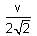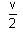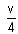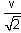All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of June Week 4 for NEET Exam
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A flower which can be divided into equal vertical halves by more than one plane of division is
- A:
Cyclic
- B:
Zygomorphic
- C:
Actinomorphic
- D:
Heteromorphic
The answer is c.
A flower which can be divided into equal vertical halves by more than one plane of division is
Cyclic
Zygomorphic
Actinomorphic
Heteromorphic

|
Trisha Vashisht answered |
Actinomorphic flowers are radially symmetrical, they are able to be divided into similar halves in more than one vertical plane.
Zygomorphic flowers are bilaterally symmetrical,they can be divided into similar halves in only one plane.
Cyclic is a type of floral organ arrangement, the floral organs are arranged in regular whorls at the node of the thalamus.
Heteromorphic is a type of incompatibilty, same species produce more than one morphological type of flower.
So the correct answer is C
Zygomorphic flowers are bilaterally symmetrical,they can be divided into similar halves in only one plane.
Cyclic is a type of floral organ arrangement, the floral organs are arranged in regular whorls at the node of the thalamus.
Heteromorphic is a type of incompatibilty, same species produce more than one morphological type of flower.
So the correct answer is C
Flowers in which only one set of essential organs is present are said to be- a)Polygamous
- b)Bisexual
- c)Dioecious
- d)Unisexual
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Flowers in which only one set of essential organs is present are said to be
a)
Polygamous
b)
Bisexual
c)
Dioecious
d)
Unisexual
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
POLYGAMY ⇒ The condition of bearing some flowers with stamens only, some with pistils only, and some with both, on the same or different plants.
BISEXUAL ⇒ The flower having both male and female reproductive organ on the same plant.
DIOECIOUS ⇒ Both male and female plants may have flowers, but one will have "male" flowers and the other "female" flowers.
UNISEXTUAL ⇒ The flower which has only one essential worl either male or female.
A scar on the seed coat through which the developing seed is attached to the fruit is- a)Hypocotyl
- b)Coleorhiza
- c)Epicotyl
- d)Hilum
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A scar on the seed coat through which the developing seed is attached to the fruit is
a)
Hypocotyl
b)
Coleorhiza
c)
Epicotyl
d)
Hilum
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
The outer layer is called testa and the inner layer is called tegmen. There is a scar on the seed coat through which the developing seed was attached to the fruit. This scar is called hilum.
Two cylindrical vessels of equal cross-sectional area 16 cm2 contain water up to heights 100 cm and 150 cm, respectively. The vessels are interconnected so that the water levels in them become equal. The work done by the force of gravity during the process is: [Take density of water = 103 kg/m3 and g = 10 ms-2]
- a)0.25 J
- b)12 J
- c)8 J
- d)1 J
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two cylindrical vessels of equal cross-sectional area 16 cm2 contain water up to heights 100 cm and 150 cm, respectively. The vessels are interconnected so that the water levels in them become equal. The work done by the force of gravity during the process is: [Take density of water = 103 kg/m3 and g = 10 ms-2]
a)
0.25 J
b)
12 J
c)
8 J
d)
1 J
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
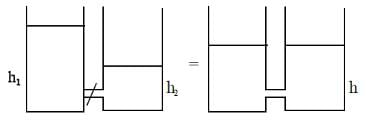
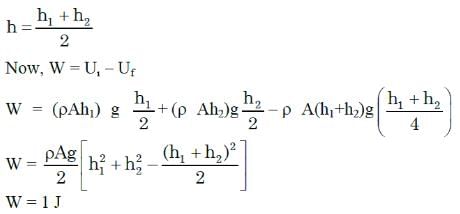
A flower which can be divided into equal vertical halves by more than one plane of division is- a)Cyclic
- b)Zygomorphic
- c)Actinomorphic
- d)Heteromorphic
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A flower which can be divided into equal vertical halves by more than one plane of division is
a)
Cyclic
b)
Zygomorphic
c)
Actinomorphic
d)
Heteromorphic
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
A actinomorphic flower is a type of flower that possesses radial symmetry. Any type of cut through the center will divide the flower into two equal parts.
Also known as "star-shaped", “regular”, “radial” or a “polysymmetric” flower, actinomorphic flowers can be bisected at any point and have two identical halves. Most flowers are actinomorphic. On a higher level, this is known as floral symmetry.
The launching mechanism of a toy gun consists of a spring of unknown spring constant. When the spring is compressed 0.120 m, the gun, when fired vertically, is able to launch a 35.0-g projectile to a maximum height of 20.0 m above the position of the projectile before firing. Neglecting all resistive forces, determine the spring constant.- a)903 N/m
- b)993 N/m
- c)953 N/m
- d)873 N/m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The launching mechanism of a toy gun consists of a spring of unknown spring constant. When the spring is compressed 0.120 m, the gun, when fired vertically, is able to launch a 35.0-g projectile to a maximum height of 20.0 m above the position of the projectile before firing. Neglecting all resistive forces, determine the spring constant.
a)
903 N/m
b)
993 N/m
c)
953 N/m
d)
873 N/m

|
Mrinalini Bose answered |
Explanation:
Potential energy of spring converted in to potential energy
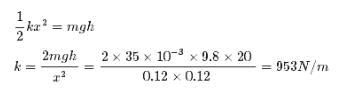
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of dicotyledonous seeds?
- a)They have a single cotyledon.
- b)The endosperm is well-developed and absorbs the cotyledons.
- c)The seed possesses two embryonic leaves or cotyledons
- d)The seed coat is absent.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of dicotyledonous seeds?
a)
They have a single cotyledon.
b)
The endosperm is well-developed and absorbs the cotyledons.
c)
The seed possesses two embryonic leaves or cotyledons
d)
The seed coat is absent.
|
|
Anu Saha answered |
**Characteristic feature of dicotyledonous seeds: The embryo possesses one seed leaf (cotyledon)**
Dicotyledonous seeds are seeds that come from angiosperms (flowering plants) belonging to the class Magnoliopsida. These seeds have several characteristic features, and one of the most distinctive features is that the embryo possesses one seed leaf or cotyledon.
**Explanation:**
1. **Cotyledons:** Cotyledons are the first leaves that emerge from the embryo of a seed. In dicotyledonous seeds, the embryo possesses two cotyledons. These cotyledons serve as a food source for the developing seedling until it becomes photosynthetically active. They are usually thick and fleshy in nature.
2. **Embryo:** The embryo is the tiny, undeveloped plant inside the seed. In dicotyledonous seeds, the embryo possesses two cotyledons. However, the statement in the question is incorrect as it states that the embryo possesses one cotyledon.
3. **Endosperm:** The endosperm is a tissue that provides nourishment to the developing embryo in some seeds. In dicotyledonous seeds, the endosperm is present but is usually not well-developed. Instead, the cotyledons take over the role of storing and supplying nutrients to the growing seedling.
4. **Seed coat:** The seed coat is the protective covering of the seed. It is formed from the outer layer of the ovule after fertilization. In dicotyledonous seeds, the seed coat is present and serves to protect the embryo and its food reserves from damage and desiccation.
In summary, the correct characteristic feature of dicotyledonous seeds is that the embryo possesses two seed leaves or cotyledons. This feature distinguishes them from monocotyledonous seeds, which have only one seed leaf. The endosperm in dicotyledonous seeds is usually not well-developed, and the seed coat is present for protection.
Dicotyledonous seeds are seeds that come from angiosperms (flowering plants) belonging to the class Magnoliopsida. These seeds have several characteristic features, and one of the most distinctive features is that the embryo possesses one seed leaf or cotyledon.
**Explanation:**
1. **Cotyledons:** Cotyledons are the first leaves that emerge from the embryo of a seed. In dicotyledonous seeds, the embryo possesses two cotyledons. These cotyledons serve as a food source for the developing seedling until it becomes photosynthetically active. They are usually thick and fleshy in nature.
2. **Embryo:** The embryo is the tiny, undeveloped plant inside the seed. In dicotyledonous seeds, the embryo possesses two cotyledons. However, the statement in the question is incorrect as it states that the embryo possesses one cotyledon.
3. **Endosperm:** The endosperm is a tissue that provides nourishment to the developing embryo in some seeds. In dicotyledonous seeds, the endosperm is present but is usually not well-developed. Instead, the cotyledons take over the role of storing and supplying nutrients to the growing seedling.
4. **Seed coat:** The seed coat is the protective covering of the seed. It is formed from the outer layer of the ovule after fertilization. In dicotyledonous seeds, the seed coat is present and serves to protect the embryo and its food reserves from damage and desiccation.
In summary, the correct characteristic feature of dicotyledonous seeds is that the embryo possesses two seed leaves or cotyledons. This feature distinguishes them from monocotyledonous seeds, which have only one seed leaf. The endosperm in dicotyledonous seeds is usually not well-developed, and the seed coat is present for protection.
A 100000 kg engine is moving up a slope of gradient 5o at a speed of 100 m/hr. The coefficient of friction between the engine and the rails is 0.1. If the engine has an efficiency of 4% for converting heat into work, find the amount of coal, the engine has to burn up in one hour. (Burning of 1 kg of coal yields 50000 J.)- a)4.577 Kg
- b)8154 Kg
- c)91.5 Kg
- d)9154 Kg
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A 100000 kg engine is moving up a slope of gradient 5o at a speed of 100 m/hr. The coefficient of friction between the engine and the rails is 0.1. If the engine has an efficiency of 4% for converting heat into work, find the amount of coal, the engine has to burn up in one hour. (Burning of 1 kg of coal yields 50000 J.)
a)
4.577 Kg
b)
8154 Kg
c)
91.5 Kg
d)
9154 Kg

|
EduRev NEET answered |
The forces are shown in Figure.
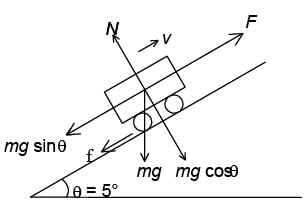
Net force to move the engine up the slope.
F = μN + mg sin θ
= mg (μ cos θ + sin θ)
If the engine has to apply an upward force equal to F, power of engine, P = Fv
where v is the velocity equal to 100 m/hr.
Work done by engine, W = Pt = Fvt
Efficiency of engine,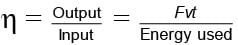
Energy used by engine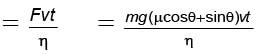
m = 100000 kg, μ = 0.1, θ = 5°, v = 100 m/hr, t = 1 hr
η = 4/100 = 0.04
Energy used by engine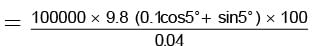

As 1 kg coal yields 50000 J, we have the amount of coal burnt up
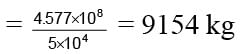

Net force to move the engine up the slope.
F = μN + mg sin θ
= mg (μ cos θ + sin θ)
If the engine has to apply an upward force equal to F, power of engine, P = Fv
where v is the velocity equal to 100 m/hr.
Work done by engine, W = Pt = Fvt
Efficiency of engine,
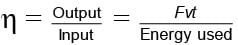
Energy used by engine
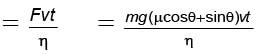
m = 100000 kg, μ = 0.1, θ = 5°, v = 100 m/hr, t = 1 hr
η = 4/100 = 0.04
Energy used by engine
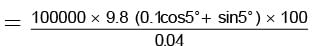

As 1 kg coal yields 50000 J, we have the amount of coal burnt up
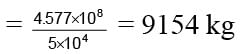
Physically, the notion of potential energy is applicable only to- a)The class of forces where work done against the force gets stored up as energy.
- b)The class of forces where work done against the force gets dissipated
- c)The class of forces where work done against the force gets converted to thermal energy
- d)The class of forces where work done against the force gets converted to kinetic energy
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Physically, the notion of potential energy is applicable only to
a)
The class of forces where work done against the force gets stored up as energy.
b)
The class of forces where work done against the force gets dissipated
c)
The class of forces where work done against the force gets converted to thermal energy
d)
The class of forces where work done against the force gets converted to kinetic energy
|
|
Mahi Nair answered |
Understanding Potential Energy
Potential energy is a crucial concept in physics that applies specifically to certain types of forces. It is essential to grasp which forces allow for the accumulation of energy based on work done against them.
Class of Forces for Potential Energy
- Definition: Potential energy is defined as the energy stored in an object due to its position or configuration.
- Work Done Against Force: The key aspect is that potential energy arises when work is done against a conservative force.
Conservative Forces
- Examples: Gravitational force and elastic force (like a spring) are classic examples of conservative forces.
- Energy Storage: When work is done against these forces, energy is stored in the system, which can later be converted back into kinetic energy or work.
Non-Conservative Forces
- Dissipative Forces: Forces such as friction or air resistance do not allow for the storage of potential energy.
- Energy Dissipation: When work is done against these forces, energy is transformed into thermal energy, not stored.
Key Takeaway
- Potential Energy Applicability: Therefore, the notion of potential energy is applicable only to the class of forces where work done against the force gets stored up as energy. This is why option 'A' is the correct choice.
Understanding these distinctions helps clarify when and how potential energy can be effectively utilized in physical systems.
Potential energy is a crucial concept in physics that applies specifically to certain types of forces. It is essential to grasp which forces allow for the accumulation of energy based on work done against them.
Class of Forces for Potential Energy
- Definition: Potential energy is defined as the energy stored in an object due to its position or configuration.
- Work Done Against Force: The key aspect is that potential energy arises when work is done against a conservative force.
Conservative Forces
- Examples: Gravitational force and elastic force (like a spring) are classic examples of conservative forces.
- Energy Storage: When work is done against these forces, energy is stored in the system, which can later be converted back into kinetic energy or work.
Non-Conservative Forces
- Dissipative Forces: Forces such as friction or air resistance do not allow for the storage of potential energy.
- Energy Dissipation: When work is done against these forces, energy is transformed into thermal energy, not stored.
Key Takeaway
- Potential Energy Applicability: Therefore, the notion of potential energy is applicable only to the class of forces where work done against the force gets stored up as energy. This is why option 'A' is the correct choice.
Understanding these distinctions helps clarify when and how potential energy can be effectively utilized in physical systems.
The pi-bond involves __________- a)axial overlapping
- b)side-wise overlapping
- c)end to end type of overlapping
- d)head-on overlapping
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The pi-bond involves __________
a)
axial overlapping
b)
side-wise overlapping
c)
end to end type of overlapping
d)
head-on overlapping
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
A pi-bond is a type of covalent bond in which the internuclear axes of the atoms are parallel to each other and for side-wise overlapping. The bond formed here is perpendicular to the internuclear axes.
A body is slowly lowered on to a massive platform moving horizontally at a speed of 4 m/s. through what distance will the body slide relative to the platform? (The coefficient of friction is 0.2; g = 10 m/s2)- a)2 m
- b)1 m
- c)4 m
- d)10 m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A body is slowly lowered on to a massive platform moving horizontally at a speed of 4 m/s. through what distance will the body slide relative to the platform? (The coefficient of friction is 0.2; g = 10 m/s2)
a)
2 m
b)
1 m
c)
4 m
d)
10 m
|
|
Advait Joshi answered |
Understanding the Problem
The body is being lowered onto a platform that is moving horizontally at a speed of 4 m/s. The coefficient of friction between the body and the platform is 0.2. We need to determine how far the body will slide relative to the platform.
Calculating the Forces
- The weight of the body (W) can be calculated using the equation:
W = m * g
Where g = 10 m/s².
- The frictional force (F_f) acting on the body is given by:
F_f = μ * N
Where μ is the coefficient of friction (0.2), and N is the normal force, which equals the weight of the body (W).
Setting Up the Equations
- The maximum frictional force before sliding occurs:
F_f = 0.2 * W = 0.2 * m * g
- The body will slide when the friction is overcome by the inertial force due to the platform's movement.
Determining the Distance
- The critical speed at which the body can remain at rest on the platform is determined by the maximum frictional force. If the platform moves at 4 m/s, we can calculate the distance (d) it will slide before coming to rest relative to the platform.
- Applying the equation of motion under constant acceleration for sliding:
d = (v^2)/(2 * a)
where v = initial relative speed (4 m/s) and a = deceleration due to friction.
- Deceleration (a) due to friction is:
a = F_f/m = μ * g = 0.2 * 10 = 2 m/s².
- Substituting the values:
d = (4^2)/(2 * 2) = 16/4 = 4 m.
Conclusion
The body will slide a distance of 4 meters relative to the platform before stopping, confirming that the correct answer is option 'C'.
The body is being lowered onto a platform that is moving horizontally at a speed of 4 m/s. The coefficient of friction between the body and the platform is 0.2. We need to determine how far the body will slide relative to the platform.
Calculating the Forces
- The weight of the body (W) can be calculated using the equation:
W = m * g
Where g = 10 m/s².
- The frictional force (F_f) acting on the body is given by:
F_f = μ * N
Where μ is the coefficient of friction (0.2), and N is the normal force, which equals the weight of the body (W).
Setting Up the Equations
- The maximum frictional force before sliding occurs:
F_f = 0.2 * W = 0.2 * m * g
- The body will slide when the friction is overcome by the inertial force due to the platform's movement.
Determining the Distance
- The critical speed at which the body can remain at rest on the platform is determined by the maximum frictional force. If the platform moves at 4 m/s, we can calculate the distance (d) it will slide before coming to rest relative to the platform.
- Applying the equation of motion under constant acceleration for sliding:
d = (v^2)/(2 * a)
where v = initial relative speed (4 m/s) and a = deceleration due to friction.
- Deceleration (a) due to friction is:
a = F_f/m = μ * g = 0.2 * 10 = 2 m/s².
- Substituting the values:
d = (4^2)/(2 * 2) = 16/4 = 4 m.
Conclusion
The body will slide a distance of 4 meters relative to the platform before stopping, confirming that the correct answer is option 'C'.
A bolt of mass 0.3 kg falls from the ceiling of an elevator moving down with an uniform speed of 7 m/s. It hits the floor of the elevator (length of the elevator = 3 m) and does not rebound. What is the heat produced by the impact?- a)8.11 J
- b)8.42 J
- c)9.22 J
- d)8.82 J
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A bolt of mass 0.3 kg falls from the ceiling of an elevator moving down with an uniform speed of 7 m/s. It hits the floor of the elevator (length of the elevator = 3 m) and does not rebound. What is the heat produced by the impact?
a)
8.11 J
b)
8.42 J
c)
9.22 J
d)
8.82 J

|
Manisha Patel answered |
Explanation:
Whole of the potential energy of bolt converted in to heat energy
heat produced by the impact = mgh =
0.3×9.8×3=8.82J
What is the electronic configuration of carbon in it’s excited state?- a)1s22s22p4
- b)1s22s12p3
- c)1s22s22p5
- d)1s22s12p4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the electronic configuration of carbon in it’s excited state?
a)
1s22s22p4
b)
1s22s
1
2p3c)
1s22s22p5
d)
1s22s12p4

|
Ambition Institute answered |
The electronic configuration of carbon in its ground state is given by 1s22s22p4. When it’s in an excited state, that is when it loses an electron, that would be from 2p-orbital. So the excited state’s electronic configuration is 1s22s
1
2p3.The part of the fruit that develops from the ovary wall is called__________.- a)Pericarp
- b)Seed coat
- c)Endosperm
- d)Cotyledon
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The part of the fruit that develops from the ovary wall is called__________.
a)
Pericarp
b)
Seed coat
c)
Endosperm
d)
Cotyledon

|
Stepway Academy answered |
The pericarp is the part of the fruit that develops from the ovary wall. After fertilization, the ovary undergoes changes and develops into a mature fruit. The pericarp consists of three layers: the exocarp, mesocarp, and endocarp.
So the correct answer is A
So the correct answer is A
A 60 HP electric motor lifts an elevator having a maximum total load capacity of 2000 kg. If the frictional force on the elevator is 4000 N, the speed of the elevator at full load is close to: (1 HP = 746 W, g = 10 ms-2)- a)1.5 ms-1
- b)1.9 ms-1
- c)1.7 ms-1
- d)2.0 ms-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A 60 HP electric motor lifts an elevator having a maximum total load capacity of 2000 kg. If the frictional force on the elevator is 4000 N, the speed of the elevator at full load is close to: (1 HP = 746 W, g = 10 ms-2)
a)
1.5 ms-1
b)
1.9 ms-1
c)
1.7 ms-1
d)
2.0 ms-1
|
|
Sagar Choudhary answered |
Given Data
- Power of the motor: 60 HP
- Load capacity: 2000 kg
- Frictional force: 4000 N
- Acceleration due to gravity (g): 10 m/s²
- Conversion: 1 HP = 746 W
Step 1: Calculate the Power in Watts
- Total power of the motor in watts:
- 60 HP x 746 W/HP = 44760 W
Step 2: Calculate the Weight of the Elevator
- Total weight (W) of the elevator (including the load):
- W = mass x g
- W = 2000 kg x 10 m/s² = 20000 N
Step 3: Determine the Net Force Acting on the Elevator
- Net force (F_net) is calculated as:
- F_net = Power / Speed
- However, the total force also includes the frictional force:
- F_net = Weight + Friction
- F_net = 20000 N + 4000 N = 24000 N
Step 4: Calculate the Speed of the Elevator
- We know that Power = Force x Speed. Rearranging gives:
- Speed = Power / Force
- Here, Force = F_net = 24000 N
- Speed = 44760 W / 24000 N = 1.865 m/s, which rounds to approximately 1.9 m/s.
Conclusion
The speed of the elevator at full load, considering the friction, is close to 1.9 m/s, confirming that option 'B' is the correct answer.
- Power of the motor: 60 HP
- Load capacity: 2000 kg
- Frictional force: 4000 N
- Acceleration due to gravity (g): 10 m/s²
- Conversion: 1 HP = 746 W
Step 1: Calculate the Power in Watts
- Total power of the motor in watts:
- 60 HP x 746 W/HP = 44760 W
Step 2: Calculate the Weight of the Elevator
- Total weight (W) of the elevator (including the load):
- W = mass x g
- W = 2000 kg x 10 m/s² = 20000 N
Step 3: Determine the Net Force Acting on the Elevator
- Net force (F_net) is calculated as:
- F_net = Power / Speed
- However, the total force also includes the frictional force:
- F_net = Weight + Friction
- F_net = 20000 N + 4000 N = 24000 N
Step 4: Calculate the Speed of the Elevator
- We know that Power = Force x Speed. Rearranging gives:
- Speed = Power / Force
- Here, Force = F_net = 24000 N
- Speed = 44760 W / 24000 N = 1.865 m/s, which rounds to approximately 1.9 m/s.
Conclusion
The speed of the elevator at full load, considering the friction, is close to 1.9 m/s, confirming that option 'B' is the correct answer.
A 50.0-kg marathon runner runs up the stairs to the top of a 443-m-tall Tower. To lift herself to the top in 15.0 minutes, what must be her average power output?- a)241 W
- b)201 W
- c)221 W
- d)261 W
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A 50.0-kg marathon runner runs up the stairs to the top of a 443-m-tall Tower. To lift herself to the top in 15.0 minutes, what must be her average power output?
a)
241 W
b)
201 W
c)
221 W
d)
261 W
|
|
Nishanth Saini answered |
Understanding the Problem
To find the average power output of the marathon runner, we need to calculate the work done against gravity and then divide it by the time taken.
Step 1: Calculate the Work Done
- The work done (W) against gravity can be calculated using the formula:
- W = m * g * h
- Where:
- m = mass of the runner = 50.0 kg
- g = acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s²
- h = height of the tower = 443 m
- Substituting the values:
- W = 50.0 kg * 9.81 m/s² * 443 m
- W ≈ 217,791.5 J (joules)
Step 2: Calculate the Time Taken
- The time taken (t) is given as 15.0 minutes, which we need to convert into seconds:
- t = 15.0 min * 60 s/min = 900 s
Step 3: Calculate Average Power Output
- Average power (P) can be calculated using the formula:
- P = W / t
- Substituting the values:
- P = 217,791.5 J / 900 s
- P ≈ 241 W (watts)
Conclusion
Thus, the average power output of the marathon runner while running up the stairs to the top of the tower is approximately 241 watts, which corresponds to option 'A'. This value reflects the energy expended per unit time while performing the work of lifting her own body weight against gravity.
To find the average power output of the marathon runner, we need to calculate the work done against gravity and then divide it by the time taken.
Step 1: Calculate the Work Done
- The work done (W) against gravity can be calculated using the formula:
- W = m * g * h
- Where:
- m = mass of the runner = 50.0 kg
- g = acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s²
- h = height of the tower = 443 m
- Substituting the values:
- W = 50.0 kg * 9.81 m/s² * 443 m
- W ≈ 217,791.5 J (joules)
Step 2: Calculate the Time Taken
- The time taken (t) is given as 15.0 minutes, which we need to convert into seconds:
- t = 15.0 min * 60 s/min = 900 s
Step 3: Calculate Average Power Output
- Average power (P) can be calculated using the formula:
- P = W / t
- Substituting the values:
- P = 217,791.5 J / 900 s
- P ≈ 241 W (watts)
Conclusion
Thus, the average power output of the marathon runner while running up the stairs to the top of the tower is approximately 241 watts, which corresponds to option 'A'. This value reflects the energy expended per unit time while performing the work of lifting her own body weight against gravity.
In an Inelastic Collision,- a)the total kinetic energy of the system is the same after the collision as before
- b)the total kinetic energy of the system is the zero after the collision.
- c)the total kinetic energy after the collision is less than before the collision
- d)the total kinetic energy of the system is greater than the total kinetic energy before
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In an Inelastic Collision,
a)
the total kinetic energy of the system is the same after the collision as before
b)
the total kinetic energy of the system is the zero after the collision.
c)
the total kinetic energy after the collision is less than before the collision
d)
the total kinetic energy of the system is greater than the total kinetic energy before
|
|
Isha Khanna answered |
Understanding Inelastic Collisions
Inelastic collisions are a fundamental concept in physics, particularly in mechanics. Here's an explanation of why the correct answer is option 'C'.
Definition of Inelastic Collision
- An inelastic collision occurs when two objects collide and stick together or deform.
- Unlike elastic collisions, kinetic energy is not conserved in inelastic collisions.
Total Kinetic Energy Before and After
- In an inelastic collision, the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is less than the total kinetic energy before the collision.
- This loss of kinetic energy is transformed into other forms of energy, such as heat, sound, or deformation of the colliding bodies.
Why Option 'C' is Correct
- Kinetic energy is a measure of motion. During an inelastic collision, some of this energy is lost due to factors like:
- Deformation of the objects
- Generation of heat
- Sound produced during the collision
- Therefore, option 'C' accurately states that the total kinetic energy after the collision is less than before.
Examples of Inelastic Collisions
- Car accidents where vehicles crumple upon impact.
- A football colliding with a player’s foot and losing speed after the kick.
Conclusion
In summary, inelastic collisions result in a decrease in the total kinetic energy of the system, making option 'C' the correct choice. Understanding this concept is crucial for solving problems related to momentum and energy in physics, especially in contexts like NEET examinations.
Inelastic collisions are a fundamental concept in physics, particularly in mechanics. Here's an explanation of why the correct answer is option 'C'.
Definition of Inelastic Collision
- An inelastic collision occurs when two objects collide and stick together or deform.
- Unlike elastic collisions, kinetic energy is not conserved in inelastic collisions.
Total Kinetic Energy Before and After
- In an inelastic collision, the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is less than the total kinetic energy before the collision.
- This loss of kinetic energy is transformed into other forms of energy, such as heat, sound, or deformation of the colliding bodies.
Why Option 'C' is Correct
- Kinetic energy is a measure of motion. During an inelastic collision, some of this energy is lost due to factors like:
- Deformation of the objects
- Generation of heat
- Sound produced during the collision
- Therefore, option 'C' accurately states that the total kinetic energy after the collision is less than before.
Examples of Inelastic Collisions
- Car accidents where vehicles crumple upon impact.
- A football colliding with a player’s foot and losing speed after the kick.
Conclusion
In summary, inelastic collisions result in a decrease in the total kinetic energy of the system, making option 'C' the correct choice. Understanding this concept is crucial for solving problems related to momentum and energy in physics, especially in contexts like NEET examinations.
The bond enthalpy of ___________ molecule is 435.8 kJ mol-1.- a)Hydrogen
- b)Oxygen
- c)Nitrogen
- d)Helium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The bond enthalpy of ___________ molecule is 435.8 kJ mol-1.
a)
Hydrogen
b)
Oxygen
c)
Nitrogen
d)
Helium
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The amount of energy that is required to break a chemical bond in a molecule into individual atoms is known as bond enthalpy. 435.8 kJ mol-1 is required to dissociate a hydrogen molecule into two hydrogen atoms.
Which of the following is not a homonuclear diatomic molecule?- a)H2
- b)N2
- c)O2
- d)HCl
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a homonuclear diatomic molecule?
a)
H2
b)
N2
c)
O2
d)
HCl
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
The molecule that is formed from the same element is known as a homonuclear molecule and the molecule that is made up of 2 atoms is called a diatomic molecule. But HCl is not a homonuclear diatomic molecule as it has different atoms.
Which type of bond is present between hydrogens in hydrogen molecule?- a)Sigma bond
- b)Pi bond
- c)Ionic bond
- d)Metallic bond
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of bond is present between hydrogens in hydrogen molecule?
a)
Sigma bond
b)
Pi bond
c)
Ionic bond
d)
Metallic bond
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
The head-on or end to end type of overlapping is present in sigma bond. A sigma bond is a type of covalent bond. It may also be called an axial overlap. In case of the hydrogen molecule, its s-s overlapping.
S.I unit of power is- a)Angstrom
- b)Joule
- c)Newton
- d)Watt
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
S.I unit of power is
a)
Angstrom
b)
Joule
c)
Newton
d)
Watt

|
Muskaan Mishra answered |
Explanation:The SI unit of power, equivalent to one joule per second, corresponding to the rate of consumption of energy (Work done).
A __________ overlap doesn’t result in the formation of a bond.- a)positive
- b)negative
- c)zero
- d)rational
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A __________ overlap doesn’t result in the formation of a bond.
a)
positive
b)
negative
c)
zero
d)
rational
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Zero overlap means that the orbitals don’t overlap at all. When there is no overlapping the bond formation doesn’t occur. As we all know that the extent of overlapping is dependent on the strength of the bond.
s-orbitals are nondirectional because of- a)spherical symmetry
- b)their small size
- c)being first orbital
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
s-orbitals are nondirectional because of
a)
spherical symmetry
b)
their small size
c)
being first orbital
d)
All of the above
|
|
Neha Chakraborty answered |
Explanation:
S-orbitals are the spherical-shaped orbitals and are designated as 1s, 2s, 3s, and so on. They are present in the first energy level and other higher energy levels.
The s-orbitals are nondirectional because of the following reasons:
Spherical Symmetry:
- The s-orbitals are spherical in shape and have the same probability of finding an electron in any direction from the nucleus.
- Due to this, the electrons in s-orbitals are equally distributed in all the directions around the nucleus.
- Thus, s-orbitals are considered to be nondirectional in nature.
Small Size:
- The s-orbitals are smaller in size as compared to the p, d, and f orbitals.
- Due to their small size, they do not have any specific direction of orientation.
Being First Orbital:
- The s-orbitals are the first orbitals to be filled in an atom.
- As they are the first to be filled, they do not have any other orbitals to interact with, which makes them nondirectional.
Conclusion:
Hence, we can conclude that the s-orbitals are nondirectional due to their spherical symmetry, small size, and being the first orbital to be filled in an atom.
S-orbitals are the spherical-shaped orbitals and are designated as 1s, 2s, 3s, and so on. They are present in the first energy level and other higher energy levels.
The s-orbitals are nondirectional because of the following reasons:
Spherical Symmetry:
- The s-orbitals are spherical in shape and have the same probability of finding an electron in any direction from the nucleus.
- Due to this, the electrons in s-orbitals are equally distributed in all the directions around the nucleus.
- Thus, s-orbitals are considered to be nondirectional in nature.
Small Size:
- The s-orbitals are smaller in size as compared to the p, d, and f orbitals.
- Due to their small size, they do not have any specific direction of orientation.
Being First Orbital:
- The s-orbitals are the first orbitals to be filled in an atom.
- As they are the first to be filled, they do not have any other orbitals to interact with, which makes them nondirectional.
Conclusion:
Hence, we can conclude that the s-orbitals are nondirectional due to their spherical symmetry, small size, and being the first orbital to be filled in an atom.
The strength of covalent ___________ extent of overlapping of orbitals.- a)may be or may not be related
- b)is independent on
- c)is dependent on
- d)is not related to
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The strength of covalent ___________ extent of overlapping of orbitals.
a)
may be or may not be related
b)
is independent on
c)
is dependent on
d)
is not related to
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
As per the concept of valence bond theory, the partial merging of atomic orbitals id knowns as overlapping. The extent of overlapping is directly proportional to the strength of the covalent bond, i.e. it is dependent.
A positive overlap is same as ________- a)out-phase overlap
- b)negative overlap
- c)zero overlap
- d)in-phase overlap
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A positive overlap is same as ________
a)
out-phase overlap
b)
negative overlap
c)
zero overlap
d)
in-phase overlap
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
A positive overlap results in bond formation. When 2 p-orbitals are in phase, both the positive lobes overlap, thus creating a positive overlap and result in the bond formation, thus it is called in-phase overlap.
A stone of mass m tied to a string is being whirled in a vertical circle with a uniform speed. The tension in the string is- a)the same throughout the motion
- b)minimum at the highest position of the circular path
- c)minimum at the lowest position of the circular path
- d)minimum when the rope is in the horizontal position
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A stone of mass m tied to a string is being whirled in a vertical circle with a uniform speed. The tension in the string is
a)
the same throughout the motion
b)
minimum at the highest position of the circular path
c)
minimum at the lowest position of the circular path
d)
minimum when the rope is in the horizontal position
|
|
Mahi Nair answered |
Understanding Tension in Circular Motion
When a stone of mass m is tied to a string and whirled in a vertical circle, the tension in the string varies based on the position of the stone in the circle.
Key Factors Affecting Tension
- Centripetal Force Requirement: The stone requires a centripetal force to maintain its circular motion, which is provided by the tension in the string and the weight of the stone (mg).
- Position of the Stone: The tension is influenced by the gravitational force acting on the stone and the required centripetal force at different positions in the circle.
Minimum Tension at the Highest Position
- At the Highest Point:
- The forces acting on the stone are the tension (T) and the weight (mg), both acting downwards.
- The net force providing centripetal acceleration is (T + mg).
- Therefore, T + mg = mv^2, leading to T = mv^2 - mg.
- At this position, tension is at its minimum because it is supplemented by the weight of the stone.
- At the Lowest Point:
- The forces acting are the tension (T) acting upwards and the weight (mg) acting downwards.
- The net centripetal force is T - mg, which means T = mv^2 + mg.
- Here, tension is maximum as it has to overcome gravity as well as provide the necessary centripetal force.
Conclusion
- Horizontal Position: The tension is neither at its maximum nor minimum but is influenced by horizontal forces.
Thus, the correct answer is that the tension in the string is minimum at the highest position of the circular path.
When a stone of mass m is tied to a string and whirled in a vertical circle, the tension in the string varies based on the position of the stone in the circle.
Key Factors Affecting Tension
- Centripetal Force Requirement: The stone requires a centripetal force to maintain its circular motion, which is provided by the tension in the string and the weight of the stone (mg).
- Position of the Stone: The tension is influenced by the gravitational force acting on the stone and the required centripetal force at different positions in the circle.
Minimum Tension at the Highest Position
- At the Highest Point:
- The forces acting on the stone are the tension (T) and the weight (mg), both acting downwards.
- The net force providing centripetal acceleration is (T + mg).
- Therefore, T + mg = mv^2, leading to T = mv^2 - mg.
- At this position, tension is at its minimum because it is supplemented by the weight of the stone.
- At the Lowest Point:
- The forces acting are the tension (T) acting upwards and the weight (mg) acting downwards.
- The net centripetal force is T - mg, which means T = mv^2 + mg.
- Here, tension is maximum as it has to overcome gravity as well as provide the necessary centripetal force.
Conclusion
- Horizontal Position: The tension is neither at its maximum nor minimum but is influenced by horizontal forces.
Thus, the correct answer is that the tension in the string is minimum at the highest position of the circular path.
In which case is the work done zero?- a)Force and displacement are at an angle of 75o
- b)Force and displacement are at an angle of 45o
- c)Force and displacement are in the same direction
- d)Force and displacement are perpendicular to each other
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which case is the work done zero?
a)
Force and displacement are at an angle of 75o
b)
Force and displacement are at an angle of 45o
c)
Force and displacement are in the same direction
d)
Force and displacement are perpendicular to each other

|
Simran Mishra answered |
Explanation:Work done is given as
W = Fdcosθ
Here θ is the angle between F and d if both are perpendicular then θ = 90 degree so cosθ = 0 and thus work done is 0 .
Which part of a flower contains the female reproductive organs?- a)Stamen
- b)Pistil
- c)Petal
- d)Sepal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of a flower contains the female reproductive organs?
a)
Stamen
b)
Pistil
c)
Petal
d)
Sepal

|
Stepway Academy answered |
The pistil, also known as the carpel, is the female reproductive organ of a flower. It is located in the center of the flower and consists of several parts. The main parts of the pistil include the stigma, style, and ovary.
So the correct answer is B
So the correct answer is B
Given below is the plot of a potential energy function U(x) for a system, in which a particle is in one dimensional motion, while a conservative force F(x) acts on it. Suppose that Emech = 8 J, the incorrect statement for this system is:
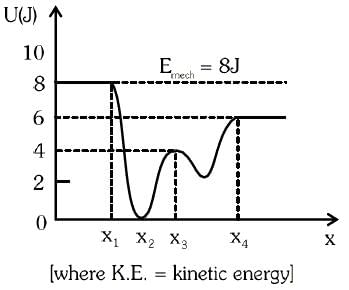
- a)At x < x1, K.E. is smallest and the particle is moving at the slowed speed.
- b)At x = x2, K.E. is greatest and the particle is moving at the fastest speed.
- c)At x = x3, K.E. = 4 J.
- d)At x > x4, K.E. is constant throughout the region.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below is the plot of a potential energy function U(x) for a system, in which a particle is in one dimensional motion, while a conservative force F(x) acts on it. Suppose that Emech = 8 J, the incorrect statement for this system is:


a)
At x < x1, K.E. is smallest and the particle is moving at the slowed speed.
b)
At x = x2, K.E. is greatest and the particle is moving at the fastest speed.
c)
At x = x3, K.E. = 4 J.
d)
At x > x4, K.E. is constant throughout the region.

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Emech. = 8 J
(A) At x < x1, U = constant = 8 J
K = Emech - U = 8 - 8 = 0 J
The particle is at rest.
(A) At x < x1, U = constant = 8 J
K = Emech - U = 8 - 8 = 0 J
The particle is at rest.
(B) At x = x2, U = 0 ⇒ Emech. = K = 8 J
K.E. is greatest and the particle is moving at fastest speed.
K.E. is greatest and the particle is moving at fastest speed.
(C) At x = x3, U = 4 J
U + K = 8 J
K = 4 J
U + K = 8 J
K = 4 J
Hence the incorrect statement is : at x < x1, K.E is smallest and the particle is moving at the slowest speed.
(D) At x > x4, U = constant = 6 J
K = Emech. - U = 2 J = constant
K = Emech. - U = 2 J = constant
In Monocotyledonous seeds, the food is stored in the_______.- a)Cotyledons
- b)Endosperm
- c)Seed coat
- d)Embryo axis
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In Monocotyledonous seeds, the food is stored in the_______.
a)
Cotyledons
b)
Endosperm
c)
Seed coat
d)
Embryo axis

|
Bs Academy answered |
In Monocots, during seed development, the endosperm is formed. The endosperm is a tissue that surrounds the embryo and serves as a nutrient reserve. It contains stored carbohydrates, proteins, oils, and other nutrients necessary for the growth and development of the embryo after germination.
So the correct answer is B
So the correct answer is B
A particle of mass 1 kg is hanging from a spring of force constant 100 Nm-1. The mass is pulled slightly downward and released, so that it executes free simple harmonic motion with time period T. The time when the kinetic energy and potential energy of the system will become equal is 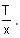 The value of x is _______. (in integers)
The value of x is _______. (in integers)- a)5
- b)6
- c)7
- d)8
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle of mass 1 kg is hanging from a spring of force constant 100 Nm-1. The mass is pulled slightly downward and released, so that it executes free simple harmonic motion with time period T. The time when the kinetic energy and potential energy of the system will become equal is 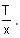 The value of x is _______. (in integers)
The value of x is _______. (in integers)
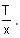 The value of x is _______. (in integers)
The value of x is _______. (in integers)a)
5
b)
6
c)
7
d)
8

|
Ambition Institute answered |
The time when the kinetic energy and potential energy of the system become equal can be determined as follows:
The condition for equal kinetic and potential energy is given by:
Kinetic Energy (KE) = Potential Energy (PE)
Kinetic Energy (KE) = Potential Energy (PE)
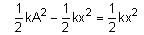
⇒ A2 = 2x2
The displacement X is given by: X = A sin(ωt)
Solving these equations,
A2 = 2x2
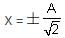
X = A sinωt
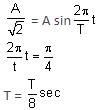
x = 8 sec
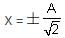
X = A sinωt
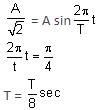
x = 8 sec
A particle experiences a variable force 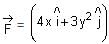 in a horizontal x-y plane. Assume distance in meters and force in newton. If the particle moves from point (1, 2) to point (2, 3) in the x-y plane; then kinetic energy changes by
in a horizontal x-y plane. Assume distance in meters and force in newton. If the particle moves from point (1, 2) to point (2, 3) in the x-y plane; then kinetic energy changes by- a)50.0 J
- b)12.5 J
- c)25.0 J
- d)0 J
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle experiences a variable force 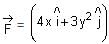 in a horizontal x-y plane. Assume distance in meters and force in newton. If the particle moves from point (1, 2) to point (2, 3) in the x-y plane; then kinetic energy changes by
in a horizontal x-y plane. Assume distance in meters and force in newton. If the particle moves from point (1, 2) to point (2, 3) in the x-y plane; then kinetic energy changes by
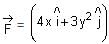 in a horizontal x-y plane. Assume distance in meters and force in newton. If the particle moves from point (1, 2) to point (2, 3) in the x-y plane; then kinetic energy changes by
in a horizontal x-y plane. Assume distance in meters and force in newton. If the particle moves from point (1, 2) to point (2, 3) in the x-y plane; then kinetic energy changes bya)
50.0 J
b)
12.5 J
c)
25.0 J
d)
0 J

|
Top Rankers answered |
The change in kinetic energy of a particle moving in a horizontal plane can be determined using the work-energy theorem. The theorem states that the work done by a force on a particle equals the change in its kinetic energy. We Know that,
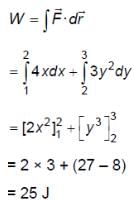
The structure that develops into the seed after fertilization is the__________.- a)Ovary
- b)Anther
- c)Ovule
- d)Stigma
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The structure that develops into the seed after fertilization is the__________.
a)
Ovary
b)
Anther
c)
Ovule
d)
Stigma

|
Bs Academy answered |
Once fertilization occurs, the ovule undergoes various changes and develops into a seed. The fertilized ovule contains an embryo, which is the future plant, and it is surrounded by protective layers such as the seed coat. The ovule provides nourishment to the developing embryo until it matures into a seed.
So the correct answer is C
So the correct answer is C
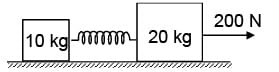
Two masses 10 kg and 20 kg are connected by a massless spring. A force of 200 N acts on 20 kg mass. At the instant when the 10 kg mass has an acceleration 12 m/s2 the energy stored in the spring (k = 2400 N/m) will be
- a)3J
- b)5J
- c)30J
- d)0.5J
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two masses 10 kg and 20 kg are connected by a massless spring. A force of 200 N acts on 20 kg mass. At the instant when the 10 kg mass has an acceleration 12 m/s2 the energy stored in the spring (k = 2400 N/m) will be


a)
3J
b)
5J
c)
30J
d)
0.5J

|
EduRev NEET answered |
F = 10× 12 = 120 N
F = kx = 2400 x
∴ x = 1/20
Energy stored in the spring E = 1/2 Kx2
= 1/2 × 2400 × 1/400 = 3J
F = kx = 2400 x
∴ x = 1/20
Energy stored in the spring E = 1/2 Kx2
= 1/2 × 2400 × 1/400 = 3J
The oxygen molecule is paramagnetic. It can be explained by- a)Resonance
- b)Hybridisation
- c)Valence bond theory
- d)Molecular orbital theory
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxygen molecule is paramagnetic. It can be explained by
a)
Resonance
b)
Hybridisation
c)
Valence bond theory
d)
Molecular orbital theory
|
|
Megha Joshi answered |
Explanation:
Molecular Orbital Theory:
The molecular orbital theory (MO theory) is a model used to explain the electronic structure of molecules. According to this theory, electrons in a molecule are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms but rather exist in molecular orbitals that are spread over the entire molecule. These molecular orbitals are formed by the combination of atomic orbitals from the participating atoms.
Paramagnetism:
Paramagnetism refers to the property of a substance to be attracted to an external magnetic field. It occurs when there are unpaired electrons in the molecular orbitals of a substance.
Oxygen Molecule:
The oxygen molecule (O2) consists of two oxygen atoms, each with six valence electrons. In the ground state, these electrons occupy the 2s and 2p orbitals of the oxygen atoms.
Molecular Orbital Diagram:
The molecular orbital diagram for O2 can be constructed by combining the atomic orbitals of the oxygen atoms. The 2s orbitals of the oxygen atoms combine to form a sigma (σ) bonding orbital and a sigma* (σ*) antibonding orbital. Similarly, the 2p orbitals combine to form two pi (π) bonding orbitals and two pi* (π*) antibonding orbitals.
Electronic Configuration:
In the ground state of O2, the electrons fill the molecular orbitals according to Hund's rule and the aufbau principle. The sigma bonding orbital is filled with two electrons of opposite spin, followed by the two pi bonding orbitals, each filled with two electrons. This gives a total of six electrons in the bonding orbitals and two electrons in the antibonding orbitals.
Paramagnetic Nature:
The paramagnetic nature of O2 can be explained by the presence of two unpaired electrons in the pi* antibonding orbitals. These unpaired electrons have parallel spins, which make the oxygen molecule attracted to an external magnetic field. Therefore, O2 is considered paramagnetic.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the paramagnetic nature of the oxygen molecule can be explained by the molecular orbital theory. The presence of two unpaired electrons in the pi* antibonding orbitals leads to the attraction of O2 to an external magnetic field.
Molecular Orbital Theory:
The molecular orbital theory (MO theory) is a model used to explain the electronic structure of molecules. According to this theory, electrons in a molecule are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms but rather exist in molecular orbitals that are spread over the entire molecule. These molecular orbitals are formed by the combination of atomic orbitals from the participating atoms.
Paramagnetism:
Paramagnetism refers to the property of a substance to be attracted to an external magnetic field. It occurs when there are unpaired electrons in the molecular orbitals of a substance.
Oxygen Molecule:
The oxygen molecule (O2) consists of two oxygen atoms, each with six valence electrons. In the ground state, these electrons occupy the 2s and 2p orbitals of the oxygen atoms.
Molecular Orbital Diagram:
The molecular orbital diagram for O2 can be constructed by combining the atomic orbitals of the oxygen atoms. The 2s orbitals of the oxygen atoms combine to form a sigma (σ) bonding orbital and a sigma* (σ*) antibonding orbital. Similarly, the 2p orbitals combine to form two pi (π) bonding orbitals and two pi* (π*) antibonding orbitals.
Electronic Configuration:
In the ground state of O2, the electrons fill the molecular orbitals according to Hund's rule and the aufbau principle. The sigma bonding orbital is filled with two electrons of opposite spin, followed by the two pi bonding orbitals, each filled with two electrons. This gives a total of six electrons in the bonding orbitals and two electrons in the antibonding orbitals.
Paramagnetic Nature:
The paramagnetic nature of O2 can be explained by the presence of two unpaired electrons in the pi* antibonding orbitals. These unpaired electrons have parallel spins, which make the oxygen molecule attracted to an external magnetic field. Therefore, O2 is considered paramagnetic.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the paramagnetic nature of the oxygen molecule can be explained by the molecular orbital theory. The presence of two unpaired electrons in the pi* antibonding orbitals leads to the attraction of O2 to an external magnetic field.
In an elastic collision- a)the total kinetic energy of the system is less than the total kinetic energy before
- b)the total kinetic energy of the system is the zero after the collision.
- c)the total kinetic energy of the system is the same after the collision as before.
- d)the total kinetic energy of the system is greater than the total kinetic energy before
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In an elastic collision
a)
the total kinetic energy of the system is less than the total kinetic energy before
b)
the total kinetic energy of the system is the zero after the collision.
c)
the total kinetic energy of the system is the same after the collision as before.
d)
the total kinetic energy of the system is greater than the total kinetic energy before

|
Mansi Chopra answered |
Explanation:kinetic energy is transferred to other forms of energy—such as thermal energy, potential energy, and sound—during the collision process. After collision if recovery of kinetic energy is 100% then it is called elastic collision.So that in an elastic collision the total kinetic energy of the system is the same after the collision as before.
Chapter doubts & questions for June Week 4 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of June Week 4 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily