All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of October Week 2 for NEET Exam
Ca(HCO3)2 is strongly heated and after equilibrium is attained, temperature changed to 25° C.
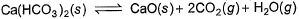
Kp = 36 (pressure taken in atm)
Thus, pressure set up due to CO2 is- a)36 atm
- b)18 atm
- c)12 atm
- d)6 atm
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Ca(HCO3)2 is strongly heated and after equilibrium is attained, temperature changed to 25° C.
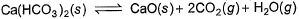
Kp = 36 (pressure taken in atm)
Thus, pressure set up due to CO2 is
Kp = 36 (pressure taken in atm)
Thus, pressure set up due to CO2 is
a)
36 atm
b)
18 atm
c)
12 atm
d)
6 atm
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The reaction is as follow:-
Ca(HCO3)2(s)⇌CaO(s) + 2CO2 (g) + H2O(g)
At 25° C H2O goes in liquid state
Kp = (PCaO)1×(PCO2)2
(PCa(HCO3)2)
Since, Ca(HCO3)2, CaO and H2O are not in gaseous state, so their partial pressure is taken 1.
Putting all values, we have
36 = (PCO2)2
Or PCO2 = 6 atm
Ca(HCO3)2(s)⇌CaO(s) + 2CO2 (g) + H2O(g)
At 25° C H2O goes in liquid state
Kp = (PCaO)1×(PCO2)2
(PCa(HCO3)2)
Since, Ca(HCO3)2, CaO and H2O are not in gaseous state, so their partial pressure is taken 1.
Putting all values, we have
36 = (PCO2)2
Or PCO2 = 6 atm
Water is flowing through a pipe under constant pressure. At some place the pipe becomes narrow. The pressure of water at this place:- a)remains the same
- b)depends on several factors
- c)decreases
- d)increases
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is flowing through a pipe under constant pressure. At some place the pipe becomes narrow. The pressure of water at this place:
a)
remains the same
b)
depends on several factors
c)
decreases
d)
increases
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
We know that the continuity theorem says that if the cross sectional area of the water flow decreases, the speed must increase to maintain the volume of water flown. And according to Bernoulli's principle if the speed of water flow increases , then the pressure must decrease.
Graphite is added to a vessel that contains CO2(g) at a pressure of 0.830 atm at a certain high temperature. The pressure rises due to a reaction that produces CO (g). The total pressure reaches an equilibrium value of 1.366 atm. Calculate the equilibrium constant of the following reaction.
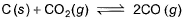
- a)2.909 atm
- b)6.909 atm
- c)4.909 atm
- d)3.909 atm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Graphite is added to a vessel that contains CO2(g) at a pressure of 0.830 atm at a certain high temperature. The pressure rises due to a reaction that produces CO (g). The total pressure reaches an equilibrium value of 1.366 atm. Calculate the equilibrium constant of the following reaction.
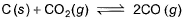
a)
2.909 atm
b)
6.909 atm
c)
4.909 atm
d)
3.909 atm
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |

Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. Vapour pressure of NH4HS (s)is 20 mm at 25°C, for
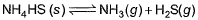
Total pressure when NH4HS (s) dissociates at 25°Cin a vessel which already contains H2S (g)at a pressure of 15 mm, is- a)25 mm
- b)50 mm
- c)5 mm
- d)10 mm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Vapour pressure of NH4HS (s)is 20 mm at 25°C, for
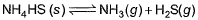
Total pressure when NH4HS (s) dissociates at 25°Cin a vessel which already contains H2S (g)at a pressure of 15 mm, is
Total pressure when NH4HS (s) dissociates at 25°Cin a vessel which already contains H2S (g)at a pressure of 15 mm, is
a)
25 mm
b)
50 mm
c)
5 mm
d)
10 mm
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
NH4HS -------> NH3 + H2S
Let P be the pressure at eq. of NH3 and H2S.
Therefore, Kp = P2
= (20 / 2)2
= 100 mm
= 100
Also, Kp = (15 + P) (P)
100 = 15 P + P2
P2 + 15 P – 100 = 0
P = 5
Total pressure = 15 + 2(P)
= 15 + 2(5)
= 25 mm
NH4HS -------> NH3 + H2S
Let P be the pressure at eq. of NH3 and H2S.
Therefore, Kp = P2
= (20 / 2)2
= 100 mm
= 100
Also, Kp = (15 + P) (P)
100 = 15 P + P2
P2 + 15 P – 100 = 0
P = 5
Total pressure = 15 + 2(P)
= 15 + 2(5)
= 25 mm
Air is streaming past a horizontal airplane wing such that its speed is 120 m/s over the upper surface and 90 m/s at the lower surface. If the density of the air is 1.3 kg/m3and the wing is 10 m long and has an average width of 2 m, then the difference of pressure on the two sides of the wing is- a)4.095 Pa
- b)409.5 Pa
- c)4095 Pa
- d)40.95 Pa
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Air is streaming past a horizontal airplane wing such that its speed is 120 m/s over the upper surface and 90 m/s at the lower surface. If the density of the air is 1.3 kg/m3and the wing is 10 m long and has an average width of 2 m, then the difference of pressure on the two sides of the wing is
a)
4.095 Pa
b)
409.5 Pa
c)
4095 Pa
d)
40.95 Pa
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Applying Bernoulli's principle, we have
P1+1/2ρv12=P2+1/2ρv22
⇒P2−P1=1/2ρ (v2/1−v2/2)
⇒ΔP=1/2×1.3× (1202−902)
⇒ΔP=0.65× (120+90) × (120−90)
⇒ΔP=0.65×210×30=4095Pa
P1+1/2ρv12=P2+1/2ρv22
⇒P2−P1=1/2ρ (v2/1−v2/2)
⇒ΔP=1/2×1.3× (1202−902)
⇒ΔP=0.65× (120+90) × (120−90)
⇒ΔP=0.65×210×30=4095Pa
Assume following equilibria when total pressure set up in each are equal to 1 atm, and equilibrium constant (Kp) as K1; K2 and K3
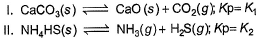
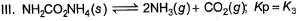
Thus,- a) K1 = K2 = K3
- b)K1 < K2 < K3
- c)K3 < K2 < K1
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assume following equilibria when total pressure set up in each are equal to 1 atm, and equilibrium constant (Kp) as K1; K2 and K3
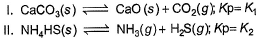
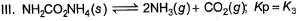
Thus,
Thus,
a)
K1 = K2 = K3
b)
K1 < K2 < K3
c)
K3 < K2 < K1
d)
None of these

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
The correct answer is option C
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
Kp = k1 = Pco2
total pressure of container P
k1 = p
NH4HS → NH3 + H2S
PNH3 = PH2S = P0
P0 + P0 = p (total pressure)
P0 = p/2
k2 = kp = [PNH3][PH2s] p24
NH2CoNH2 → 2NH3 + CO2
PNH3 = 2P0 PCO2 = P0
2P0 + P0 = P
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
Kp = k1 = Pco2
total pressure of container P
k1 = p
NH4HS → NH3 + H2S
PNH3 = PH2S = P0
P0 + P0 = p (total pressure)
P0 = p/2
k2 = kp = [PNH3][PH2s] p24
NH2CoNH2 → 2NH3 + CO2
PNH3 = 2P0 PCO2 = P0
2P0 + P0 = P
At 1000 K, pressure of CO2 in equilibrium with CaCO3 and CaO is equal to 2.105 atm. The equilibrium constant for the reaction,
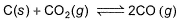
is 1.9 at the same temperature when pressure are in atm. Solid C, CaO, and CaCO3 are mixed and allowed to come to equilibrium at 1000 K in a closed vessel.Q. What is the pressure of CO (g)at equilibrium (in atm)?
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
At 1000 K, pressure of CO2 in equilibrium with CaCO3 and CaO is equal to 2.105 atm. The equilibrium constant for the reaction,
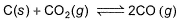
is 1.9 at the same temperature when pressure are in atm. Solid C, CaO, and CaCO3 are mixed and allowed to come to equilibrium at 1000 K in a closed vessel.
is 1.9 at the same temperature when pressure are in atm. Solid C, CaO, and CaCO3 are mixed and allowed to come to equilibrium at 1000 K in a closed vessel.
Q. What is the pressure of CO (g)at equilibrium (in atm)?

|
Learners Habitat answered |
K= (partial pressure of co2/(partial pressure of co2)
since k =1.9
So 1.9 = (partial pressure of co)2/2.105
(partial pressure of co)2 =2.105×1.9
= 3.99 = 4
(partial pressure of co) =2
since k =1.9
So 1.9 = (partial pressure of co)2/2.105
(partial pressure of co)2 =2.105×1.9
= 3.99 = 4
(partial pressure of co) =2
Ca(HCO3)2 decomposes as,
Ca (HCO3)2(s) ⇌ CaCO3(s) + H2O(g) + CO2(g)
Equilibrium pressure is found to be 0.12 bar. What is pco2 if the reaction mixture also contains H2O(g)at 0.20 bar?
- a) 0.20 bar
- b) 0.017 ba
- c)0.040 bar
- d)0.10 bar
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Ca(HCO3)2 decomposes as,
Ca (HCO3)2(s) ⇌ CaCO3(s) + H2O(g) + CO2(g)
Equilibrium pressure is found to be 0.12 bar. What is pco2 if the reaction mixture also contains H2O(g)at 0.20 bar?
Equilibrium pressure is found to be 0.12 bar. What is pco2 if the reaction mixture also contains H2O(g)at 0.20 bar?
a)
0.20 bar
b)
0.017 ba
c)
0.040 bar
d)
0.10 bar

|
Top Rankers answered |

Water is flowing through a horizontal pipe in streamline flow at the narrowest part of the pipe:- a)Both pressure and the velocity remains constant
- b)velocity is maximum and pressure is minimum
- c)both the pressure and velocity are maximum
- d)both the pressure and velocity are minimum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is flowing through a horizontal pipe in streamline flow at the narrowest part of the pipe:
a)
Both pressure and the velocity remains constant
b)
velocity is maximum and pressure is minimum
c)
both the pressure and velocity are maximum
d)
both the pressure and velocity are minimum
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
In streamline flow, the product of cross section area and velocity remains constant (equation of continuity). So in the narrowest part of the pipe velocity is maximum.
And from Bernoulli's theorem, we know that the sum of potential energy, kinetic energy and pressure energy remains constant. Since pipe is horizontal potential energy is equal at all the points. So the narrowest part of pipe pressure (pressure energy) will be minimum because velocity (kinetic energy) is maximum in the narrowest part.
And from Bernoulli's theorem, we know that the sum of potential energy, kinetic energy and pressure energy remains constant. Since pipe is horizontal potential energy is equal at all the points. So the narrowest part of pipe pressure (pressure energy) will be minimum because velocity (kinetic energy) is maximum in the narrowest part.
Kc forthe decomposition of NH4HS(s) is 1.8x 10-4 at 25°C.
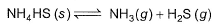
If the system already contains [NH3] = 0.020 M, then when equilibrium is reached, molar concentration are
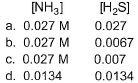
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Kc forthe decomposition of NH4HS(s) is 1.8x 10-4 at 25°C.
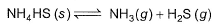
If the system already contains [NH3] = 0.020 M, then when equilibrium is reached, molar concentration are

If the system already contains [NH3] = 0.020 M, then when equilibrium is reached, molar concentration are
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
NH4HS (s) ⇋ NH3 (g) + H2S (g)
Initial 1 - -
At eqm 1-x x+0.02 x
Kc = [NH3][H2S] (Since NH4HS is solid, we ignore it.)
1.8×10-4 = (x+0.02)(x)
x2+0.02x-1.8×10-4 = 0
Applying quadratic formula; x = -0.02+√{(0.02)2-4×1.8×10-4}
= 0.033-0.020/2 = 0.0065
Therefore, concn of NH3 at equilibrium = x+0.020 = 0.0265
concn of H2S at equilibrium = x = 0.0065
So, option b is correct
Initial 1 - -
At eqm 1-x x+0.02 x
Kc = [NH3][H2S] (Since NH4HS is solid, we ignore it.)
1.8×10-4 = (x+0.02)(x)
x2+0.02x-1.8×10-4 = 0
Applying quadratic formula; x = -0.02+√{(0.02)2-4×1.8×10-4}
= 0.033-0.020/2 = 0.0065
Therefore, concn of NH3 at equilibrium = x+0.020 = 0.0265
concn of H2S at equilibrium = x = 0.0065
So, option b is correct
Equilibrium constant for the reaction PCL5⇋PCL3+CL2 is 0.0205 at 230°C and 1 atmospheric pressure if at equilibrium concentration of PCL5 is 0.235 moles liter−1liter-1and that of CL2= 0.028 moleslit−1lit-1 then conc. of PCL3 at equilibrium is- a)0.0174
- b)0.174
- c)0.0348
- d)1.74
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Equilibrium constant for the reaction PCL5⇋PCL3+CL2 is 0.0205 at 230°C and 1 atmospheric pressure if at equilibrium concentration of PCL5 is 0.235 moles liter−1liter-1and that of CL2= 0.028 moleslit−1lit-1 then conc. of PCL3 at equilibrium is
a)
0.0174
b)
0.174
c)
0.0348
d)
1.74
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |

Bernoulli’s theorem is important in the field of:- a)Photoelectric effect
- b)flow of liquids
- c)Magnetism
- d)Electrical cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Bernoulli’s theorem is important in the field of:
a)
Photoelectric effect
b)
flow of liquids
c)
Magnetism
d)
Electrical cells
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Bernoulli's theorem, in fluid dynamics, relation among the pressure, velocity, and elevation in a moving fluid (liquid or gas), the compressibility and viscosity (internal friction) of which are negligible and the flow of which is steady, or laminar.
Passage ISolid ammonium chloride is in equilibrium with ammonia and hydrogen chloride gases
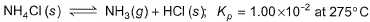
0.980 g of solid NH4CI is taken in a closed vessel of 1 L capacity and heated to 275° C.Q. Percentage decomposition of the original sample is- a)24.81%
- b)6.24%
- c)3.12%
- d)12.13%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage I
Solid ammonium chloride is in equilibrium with ammonia and hydrogen chloride gases
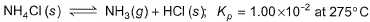
0.980 g of solid NH4CI is taken in a closed vessel of 1 L capacity and heated to 275° C.
0.980 g of solid NH4CI is taken in a closed vessel of 1 L capacity and heated to 275° C.
Q. Percentage decomposition of the original sample is
a)
24.81%
b)
6.24%
c)
3.12%
d)
12.13%

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
The state of HCl is given wrong. It will be in gaseous state.
So, the reaction be like;-
NH4Cl(s) ⇌ NH3(g) + HCl(g) kp = 1.00×10-2 at 275° C
Kp = kc(RT)2
1.00×10-2 = kc(0.0821×548)2
Or kc = 4.94×10-6
NH4Cl(s) ⇌ NH3(g) + HCl(g)
Initial 1 - -
At eqm 1-x x x
Kc = x2
x = √(4.94×10-6)
= 2.22×10-3
Therefore, NH4Cl dissociated at eqm = 2.22×10-3 × 53.5 = 0.118
%age decomposition = 0.118/0.980×100 = 12.13%
So, the reaction be like;-
NH4Cl(s) ⇌ NH3(g) + HCl(g) kp = 1.00×10-2 at 275° C
Kp = kc(RT)2
1.00×10-2 = kc(0.0821×548)2
Or kc = 4.94×10-6
NH4Cl(s) ⇌ NH3(g) + HCl(g)
Initial 1 - -
At eqm 1-x x x
Kc = x2
x = √(4.94×10-6)
= 2.22×10-3
Therefore, NH4Cl dissociated at eqm = 2.22×10-3 × 53.5 = 0.118
%age decomposition = 0.118/0.980×100 = 12.13%
For the equilibrium,
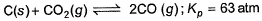
at 1000 K. If at equilibrium pCO = 10 then total pressure at equilibrium is
then total pressure at equilibrium is - a)6.30 atm
- b)0.63 atm
- c)6.93 atm
- d)69.3 atm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For the equilibrium,
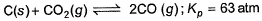
at 1000 K. If at equilibrium pCO = 10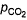 then total pressure at equilibrium is
then total pressure at equilibrium is
at 1000 K. If at equilibrium pCO = 10
a)
6.30 atm
b)
0.63 atm
c)
6.93 atm
d)
69.3 atm
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
C(s) + CO2(g) <=========> 2CO(g)
Kp = pCO2/pCO2
GIven Kp = 63 and pCO = 10pCO2
Putting the value of pCO in above equation,
63 = 100(pCO2)2/pCO2
Or pCO2 = 0.63
pCO = 6.3
Therefore, total pressure = 6.3+0.63 = 6.93 atm
Kp = pCO2/pCO2
GIven Kp = 63 and pCO = 10pCO2
Putting the value of pCO in above equation,
63 = 100(pCO2)2/pCO2
Or pCO2 = 0.63
pCO = 6.3
Therefore, total pressure = 6.3+0.63 = 6.93 atm
In the houses far away from the municipal water tanks often people find it difficult to get water on the top floor. This happens because- a)water wets the pipe
- b)the pipes are not of uniform diameter
- c)the viscosity of the water is high
- d)of loss of pressure during the flow of water
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the houses far away from the municipal water tanks often people find it difficult to get water on the top floor. This happens because
a)
water wets the pipe
b)
the pipes are not of uniform diameter
c)
the viscosity of the water is high
d)
of loss of pressure during the flow of water
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Every foot of elevation change causes a 0.433 PSI change in water pressure. If your pipe is going downhill add 0.433 PSI of pressure per vertical foot the pipe goes down. If the pipe is going uphill subtract 0.433 PSI for every vertical foot the pipe goes up.
Passage lIOne of the reactions that takes place in producing steel from iron ore is the reduction of iron (II) oxide by carbon monoxide to give iron metal and carbon dioxide.
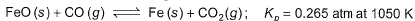
Initial partial pressure
CO(g) = 1.40 atm
CO2(g) = 0.80 atmQ. Under the given partial pressure, reaction is- a)displaced in forward side
- b)displaced in backward side
- c)in equilibrium
- d)incomplete in the absence of total pressure
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage lI
One of the reactions that takes place in producing steel from iron ore is the reduction of iron (II) oxide by carbon monoxide to give iron metal and carbon dioxide.
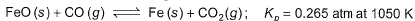
Initial partial pressure
CO(g) = 1.40 atm
CO2(g) = 0.80 atm
Initial partial pressure
CO(g) = 1.40 atm
CO2(g) = 0.80 atm
Q. Under the given partial pressure, reaction is
a)
displaced in forward side
b)
displaced in backward side
c)
in equilibrium
d)
incomplete in the absence of total pressure
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
We know that with increase in pressure on one side, reaction shifts to that side which has less no. of moles(of gaseous species). However the no. of moles are same on both sides. So the REACTION WILL REMAIN IN EQUILIBRIUM.
Ammonium carbamate dissociates as,
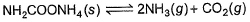
In a closed vessel containing ammonium carbamate in equilibrium with its vapour, ammonia is added such that partial pressure of NH3 now equals the original total pressure. Thus, ratio of the total pressure to the original pressure is- a)2:1
- b)31:27
- c)27 : 37
- d)
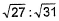
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Ammonium carbamate dissociates as,
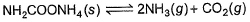
In a closed vessel containing ammonium carbamate in equilibrium with its vapour, ammonia is added such that partial pressure of NH3 now equals the original total pressure. Thus, ratio of the total pressure to the original pressure is
In a closed vessel containing ammonium carbamate in equilibrium with its vapour, ammonia is added such that partial pressure of NH3 now equals the original total pressure. Thus, ratio of the total pressure to the original pressure is
a)
2:1
b)
31:27
c)
27 : 37
d)

|
Imk Pathsala answered |
Bernoulli’s principle is based on the conservation of:- a)
- Momentum
- b)Energy and momentum both
- c)Mass
- d)Energy
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Bernoulli’s principle is based on the conservation of:
a)
- Momentum
b)
Energy and momentum both
c)
Mass
d)
Energy
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Bernoulli's principle can be derived from the principle of conservation of energy. This states that, in a steady flow, the sum of all forms of energy in a fluid along a streamline is the same at all points on that streamline.
Once the equilibrium is reached under given condition:- a)Cone, remains the same in spite of the change in temperature
- b)Cone, of all the substances presents do not change
- c)Cone, of reactants remairfs same
- d)Cone, of products remains same
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Once the equilibrium is reached under given condition:
a)
Cone, remains the same in spite of the change in temperature
b)
Cone, of all the substances presents do not change
c)
Cone, of reactants remairfs same
d)
Cone, of products remains same
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which the forward reaction rate and the reverse reaction rate are equal. The result of this equilibrium is that the concentrations of the reactants and the products do not change. However, just because concentrations aren’t changing does not mean that all chemical reaction has ceased. Just the opposite is true; chemical equilibrium is a dynamic state in which reactants are being converted into products at all times, but at the exact rate that products are being converted back into reactants. The result of such a situation is analogous to a bridge between two cities, where the rate of cars going over the bridge in each direction is exactly equal. The result is that the net number of cars on either side of the bridge does not change.
At 90° C , the following equilibrium is established :

If 0.20 mole of hydrogen and 1.0 mole of sulphur are heated to 90°C in a 1.0 dm3 flask, what will be the partial pressure of H2S gas at equilibrium?- a)0.36 atm
- b)0.38 atm
- c)0.28 atm
- d)0.26 atm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
At 90° C , the following equilibrium is established :

If 0.20 mole of hydrogen and 1.0 mole of sulphur are heated to 90°C in a 1.0 dm3 flask, what will be the partial pressure of H2S gas at equilibrium?
If 0.20 mole of hydrogen and 1.0 mole of sulphur are heated to 90°C in a 1.0 dm3 flask, what will be the partial pressure of H2S gas at equilibrium?
a)
0.36 atm
b)
0.38 atm
c)
0.28 atm
d)
0.26 atm
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Initial moles of H₂ = 0.2
Initial moles of S = 1
Kp = 6.8 * 10⁻²
Given equation:
H2(g) + S(s) ⇋ H2S(g)
Initial moles: 0.2 1
At equilibrium: (0.2-α) (1-α) α
Here, in the above equation we can see that hydrogen is the limiting reagent.
∴ Kp = α/(0.2 – α)
⇒ 6.8 * 10⁻² = α/(0.2 – α)
⇒ 1.36*10⁻² – (6.8*10⁻²)α = α
⇒ α + 0.068α = 1.36*10⁻²
⇒ α = 1.36*10⁻² / 1.068 = 1.273 * 10⁻² ← moles of H₂S
So, at equilibrium moles of H₂ = 0.2 – α = 0.2 – 1.273 * 10⁻² = 0.1873
Now, using the Ideal Gas equation,
PV = nRT ….. (i)
Where P = total pressure of the vessel
n = total no. of moles = (0.2-α) + (1-α) + α = 1.2 – α = 1.2 – 1.273*10⁻² = 1.1873
V = volume of vessel = 1 litre
R = Ideal gas constant = 0.082 L atm K⁻¹mol⁻¹
T = total temperature = 90℃ = 90+273 = 363 K
Substituting all the values in eq. (i), we get
P * 1 = 1.1873 * 0.082 * 363
⇒ P = 35.34 atm
Thus,
The partial pressure of H₂S at equilibrium
= (mole fraction of H₂S) * (total pressure)
= [1.273*10⁻² / 1.1873] * 35.34
= 0.3789 atm
≈ 0.38 atm
Initial moles of S = 1
Kp = 6.8 * 10⁻²
Given equation:
H2(g) + S(s) ⇋ H2S(g)
Initial moles: 0.2 1
At equilibrium: (0.2-α) (1-α) α
Here, in the above equation we can see that hydrogen is the limiting reagent.
∴ Kp = α/(0.2 – α)
⇒ 6.8 * 10⁻² = α/(0.2 – α)
⇒ 1.36*10⁻² – (6.8*10⁻²)α = α
⇒ α + 0.068α = 1.36*10⁻²
⇒ α = 1.36*10⁻² / 1.068 = 1.273 * 10⁻² ← moles of H₂S
So, at equilibrium moles of H₂ = 0.2 – α = 0.2 – 1.273 * 10⁻² = 0.1873
Now, using the Ideal Gas equation,
PV = nRT ….. (i)
Where P = total pressure of the vessel
n = total no. of moles = (0.2-α) + (1-α) + α = 1.2 – α = 1.2 – 1.273*10⁻² = 1.1873
V = volume of vessel = 1 litre
R = Ideal gas constant = 0.082 L atm K⁻¹mol⁻¹
T = total temperature = 90℃ = 90+273 = 363 K
Substituting all the values in eq. (i), we get
P * 1 = 1.1873 * 0.082 * 363
⇒ P = 35.34 atm
Thus,
The partial pressure of H₂S at equilibrium
= (mole fraction of H₂S) * (total pressure)
= [1.273*10⁻² / 1.1873] * 35.34
= 0.3789 atm
≈ 0.38 atm
Water is flowing through a horizontal tube. The pressure of the liquid in the portion where velocity is 2 m/s is 2 m of Hg. What will be the pressure in the portion where velocity is 4 m/s?- a)430 x 10³ Pa
- b)4.3 x 10³ Pa
- c)1.31 x 105 Pa
- d)0.43 x 10³ Pa
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is flowing through a horizontal tube. The pressure of the liquid in the portion where velocity is 2 m/s is 2 m of Hg. What will be the pressure in the portion where velocity is 4 m/s?
a)
430 x 10³ Pa
b)
4.3 x 10³ Pa
c)
1.31 x 105 Pa
d)
0.43 x 10³ Pa
|
|
Sparsh Datta answered |
We know that Pv remains constant for any fluid and for non compressible fluids like water we get that Pv is always constant.
Also as 76cm of Hg = 105 Pa
We get 2m Hg = 200/76 x 105 Pa
Thus from conservation of Pv, we get that
2 x 200/76 x 105 = 4 x P
Thus we get P = 100/76 x 105
Thus we get P = 1.31 x 105
Also as 76cm of Hg = 105 Pa
We get 2m Hg = 200/76 x 105 Pa
Thus from conservation of Pv, we get that
2 x 200/76 x 105 = 4 x P
Thus we get P = 100/76 x 105
Thus we get P = 1.31 x 105
Bernoulli’s theorem includes as a special case of:- a)Torricelli’s law
- b)Hooke’s law
- c)Archimedes’ principle
- d)Pascal’s law
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Bernoulli’s theorem includes as a special case of:
a)
Torricelli’s law
b)
Hooke’s law
c)
Archimedes’ principle
d)
Pascal’s law
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Bernoulli’s Theorem
Bernoulli’s theorem, in fluid dynamics, relation among the pressure, velocity, and elevation in a moving fluid (liquid or gas), the compressibility and viscosity (internal friction) of which are negligible and the flow of which is steady, or laminar. First derived (1738) by the Swiss mathematician Daniel Bernoulli, the theorem states, in effect, that the total mechanical energy of the flowing fluid, comprising the energy associated with fluid pressure, the gravitational potential energy of elevation, and the kinetic energy of fluid motion, remains constant. Bernoulli’s theorem is the principle of energy conservation for ideal fluids in steady, or streamline, flow and is the basis for many engineering applications.
Bernoulli’s theorem, in fluid dynamics, relation among the pressure, velocity, and elevation in a moving fluid (liquid or gas), the compressibility and viscosity (internal friction) of which are negligible and the flow of which is steady, or laminar. First derived (1738) by the Swiss mathematician Daniel Bernoulli, the theorem states, in effect, that the total mechanical energy of the flowing fluid, comprising the energy associated with fluid pressure, the gravitational potential energy of elevation, and the kinetic energy of fluid motion, remains constant. Bernoulli’s theorem is the principle of energy conservation for ideal fluids in steady, or streamline, flow and is the basis for many engineering applications.
Which enzyme catalyzes the conversion of sucrose into glucose and fructose in plants?- a)Hexokinase
- b)Invertase
- c)Phosphofructokinase
- d)Lactate dehydrogenase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Hexokinase
b)
Invertase
c)
Phosphofructokinase
d)
Lactate dehydrogenase
|
|
Sonal Reddy answered |
Enzyme Overview
The enzyme responsible for the conversion of sucrose into glucose and fructose in plants is called invertase. This process is crucial for various physiological functions in plants, particularly in carbohydrate metabolism.
Function of Invertase
- Invertase, also known as sucrose-α-D-glucosidase, catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose.
- It breaks the glycosidic bond between glucose and fructose in sucrose, resulting in free glucose and fructose.
Biological Importance
- Energy Source: The glucose produced serves as a primary energy source for plant cells.
- Sugar Transport: Fructose can also be utilized in energy production and serves as a precursor for other carbohydrates.
- Growth and Development: The availability of these simple sugars is essential for various metabolic processes, including growth and development.
Comparison with Other Enzymes
- Hexokinase: This enzyme phosphorylates glucose but does not convert sucrose.
- Phosphofructokinase: This enzyme is involved in glycolysis, acting on fructose-6-phosphate, not sucrose.
- Lactate Dehydrogenase: This enzyme is related to anaerobic respiration, specifically converting pyruvate to lactate.
Conclusion
In summary, invertase is the key enzyme that hydrolyzes sucrose into glucose and fructose, playing a vital role in plant metabolism and energy production. Understanding this enzyme's function is essential for comprehending how plants utilize carbohydrates effectively.
The enzyme responsible for the conversion of sucrose into glucose and fructose in plants is called invertase. This process is crucial for various physiological functions in plants, particularly in carbohydrate metabolism.
Function of Invertase
- Invertase, also known as sucrose-α-D-glucosidase, catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose.
- It breaks the glycosidic bond between glucose and fructose in sucrose, resulting in free glucose and fructose.
Biological Importance
- Energy Source: The glucose produced serves as a primary energy source for plant cells.
- Sugar Transport: Fructose can also be utilized in energy production and serves as a precursor for other carbohydrates.
- Growth and Development: The availability of these simple sugars is essential for various metabolic processes, including growth and development.
Comparison with Other Enzymes
- Hexokinase: This enzyme phosphorylates glucose but does not convert sucrose.
- Phosphofructokinase: This enzyme is involved in glycolysis, acting on fructose-6-phosphate, not sucrose.
- Lactate Dehydrogenase: This enzyme is related to anaerobic respiration, specifically converting pyruvate to lactate.
Conclusion
In summary, invertase is the key enzyme that hydrolyzes sucrose into glucose and fructose, playing a vital role in plant metabolism and energy production. Understanding this enzyme's function is essential for comprehending how plants utilize carbohydrates effectively.
Match the pathway with its characteristics Column I (Pathway) Column II (Characteristic) a. Glycolysis i. Occurs in cytoplasm; partial oxidation of glucose b. Alcoholic fermentation ii. Produces lactic acid under anaerobic conditions c. Lactic acid fermentation iii. Produces ethanol and CO2 in anaerobic organisms d. Aerobic respiration iv. Complete oxidation of glucose in mitochondria
- a)a-iii, b-ii, c-iv, d-i
- b)a-iv, b-i, c-iii, d-ii
- c)a-ii, b-iv, c-i, d-iii
- d) a-i, b-iii, c-ii, d-iv
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the pathway with its characteristics
| Column I (Pathway) | Column II (Characteristic) |
|---|---|
| a. Glycolysis | i. Occurs in cytoplasm; partial oxidation of glucose |
| b. Alcoholic fermentation | ii. Produces lactic acid under anaerobic conditions |
| c. Lactic acid fermentation | iii. Produces ethanol and CO2 in anaerobic organisms |
| d. Aerobic respiration | iv. Complete oxidation of glucose in mitochondria |
a)
a-iii, b-ii, c-iv, d-i
b)
a-iv, b-i, c-iii, d-ii
c)
a-ii, b-iv, c-i, d-iii
d)
a-i, b-iii, c-ii, d-iv

|
Top Rankers answered |
Glycolysis occurs in cytoplasm, alcoholic fermentation produces ethanol, lactic acid fermentation produces lactic acid, and aerobic respiration occurs in mitochondria.
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-14) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d)Passage ISolid ammonium chloride is in equilibrium with ammonia and hydrogen chloride gases
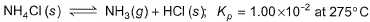
0.980 g of solid NH4CI is taken in a closed vessel of 1 L capacity and heated to 275° C.Q. Partial pressure of NH3(g) or HCI (g) at equilibrium is- a)0.10 atm
- b)1.0 atm
- c)0.01 atm
- d)1 x 10-4 atm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-14) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d)
Passage I
Solid ammonium chloride is in equilibrium with ammonia and hydrogen chloride gases
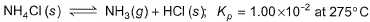
0.980 g of solid NH4CI is taken in a closed vessel of 1 L capacity and heated to 275° C.
0.980 g of solid NH4CI is taken in a closed vessel of 1 L capacity and heated to 275° C.
Q. Partial pressure of NH3(g) or HCI (g) at equilibrium is
a)
0.10 atm
b)
1.0 atm
c)
0.01 atm
d)
1 x 10-4 atm
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
The reaction is as follow:-
NH4Cl(s) ⇋ NH3(g) + HCl(g)
Kp = (pNH3)(pHCl)
1×10-2 = p2 (SInce reactant dissociates into same ratio, so the partial pressure will be same for both)
100×10-4 = p2
Or p = 10×10-2 = 0.10
So, the partial pressure of NH3 and HCl are 0.10 atm.
NH4Cl(s) ⇋ NH3(g) + HCl(g)
Kp = (pNH3)(pHCl)
1×10-2 = p2 (SInce reactant dissociates into same ratio, so the partial pressure will be same for both)
100×10-4 = p2
Or p = 10×10-2 = 0.10
So, the partial pressure of NH3 and HCl are 0.10 atm.
To which type of fluid is the Bernoulli’s theorem applicable:- a)Incompressible and anisotropic
- b)Incompressible and viscous
- c)Compressible and anisotropic
- d)Incompressible, isotropic and non viscous
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
To which type of fluid is the Bernoulli’s theorem applicable:
a)
Incompressible and anisotropic
b)
Incompressible and viscous
c)
Compressible and anisotropic
d)
Incompressible, isotropic and non viscous
|
|
Pritam Kapoor answered |
The Bernoulli principle applies to any type of fluid, including liquids and gases.
What is the total ATP gain during glycolysis from one molecule of glucose?- a)2 ATP
- b)4 ATP
- c)6 ATP
- d)8 ATP
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
2 ATP
b)
4 ATP
c)
6 ATP
d)
8 ATP

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Glycolysis directly synthesizes 4 ATP molecules, but 2 ATP are used in early steps, resulting in a net gain of 2 ATP per glucose molecule.
Why can bulky plants manage gas exchange without specialized organs?- a)All cells are dead and do not need oxygen.
- b)The distance for gas diffusion is small, and cells are near the surface.
- c)Roots actively pump oxygen into stems.
- d)Xylem tissues transport oxygen directly to leaves.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
All cells are dead and do not need oxygen.
b)
The distance for gas diffusion is small, and cells are near the surface.
c)
Roots actively pump oxygen into stems.
d)
Xylem tissues transport oxygen directly to leaves.

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Even in large plants, living cells are near the surface, diffusion distances are small, and lenticels help in gaseous exchange.
Assertion (A): Fermentation releases less than 7% of the energy stored in glucose.
Reason (R): Fermentation involves complete oxidation of glucose.- a)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Reason (R): Fermentation involves complete oxidation of glucose.
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Fermentation releases very little energy because it involves incomplete oxidation of glucose, not complete oxidation.
Which of the following is true about glycolysis?- a)It occurs in the mitochondria of all organisms.
- b)It requires oxygen for glucose breakdown.
- c)It occurs in the cytoplasm and is universal in all living organisms.
- d)It only occurs in prokaryotes.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
It occurs in the mitochondria of all organisms.
b)
It requires oxygen for glucose breakdown.
c)
It occurs in the cytoplasm and is universal in all living organisms.
d)
It only occurs in prokaryotes.

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Glycolysis is a universal pathway occurring in the cytoplasm of all living cells and does not require oxygen.
At which step of glycolysis is NADH + H⁺ generated?- a)Conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate
- b)Conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate
- c)Conversion of PGAL to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
- d)Conversion of fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate
b)
Conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate
c)
Conversion of PGAL to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
d)
Conversion of fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate

|
Lead Academy answered |
NADH + H⁺ is formed when 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGAL) is oxidized to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
Direction (Q. Nos. 15 and 16) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)Hot copper tunnings can be used as an “oxygen getter" for inert gas supplies by slowly passing the gas over the copper tunnings at 650 K.
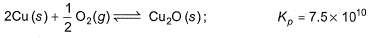 Q. How many molecules of CO2 are left in 1 L of a gas supply after equilibrium has been reached?
Q. How many molecules of CO2 are left in 1 L of a gas supply after equilibrium has been reached?
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 15 and 16) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Hot copper tunnings can be used as an “oxygen getter" for inert gas supplies by slowly passing the gas over the copper tunnings at 650 K.
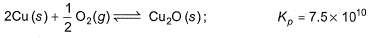
Q. How many molecules of CO2 are left in 1 L of a gas supply after equilibrium has been reached?
|
|
Aditya Oza answered |
Is it CO2 or Cu2O.
Why is oxygen availability not a problem in photosynthesizing cells?- a)Oxygen diffuses from roots to leaves.
- b)Oxygen is actively transported by xylem vessels.
- c)Oxygen is released within the cells during photosynthesis.
- d)Oxygen is stored in vacuoles for respiration.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Oxygen diffuses from roots to leaves.
b)
Oxygen is actively transported by xylem vessels.
c)
Oxygen is released within the cells during photosynthesis.
d)
Oxygen is stored in vacuoles for respiration.

|
Lead Academy answered |
During photosynthesis, oxygen is a byproduct generated within the cells themselves, making oxygen availability sufficient.
Assertion (A): Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of all living organisms.
Reason (R): Glycolysis is an anaerobic pathway that does not require oxygen.- a)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Reason (R): Glycolysis is an anaerobic pathway that does not require oxygen.
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Glycolysis is a universal, cytoplasmic pathway that does not require oxygen, making R the correct explanation of A.
Match the glycolytic intermediates with the correct carbon number: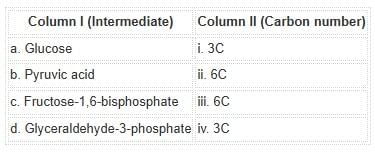
- a)a-iii, b-iv, c-ii, d-i
- b)a-i, b-ii, c-iv, d-iii
- c)a-ii, b-i, c-iii, d-iv
- d)a-iv, b-iii, c-i, d-ii
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the glycolytic intermediates with the correct carbon number:

a)
a-iii, b-iv, c-ii, d-i
b)
a-i, b-ii, c-iv, d-iii
c)
a-ii, b-i, c-iii, d-iv
d)
a-iv, b-iii, c-i, d-ii

|
Top Rankers answered |
Glucose and fructose-1,6-bisphosphate are 6-carbon compounds, while pyruvic acid and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate are 3-carbon intermediates.
Solid ammonium carbonate (NH2CO2NH4) dissociates completely into ammonia and carbon dioxide when it evaporates :
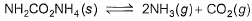
At 298 K, the total pressure of the gases in equilibrium with the solid is 0.116 atm. Derive the value of equilibrium constant Kp.- a)4p3/27
- b)6p3/27
- c)4p2/27
- d)2p3/27
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Solid ammonium carbonate (NH2CO2NH4) dissociates completely into ammonia and carbon dioxide when it evaporates :
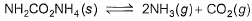
At 298 K, the total pressure of the gases in equilibrium with the solid is 0.116 atm. Derive the value of equilibrium constant Kp.
At 298 K, the total pressure of the gases in equilibrium with the solid is 0.116 atm. Derive the value of equilibrium constant Kp.
a)
4p3/27
b)
6p3/27
c)
4p2/27
d)
2p3/27

|
Sourav Dey answered |
A
Why does fermentation yield less energy compared to aerobic respiration?- a)No ATP is synthesized during fermentation.
- b)Fermentation uses ATP to produce ethanol or lactic acid.
- c)Glucose is completely oxidized in fermentation.
- d)Fermentation involves incomplete oxidation of glucose.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
No ATP is synthesized during fermentation.
b)
Fermentation uses ATP to produce ethanol or lactic acid.
c)
Glucose is completely oxidized in fermentation.
d)
Fermentation involves incomplete oxidation of glucose.

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Fermentation involves partial oxidation of glucose, leading to much less ATP production compared to complete oxidation in aerobic respiration.
Passage lIOne of the reactions that takes place in producing steel from iron ore is the reduction of iron (II) oxide by carbon monoxide to give iron metal and carbon dioxide.
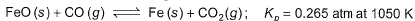
Initial partial pressure
CO(g) = 1.40 atm
CO2(g) = 0.80 atmQ. When equilibrium is attained,- a)
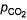 = Pco = 1-74 atm
= Pco = 1-74 atm - b)
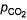 = Pco = 0.46 atm
= Pco = 0.46 atm - c)
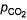 = 0-46 atm, pco = 1.74 atm
= 0-46 atm, pco = 1.74 atm - d)
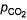 = 1.74 atm, pco = 0.46 atm
= 1.74 atm, pco = 0.46 atm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage lI
One of the reactions that takes place in producing steel from iron ore is the reduction of iron (II) oxide by carbon monoxide to give iron metal and carbon dioxide.
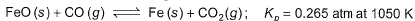
Initial partial pressure
CO(g) = 1.40 atm
CO2(g) = 0.80 atm
Initial partial pressure
CO(g) = 1.40 atm
CO2(g) = 0.80 atm
Q. When equilibrium is attained,
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Ashwini Majumdar answered |
For the given reaction,
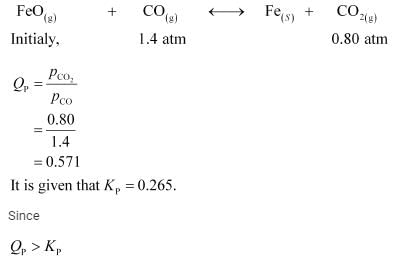
the reaction will proceed in the backward direction.
Therefore, we can say that the pressure of CO will increase while the pressure of CO
2
will decrease.Now, let the increase in pressure of CO = decrease in pressure of CO
2
be p.Then, we can write,
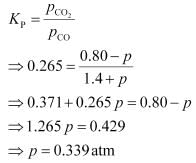
Therefore, equilibrium partial of
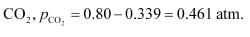
And, equilibrium partial pressure of
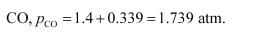
For the following equilibrium,
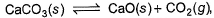

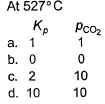
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For the following equilibrium,
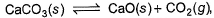

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Raghav Shukla answered |
It's a very easy
you can solve it very easily with help of le Chatlier principle
clearly pressure is of co2 only as all other components are solid and there concentrations are taken as 1
clearly putting values with help of ideal gas equation, you will get the answer
you can solve it very easily with help of le Chatlier principle
clearly pressure is of co2 only as all other components are solid and there concentrations are taken as 1
clearly putting values with help of ideal gas equation, you will get the answer
What is the role of lactate dehydrogenase in animal cells during intense exercise?- a)Converts pyruvate to ethanol
- b)Oxidizes lactic acid to pyruvate
- c)Reduces pyruvate to lactic acid
- d)Converts NADH to NADP
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Converts pyruvate to ethanol
b)
Oxidizes lactic acid to pyruvate
c)
Reduces pyruvate to lactic acid
d)
Converts NADH to NADP

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Lactate dehydrogenase catalyzes the reduction of pyruvate to lactic acid under anaerobic conditions, regenerating NAD⁺.
Match the following glycolytic enzymes with their functions:Options: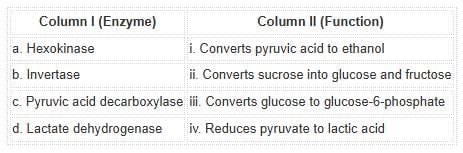
- a)a-iii, b-ii, c-i, d-iv
- b)a-ii, b-i, c-iv, d-iii
- c)a-iv, b-iii, c-ii, d-i
- d)a-i, b-iv, c-iii, d-ii
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following glycolytic enzymes with their functions:Options:

a)
a-iii, b-ii, c-i, d-iv
b)
a-ii, b-i, c-iv, d-iii
c)
a-iv, b-iii, c-ii, d-i
d)
a-i, b-iv, c-iii, d-ii

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Hexokinase phosphorylates glucose, invertase breaks sucrose, pyruvic acid decarboxylase aids ethanol formation, and lactate dehydrogenase reduces pyruvate to lactic acid.
Which of the following statements about gaseous exchange in plants is correct?- a)Plants have specialized organs like lungs for gaseous exchange.
- b)Each plant part independently manages its own gas exchange.
- c)Plants transport large volumes of gases between different parts.
- d)Woody stems have no structures for gaseous exchange.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Plants have specialized organs like lungs for gaseous exchange.
b)
Each plant part independently manages its own gas exchange.
c)
Plants transport large volumes of gases between different parts.
d)
Woody stems have no structures for gaseous exchange.

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Plants lack specialized respiratory organs, and each part (roots, stems, leaves) manages its own gas exchange through structures like stomata and lenticels.
Which enzymes are responsible for alcoholic fermentation in yeast?- a)Pyruvate dehydrogenase and alcohol oxidase
- b)Pyruvic acid decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase
- c)Lactate dehydrogenase and hexokinase
- d)Phosphofructokinase and ATP synthase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Pyruvate dehydrogenase and alcohol oxidase
b)
Pyruvic acid decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase
c)
Lactate dehydrogenase and hexokinase
d)
Phosphofructokinase and ATP synthase

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Alcoholic fermentation involves pyruvic acid decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase, converting pyruvate to ethanol and CO₂.
Chapter doubts & questions for October Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of October Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup












