urochordata and Cephalochordata?- a)In Urochordata, the notochord is present throughout the life and extends from head to tail, while in Cephalochordata, it is present only in the larval tail.
- b)In Urochordata, the notochord is present only in the larval tail, while in Cephalochordata, it extends from head to tail region and is persistent throughout their life.
- c)In both Urochordata and Cephalochordata, the notochord is present only in the larval tail.
- d)In both Urochordata and Cephalochordata, the notochord extends from head to tail and is persistent throughout their life.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements correctly describes the presence of the notochord in Urochordata and Cephalochordata?
a)
In Urochordata, the notochord is present throughout the life and extends from head to tail, while in Cephalochordata, it is present only in the larval tail.
b)
In Urochordata, the notochord is present only in the larval tail, while in Cephalochordata, it extends from head to tail region and is persistent throughout their life.
c)
In both Urochordata and Cephalochordata, the notochord is present only in the larval tail.
d)
In both Urochordata and Cephalochordata, the notochord extends from head to tail and is persistent throughout their life.

|
Bs Academy answered |
In Urochordata, the notochord is present only in the larval tail, while in Cephalochordata, it extends from head to tail region and is persistent throughout their life.
Read the following statements:
(a) Metagenesis is observed in Helminths.
(b) Echinoderms are triploblastic and coelomate animals.
(c) Round worms have organ-system level of body organization.
(d) Comb plates present in ctenophores help in digestion.
(e) Water vascular system is characteristic of Echinoderms.
Options:- a)(a), (d) and (e) are correct
- b)(b), (c) and (e) are correct
- c)(c), (d) and (e) are correct
- d)(a), (b) and (c) are correct
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
(a) Metagenesis is observed in Helminths.
(b) Echinoderms are triploblastic and coelomate animals.
(c) Round worms have organ-system level of body organization.
(d) Comb plates present in ctenophores help in digestion.
(e) Water vascular system is characteristic of Echinoderms.
Options:
a)
(a), (d) and (e) are correct
b)
(b), (c) and (e) are correct
c)
(c), (d) and (e) are correct
d)
(a), (b) and (c) are correct

|
EduRev NEET answered |
(a) Metagenesis is observed in Helminths: Incorrect. Metagenesis refers to the alternation of generations between asexual and sexual phases, observed in cnidarians, not in helminths.
(b) Echinoderms are triploblastic and coelomate animals: Correct. Echinoderms have three germ layers (triploblastic) and a true coelom.
(c) Round worms have organ-system level of body organization: Correct. Roundworms (nematodes) have an organ-system level of organization.
(d) Comb plates present in ctenophores help in digestion: Incorrect. Comb plates (ctenes) in ctenophores are used for locomotion, not digestion.
(e) Water vascular system is characteristic of Echinoderms: Correct. The water vascular system is a unique feature of echinoderms.
Thus, the correct answer is Option B.
(b) Echinoderms are triploblastic and coelomate animals: Correct. Echinoderms have three germ layers (triploblastic) and a true coelom.
(c) Round worms have organ-system level of body organization: Correct. Roundworms (nematodes) have an organ-system level of organization.
(d) Comb plates present in ctenophores help in digestion: Incorrect. Comb plates (ctenes) in ctenophores are used for locomotion, not digestion.
(e) Water vascular system is characteristic of Echinoderms: Correct. The water vascular system is a unique feature of echinoderms.
Thus, the correct answer is Option B.
The elements charecterised by the filling of 4 f-orbitals, are:- a)Alkali metals
- b)Lanthanoids
- c)Alkaline earth metals
- d)Transition elements)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The elements charecterised by the filling of 4 f-orbitals, are:
a)
Alkali metals
b)
Lanthanoids
c)
Alkaline earth metals
d)
Transition elements)
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
The f block elements are the lanthanides and actinides and are called the inner transition elements because of their placement in the periodic table due to their electron configurations. The f orbitals of the electron shell are filled with “n-2.” There is a maximum of fourteen electrons that can occupy the f orbitals.
For Atomic numbers greater than 100 IUPAC has made recommendation that until a new element ‘s discovery is proved, and its name is officially recognized, a systematic nomenclature be derived directly from the atomic number of the element using the numerical roots for 0 and numbers 1-9. The name 'sept' in this scheme corresponds to the digit- a)3
- b)8
- c)4
- d)7.0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For Atomic numbers greater than 100 IUPAC has made recommendation that until a new element ‘s discovery is proved, and its name is officially recognized, a systematic nomenclature be derived directly from the atomic number of the element using the numerical roots for 0 and numbers 1-9. The name 'sept' in this scheme corresponds to the digit
a)
3
b)
8
c)
4
d)
7.0

|
Puja Das answered |
sept is for 7.
An object of mass 5 kg is initially moving with a velocity of 10 m/s. An unbalanced force of 30 N is applied to the object in the opposite direction of its motion. Calculate the acceleration of the object.- a)6 m/s2
- b)2 m/s2
- c)4 m/s2
- d)8 m/s2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An object of mass 5 kg is initially moving with a velocity of 10 m/s. An unbalanced force of 30 N is applied to the object in the opposite direction of its motion. Calculate the acceleration of the object.
a)
6 m/s2
b)
2 m/s2
c)
4 m/s2
d)
8 m/s2
|
|
Rishabh Chavan answered |
Given:
Mass of the object (m) = 5 kg
Initial velocity (u) = 10 m/s
Force applied (F) = 30 N
To find:
Acceleration of the object (a)
Explanation:
Newton's second law of motion:
The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. It can be expressed as:
F = ma
Calculating the acceleration:
To find the acceleration of the object, we can rearrange the formula as:
a = F/m
Substituting the given values:
a = 30 N / 5 kg
a = 6 m/s^2
Therefore, the acceleration of the object is 6 m/s^2.
Answer:
The correct answer is option A) 6 m/s^2.
Mass of the object (m) = 5 kg
Initial velocity (u) = 10 m/s
Force applied (F) = 30 N
To find:
Acceleration of the object (a)
Explanation:
Newton's second law of motion:
The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. It can be expressed as:
F = ma
Calculating the acceleration:
To find the acceleration of the object, we can rearrange the formula as:
a = F/m
Substituting the given values:
a = 30 N / 5 kg
a = 6 m/s^2
Therefore, the acceleration of the object is 6 m/s^2.
Answer:
The correct answer is option A) 6 m/s^2.
Starting from rest, a body slides down a 45∘ inclined plane in twice the time it takes to slide the same distance in the absence of friction. What is the coefficient of friction between the body and the inclined plane?- a)√3/2
- b)3/4
- c)1/2
- d)1/4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Starting from rest, a body slides down a 45∘ inclined plane in twice the time it takes to slide the same distance in the absence of friction. What is the coefficient of friction between the body and the inclined plane?
a)
√3/2
b)
3/4
c)
1/2
d)
1/4

|
Stepway Academy answered |
For a frictionless surface,
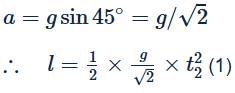
In the presence of friction,
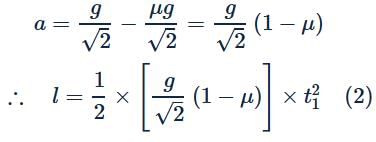
Dividing eq. (2) by eq. (1), we get
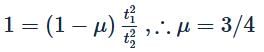
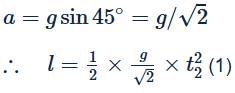
In the presence of friction,
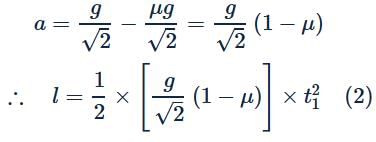
Dividing eq. (2) by eq. (1), we get
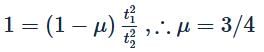
In the modern periodic table- a)The horizontal rows are called series and the vertical columns, groups.
- b)The horizontal rows are called periods and the vertical columns, groups.
- c)The horizontal rows are called groups and the vertical columns, periods
- d)The horizontal rows are called periods and the vertical columns, series.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the modern periodic table
a)
The horizontal rows are called series and the vertical columns, groups.
b)
The horizontal rows are called periods and the vertical columns, groups.
c)
The horizontal rows are called groups and the vertical columns, periods
d)
The horizontal rows are called periods and the vertical columns, series.

|
Nilesh Chawla answered |
Horizontal rows are periods while vertical column are groups.
f block of the Periodic Table consists of- a)The first two groups of the periodic table
- b)halogens (Group 17) and the chalcogens (Group 16)
- c)Groups 13 and 14 “Transition Elements”.
- d)The two rows of elements at the bottom of the Periodic Table, called the Lanthanides, Ce(Z = 58) ñ Lu(Z = 71) and Actinoids
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
f block of the Periodic Table consists of
a)
The first two groups of the periodic table
b)
halogens (Group 17) and the chalcogens (Group 16)
c)
Groups 13 and 14 “Transition Elements”.
d)
The two rows of elements at the bottom of the Periodic Table, called the Lanthanides, Ce(Z = 58) ñ Lu(Z = 71) and Actinoids

|
Uday Chakraborty answered |
Lanthanides, Ce(Z = 58) ñ Lu(Z = 71) and Actinoids comprises of f block elements.
Ionization enthalpy increases across a period because- a)outermost electrons are held more and more tightly
- b)screening is more effective
- c)outermost electrons are not held tightly
- d)shielding is more effective
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ionization enthalpy increases across a period because
a)
outermost electrons are held more and more tightly
b)
screening is more effective
c)
outermost electrons are not held tightly
d)
shielding is more effective

|
Swara Saha answered |
as we move from left to right in a period atomic radii decreases and due to effective nuclear charge outermost electrons are held more closely to the nucleus.
Dmitri Mendeleev (1834-1907) and the German chemist, Lothar Meyer (1830-1895) proposed arranging elements in- a)increasing order of their atomic weights
- b)decreasing order of their atomic weights
- c)decreasing order of their atomic numbers
- d)increasing order of their atomic numbers
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Dmitri Mendeleev (1834-1907) and the German chemist, Lothar Meyer (1830-1895) proposed arranging elements in
a)
increasing order of their atomic weights
b)
decreasing order of their atomic weights
c)
decreasing order of their atomic numbers
d)
increasing order of their atomic numbers

|
Jatin Sharma answered |
They arranged elements in increasing order of atomic weights.
It is now recognized that the ‘Modern Periodic Law’ is essentially the consequence of the- a)periodic variation in electronic configurations
- b)periodic variations in the element lattice
- c)periodic variation in chemical bonds
- d)periodic variation in chemical properties
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
It is now recognized that the ‘Modern Periodic Law’ is essentially the consequence of the
a)
periodic variation in electronic configurations
b)
periodic variations in the element lattice
c)
periodic variation in chemical bonds
d)
periodic variation in chemical properties

|
Arjun Saini answered |
Modern periodic law is essentially the result of periodic variation and electronic configuration.
A car of mass 1000 kg is moving at a velocity of 20 m/s. Suddenly, the driver applies the brakes, and the car comes to a stop in 4 seconds. What is the magnitude of the average force exerted by the brakes on the car? (Assume no external forces are acting on the car)
- a)5000 N
- b)250 N
- c)1000 N
- d)2000 N
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A car of mass 1000 kg is moving at a velocity of 20 m/s. Suddenly, the driver applies the brakes, and the car comes to a stop in 4 seconds. What is the magnitude of the average force exerted by the brakes on the car? (Assume no external forces are acting on the car)
a)
5000 N
b)
250 N
c)
1000 N
d)
2000 N
|
|
Anshu Saha answered |
Solution:
Given:
Mass of the car, m = 1000 kg
Initial velocity, u = 20 m/s
Final Velocity, v = 0 (since the car comes to a stop)
Time taken, t = 4 s
Acceleration, a = ?
Force, F = ?
Using the kinematic equation,
v = u + at
0 = 20 + a × 4
a = -5 m/s² (negative because the car is decelerating)
Using Newton's second law of motion,
F = ma
F = 1000 kg × (-5 m/s²)
F = -5000 N (negative because the force is acting opposite to the direction of motion)
Taking the magnitude of force,
F = 5000 N
Therefore, the magnitude of the average force exerted by the brakes on the car is 500 N.
Option (a) is the correct answer.
Given:
Mass of the car, m = 1000 kg
Initial velocity, u = 20 m/s
Final Velocity, v = 0 (since the car comes to a stop)
Time taken, t = 4 s
Acceleration, a = ?
Force, F = ?
Using the kinematic equation,
v = u + at
0 = 20 + a × 4
a = -5 m/s² (negative because the car is decelerating)
Using Newton's second law of motion,
F = ma
F = 1000 kg × (-5 m/s²)
F = -5000 N (negative because the force is acting opposite to the direction of motion)
Taking the magnitude of force,
F = 5000 N
Therefore, the magnitude of the average force exerted by the brakes on the car is 500 N.
Option (a) is the correct answer.
Chapter doubts & questions for June Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of June Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup