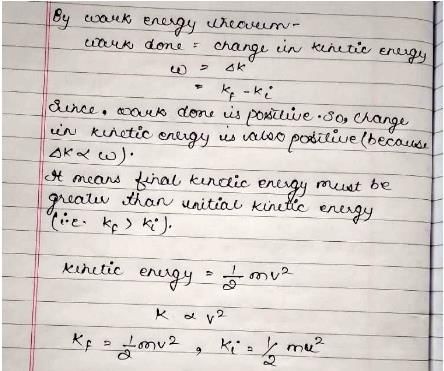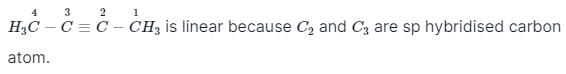All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of July Week 1 for NEET Exam
Hybridisation of Acetylene is- a)sp
- b)sp2
- c)sp3
- d)dsp2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Hybridisation of Acetylene is
a)
sp
b)
sp2
c)
sp3
d)
dsp2
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Since acetylene is made up of triple bond. So the hybridization of carbon in acetylene is sp.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-11) This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Assuming that Hund's rule is violated, the bond order and magnetic nature of the diatomic molecule B2 is
- a)1 and diamagnetic
- b)0 and diamagnetic
- c)1 and paramagnetic
- d)0 and paramagnetic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-11) This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Assuming that Hund's rule is violated, the bond order and magnetic nature of the diatomic molecule B2 is
a)
1 and diamagnetic
b)
0 and diamagnetic
c)
1 and paramagnetic
d)
0 and paramagnetic
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |

Bicarpellary, syncarpous ovary with axile placentation is seen in the plants of family_______.
- a)Malvaceae
- b)Asteraceae
- c)Solanaceae
- d)Caesalpiniaceae
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Bicarpellary, syncarpous ovary with axile placentation is seen in the plants of family_______.
a)
Malvaceae
b)
Asteraceae
c)
Solanaceae
d)
Caesalpiniaceae
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Solanaceae or nightshades are an economically important family of flowering plants. The family ranges from annual and perennial herbs to vines, epiphytes, shrubs and trees.
In Solanaceae, the gynoecium is Bicarpellary, syncarpous, ovary superior, bilocular, axile placentation, placenta swollen, many ovules in each locule, ovary obliquely placed, style simple; stigma bifid or capitate.
So, the correct answer is 'Solanaceae'.
Two moving particle P and Q are 10 m apart at a certain instant. The velocity of P is 8m/s making an angle 30° with the line joining P and Q and that of Q is 6m/s making an angle 30° with PQ as shown in the figure. Then angular velocity of P with respect to Q is 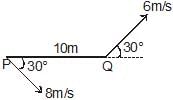
- a)Zero
- b)0.1 rad/sec
- c)0.4 rad/sec
- d)0.7 rad sec
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two moving particle P and Q are 10 m apart at a certain instant. The velocity of P is 8m/s making an angle 30° with the line joining P and Q and that of Q is 6m/s making an angle 30° with PQ as shown in the figure. Then angular velocity of P with respect to Q is
a)
Zero
b)
0.1 rad/sec
c)
0.4 rad/sec
d)
0.7 rad sec
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
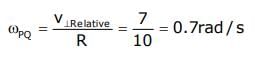
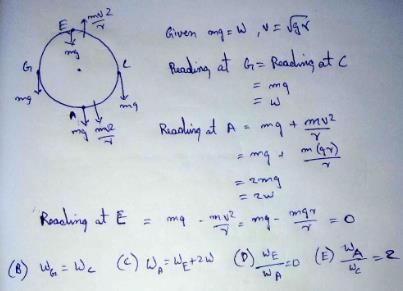
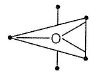
A machine, in an amusement park, consists of a cage at the end of one arm, hinged at O. The cage revolves along a vertical circle of radius r (ABCDEFGH) about its hinge O, at constant linear speedv = 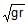 . The cage is so attached that the man of weight `w' standing on a weighing machine, inside the cage, is always vertical. Then which of the following is correct
. The cage is so attached that the man of weight `w' standing on a weighing machine, inside the cage, is always vertical. Then which of the following is correct
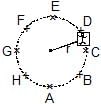
- a)The reading of his weight on the machine is the same at all positions
- b)The weight reading at A is greater than the weight reading at E by 2 w.
- c)The weight reading at G = w
- d)The ratio of the weight reading at E to that at A=0
- e)The ratio of the weight reading at A to that at C=2
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D,E'. Can you explain this answer?
A machine, in an amusement park, consists of a cage at the end of one arm, hinged at O. The cage revolves along a vertical circle of radius r (ABCDEFGH) about its hinge O, at constant linear speed
v = 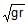 . The cage is so attached that the man of weight `w' standing on a weighing machine, inside the cage, is always vertical. Then which of the following is correct
. The cage is so attached that the man of weight `w' standing on a weighing machine, inside the cage, is always vertical. Then which of the following is correct

a)
The reading of his weight on the machine is the same at all positions
b)
The weight reading at A is greater than the weight reading at E by 2 w.
c)
The weight reading at G = w
d)
The ratio of the weight reading at E to that at A=0
e)
The ratio of the weight reading at A to that at C=2

|
Crafty Classes answered |
No work is done by a force on an object if- a)The force is always perpendicular to its velocity
- b)The force is always perpendicular to its acceleration
- c)The object is stationary but the point of application of the force moves on the object.
- d)The object moves in such a way that the point of application of the force remains fixed.
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
No work is done by a force on an object if
a)
The force is always perpendicular to its velocity
b)
The force is always perpendicular to its acceleration
c)
The object is stationary but the point of application of the force moves on the object.
d)
The object moves in such a way that the point of application of the force remains fixed.
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Work done = f.ds
So on perpendicular application for product becomes zero so no work is done
So on perpendicular application for product becomes zero so no work is done
Hydrogen bonds are formed in many compounds e.g., H2O, HF, NH3 . The boiling point of such compounds depends to a large extent on the strength of hydrogen bond and the number of hydrogen bonds. The correct decreasing order of the boiling points of above compounds is :
- a)HF > H2O > NH3
- b)H2O > HF > NH3
- c)NH3 > HF > H2O
- d)NH3 > H2O > HF
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen bonds are formed in many compounds e.g., H2O, HF, NH3 . The boiling point of such compounds depends to a large extent on the strength of hydrogen bond and the number of hydrogen bonds. The correct decreasing order of the boiling points of above compounds is :
a)
HF > H2O > NH3
b)
H2O > HF > NH3
c)
NH3 > HF > H2O
d)
NH3 > H2O > HF
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
H2O>HF>NH3
Strength of hydrogen bonding depends on the size and electronegativity of the atom.
Smaller the size of the atom, greater is the electronegativity and hence stronger is the H−bonding. Thus, the order of strength of H-bonding is H...F>H...O>H...N.
But each HF molecule is linked only to two other HF molecules while each H2O molecule is linked to four other H2O molecules through H−bonding.
Hence, the decreasing order of boiling points is H2O>HF>NH3.
In which one of the following species the central atom has the type of hybridisation which si not the same as that present in the other three? - a)SF4
- b)I3-
- c)SbCl52-
- d)PCl5
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which one of the following species the central atom has the type of hybridisation which si not the same as that present in the other three?
a)
SF4
b)
I3-
c)
SbCl52-
d)
PCl5
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Molecules having the same number of hybrid orbitals, have same hybridisation and number of hybrid oebitals.
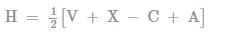
where,
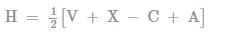
where,
V= number of valance electrons of central atom
X = number of monovalent atoms
C= charge on cation
A = charge on anion
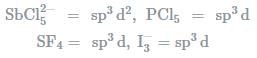
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of the Solanaceae family?- a)Taproot system
- b)Climbing stems
- c)Pinnately compound leaves
- d)Epipetalous anthers
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of the Solanaceae family?
a)
Taproot system
b)
Climbing stems
c)
Pinnately compound leaves
d)
Epipetalous anthers

|
Manohar Babu answered |
Ncert page 80 epipetalous for solanaceae (to be frank, epiphyllous is regarding to parianth but not to corolla)
A box of mass m is released from rest at position on the frictionless curved track shown. It slides a distance d along the track in time t to reach position 2, dropping a vertical distance h. Let v and a be the instantaneous speed and instantaneous acceleration, respectively, of the box at position 2. Which of the following equations is valid for this situation? 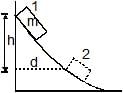
- a)h = vt
- b)h = (1/2)gt2
- c)mgh = (1/2)mv2
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A box of mass m is released from rest at position on the frictionless curved track shown. It slides a distance d along the track in time t to reach position 2, dropping a vertical distance h. Let v and a be the instantaneous speed and instantaneous acceleration, respectively, of the box at position 2. Which of the following equations is valid for this situation?
a)
h = vt
b)
h = (1/2)gt2
c)
mgh = (1/2)mv2
d)
none

|
Imk Pathsala answered |
According to the Work Energy Theorem,
Change in PE = Change in KE
So, mgh = ½ mv2
Hence C
Forum id- 1775160
For complete circle v = √(5gl)
mgh = ½mv2
So, h = 2.5R
Change in PE = Change in KE
So, mgh = ½ mv2
Hence C
Forum id- 1775160
For complete circle v = √(5gl)
mgh = ½mv2
So, h = 2.5R
A stone of mass of 16 kg is attached to a string 144 m long and is whirled in a horizontal smooth surface. The maximum tension the string can withstand is 16 newton. The maximum speed of revolution of the stone without breaking it, will be :- a)20 ms-1
- b)16 ms-1
- c)14 ms-1
- d)12 ms-1
Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
A stone of mass of 16 kg is attached to a string 144 m long and is whirled in a horizontal smooth surface. The maximum tension the string can withstand is 16 newton. The maximum speed of revolution of the stone without breaking it, will be :
a)
20 ms-1
b)
16 ms-1
c)
14 ms-1
d)
12 ms-1
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
T= (mv2max)/r
16 = (16 v2max)/144
v2max = 12 m/s
16 = (16 v2max)/144
v2max = 12 m/s
The minimum value of H required so that the particle makes a complete vertical circle is given by- a)5 R
- b)4 R
- c)2.5 R
- d)2 R
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The minimum value of H required so that the particle makes a complete vertical circle is given by
a)
5 R
b)
4 R
c)
2.5 R
d)
2 R
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
For complete circle v = √(5gl)
mgh = ½mv2
So, h = 2.5R
mgh = ½mv2
So, h = 2.5R
Which family is known for its plants with taproot system and includes herbs, shrubs, small trees, and climbers?- a)Solanaceae
- b)Fabaceae
- c)Liliaceae
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which family is known for its plants with taproot system and includes herbs, shrubs, small trees, and climbers?
a)
Solanaceae
b)
Fabaceae
c)
Liliaceae
d)
None of the above

|
Manohar Babu answered |
Ambiguity options fabaceae also show the same. hence both a and b is correct.
Which of the following statement is incorrect regarding NO2 molecule?- a)It has one unpaired electron is one of the sp2-hybridised orbital
- b)It is coloured due to unpaired electron
- c)It is deeply coloured in dimeric form
- d)Paramagnetic behaviour is lost in dimeric form
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is incorrect regarding NO2 molecule?
a)
It has one unpaired electron is one of the sp2-hybridised orbital
b)
It is coloured due to unpaired electron
c)
It is deeply coloured in dimeric form
d)
Paramagnetic behaviour is lost in dimeric form
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
NO2 molecule has unpaired electrons which are responsible for its brown colour and paramagnetic behavior.
Direction (Q. Nos. 12 and 14) This sectionis based on statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the code given below.Q. Statement I : BF3 molecule is planar but NF3 is pyramidal.Statement II : N atom is smaller than B.- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 12 and 14) This sectionis based on statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the code given below.
Q.
Statement I : BF3 molecule is planar but NF3 is pyramidal.
Statement II : N atom is smaller than B.
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
|
|
Amrita Choudhary answered |
Statement I : BF3 molecule is planar but NF3 is pyramidal.
Statement II : N atom is smaller than B.
The correct answer is option 'B', which states that both Statement I and Statement II are correct, but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I. Let's analyze each statement individually and then discuss the relationship between them.
Statement I explanation:
BF3 molecule is planar because it follows the VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory. According to this theory, the electron pairs around the central atom repel each other and try to get as far away as possible, resulting in a molecular shape that minimizes electron pair repulsion. In the case of BF3, the boron atom has three bonded pairs of electrons and no lone pair of electrons. The repulsion between these electron pairs causes them to arrange themselves in a trigonal planar geometry, resulting in a planar molecule.
NF3 molecule, on the other hand, is pyramidal because of the presence of a lone pair of electrons on the central nitrogen atom. The lone pair of electrons exerts greater repulsion compared to the bonded pairs of electrons, causing the molecular shape to deviate from the ideal tetrahedral arrangement. The three bonded pairs of electrons arrange themselves in a trigonal pyramid geometry, resulting in a pyramidal molecule.
Statement II explanation:
The statement says that the nitrogen atom is smaller than the boron atom. This is true because the atomic radius of nitrogen is smaller than that of boron. Atomic radius is defined as the distance between the nucleus of an atom and the outermost shell of electrons. As we move across a period in the periodic table from left to right, the atomic radius generally decreases. Nitrogen is located to the right of boron in the periodic table, so its atomic radius is smaller.
Relationship between Statement I and Statement II:
Statement II does not provide a direct explanation for why BF3 is planar and NF3 is pyramidal. The difference in molecular shape between these two molecules is primarily due to the presence or absence of a lone pair of electrons on the central atom rather than the size of the atom. The planarity of BF3 is a result of the absence of a lone pair, while the pyramidal shape of NF3 is a result of the presence of a lone pair. Therefore, while Statement II is true, it is not the correct explanation for the difference in molecular shape between BF3 and NF3.
Statement II : N atom is smaller than B.
The correct answer is option 'B', which states that both Statement I and Statement II are correct, but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I. Let's analyze each statement individually and then discuss the relationship between them.
Statement I explanation:
BF3 molecule is planar because it follows the VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory. According to this theory, the electron pairs around the central atom repel each other and try to get as far away as possible, resulting in a molecular shape that minimizes electron pair repulsion. In the case of BF3, the boron atom has three bonded pairs of electrons and no lone pair of electrons. The repulsion between these electron pairs causes them to arrange themselves in a trigonal planar geometry, resulting in a planar molecule.
NF3 molecule, on the other hand, is pyramidal because of the presence of a lone pair of electrons on the central nitrogen atom. The lone pair of electrons exerts greater repulsion compared to the bonded pairs of electrons, causing the molecular shape to deviate from the ideal tetrahedral arrangement. The three bonded pairs of electrons arrange themselves in a trigonal pyramid geometry, resulting in a pyramidal molecule.
Statement II explanation:
The statement says that the nitrogen atom is smaller than the boron atom. This is true because the atomic radius of nitrogen is smaller than that of boron. Atomic radius is defined as the distance between the nucleus of an atom and the outermost shell of electrons. As we move across a period in the periodic table from left to right, the atomic radius generally decreases. Nitrogen is located to the right of boron in the periodic table, so its atomic radius is smaller.
Relationship between Statement I and Statement II:
Statement II does not provide a direct explanation for why BF3 is planar and NF3 is pyramidal. The difference in molecular shape between these two molecules is primarily due to the presence or absence of a lone pair of electrons on the central atom rather than the size of the atom. The planarity of BF3 is a result of the absence of a lone pair, while the pyramidal shape of NF3 is a result of the presence of a lone pair. Therefore, while Statement II is true, it is not the correct explanation for the difference in molecular shape between BF3 and NF3.
NH4NO3 and NH4NO2 differ is
- a) hybridisation of N of the anion
- b) hybridisation of N of the cation and anion both
- c) decomposition product
- d) structure of the anion
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
NH4NO3 and NH4NO2 differ is
a)
hybridisation of N of the anionb)
hybridisation of N of the cation and anion bothc)
decomposition productd)
structure of the anion

|
Kritika Bajaj answered |
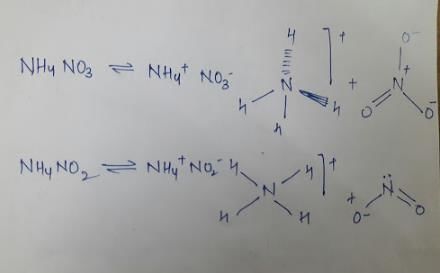
Hence we see that the two species differ in the hybridisation of Cation and anion, decomposition product and structure of anion.
The magnitude of displacement of a particle moving in a circle of radius a with constant angular speed w varies with time t as- a)2 a sin wt
- b)
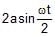
- c)2a cos wt
- d)
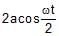
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The magnitude of displacement of a particle moving in a circle of radius a with constant angular speed w varies with time t as
a)
2 a sin wt
b)
c)
2a cos wt
d)
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
If a particle is moving with angular velocity=ω
Its angle of rotation is given by ωt
Now displacement= length of line AB
Position vector of a particle is given by
R =iacosωt + jasinωt
Ro=ai
displacement =R−Ro
=a(cosωt−1)i+asinωj
d=√[(a(cosωt-1))2+(asinω)2]
=a√(2(1-cosωt))=a√(2×2(sinωt/2)2)=2asinωt/2
Its angle of rotation is given by ωt
Now displacement= length of line AB
Position vector of a particle is given by
R =iacosωt + jasinωt
Ro=ai
displacement =R−Ro
=a(cosωt−1)i+asinωj
d=√[(a(cosωt-1))2+(asinω)2]
=a√(2(1-cosωt))=a√(2×2(sinωt/2)2)=2asinωt/2
The potential energy in joules of a particle of mass 1 kg moving in a plane is given by U = 3x + 4y, the position coordinates of the point being x and y, measured in meters. If the particle is initially at rest at (6, 4), then- a)Its acceleration is of magnitude 5 m/s2
- b)Its speed when it crosses the y-axis is 10 m/s
- c)It crosses the y-axis (x = 0) at y = _4
- d)It moves in a straight line passing through the origin (0, 0)
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
The potential energy in joules of a particle of mass 1 kg moving in a plane is given by U = 3x + 4y, the position coordinates of the point being x and y, measured in meters. If the particle is initially at rest at (6, 4), then
a)
Its acceleration is of magnitude 5 m/s2
b)
Its speed when it crosses the y-axis is 10 m/s
c)
It crosses the y-axis (x = 0) at y = _4
d)
It moves in a straight line passing through the origin (0, 0)
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
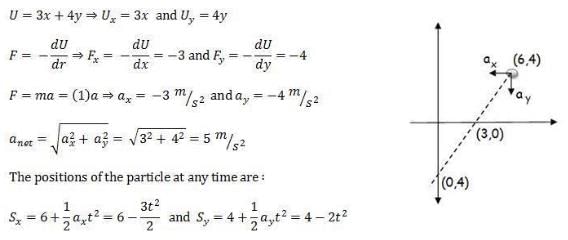
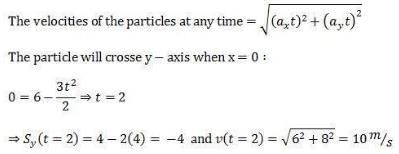 Similarly you can find that the particle crosses x - axis at (3, 0) with a velocity 7.07 m/s
Similarly you can find that the particle crosses x - axis at (3, 0) with a velocity 7.07 m/sWork done by force of friction- a)Can be zero
- b)Can be positive
- c)Can be negative
- d)Information insufficient
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Work done by force of friction
a)
Can be zero
b)
Can be positive
c)
Can be negative
d)
Information insufficient
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Since the motion of the body can be placed in the direction of friction, opposite to the direction of motion and even can not be placed in any motion.
So, Work done by force of friction can be zero, negative, and can be positive.
So, Work done by force of friction can be zero, negative, and can be positive.
Statement I : B atom is sp2-hybridised in B2H6.Statement II : There is no lone pair or unpaired electron in B2H6.- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement I : B atom is sp2-hybridised in B2H6.
Statement II : There is no lone pair or unpaired electron in B2H6.
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
(d) B2H6 has following types of bonding
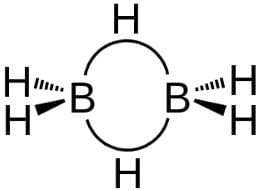
Bridging H-atoms and B-atoms are electron deficient. Each B-atom is however, joined to four H-atoms thus sp3-hybridised.
There is no lone pair or unpaired electron.
Thus, Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.

Bridging H-atoms and B-atoms are electron deficient. Each B-atom is however, joined to four H-atoms thus sp3-hybridised.
There is no lone pair or unpaired electron.
Thus, Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
Which of the following is not a correct floral character of the members of the family Solanaceae?- a)Flower : Zygomorphic
- b)Calyx: Valvate aestivation
- c)Stamens: Epipetalous
- d)Fruit: Berry or capsule
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a correct floral character of the members of the family Solanaceae?
a)
Flower : Zygomorphic
b)
Calyx: Valvate aestivation
c)
Stamens: Epipetalous
d)
Fruit: Berry or capsule
|
|
Sinjini Das answered |
Answer:
The correct answer is option A) Flower: Zygomorphic.
Explanation:
The family Solanaceae, also known as the nightshade family, includes a wide variety of flowering plants. These plants have several distinct floral characteristics that help differentiate them from other families. Let's examine each of the given options to understand why option A is incorrect.
a) Flower: Zygomorphic:
Zygomorphic flowers are those that can be divided into symmetrical halves along only one plane. In Solanaceae, the flowers are typically actinomorphic, which means they are radially symmetrical and can be divided into similar halves along multiple planes. This feature allows for easier pollination by a wide range of pollinators. Therefore, option A is incorrect.
b) Calyx: Valvate aestivation:
Aestivation refers to the arrangement of floral parts in the bud. Valvate aestivation means that the sepals in the calyx overlap at the margins without any part being inside or outside the others. This is a correct floral character of Solanaceae. The sepals are usually green and fused at the base, forming a tubular or bell-shaped calyx.
c) Stamens: Epipetalous:
Epipetalous stamens are those that are attached to the petals. In Solanaceae, the stamens are often epipetalous, meaning they are attached to the corolla (petals) of the flower. This arrangement is common in many plants of the family and can be observed in flowers such as tomato, potato, and tobacco.
d) Fruit: Berry or capsule:
The fruit in Solanaceae can be either a berry or a capsule. A berry is a fleshy fruit with multiple seeds embedded in the pulp, such as tomatoes or peppers. On the other hand, a capsule is a dry fruit that opens to release its seeds, such as in the case of the genus Datura or Physalis. This is a correct floral character of Solanaceae.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option A) Flower: Zygomorphic, as the flowers of Solanaceae are typically actinomorphic rather than zygomorphic.
The correct answer is option A) Flower: Zygomorphic.
Explanation:
The family Solanaceae, also known as the nightshade family, includes a wide variety of flowering plants. These plants have several distinct floral characteristics that help differentiate them from other families. Let's examine each of the given options to understand why option A is incorrect.
a) Flower: Zygomorphic:
Zygomorphic flowers are those that can be divided into symmetrical halves along only one plane. In Solanaceae, the flowers are typically actinomorphic, which means they are radially symmetrical and can be divided into similar halves along multiple planes. This feature allows for easier pollination by a wide range of pollinators. Therefore, option A is incorrect.
b) Calyx: Valvate aestivation:
Aestivation refers to the arrangement of floral parts in the bud. Valvate aestivation means that the sepals in the calyx overlap at the margins without any part being inside or outside the others. This is a correct floral character of Solanaceae. The sepals are usually green and fused at the base, forming a tubular or bell-shaped calyx.
c) Stamens: Epipetalous:
Epipetalous stamens are those that are attached to the petals. In Solanaceae, the stamens are often epipetalous, meaning they are attached to the corolla (petals) of the flower. This arrangement is common in many plants of the family and can be observed in flowers such as tomato, potato, and tobacco.
d) Fruit: Berry or capsule:
The fruit in Solanaceae can be either a berry or a capsule. A berry is a fleshy fruit with multiple seeds embedded in the pulp, such as tomatoes or peppers. On the other hand, a capsule is a dry fruit that opens to release its seeds, such as in the case of the genus Datura or Physalis. This is a correct floral character of Solanaceae.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option A) Flower: Zygomorphic, as the flowers of Solanaceae are typically actinomorphic rather than zygomorphic.
Tobacco and Petunia belong to family- a)Solanaceae
- b)Poaceae
- c)Brassicaceae
- d)Fabaceae
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Tobacco and Petunia belong to family
a)
Solanaceae
b)
Poaceae
c)
Brassicaceae
d)
Fabaceae

|
Harihara Samavela answered |
Epiphyllous stamen, superior ovary with bicarpel synacarpous obliquely placed ovary characters are present in these plants
What is the characteristic floral formula of the Leguminosae (Fabaceae) family?- a)5 sepals, 5 petals, 6 stamens (5 long, 1 short), and a superior ovary
- b)5 sepals, 5 petals, numerous stamens, and a single compound ovary
- c)4 sepals, 4 petals, 6 stamens, and a superior ovary
- d)4 sepals, 4 petals, numerous stamens, and an inferior ovary
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
5 sepals, 5 petals, 6 stamens (5 long, 1 short), and a superior ovary
b)
5 sepals, 5 petals, numerous stamens, and a single compound ovary
c)
4 sepals, 4 petals, 6 stamens, and a superior ovary
d)
4 sepals, 4 petals, numerous stamens, and an inferior ovary
|
|
Amrita Khanna answered |
Floral Formula of Leguminosae (Fabaceae) Family
The Leguminosae family, also known as Fabaceae, is characterized by specific floral structures that play a crucial role in their reproductive strategies.
Key Features of the Floral Formula:
- 5 Sepals: The flowers typically have five sepals that form the calyx, providing protection to the developing flower.
- 5 Petals: The corolla consists of five petals, which can be differentiated into a banner (the largest petal), two wings, and a keel (formed by the two lower petals). This arrangement aids in attracting pollinators.
- Numerous Stamens: The floral structure includes numerous stamens, which are responsible for producing pollen. Often, they are arranged in a unique way, with some being longer than others. This arrangement is essential for effective pollination.
- Compound Ovary: The ovary is typically superior and is often compound, meaning it consists of multiple fused carpels. This structure leads to the formation of legumes, which are the characteristic fruit of this family.
Conclusion
Therefore, the correct floral formula for the Leguminosae (Fabaceae) family is:
- 5 sepals, 5 petals, numerous stamens, and a single compound ovary.
This description aligns with option 'b', highlighting the intricate floral design that promotes efficient reproduction and adapts well to various pollinators. Understanding these features helps in recognizing the diversity and ecological significance of this plant family.
The Leguminosae family, also known as Fabaceae, is characterized by specific floral structures that play a crucial role in their reproductive strategies.
Key Features of the Floral Formula:
- 5 Sepals: The flowers typically have five sepals that form the calyx, providing protection to the developing flower.
- 5 Petals: The corolla consists of five petals, which can be differentiated into a banner (the largest petal), two wings, and a keel (formed by the two lower petals). This arrangement aids in attracting pollinators.
- Numerous Stamens: The floral structure includes numerous stamens, which are responsible for producing pollen. Often, they are arranged in a unique way, with some being longer than others. This arrangement is essential for effective pollination.
- Compound Ovary: The ovary is typically superior and is often compound, meaning it consists of multiple fused carpels. This structure leads to the formation of legumes, which are the characteristic fruit of this family.
Conclusion
Therefore, the correct floral formula for the Leguminosae (Fabaceae) family is:
- 5 sepals, 5 petals, numerous stamens, and a single compound ovary.
This description aligns with option 'b', highlighting the intricate floral design that promotes efficient reproduction and adapts well to various pollinators. Understanding these features helps in recognizing the diversity and ecological significance of this plant family.
A particle with constant total energy E moves in one dimension in a region where the potential energy is U(x). The speed of the particle is zero where- a) U(x) = E
- b)U(x) = 0
- c)
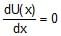
- d)
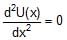
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle with constant total energy E moves in one dimension in a region where the potential energy is U(x). The speed of the particle is zero where
a)
U(x) = E
b)
U(x) = 0
c)
d)
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
If the total energy is E that means that E = U(x) + KE and if KE = 0 then E = U(x)
One end of a light spring of spring constant k is fixed to a wall and the other end is tied to a block placed on a smooth horizontal surface. In a displacement, the work done by the spring is 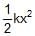 . The possible cases are:
. The possible cases are:- a)The spring was initially compressed by a distance x and was finally in its natural length
- b)It was initially stretched by a distance x and finally was in its natural length
- c)It was initially in its natural length and finally in a compressed position.
- d)It was initially in its natural length and finally in a stretched position.
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
One end of a light spring of spring constant k is fixed to a wall and the other end is tied to a block placed on a smooth horizontal surface. In a displacement, the work done by the spring is 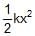 . The possible cases are:
. The possible cases are:
a)
The spring was initially compressed by a distance x and was finally in its natural length
b)
It was initially stretched by a distance x and finally was in its natural length
c)
It was initially in its natural length and finally in a compressed position.
d)
It was initially in its natural length and finally in a stretched position.
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Stored elastic potential energy of spring =1/2kx2 where x is compression or elongation of spring from its natural length. In this position the spring can do work on the block tied to it, which is equal to 1/2kx2, so both option (a) & b are correct.
A person applies a constant force 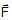 on a particle of mass m and finds that the particle moves in a circle of radius r with a uniform speed v as seen (in the plane of motion) from an inertial frame of reference
on a particle of mass m and finds that the particle moves in a circle of radius r with a uniform speed v as seen (in the plane of motion) from an inertial frame of reference- a)This is not possible.
- b)There are other forces on the particle.
- c)The resultant of the other forces is
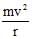 towards the centre.
towards the centre. - d)The resultant of the other forces varies in magnitude as well as in direction.
Correct answer is option 'B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
A person applies a constant force 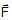 on a particle of mass m and finds that the particle moves in a circle of radius r with a uniform speed v as seen (in the plane of motion) from an inertial frame of reference
on a particle of mass m and finds that the particle moves in a circle of radius r with a uniform speed v as seen (in the plane of motion) from an inertial frame of reference
a)
This is not possible.
b)
There are other forces on the particle.
c)
The resultant of the other forces is 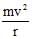 towards the centre.
towards the centre.
d)
The resultant of the other forces varies in magnitude as well as in direction.
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The person applies ‘F’ constantly in a fixed direction. So, to keep the particle in constant circular motion of radius ‘r’ and uniform speed ‘v’, some other force whose resultant varies in magnitude and direction also act on the particle. Since the resultant of F and other force has to have constant magnitude but varying direction, the magnitude and direction of the other force has to change from point to point on circle.
If there are five electron pairs in outer shell, then structure and bond angle as predicted by Sidgwick-Powell theory is- a)octahedral, (90°)
- b)trigonal bipyramidal, (120° and 90°)
- c)pentagonal bipyramidal (72° and 90°)
- d)tetrahedral, (90°)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If there are five electron pairs in outer shell, then structure and bond angle as predicted by Sidgwick-Powell theory is
a)
octahedral, (90°)
b)
trigonal bipyramidal, (120° and 90°)
c)
pentagonal bipyramidal (72° and 90°)
d)
tetrahedral, (90°)

|
Moumita Chakraborty answered |
Three electron pairs are inclined at 120°.
Two electron-pairs are at 90° with the first three.
Structure is trigonal bipyramidal.
Two electron-pairs are at 90° with the first three.
Structure is trigonal bipyramidal.
A block of mass m slides down a plane inclined at an angle q. Which of the following will NOT increase the energy lost by the block due to friction ?- a)Increasing the angle of inclination
- b)Increasing the distance that the block travels
- c)Increasing the acceleration due to gravity
- d)Increasing the mass of the block
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A block of mass m slides down a plane inclined at an angle q. Which of the following will NOT increase the energy lost by the block due to friction ?
a)
Increasing the angle of inclination
b)
Increasing the distance that the block travels
c)
Increasing the acceleration due to gravity
d)
Increasing the mass of the block
|
|
Akash Chakraborty answered |

The correct statement is- a)The block will cross the mean position
- b)The block come to rest when the forces acting on it are exactly balanced
- c)The block will come to rest when the work done by friction becomes equal to the change in energy stored in spring.
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statement is
a)
The block will cross the mean position
b)
The block come to rest when the forces acting on it are exactly balanced
c)
The block will come to rest when the work done by friction becomes equal to the change in energy stored in spring.
d)
None
|
|
Upasana Roy answered |
The question is incomplete and doesn’t make sense by itself. It should be changed to:
“A spring block system is placed on a rough horizontal floor. The block is pulled towards right to give spring an elongation less than 2μmg/K but more than μmg/K and released.
The correct statement is:”
Also add this image
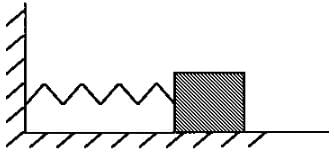
Initially the spring block system will have only one form of energy and that will be spring potential energy stored in it. After the system is released from this position it starts to oscillate to and fro with friction acting on it. When the system comes to rest then the total stored potential energy will be converted into the work done by the frictional force on the block.
“A spring block system is placed on a rough horizontal floor. The block is pulled towards right to give spring an elongation less than 2μmg/K but more than μmg/K and released.
The correct statement is:”
Also add this image

Initially the spring block system will have only one form of energy and that will be spring potential energy stored in it. After the system is released from this position it starts to oscillate to and fro with friction acting on it. When the system comes to rest then the total stored potential energy will be converted into the work done by the frictional force on the block.
A particle A moves along a circle of radius R = 50 cm so that its radius vector r relative to the point O (Fig.) rotates with the constant angular velocity w = 0.40 rad/s. Then modulus of the velocity of the particle, and the modulus of its total acceleration will be 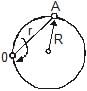
- a) v = 0.4 m/s, a = 0.4 m/s2
- b) v = 0.32 m/s, a = 0.32 m/s2
- c) v = 0.32 m/s, a = 0.4 m/s2
- d) v = 0.4 m/s, a = 0.32 m/s2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle A moves along a circle of radius R = 50 cm so that its radius vector r relative to the point O (Fig.) rotates with the constant angular velocity w = 0.40 rad/s. Then modulus of the velocity of the particle, and the modulus of its total acceleration will be
a)
v = 0.4 m/s, a = 0.4 m/s2
b)
v = 0.32 m/s, a = 0.32 m/s2
c)
v = 0.32 m/s, a = 0.4 m/s2
d)
v = 0.4 m/s, a = 0.32 m/s2
|
|
T.ttttt answered |
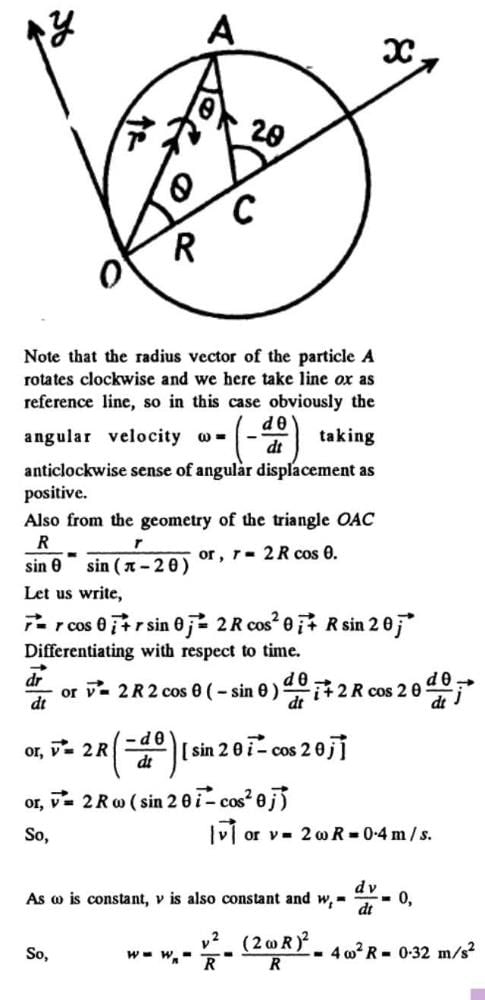
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of the Malvaceae family that distinguishes it from other plant families?- a)The presence of a superior ovary with parietal placentation
- b)Monadelphous stamens surrounding the pistil
- c)A single carpel with basal placentation
- d)A four-petaled corolla in cruciform arrangement
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
The presence of a superior ovary with parietal placentation
b)
Monadelphous stamens surrounding the pistil
c)
A single carpel with basal placentation
d)
A four-petaled corolla in cruciform arrangement

|
Lead Academy answered |
The Malvaceae family is known for having monadelphous stamens, where numerous stamens are fused into a tube encircling the pistil. This is a distinctive characteristic of the family.
Which of the following is a key feature of the Gramineae (Poaceae) family regarding its inflorescence?- a)The inflorescence is a raceme, with pedicellate flowers
- b)The inflorescence is a capitulum with ray and disk florets
- c)The inflorescence is a spike or panicle composed of spikelets
- d)The inflorescence is a solitary flower, often large and showy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
The inflorescence is a raceme, with pedicellate flowers
b)
The inflorescence is a capitulum with ray and disk florets
c)
The inflorescence is a spike or panicle composed of spikelets
d)
The inflorescence is a solitary flower, often large and showy
|
|
Amrita Khanna answered |
Key Features of Gramineae (Poaceae) Inflorescence
The Gramineae family, commonly known as Poaceae or the grass family, exhibits unique characteristics in its inflorescence, which is crucial for plant reproduction.
Inflorescence Structure
- The inflorescence of Gramineae is typically a spike or panicle.
- A spike consists of a central axis with flowers (spikelets) directly attached, while a panicle is a branched cluster of spikelets.
Spikelets Definition
- Spikelets are the basic units of the inflorescence, each containing one or more florets.
- Each spikelet is subtended by two bracts called glumes, which protect the developing flowers.
Reproductive Efficiency
- The structure of the inflorescence allows for efficient pollination, primarily by wind (anemophily).
- This adaptation is vital for the reproduction of grasses in various habitats.
Variability in Gramineae
- While the general form is a spike or panicle, some species may exhibit variations, yet they will still fall within these categories.
- This family includes important crops like wheat, rice, and corn, showcasing the economic significance of their inflorescence structure.
Conclusion
- In summary, the key feature of the Gramineae (Poaceae) family regarding its inflorescence is its formation of spikes or panicles composed of spikelets, facilitating reproduction and adaptation in diverse environments.
The Gramineae family, commonly known as Poaceae or the grass family, exhibits unique characteristics in its inflorescence, which is crucial for plant reproduction.
Inflorescence Structure
- The inflorescence of Gramineae is typically a spike or panicle.
- A spike consists of a central axis with flowers (spikelets) directly attached, while a panicle is a branched cluster of spikelets.
Spikelets Definition
- Spikelets are the basic units of the inflorescence, each containing one or more florets.
- Each spikelet is subtended by two bracts called glumes, which protect the developing flowers.
Reproductive Efficiency
- The structure of the inflorescence allows for efficient pollination, primarily by wind (anemophily).
- This adaptation is vital for the reproduction of grasses in various habitats.
Variability in Gramineae
- While the general form is a spike or panicle, some species may exhibit variations, yet they will still fall within these categories.
- This family includes important crops like wheat, rice, and corn, showcasing the economic significance of their inflorescence structure.
Conclusion
- In summary, the key feature of the Gramineae (Poaceae) family regarding its inflorescence is its formation of spikes or panicles composed of spikelets, facilitating reproduction and adaptation in diverse environments.
Statement I : BCI3 exists as monomer while AICI3 exists as dimer.Statement II : Boron atom is too small to form the stable 4-membered ring system- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement I : BCI3 exists as monomer while AICI3 exists as dimer.
Statement II : Boron atom is too small to form the stable 4-membered ring system
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect

|
Gowri Kulkarni answered |
Size of B is too small to form stable 4-membered ring system. (Also delocalised n-bonding is disturbed). Hence, dimerofBCI3is not formed.
Dimer AI2CI6 is stable due to stable ring
Thus, Statements I and II both are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement
Tangential acceleration of a particle moving in a circle of radius 1 m varies with time t as (initial velocity of particle is zero). Time after which total cceleration of particle makes and angle of 30º with radial acceleration is 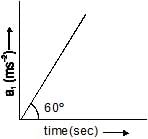
- a)4 sec
- b)4/3 sec
- c)22/3 sec
- d)
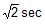
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Tangential acceleration of a particle moving in a circle of radius 1 m varies with time t as (initial velocity of particle is zero). Time after which total cceleration of particle makes and angle of 30º with radial acceleration is
a)
4 sec
b)
4/3 sec
c)
22/3 sec
d)

|
Niladrita Chakraborty answered |
I think this ans is incorrect
In the Compositae (Asteraceae) family, what is the function of the pappus in the fruit?- a)It aids in pollination
- b)It protects the seed from desiccation
- c)It helps in seed dispersal by wind
- d)It attracts pollinators to the flower
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
It aids in pollination
b)
It protects the seed from desiccation
c)
It helps in seed dispersal by wind
d)
It attracts pollinators to the flower

|
Top Rankers answered |
The pappus in Compositae fruits is a modified calyx that helps in wind dispersal of seeds, often resembling a tuft of hairs, bristles, or scales.
Select the correct statement(s) about ethene.- a)C-atom is sp2-hybridised
- b)On hydrogenation hybridisation of carbon and bond angle both changes
- c)nodal plane of π-bond is located in molecular plane
- d)C— H bond length is also affected on hydrogenation
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement(s) about ethene.
a)
C-atom is sp2-hybridised
b)
On hydrogenation hybridisation of carbon and bond angle both changes
c)
nodal plane of π-bond is located in molecular plane
d)
C— H bond length is also affected on hydrogenation

|
Rithika Mukherjee answered |
(C— H ) bond length < (C— H ) bond length
Nodal, plane of π-bond is located in molecular plane.
Direction (Q. Nos. 20-21) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.Q. Match the following compounds given in Column I with their geometry given is Column II
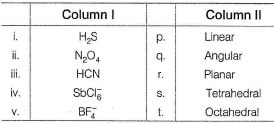

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 20-21) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q. Match the following compounds given in Column I with their geometry given is Column II
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Select the characters which are not applicable to the family Solanaceae.
(i) Epipetalous and syngenesious anthers
(ii) Stamens six and are arranged in two whorls
(iii) Bicarpellary, synchronous and inferior ovary
(iv) Bicarpellary and synchronous ovary- a)(ii) and (iii) only
- b)(i), (ii) and (iii) only
- c)(ii), (iv) and (i) only
- d)(i) and (iii) only
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the characters which are not applicable to the family Solanaceae.
(i) Epipetalous and syngenesious anthers
(ii) Stamens six and are arranged in two whorls
(iii) Bicarpellary, synchronous and inferior ovary
(iv) Bicarpellary and synchronous ovary
(i) Epipetalous and syngenesious anthers
(ii) Stamens six and are arranged in two whorls
(iii) Bicarpellary, synchronous and inferior ovary
(iv) Bicarpellary and synchronous ovary
a)
(ii) and (iii) only
b)
(i), (ii) and (iii) only
c)
(ii), (iv) and (i) only
d)
(i) and (iii) only

|
Ambition Institute answered |
The flowers of Solanaceae are bisexual and actinomorphic. The perianth and androecium whorls are pentamerous. The calyx is synsepalous. The corolla is sympetalous. The six stamens are distinct, alternating with the lobes of the corolla and adnate to the corolla tube or perigynous zone. The gynoecium consists of two carpels, a single style and a superior ovary with two locules by false partitioning, each with numerous axile ovules.
What does a dot on the top of a floral diagram represent?- a)The fragrance of the flower
- b)The position of the flower on the mother axis
- c)The color of the flower
- d)The size of the flower's petals
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What does a dot on the top of a floral diagram represent?
a)
The fragrance of the flower
b)
The position of the flower on the mother axis
c)
The color of the flower
d)
The size of the flower's petals
|
|
Arpita Saha answered |
Explanation:
Position of the flower on the mother axis:
- The dot on the top of a floral diagram represents the position of the flower on the mother axis.
- The mother axis is the central axis from which all the floral parts arise.
- The dot serves as a reference point to indicate where the flower is located on the floral diagram in relation to the mother axis.
Significance of the dot:
- The position of the flower on the mother axis is crucial for understanding the arrangement of floral parts in a flower.
- It helps in identifying the relative positions of various floral organs such as sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels.
- By knowing the position of the flower on the mother axis, one can determine the symmetry, fusion, and other structural features of the flower.
Importance in floral studies:
- Floral diagrams are essential tools for botanists and students studying plant morphology.
- They provide a visual representation of the floral structure, making it easier to compare and classify different types of flowers.
- Understanding the position of the flower on the mother axis helps in accurately interpreting the floral diagram and deciphering the structural characteristics of the flower.
Therefore, the dot on the top of a floral diagram represents the position of the flower on the mother axis, aiding in the detailed study and analysis of floral structures.
Position of the flower on the mother axis:
- The dot on the top of a floral diagram represents the position of the flower on the mother axis.
- The mother axis is the central axis from which all the floral parts arise.
- The dot serves as a reference point to indicate where the flower is located on the floral diagram in relation to the mother axis.
Significance of the dot:
- The position of the flower on the mother axis is crucial for understanding the arrangement of floral parts in a flower.
- It helps in identifying the relative positions of various floral organs such as sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels.
- By knowing the position of the flower on the mother axis, one can determine the symmetry, fusion, and other structural features of the flower.
Importance in floral studies:
- Floral diagrams are essential tools for botanists and students studying plant morphology.
- They provide a visual representation of the floral structure, making it easier to compare and classify different types of flowers.
- Understanding the position of the flower on the mother axis helps in accurately interpreting the floral diagram and deciphering the structural characteristics of the flower.
Therefore, the dot on the top of a floral diagram represents the position of the flower on the mother axis, aiding in the detailed study and analysis of floral structures.
Molecule MX3 (atomic number M < 21) has zero dipole moment, the sigma bonding orbitals used by M are- a)purep
- b)sp-hybridised
- c)sp2-hybridised
- d)sp3-hybridised
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Molecule MX3 (atomic number M < 21) has zero dipole moment, the sigma bonding orbitals used by M are
a)
purep
b)
sp-hybridised
c)
sp2-hybridised
d)
sp3-hybridised
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
For resultant dipole moment for a molecule MX3 , the molecule must be trigonal i.e SP2 hybridised orbital should be used by M.
Hence C is the correct answer.
A cart moves with a constant speed along a horizontal circular path. From the cart, a particle is thrown up vertically with respect to the cart- a)The particle will land somewhere on the circular path
- b)The particle will land outside the circular path
- c)The particle will follow an elliptical path
- d)The particle will follow a parabolic path
Correct answer is option 'B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
A cart moves with a constant speed along a horizontal circular path. From the cart, a particle is thrown up vertically with respect to the cart
a)
The particle will land somewhere on the circular path
b)
The particle will land outside the circular path
c)
The particle will follow an elliptical path
d)
The particle will follow a parabolic path
|
|
Arka Desai answered |
The particle will land outside the circle because its initial velocity in horizontal direction is in the tangential direction and its point of projection is somewhere at the circumference of the circle.
Also its path will be parabolic because it is a case of projectile motion with velocity in horizontal as well as vertical direction.
Also its path will be parabolic because it is a case of projectile motion with velocity in horizontal as well as vertical direction.
A ball of mass m is attached to the lower end of light vertical spring of force constant k. The upper end of the spring is fixed. The ball is released from rest with the spring at its normal (unstreched) length, comes to rest again after descending through a distance x.- a) x = mg/k
- b) x = 2 mg/k
- c)The ball will have no acceleration at the position where it has descended through x/2.
- d)The ball will have an upward acceleration equal to g at its lowermost position.
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
A ball of mass m is attached to the lower end of light vertical spring of force constant k. The upper end of the spring is fixed. The ball is released from rest with the spring at its normal (unstreched) length, comes to rest again after descending through a distance x.
a)
x = mg/k
b)
x = 2 mg/k
c)
The ball will have no acceleration at the position where it has descended through x/2.
d)
The ball will have an upward acceleration equal to g at its lowermost position.
|
|
Sparsh Datta answered |
The ball is at rest, it has maximum potential energy. When the ball is released from rest with the spring at its normal (unstretched) length it loses some potential energy and energy of spring increases. Hence, loss in potential energy of the ball is equal to gain in potential energy of spring.
∴mgx=1/2kx2
∴x=2mg/k
Also, for x′=x/2,
kx′=mg i.e. forces are equal thus, the ball will have no acceleration at the position where it has descended through 2x.
And when ball is at lowermost position, the spring force will be
kx=2mg
Hence, the ball will have an upward acceleration equal to g at its lowermost position.
∴mgx=1/2kx2
∴x=2mg/k
Also, for x′=x/2,
kx′=mg i.e. forces are equal thus, the ball will have no acceleration at the position where it has descended through 2x.
And when ball is at lowermost position, the spring force will be
kx=2mg
Hence, the ball will have an upward acceleration equal to g at its lowermost position.
A spot light S rotates in a horizontal plane with a constant angular velocity of 0.1 rad/s. The spot of light p moves along the wall at a distance 3 m. What is the velocity of the spot P when q = 45° ? 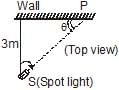
- a)0.6 m/s
- b) 0.5 m/s
- c)0.4 m/s
- d) 0.3 m/s
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A spot light S rotates in a horizontal plane with a constant angular velocity of 0.1 rad/s. The spot of light p moves along the wall at a distance 3 m. What is the velocity of the spot P when q = 45° ?
a)
0.6 m/s
b)
0.5 m/s
c)
0.4 m/s
d)
0.3 m/s

|
Crafty Classes answered |
Linear Velocity of rotating object ν=ωr/sinθ
ω= angular velocity=0.1 rad/s
r is the distance of object from centre.
Angle = 45o
r = d/cosθ [where d is the distance from the spot light to wall] = 3/cos45o
Velocity = ν = ωr/sinθ
= [0.1x3/cos45degree]/sin45degree
= 0.1x3/sin45 degreecos45degree
= 0.3/[1√2 x 1 /2]
= 2x0.3
= 0.6m/s
The velocity of the spot P is 0.6 m/s
ω= angular velocity=0.1 rad/s
r is the distance of object from centre.
Angle = 45o
r = d/cosθ [where d is the distance from the spot light to wall] = 3/cos45o
Velocity = ν = ωr/sinθ
= [0.1x3/cos45degree]/sin45degree
= 0.1x3/sin45 degreecos45degree
= 0.3/[1√2 x 1 /2]
= 2x0.3
= 0.6m/s
The velocity of the spot P is 0.6 m/s
A simple pendulum of length l and mass (bob) M is oscillating in a plane about a vertical line between angular limits _f and f. For an angular displacement q, [|q| < f] the tension in the string and velocity of the bob are T and v respectively. The following relations hold good under the above conditions :- a)T cos q = Mg
- b)T _ Mg cos q =
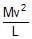
- c)Tangential acc. = g sin q
- d)T = Mg cos q
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
A simple pendulum of length l and mass (bob) M is oscillating in a plane about a vertical line between angular limits _f and f. For an angular displacement q, [|q| < f] the tension in the string and velocity of the bob are T and v respectively. The following relations hold good under the above conditions :
a)
T cos q = Mg
b)
T _ Mg cos q = 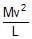
c)
Tangential acc. = g sin q
d)
T = Mg cos q
|
|
Ankita Patel answered |
The tangential acceleration is clearly gsinθ, by simply taking the components of the tension vector.
And the net for on the bob is
F = T – mgcosθ
And it will be equal to centripetal force, so,
T – mgcosθ = Mv2/l
And the net for on the bob is
F = T – mgcosθ
And it will be equal to centripetal force, so,
T – mgcosθ = Mv2/l
A particle moves along an arc of a circle of radius R. Its velocity depends on the distance covered as v = a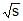 , where a is a constant then the angle a between the vector of the total acceleration and the vector of velocity as a function of s will be
, where a is a constant then the angle a between the vector of the total acceleration and the vector of velocity as a function of s will be- a)Tana =
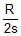
- b)Tana = 2s / R
- c)Tana =

- d)Tana =
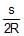
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle moves along an arc of a circle of radius R. Its velocity depends on the distance covered as v = a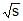 , where a is a constant then the angle a between the vector of the total acceleration and the vector of velocity as a function of s will be
, where a is a constant then the angle a between the vector of the total acceleration and the vector of velocity as a function of s will be
a)
Tana = 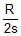
b)
Tana = 2s / R
c)
Tana = 
d)
Tana = 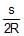
|
|
Arjun Gupta answered |

Direction (Q. Nos. 22) This section contains 1 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)Q. Most acidic H in the following compound is attached to C-atoms denoted by at S-N. ( ) ...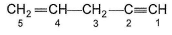
Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 22) This section contains 1 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q. Most acidic H in the following compound is attached to C-atoms denoted by at S-N. ( ) ...

|
Kritika Bajaj answered |
Electronegativity of
sp3 < sp2 < sp-hybridised C-atom
(Greater the s-character, greater the electronegativity).
(C— H) electron pair is taken out by most (EN) atom most easily, making it is acidic.
sp3 < sp2 < sp-hybridised C-atom
(Greater the s-character, greater the electronegativity).
(C— H) electron pair is taken out by most (EN) atom most easily, making it is acidic.
Chapter doubts & questions for July Week 1 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of July Week 1 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily