All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of September Week 3 for NEET Exam
The splitting of water molecule is take place inside
a)Outer membraneb)Lumenc)Stromad)Inner membrane Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Vibhor Goyal answered |
Splitting of water takes place near PS II, located in the inner side of the thylakoid membrane.
Splitting of water releases oxygen in the atmosphere and generates a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane.
The splitting of water molecules is associated with- a)PS II
- b)PS I
- c)Cyclic phosphorylation
- d)Non-cyclic phosphorylation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The splitting of water molecules is associated with
a)
PS II
b)
PS I
c)
Cyclic phosphorylation
d)
Non-cyclic phosphorylation
|
|
Swara Sarkar answered |
This is achieved by electrons available due to splitting of water. The splitting of water is associated with the PS II; water is split into H+, [O] and electrons.
The equilibrium constant for a reaction is 10. Calculate the value of ΔG° at 300K , R = R =8.314 JK−1mol−1
- a)-5.527 kJ/mol–
- b)4.744 kJ/mol
- c)-4.744 kJ/mol–
- d)- 5.744 kJ/mol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The equilibrium constant for a reaction is 10. Calculate the value of ΔG° at 300K , R = R =8.314 JK−1mol−1
a)
-5.527 kJ/mol–
b)
4.744 kJ/mol
c)
-4.744 kJ/mol–
d)
- 5.744 kJ/mol

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The value of equilibrium constant(k) = 10
∆G° = -2.303RTlogk
On calculating values, we will get ∆G° = -5.744kJmol-1
∆G° = -2.303RTlogk
On calculating values, we will get ∆G° = -5.744kJmol-1
In PSI, the reaction centre the chlorophyll a has an absorption peak at- a)780nm
- b)700nm
- c)680nm
- d)800nm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In PSI, the reaction centre the chlorophyll a has an absorption peak at
a)
780nm
b)
700nm
c)
680nm
d)
800nm
|
|
Vartika Shukla (NEET Aspirant) answered |
In PS-I, the reaction centre chlorophyll a has an absorption peak at 700 nm, hence, is called P 700 while in PS-H, it has absorption maxima at 680 nm, so is called P 680.
so the correct answer is b) 700nm
so the correct answer is b) 700nm
Solarisation is- a)Effect of solar light
- b)Destruction of chlorophyll
- c)Formation of chlorophyll
- d)Utilisation of sunlight
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Solarisation is
a)
Effect of solar light
b)
Destruction of chlorophyll
c)
Formation of chlorophyll
d)
Utilisation of sunlight
|
|
Muskaan Dasgupta answered |
Solarisation is the process of destruction of chlorophyll due to prolonged exposure to sunlight. This phenomenon is commonly observed in plants that grow in areas with high solar radiation. Here is a detailed explanation of the process:
Explanation:
Chlorophyll is the green pigment present in the leaves of plants. It plays a crucial role in photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. However, prolonged exposure to sunlight can damage the chlorophyll molecules, leading to their destruction. This process is known as solarisation.
Solarisation occurs due to the following reasons:
1. High intensity of sunlight: Plants that grow in areas with high solar radiation are more prone to solarisation. This is because the intensity of sunlight in these areas is much higher than in other regions.
2. Extended exposure to sunlight: The longer a plant is exposed to sunlight, the greater the damage to its chlorophyll molecules. This is why solarisation is more common during the summer months, when the days are longer and the sun is more intense.
Effects of solarisation:
1. Reduced photosynthesis: Solarisation damages the chlorophyll molecules, which reduces the plant's ability to carry out photosynthesis. This can lead to stunted growth and reduced yield.
2. Loss of colour: As the chlorophyll molecules are destroyed, the leaves of the plant lose their green colour and turn yellow or brown.
3. Increased susceptibility to pests and diseases: Plants that have been solarised are more susceptible to pests and diseases, as their weakened state makes them more vulnerable to attack.
Prevention of solarisation:
1. Shade: Providing shade to the plants can reduce their exposure to sunlight and prevent solarisation. This can be done by using shade cloth or by planting the crops under trees.
2. Watering: Regular watering can help cool down the plants and reduce the damage caused by solarisation.
3. Timely harvesting: Harvesting the crops before they are fully mature can reduce their exposure to sunlight and prevent solarisation.
In conclusion, solarisation is the process of destruction of chlorophyll due to prolonged exposure to sunlight. It can have a negative impact on plant growth and yield, and can be prevented by providing shade, regular watering, and timely harvesting.
Explanation:
Chlorophyll is the green pigment present in the leaves of plants. It plays a crucial role in photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. However, prolonged exposure to sunlight can damage the chlorophyll molecules, leading to their destruction. This process is known as solarisation.
Solarisation occurs due to the following reasons:
1. High intensity of sunlight: Plants that grow in areas with high solar radiation are more prone to solarisation. This is because the intensity of sunlight in these areas is much higher than in other regions.
2. Extended exposure to sunlight: The longer a plant is exposed to sunlight, the greater the damage to its chlorophyll molecules. This is why solarisation is more common during the summer months, when the days are longer and the sun is more intense.
Effects of solarisation:
1. Reduced photosynthesis: Solarisation damages the chlorophyll molecules, which reduces the plant's ability to carry out photosynthesis. This can lead to stunted growth and reduced yield.
2. Loss of colour: As the chlorophyll molecules are destroyed, the leaves of the plant lose their green colour and turn yellow or brown.
3. Increased susceptibility to pests and diseases: Plants that have been solarised are more susceptible to pests and diseases, as their weakened state makes them more vulnerable to attack.
Prevention of solarisation:
1. Shade: Providing shade to the plants can reduce their exposure to sunlight and prevent solarisation. This can be done by using shade cloth or by planting the crops under trees.
2. Watering: Regular watering can help cool down the plants and reduce the damage caused by solarisation.
3. Timely harvesting: Harvesting the crops before they are fully mature can reduce their exposure to sunlight and prevent solarisation.
In conclusion, solarisation is the process of destruction of chlorophyll due to prolonged exposure to sunlight. It can have a negative impact on plant growth and yield, and can be prevented by providing shade, regular watering, and timely harvesting.
Photorespiration does not occur in- a)C4 plants
- b)C3 plants
- c)Algae
- d)Bacteria
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Photorespiration does not occur in
a)
C4 plants
b)
C3 plants
c)
Algae
d)
Bacteria
|
|
Awantika Gupta answered |
Photorespiration is a wastefull process because it doesn't synthesis ATP.
but in new ncert it is mentioned that the requirements of photorespiration is not known yet.
but in new ncert it is mentioned that the requirements of photorespiration is not known yet.
Which of the following stages of calvin cycle are in correct order?- a)Carboxylation, reduction, regeneration
- b)Regeneration,carboxylation, reduction
- c)Regeneration,reduction,carboxylation
- d)Carboxylation,regeneration,reduction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following stages of calvin cycle are in correct order?
a)
Carboxylation, reduction, regeneration
b)
Regeneration,carboxylation, reduction
c)
Regeneration,reduction,carboxylation
d)
Carboxylation,regeneration,reduction
|
|
Smruti Sucharita answered |
##ncert refer kro yrr... directly Diya hua h..
Dark fixation of CO2 in CAM plants is called ocification because it produces- a)Tartaric acid
- b)Oxaloacetic acid
- c)Malic acid
- d)Formic acid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Dark fixation of CO2 in CAM plants is called ocification because it produces
a)
Tartaric acid
b)
Oxaloacetic acid
c)
Malic acid
d)
Formic acid
|
|
Gopikas S answered |
The principal metabolic feature of CAM plants is assimilation of CO2 at night into malic acid which is stored in the vacuole. Malate is generated in the reaction catalyzed by PEP carboxylase and PEP is, in turn, generated by degradation of starch or soluble sugars. During the day, malate is released from the vacuole and is decarboxylated to provide CO2 for fixation in the Benson–Calvin cycle behind closed stomata. Starch and sugars are then resynthesized .
PGA as the first CO2 fixation product was discovered in photosynthesis of- a)Angiosperm
- b)Bryophytes
- c)Algae
- d)Gymnosperm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
PGA as the first CO2 fixation product was discovered in photosynthesis of
a)
Angiosperm
b)
Bryophytes
c)
Algae
d)
Gymnosperm
|
|
Abhiram Basu answered |
Photosynthesis and CO2 fixation
Photosynthesis is a process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into organic compounds and oxygen. This process is essential for life on earth as it produces the oxygen that we breathe and provides food for organisms that cannot produce their own.
CO2 fixation is the process by which carbon dioxide is transformed into an organic molecule that can be used by living organisms. This process is important because carbon dioxide is an essential component of the atmosphere, but it is not readily available to most organisms in its gaseous form.
PGA as the first CO2 fixation product
PGA (phosphoglyceric acid) is the first stable product of CO2 fixation in photosynthesis. It is formed when carbon dioxide combines with a five-carbon sugar called ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme Rubisco (ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase).
Discovery of PGA
The discovery of PGA as the first CO2 fixation product was made by Melvin Calvin and his colleagues in the 1940s. They used radioactive carbon-14 to trace the movement of carbon through the photosynthetic process and discovered that PGA was the first stable product of CO2 fixation.
Source of PGA
PGA is produced in the stroma of the chloroplasts in plant cells. It is then used to make glucose and other organic compounds through a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions known as the Calvin cycle.
Role of algae in PGA discovery
Algae played a crucial role in the discovery of PGA as the first CO2 fixation product. Algae are photosynthetic organisms that are capable of fixing carbon dioxide in a similar way to plants. They were used by Calvin and his colleagues as a model system to study photosynthesis and CO2 fixation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, PGA was discovered as the first CO2 fixation product in photosynthesis by Melvin Calvin and his colleagues in the 1940s. This discovery was made using algae as a model system and has since been confirmed in plants and other photosynthetic organisms.
Photosynthesis is a process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into organic compounds and oxygen. This process is essential for life on earth as it produces the oxygen that we breathe and provides food for organisms that cannot produce their own.
CO2 fixation is the process by which carbon dioxide is transformed into an organic molecule that can be used by living organisms. This process is important because carbon dioxide is an essential component of the atmosphere, but it is not readily available to most organisms in its gaseous form.
PGA as the first CO2 fixation product
PGA (phosphoglyceric acid) is the first stable product of CO2 fixation in photosynthesis. It is formed when carbon dioxide combines with a five-carbon sugar called ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme Rubisco (ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase).
Discovery of PGA
The discovery of PGA as the first CO2 fixation product was made by Melvin Calvin and his colleagues in the 1940s. They used radioactive carbon-14 to trace the movement of carbon through the photosynthetic process and discovered that PGA was the first stable product of CO2 fixation.
Source of PGA
PGA is produced in the stroma of the chloroplasts in plant cells. It is then used to make glucose and other organic compounds through a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions known as the Calvin cycle.
Role of algae in PGA discovery
Algae played a crucial role in the discovery of PGA as the first CO2 fixation product. Algae are photosynthetic organisms that are capable of fixing carbon dioxide in a similar way to plants. They were used by Calvin and his colleagues as a model system to study photosynthesis and CO2 fixation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, PGA was discovered as the first CO2 fixation product in photosynthesis by Melvin Calvin and his colleagues in the 1940s. This discovery was made using algae as a model system and has since been confirmed in plants and other photosynthetic organisms.
In sugarcane, CO2 is fixed in malic acid with the help of enzyme- a)Ribulose phosphate kinase
- b)RuBP carboxylase
- c)Fructose phosphotase
- d)PEP carboxylase
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In sugarcane, CO2 is fixed in malic acid with the help of enzyme
a)
Ribulose phosphate kinase
b)
RuBP carboxylase
c)
Fructose phosphotase
d)
PEP carboxylase
|
|
Jay Kumar answered |
In C4 plants, Carbon dioxide is fixed in malic acid with the help of enzyme phosphoenel pyruvate (PEP). Malic acid is a four carbon compound that later change into oxyloacetic acid.
Which of the following statements is correct about the process of evaporation of water from an open beaker?- a)It is a spontaneous and endothermic process.
- b)It is a non-spontaneous and endothermic process.
- c)It is a spontaneous and exothermic process.
- d)It is a non-spontaneous and exothermic process.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is correct about the process of evaporation of water from an open beaker?
a)
It is a spontaneous and endothermic process.
b)
It is a non-spontaneous and endothermic process.
c)
It is a spontaneous and exothermic process.
d)
It is a non-spontaneous and exothermic process.
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Evaporation of water from an open pot is a spontaneous process. As it starts on its own without any external agent. However it takes heat from surrounding means that it is endothermic.
A hollow spherical shell is compressed to half its radius. The gravitational potential at the centre- a)Increases
- b) Decreases
- c) Remains same
- d)Ruring the compression increases then returns at the previous value
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A hollow spherical shell is compressed to half its radius. The gravitational potential at the centre
a)
Increases
b)
Decreases
c)
Remains same
d)
Ruring the compression increases then returns at the previous value
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Gravitational Potential V = -GM/R for hollow spherical shell at the centre. If we replace R by R/2 then we get V = -2GM/R. Therefore it decreases.
A body of mass m rises to height h = R/5 from the earth's surface, where R is earth's radius. If g is acceleration due to gravity at earth's surface, the increase in potential energy is- a)Mg/h
- b)
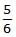 mgh
mgh - c)
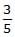 mgh
mgh - d)
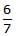 mgh
mgh
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A body of mass m rises to height h = R/5 from the earth's surface, where R is earth's radius. If g is acceleration due to gravity at earth's surface, the increase in potential energy is
a)
Mg/h
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Initial PE = -GMm/R
Final PE = -GMm/R+h, (h=R/5)
Increase in PE = final - initial
= -GMm/R + (R/5) - (-GMm/R)
=GMm(1/R - 5/6R)
=GMm/R * 1/6
= gmR/6 (g= GM/R)
=gm5h/6 (h=R/5)
Final PE = -GMm/R+h, (h=R/5)
Increase in PE = final - initial
= -GMm/R + (R/5) - (-GMm/R)
=GMm(1/R - 5/6R)
=GMm/R * 1/6
= gmR/6 (g= GM/R)
=gm5h/6 (h=R/5)
The mass and diameter of a planet are twice those of earth. What will be the period of oscillation of a pendulum on this planet if it is a seconds pendulum on earth ?- a)
 second
second - b)
 seconds
seconds - c)
 second
second - d)
 second
second
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The mass and diameter of a planet are twice those of earth. What will be the period of oscillation of a pendulum on this planet if it is a seconds pendulum on earth ?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
As Mp=2Me and Dp=2De
or Rp=2Re
Hence, gp= GMp/(Rp)2 =G(2Me)/(2Re)2 = GMe/2Re2 =ge/2
Time period of pendulum on the planet Tp=2π√ l/gp
Tp=2π√2l/ge=√2×2π√l/ge=√2×Te
Tp=√2×2=2√2s
or Rp=2Re
Hence, gp= GMp/(Rp)2 =G(2Me)/(2Re)2 = GMe/2Re2 =ge/2
Time period of pendulum on the planet Tp=2π√ l/gp
Tp=2π√2l/ge=√2×2π√l/ge=√2×Te
Tp=√2×2=2√2s
Carbon dioxide is fixed in- a)Dark reaction
- b)Anaerobic respiration
- c)Aerobic respiration
- d)Light reaction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Carbon dioxide is fixed in
a)
Dark reaction
b)
Anaerobic respiration
c)
Aerobic respiration
d)
Light reaction
|
|
Afifa Aaliya answered |
Carbon dioxide fixation takes place in absence of sunlight. Dark reaction make use of these organic energy molecules ATP and NADPH. This reaction cycle is also called as Calvin benison cycle. It occurs in the stroma. It requires to fix carbon dioxide into carbohydrates.
So option " A " is correct answer.
So option " A " is correct answer.
For a spontaneous chemical process, the free energy change is- a)not measurable
- b)negative
- c)positive
- d)zero
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For a spontaneous chemical process, the free energy change is
a)
not measurable
b)
negative
c)
positive
d)
zero

|
Ameya Basu answered |
The sign of ΔG will change from positive to negative (or vice versa) where T = ΔH/ΔS. In cases where ΔG is: negative, the process is spontaneous and may proceed in the forward direction as written. positive, the process is non-spontaneous as written, but it may proceed spontaneously in the reverse direction.
If the kinetic energy of a satellite orbiting around the earth is doubled then -- a) The satellite will escape into the space.
- b)The satellite will fall down on the earth
- c) Radius of its orbit will be doubled
- d)Radius of its orbit will become half.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If the kinetic energy of a satellite orbiting around the earth is doubled then -
a)
The satellite will escape into the space.
b)
The satellite will fall down on the earth
c)
Radius of its orbit will be doubled
d)
Radius of its orbit will become half.
|
|
Janhavi Menon answered |
Understanding Satellite Kinetic Energy
When a satellite orbits the Earth, its kinetic energy is determined by its speed and the gravitational pull it experiences. The kinetic energy (KE) of a satellite can be expressed as:
- KE = (1/2) mv^2
Where m is the mass of the satellite and v is its orbital speed.
Effect of Doubling Kinetic Energy
If the kinetic energy of the satellite is doubled:
- New KE = 2 * KE
This implies that the speed of the satellite must increase. Since kinetic energy is proportional to the square of the velocity, to double the kinetic energy, the velocity must be increased by a factor of sqrt(2).
Consequences of Increased Speed
- Increased orbital speed means the satellite will no longer be in a stable orbit. The gravitational force is not enough to keep it in a circular path.
- As a result, the satellite will move into a higher, elliptical trajectory, and eventually escape Earth's gravitational influence.
Options Analysis
Let’s analyze the options provided:
- a) The satellite will escape into space. (Correct)
- b) The satellite will fall down on the Earth. (Incorrect) - Increased speed means it would not fall.
- c) The radius of its orbit will be doubled. (Incorrect) - The orbit will change but not necessarily double.
- d) The radius of its orbit will become half. (Incorrect) - Similar reasoning as above.
Conclusion
Doubling the kinetic energy increases the satellite's speed sufficiently to overcome Earth's gravity, leading it to escape into space. Thus, the correct answer is option 'A'.
When a satellite orbits the Earth, its kinetic energy is determined by its speed and the gravitational pull it experiences. The kinetic energy (KE) of a satellite can be expressed as:
- KE = (1/2) mv^2
Where m is the mass of the satellite and v is its orbital speed.
Effect of Doubling Kinetic Energy
If the kinetic energy of the satellite is doubled:
- New KE = 2 * KE
This implies that the speed of the satellite must increase. Since kinetic energy is proportional to the square of the velocity, to double the kinetic energy, the velocity must be increased by a factor of sqrt(2).
Consequences of Increased Speed
- Increased orbital speed means the satellite will no longer be in a stable orbit. The gravitational force is not enough to keep it in a circular path.
- As a result, the satellite will move into a higher, elliptical trajectory, and eventually escape Earth's gravitational influence.
Options Analysis
Let’s analyze the options provided:
- a) The satellite will escape into space. (Correct)
- b) The satellite will fall down on the Earth. (Incorrect) - Increased speed means it would not fall.
- c) The radius of its orbit will be doubled. (Incorrect) - The orbit will change but not necessarily double.
- d) The radius of its orbit will become half. (Incorrect) - Similar reasoning as above.
Conclusion
Doubling the kinetic energy increases the satellite's speed sufficiently to overcome Earth's gravity, leading it to escape into space. Thus, the correct answer is option 'A'.
Blackman's law is related to - a)respiration
- b)transpiration
- c)root pressure
- d)photosynthesis.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Blackman's law is related to
a)
respiration
b)
transpiration
c)
root pressure
d)
photosynthesis.

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Blackman formulated the principle of limiting factors. He studied the effect of CO2 concentration, light intensity and temperature on the rate of photosynthesis.
Light reaction otherwise called as- a)Photochemical phase
- b)Carboxylation
- c)Regeneration
- d)Biosynthetic phase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Light reaction otherwise called as
a)
Photochemical phase
b)
Carboxylation
c)
Regeneration
d)
Biosynthetic phase
|
|
Vishal Kumar answered |
Photochemical Phase (Light or Hill Reaction): It occurs inside the thylakoids, especially those of grana region. Photochemical step is dependent upon light.
Calvin cycle is discovered by- a)Melvin Calvin
- b)Blackmann
- c)Cornelius van neil
- d)Hatch and Slack
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Calvin cycle is discovered by
a)
Melvin Calvin
b)
Blackmann
c)
Cornelius van neil
d)
Hatch and Slack
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
The cycle was discovered in 1950 by Melvin Calvin, James Bassham, and Andrew Benson at the University of California, Berkeley by using the radioactive isotope carbon-14. Photosynthesis occurs in two stages in a cell.
Which of the following is true about a spontaneous process?- a)Spontaneity does not depend on Gibbs energy.
- b)Gibbs energy change is less than 0.
- c)Gibbs energy change is 0.
- d)Gibbs energy change is greater than 0.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is true about a spontaneous process?
a)
Spontaneity does not depend on Gibbs energy.
b)
Gibbs energy change is less than 0.
c)
Gibbs energy change is 0.
d)
Gibbs energy change is greater than 0.

|
Ameya Basu answered |
A spontaneous process is the time-evolution of a system in which it releases free energy and it moves to a lower, more thermodynamically stable energy state. For cases involving an isolated system where no energy is exchanged with the surroundings, spontaneous processes are characterized by an increase in entropy
Which of the following is extensive property?- a)Specific heat capacity
- b)Entropy
- c)Temperature
- d)Refractive index
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is extensive property?
a)
Specific heat capacity
b)
Entropy
c)
Temperature
d)
Refractive index
|
|
Tanishq Unni answered |
Extensive Property:
An extensive property is a physical property of a system that depends on the amount of substance present in the system. In other words, extensive properties are additive and scale with the size or amount of the system. The value of an extensive property changes when the size or amount of the system changes.
Explanation:
Out of the given options, the correct answer is option 'B' - Entropy.
Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness of a system. It is a thermodynamic property that quantifies the number of microscopic configurations that a system can have. Entropy is an extensive property because it depends on the size or amount of the system.
Comparison with Other Options:
a) Specific Heat Capacity:
Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by a certain amount. It is an intensive property because it does not depend on the amount of substance present. The specific heat capacity of a substance remains the same regardless of the size or amount of the substance.
b) Entropy:
As mentioned earlier, entropy is an extensive property as it depends on the amount of substance present in the system. If the system size or amount changes, the entropy of the system will also change proportionally.
c) Temperature:
Temperature is an intensive property because it does not depend on the amount of substance present. The temperature of a substance remains the same regardless of the size or amount of the substance.
d) Refractive Index:
Refractive index is a measure of how light propagates through a medium. It is an intensive property because it does not depend on the amount of substance present. The refractive index of a substance remains the same regardless of the size or amount of the substance.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, entropy is the only extensive property. It is a thermodynamic property that depends on the amount of substance present in the system. The other options, specific heat capacity, temperature, and refractive index, are intensive properties that do not depend on the amount of substance present.
An extensive property is a physical property of a system that depends on the amount of substance present in the system. In other words, extensive properties are additive and scale with the size or amount of the system. The value of an extensive property changes when the size or amount of the system changes.
Explanation:
Out of the given options, the correct answer is option 'B' - Entropy.
Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness of a system. It is a thermodynamic property that quantifies the number of microscopic configurations that a system can have. Entropy is an extensive property because it depends on the size or amount of the system.
Comparison with Other Options:
a) Specific Heat Capacity:
Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by a certain amount. It is an intensive property because it does not depend on the amount of substance present. The specific heat capacity of a substance remains the same regardless of the size or amount of the substance.
b) Entropy:
As mentioned earlier, entropy is an extensive property as it depends on the amount of substance present in the system. If the system size or amount changes, the entropy of the system will also change proportionally.
c) Temperature:
Temperature is an intensive property because it does not depend on the amount of substance present. The temperature of a substance remains the same regardless of the size or amount of the substance.
d) Refractive Index:
Refractive index is a measure of how light propagates through a medium. It is an intensive property because it does not depend on the amount of substance present. The refractive index of a substance remains the same regardless of the size or amount of the substance.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, entropy is the only extensive property. It is a thermodynamic property that depends on the amount of substance present in the system. The other options, specific heat capacity, temperature, and refractive index, are intensive properties that do not depend on the amount of substance present.
The value of ΔS for spontaneous process is- a)ΔSTotal is constant
- b)ΔSTotal > 0
- c)ΔSTotal < 0
- d)ΔSTotal = 0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of ΔS for spontaneous process is
a)
ΔSTotal is constant
b)
ΔSTotal > 0
c)
ΔSTotal < 0
d)
ΔSTotal = 0

|
Prisha Yadav answered |
Something is subjective and can vary depending on individual perspectives and circumstances. It can be determined based on various factors such as usefulness, scarcity, demand, and personal preferences.
What is the change in the entropy of water, When ice melts into water?- a)Entropy of water increases.
- b)Entropy of water becomes zero.
- c)Entropy of water decreases.
- d)Entropy of water remains same.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the change in the entropy of water, When ice melts into water?
a)
Entropy of water increases.
b)
Entropy of water becomes zero.
c)
Entropy of water decreases.
d)
Entropy of water remains same.

|
Raghav Yadav answered |
The greater the randomness in a system, greater is its entropy. The randomness is greater in liquid state as compared to solid state so the entropy increases when ice melts into water.
Two point masses of mass 4m and m respectively separated by d distance are revolving under mutual force of attraction. Ratio of their kinetic energies will be- a)1 : 4
- b)1 : 5
- c)1 : 1
- d)1 : 2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two point masses of mass 4m and m respectively separated by d distance are revolving under mutual force of attraction. Ratio of their kinetic energies will be
a)
1 : 4
b)
1 : 5
c)
1 : 1
d)
1 : 2
|
|
Jay Kumar answered |
Understanding the Problem
Two point masses, 4m and m, are revolving around their common center of mass due to the gravitational force between them. We need to find the ratio of their kinetic energies.
Center of Mass (COM)
- For two point masses, the center of mass can be calculated using the formula:
r_COM = (m1 * r1 + m2 * r2) / (m1 + m2)
- Here, the center of mass will be closer to the larger mass (4m), meaning the distance from the center of mass to mass 4m will be less than the distance to mass m.
Distance from the Center of Mass
- Let the distance from the center of mass to mass 4m be r1 and to mass m be r2.
- Since the masses are 4m and m, we have:
r1 = (m / (4m + m)) * d = (1/5)d
r2 = (4m / (4m + m)) * d = (4/5)d
Kinetic Energy (KE) Formula
- The kinetic energy of a mass in circular motion is given by:
KE = (1/2)mv^2
- For the two masses, we can express their kinetic energies as:
KE_1 (for mass 4m) = (1/2)(4m)(v1^2)
KE_2 (for mass m) = (1/2)(m)(v2^2)
Velocity Relationship
- For two bodies in circular motion about a common center, the ratio of their velocities is inversely proportional to the ratio of their distances from the center of mass:
v1 / v2 = r2 / r1 = (4/5) / (1/5) = 4
Calculating the Ratio of Kinetic Energies
- Substituting the velocity relationship, we find:
KE_1 : KE_2 = (4)(4m) : (1)(m) = 16m : m = 16 : 1
- However, since we are looking for kinetic energy per unit mass, we can simplify further:
The ratio becomes 1 : 4.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option 'A': the ratio of their kinetic energies is 1 : 4.
Two point masses, 4m and m, are revolving around their common center of mass due to the gravitational force between them. We need to find the ratio of their kinetic energies.
Center of Mass (COM)
- For two point masses, the center of mass can be calculated using the formula:
r_COM = (m1 * r1 + m2 * r2) / (m1 + m2)
- Here, the center of mass will be closer to the larger mass (4m), meaning the distance from the center of mass to mass 4m will be less than the distance to mass m.
Distance from the Center of Mass
- Let the distance from the center of mass to mass 4m be r1 and to mass m be r2.
- Since the masses are 4m and m, we have:
r1 = (m / (4m + m)) * d = (1/5)d
r2 = (4m / (4m + m)) * d = (4/5)d
Kinetic Energy (KE) Formula
- The kinetic energy of a mass in circular motion is given by:
KE = (1/2)mv^2
- For the two masses, we can express their kinetic energies as:
KE_1 (for mass 4m) = (1/2)(4m)(v1^2)
KE_2 (for mass m) = (1/2)(m)(v2^2)
Velocity Relationship
- For two bodies in circular motion about a common center, the ratio of their velocities is inversely proportional to the ratio of their distances from the center of mass:
v1 / v2 = r2 / r1 = (4/5) / (1/5) = 4
Calculating the Ratio of Kinetic Energies
- Substituting the velocity relationship, we find:
KE_1 : KE_2 = (4)(4m) : (1)(m) = 16m : m = 16 : 1
- However, since we are looking for kinetic energy per unit mass, we can simplify further:
The ratio becomes 1 : 4.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option 'A': the ratio of their kinetic energies is 1 : 4.
If the radius and density of a planet are two times and half respectively of those of earth, find the intensity of gravitational field at planet surface and escape velocity from planet.- a)1584 km/sec.
- b)15.84 km/sec.
- c)160 km/sec.
- d)16.84 km/sec.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the radius and density of a planet are two times and half respectively of those of earth, find the intensity of gravitational field at planet surface and escape velocity from planet.
a)
1584 km/sec.
b)
15.84 km/sec.
c)
160 km/sec.
d)
16.84 km/sec.

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Acceleration due to gravity g = 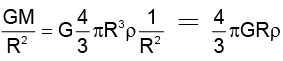
Thus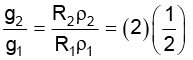 = 1 ∴ g2 = g1 = g
= 1 ∴ g2 = g1 = g
Escape velocity Ve =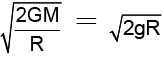
∴ Escape velocity at planet =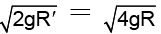
= (√2) (11.2km / sec ) = 15.84 km/sec.
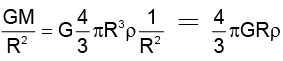
Thus
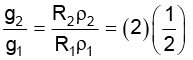 = 1 ∴ g2 = g1 = g
= 1 ∴ g2 = g1 = gEscape velocity Ve =
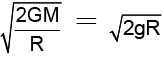
∴ Escape velocity at planet =
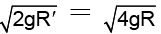
= (√2) (11.2km / sec ) = 15.84 km/sec.
Which one has Kranz anatomy?- a)Potato
- b)Maize
- c)Wheat
- d)Rice
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one has Kranz anatomy?
a)
Potato
b)
Maize
c)
Wheat
d)
Rice
|
|
Manisha Sarkar answered |
Maize (option B) has Kranz anatomy.
Explanation:
Maize, also known as corn, is a C4 plant that exhibits a specialized leaf anatomy called Kranz anatomy. Kranz anatomy is characterized by the presence of two distinct types of photosynthetic cells: bundle sheath cells and mesophyll cells.
Bundle sheath cells:
- In maize, the bundle sheath cells are arranged in a ring-like manner around the vascular bundles.
- They are tightly packed and contain numerous chloroplasts.
- The walls of bundle sheath cells are thickened and contain many plasmodesmata, which allow for the exchange of metabolites between cells.
- The bundle sheath cells are responsible for the initial fixation of carbon dioxide (CO2) during photosynthesis.
Mesophyll cells:
- The mesophyll cells of maize leaves surround the bundle sheath cells.
- They are loosely arranged and contain fewer chloroplasts compared to bundle sheath cells.
- The mesophyll cells are involved in the initial uptake of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Kranz anatomy and C4 photosynthesis:
- Kranz anatomy is a structural adaptation that enhances the efficiency of C4 photosynthesis.
- C4 photosynthesis is a biochemical pathway that helps plants overcome the limitations of the traditional C3 pathway, especially under high light and high temperature conditions.
- In C4 plants like maize, carbon dioxide is initially fixed into a four-carbon compound in the mesophyll cells, thanks to the enzyme phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEP carboxylase).
- The four-carbon compound is then transported to the bundle sheath cells, where it is decarboxylated to release CO2.
- The CO2 released in the bundle sheath cells is then used in the Calvin cycle for the synthesis of sugars.
- This spatial separation of initial CO2 fixation and the Calvin cycle helps reduce photorespiration and increases the efficiency of carbon fixation.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, maize (option B) exhibits Kranz anatomy, which is a specialized leaf anatomy found in C4 plants. This anatomical adaptation enhances the efficiency of C4 photosynthesis, allowing maize to thrive in environments with high light and temperature conditions.
Explanation:
Maize, also known as corn, is a C4 plant that exhibits a specialized leaf anatomy called Kranz anatomy. Kranz anatomy is characterized by the presence of two distinct types of photosynthetic cells: bundle sheath cells and mesophyll cells.
Bundle sheath cells:
- In maize, the bundle sheath cells are arranged in a ring-like manner around the vascular bundles.
- They are tightly packed and contain numerous chloroplasts.
- The walls of bundle sheath cells are thickened and contain many plasmodesmata, which allow for the exchange of metabolites between cells.
- The bundle sheath cells are responsible for the initial fixation of carbon dioxide (CO2) during photosynthesis.
Mesophyll cells:
- The mesophyll cells of maize leaves surround the bundle sheath cells.
- They are loosely arranged and contain fewer chloroplasts compared to bundle sheath cells.
- The mesophyll cells are involved in the initial uptake of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Kranz anatomy and C4 photosynthesis:
- Kranz anatomy is a structural adaptation that enhances the efficiency of C4 photosynthesis.
- C4 photosynthesis is a biochemical pathway that helps plants overcome the limitations of the traditional C3 pathway, especially under high light and high temperature conditions.
- In C4 plants like maize, carbon dioxide is initially fixed into a four-carbon compound in the mesophyll cells, thanks to the enzyme phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEP carboxylase).
- The four-carbon compound is then transported to the bundle sheath cells, where it is decarboxylated to release CO2.
- The CO2 released in the bundle sheath cells is then used in the Calvin cycle for the synthesis of sugars.
- This spatial separation of initial CO2 fixation and the Calvin cycle helps reduce photorespiration and increases the efficiency of carbon fixation.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, maize (option B) exhibits Kranz anatomy, which is a specialized leaf anatomy found in C4 plants. This anatomical adaptation enhances the efficiency of C4 photosynthesis, allowing maize to thrive in environments with high light and temperature conditions.
In the evaporation of water, the entropy- a)does not change
- b)increases
- c)decreases
- d)first increases and then decreases
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the evaporation of water, the entropy
a)
does not change
b)
increases
c)
decreases
d)
first increases and then decreases

|
Avi Chawla answered |
Explanation:
The concept of entropy:
Entropy is a thermodynamic property that measures the degree of disorder or randomness in a system. It is denoted by the symbol 'S'. The entropy of a substance increases with an increase in its disorder.
Evaporation of water:
Evaporation is the process by which water molecules in a liquid state gain enough energy to become vapor or gas molecules. It occurs at the surface of the liquid and is a phase transition from the liquid phase to the gas phase.
Entropy change during evaporation:
During evaporation, water molecules at the surface of the liquid gain energy from the surroundings and overcome the intermolecular forces holding them together. They then escape into the gas phase, resulting in the conversion of liquid water into water vapor.
1. Disorder of the system: The liquid state of water has a higher degree of order as compared to the gaseous state. In the liquid phase, water molecules are closely packed and have a regular arrangement, while in the gaseous phase, the molecules are randomly distributed and move freely.
2. Entropy change: As water evaporates, the disorder of the system increases. The liquid water molecules are confined to a limited space and have restricted movement, while the water vapor molecules have greater freedom and random motion. This increase in disorder leads to an increase in entropy.
Conclusion:
Therefore, during the evaporation of water, the entropy increases. Option 'B' is the correct answer.
The concept of entropy:
Entropy is a thermodynamic property that measures the degree of disorder or randomness in a system. It is denoted by the symbol 'S'. The entropy of a substance increases with an increase in its disorder.
Evaporation of water:
Evaporation is the process by which water molecules in a liquid state gain enough energy to become vapor or gas molecules. It occurs at the surface of the liquid and is a phase transition from the liquid phase to the gas phase.
Entropy change during evaporation:
During evaporation, water molecules at the surface of the liquid gain energy from the surroundings and overcome the intermolecular forces holding them together. They then escape into the gas phase, resulting in the conversion of liquid water into water vapor.
1. Disorder of the system: The liquid state of water has a higher degree of order as compared to the gaseous state. In the liquid phase, water molecules are closely packed and have a regular arrangement, while in the gaseous phase, the molecules are randomly distributed and move freely.
2. Entropy change: As water evaporates, the disorder of the system increases. The liquid water molecules are confined to a limited space and have restricted movement, while the water vapor molecules have greater freedom and random motion. This increase in disorder leads to an increase in entropy.
Conclusion:
Therefore, during the evaporation of water, the entropy increases. Option 'B' is the correct answer.
For the reaction Hg (l) ———> Hg (g) , the entropy change will have the sign:
- a)Negative
- b)Positive
- c)Both positive and negative
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For the reaction Hg (l) ———> Hg (g) , the entropy change will have the sign:
a)
Negative
b)
Positive
c)
Both positive and negative
d)
None of the above
|
|
Deepak Kumar answered |
Hg(l) is the chemical formula for liquid mercury.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct answer.a. Photochemical phase occurs inside the thylakoids, especially those of grana region.
b. Biosynthetic phase reactions occur in stroma or matrix of chloroplasts and are dependent upon light.- a)Both the statements are true.
- b)Both the statements are false.
- c)Statement 'a' is true and 'b' is false.
- d)Statement 'b' is true and 'a' is false.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements and choose the correct answer.
a. Photochemical phase occurs inside the thylakoids, especially those of grana region.
b. Biosynthetic phase reactions occur in stroma or matrix of chloroplasts and are dependent upon light.
b. Biosynthetic phase reactions occur in stroma or matrix of chloroplasts and are dependent upon light.
a)
Both the statements are true.
b)
Both the statements are false.
c)
Statement 'a' is true and 'b' is false.
d)
Statement 'b' is true and 'a' is false.
|
|
Rhea Sharma answered |
Explanation:
Statement a: Photochemical phase occurs inside the thylakoids, especially those of the grana region.
- The thylakoids are membrane-bound compartments inside the chloroplast where the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur.
- The grana are stacks of thylakoids where the chlorophyll molecules are located, allowing for the absorption of light energy.
Statement b: Biosynthetic phase reactions occur in the stroma or matrix of chloroplasts and are dependent upon light.
- The biosynthetic phase, also known as the Calvin cycle or light-independent reactions, takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast.
- During this phase, energy from the light-dependent reactions is used to convert carbon dioxide into glucose through a series of enzymatic reactions.
Conclusion:
- Both statements are partially correct. Statement a is true as the photochemical phase indeed occurs inside the thylakoids, particularly in the grana region. However, statement b is false as the biosynthetic phase reactions occur in the stroma, not dependent upon light.
Statement a: Photochemical phase occurs inside the thylakoids, especially those of the grana region.
- The thylakoids are membrane-bound compartments inside the chloroplast where the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur.
- The grana are stacks of thylakoids where the chlorophyll molecules are located, allowing for the absorption of light energy.
Statement b: Biosynthetic phase reactions occur in the stroma or matrix of chloroplasts and are dependent upon light.
- The biosynthetic phase, also known as the Calvin cycle or light-independent reactions, takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast.
- During this phase, energy from the light-dependent reactions is used to convert carbon dioxide into glucose through a series of enzymatic reactions.
Conclusion:
- Both statements are partially correct. Statement a is true as the photochemical phase indeed occurs inside the thylakoids, particularly in the grana region. However, statement b is false as the biosynthetic phase reactions occur in the stroma, not dependent upon light.
The height above surface of earth where the value of gravitational acceleration is one fourth of that at surface, will be- a) Re/4
- b) Re/2
- c)3Re/4
- d)Re
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The height above surface of earth where the value of gravitational acceleration is one fourth of that at surface, will be
a)
Re/4
b)
Re/2
c)
3Re/4
d)
Re
|
|
Krithika Kumar answered |
Understanding Gravitational Acceleration
Gravitational acceleration at the surface of the Earth (g) is approximately 9.81 m/s². As you move away from the Earth's surface, gravitational acceleration decreases according to the formula:
g' = g / (1 + h/R)²
Where:
- g' is the gravitational acceleration at height h,
- g is the gravitational acceleration at the surface (9.81 m/s²),
- R is the radius of the Earth (approximately 6400 km),
- h is the height above the surface.
Condition for One Fourth of Surface Gravity
To find the height where gravitational acceleration is one fourth of that at the surface, we set up the equation:
g' = g/4
Substituting the formula:
g / (1 + h/R)² = g/4
This simplifies to:
1 / (1 + h/R)² = 1/4
Taking the square root of both sides gives:
1/(1 + h/R) = 1/2
From this, we can derive:
1 + h/R = 2
This leads to:
h/R = 2 - 1
Thus,
h/R = 1
h = R
Conclusion: Height Above Earth's Surface
The height at which gravitational acceleration is one fourth of that at the Earth's surface is equal to the radius of the Earth (R). Therefore, the correct answer is:
Option D: Re
Gravitational acceleration at the surface of the Earth (g) is approximately 9.81 m/s². As you move away from the Earth's surface, gravitational acceleration decreases according to the formula:
g' = g / (1 + h/R)²
Where:
- g' is the gravitational acceleration at height h,
- g is the gravitational acceleration at the surface (9.81 m/s²),
- R is the radius of the Earth (approximately 6400 km),
- h is the height above the surface.
Condition for One Fourth of Surface Gravity
To find the height where gravitational acceleration is one fourth of that at the surface, we set up the equation:
g' = g/4
Substituting the formula:
g / (1 + h/R)² = g/4
This simplifies to:
1 / (1 + h/R)² = 1/4
Taking the square root of both sides gives:
1/(1 + h/R) = 1/2
From this, we can derive:
1 + h/R = 2
This leads to:
h/R = 2 - 1
Thus,
h/R = 1
h = R
Conclusion: Height Above Earth's Surface
The height at which gravitational acceleration is one fourth of that at the Earth's surface is equal to the radius of the Earth (R). Therefore, the correct answer is:
Option D: Re
The decrease in the value of g on going to a height R/2 above the earth's surface will be
- a)g/2
- b)5/9 g
- c)9/4 g
- d)3/2 g
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The decrease in the value of g on going to a height R/2 above the earth's surface will be
a)
g/2
b)
5/9 g
c)
9/4 g
d)
3/2 g
|
|
Ashish Roy answered |
g = GM/R2
g at height h
gh = GM/(R+H)2
h = R/2
gh = GM/(R + R/2)2 = GM/((9/4) (R2)) = 9/4 g
Decrease in the value of g
g − 9/4g = 9/5 g
g at height h
gh = GM/(R+H)2
h = R/2
gh = GM/(R + R/2)2 = GM/((9/4) (R2)) = 9/4 g
Decrease in the value of g
g − 9/4g = 9/5 g
Which of the following is NOT a state function?- a)q + w
- b)q
- c)qrev/T
- d)PV
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT a state function?
a)
q + w
b)
q
c)
qrev/T
d)
PV

|
Nitin Sharma answered |
A state function is the property of the system whose value depends only on the initial and final state of the system and is independent of the path. It is a state function because it is independent of the path. Heat (q) and work (W) are not state functions being path dependent.
The law of limiting factors is given by- a)Sachs
- b)Priestly
- c)Blackmann
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The law of limiting factors is given by
a)
Sachs
b)
Priestly
c)
Blackmann
d)
None of the above
|
|
Rocky Handsome answered |
¥¥In 1905, Blackman gave the Law of Limiting factors. When several factors affect any biochemical process, then this law comes into effect. This states that:
If a chemical process is affected by more than one factor, then its rate will be determined by the factor which is nearest to its minimal value. It is the factor which directly affects the process if this quantity is changed.
•Blackman's law of limiting factors determines the rate of the photosynthesis.
If a chemical process is affected by more than one factor, then its rate will be determined by the factor which is nearest to its minimal value. It is the factor which directly affects the process if this quantity is changed.
•Blackman's law of limiting factors determines the rate of the photosynthesis.
The C4 pathway is otherwise called as- a)Cyclic phosphorylation
- b)Non cyclic phosphorylation
- c)Calvin pathway
- d)Hatch and slack pathway
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The C4 pathway is otherwise called as
a)
Cyclic phosphorylation
b)
Non cyclic phosphorylation
c)
Calvin pathway
d)
Hatch and slack pathway
|
|
Ekta Gupta answered |
It is named after a scientist Hatch and slack pathway. basically this pathway helps plant to minimise water loss.. as we know that photosynthesis takes place in mesophyll cell but in this c4 pathway photosynthesis occurs in mesophyll as well as bundle sheath cell. mainly glucose molecule will form in bundle sheat cell.
On excitation, the electrons picked up by an electron acceptor is passed to- a)photons
- b)anntenae
- c)cytochromes
- d)reaction centre
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
On excitation, the electrons picked up by an electron acceptor is passed to
a)
photons
b)
anntenae
c)
cytochromes
d)
reaction centre
|
|
Prashanth Menon answered |
Electrons become excited and jump into an orbit farther from the atomic nucleus. These electrons are picked up by an electron acceptor which passes them to an electrons transport of cytochrome.
A body of mass m is situated at a distance 4Re above the earth's surface, where Re is the radius of earth. How much minimum energy be given to the body so that it may escape -- a) mgRe
- b)2mgRe
- c)
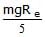
- d)
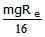
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A body of mass m is situated at a distance 4Re above the earth's surface, where Re is the radius of earth. How much minimum energy be given to the body so that it may escape -
a)
mgRe
b)
2mgRe
c)
d)

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Potential energy of the body at a distance 4Re from the surface of earth

So minimum energy required to escape the body will be mgRe/5.
Two planets A and B have the same material density. If the radius of A is twice that of B, then the ratio of the escape velocity 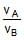 is
is- a)2
- b)
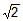
- c)
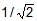
- d)1/2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two planets A and B have the same material density. If the radius of A is twice that of B, then the ratio of the escape velocity 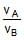 is
is
a)
2
b)
c)
d)
1/2

|
Top Rankers answered |
Let the density be d for both the planets. Given that RA = 2 RB
Now, mass of A, MA = 4 d π RA3/ 3 = 32 dπ RB3 / 3
similarly, MB = 4 dπ RB3 / 3
Escape velocity for a planet is given by V = √2 GM / R
So, VA = √2 G MA / 3 RA = √64 G dπ RB3 / 6RB =√32 G dπ RB2 / 3
Similarly, VB = 8 G dπ RB2 / 3
Taking the ratio, VA / VB = 32 G dπ RB2 / 3 × √3 / 8 G dπ RB2 = 2
Now, mass of A, MA = 4 d π RA3/ 3 = 32 dπ RB3 / 3
similarly, MB = 4 dπ RB3 / 3
Escape velocity for a planet is given by V = √2 GM / R
So, VA = √2 G MA / 3 RA = √64 G dπ RB3 / 6RB =√32 G dπ RB2 / 3
Similarly, VB = 8 G dπ RB2 / 3
Taking the ratio, VA / VB = 32 G dπ RB2 / 3 × √3 / 8 G dπ RB2 = 2
Chapter doubts & questions for September Week 3 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of September Week 3 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily